Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Modulation by microRNA: Relevance on Immunogenic Cell Death and Cancer Treatment Outcome
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
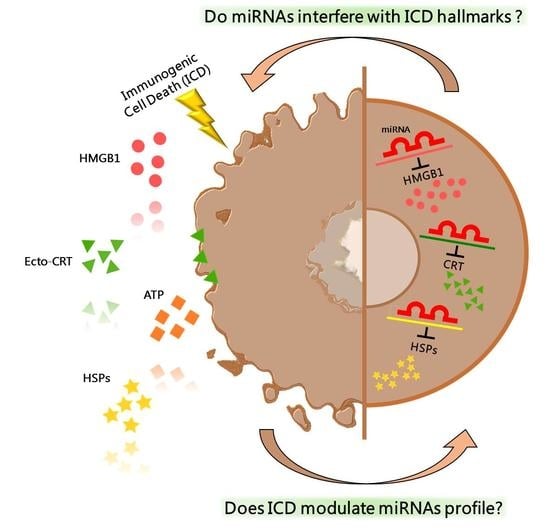
2. Immunogenic Cell Death
3. Epigenetic Regulation by miRNA
4. Epigenetic Regulation of ICD-Hallmarks by miRNA
4.1. Calreticulin
4.2. Heat Shock Proteins
4.3. HMGB1
5. Modulation of Therapeutic Outcome through Targeting DAMPs by miRNA
6. Therapeutic Combination of ICD and miRNAs: A New Opportunity
7. Future Challenges
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Kempen, T.S.; Wenink, M.H.; Leijten, E.F.A.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Boes, M. Perception of Self: Distinguishing Autoimmunity from Autoinflammation. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Buqué, A.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunogenic Cell Death in Cancer and Infectious Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares, N.; Pequignot, M.O.; Tesniere, A.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Roux, S.; Chaput, N.; Schmitt, E.; Hamai, A.; Hervas-Stubbs, S.; Obeid, M.; et al. Caspase-Dependent Immunogenicity of Doxorubicin-Induced Tumor Cell Death. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, M.J.; Nigro, A.; Mentucci, F.M.; Rumie Vittar, N.B.; Casolaro, V.; Dal Col, J. Dendritic Cells and Immunogenic Cancer Cell Death: A Combination for Improving Antitumor Immunity. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Liang, C.; Hua, J.; Meng, Q.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Ferroptosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis in Anticancer Immunity. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, A.J.; Konstantinou, M.; Goode, E.F.; Meier, P. The Diversification of Cell Death and Immunity: Memento Mori. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysko, D.V.; Garg, A.D.; Kaczmarek, A.; Krysko, O.; Agostinis, P.; Vandenabeele, P. Immunogenic Cell Death and DAMPs in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruickshank, B.; Giacomantonio, M.; Marcato, P.; McFarland, S.; Pol, J.; Gujar, S. Dying to Be Noticed: Epigenetic Regulation of Immunogenic Cell Death for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bloy, N.; Garcia, P.; Laumont, C.M.; Pitt, J.M.; Sistigu, A.; Stoll, G.; Yamazaki, T.; Bonneil, E.; Buqué, A.; Humeau, J.; et al. Immunogenic Stress and Death of Cancer Cells: Contribution of Antigenicity vs Adjuvanticity to Immunosurveillance. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 280, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela, A.; Esteller, M. Epigenetic Modifications and Human Disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucikova, J.; Kepp, O.; Kasikova, L.; Petroni, G.; Yamazaki, T.; Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; Spisek, R.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Detection of Immunogenic Cell Death and Its Relevance for Cancer Therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, M.; Tesniere, A.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Fimia, G.M.; Apetoh, L.; Perfettini, J.-L.; Castedo, M.; Mignot, G.; Panaretakis, T.; Casares, N.; et al. Calreticulin Exposure Dictates the Immunogenicity of Cancer Cell Death. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaretakis, T.; Kepp, O.; Brockmeier, U.; Tesniere, A.; Bjorklund, A.-C.; Chapman, D.C.; Durchschlag, M.; Joza, N.; Pierron, G.; van Endert, P.; et al. Mechanisms of Pre-Apoptotic Calreticulin Exposure in Immunogenic Cell Death. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.; Wang, Y.; Michaud, M.; Ma, Y.; Sukkurwala, A.Q.; Shen, S.; Kepp, O.; Métivier, D.; Galluzzi, L.; Perfettini, J.-L.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of ATP Secretion during Immunogenic Cell Death. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aymeric, L.; Apetoh, L.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Tesniere, A.; Martins, I.; Kroemer, G.; Smyth, M.J.; Zitvogel, L. Tumor Cell Death and ATP Release Prime Dendritic Cells and Efficient Anticancer Immunity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Apetoh, L.; Tesniere, A.; Aymeric, L.; Ma, Y.; Ortiz, C.; Vermaelen, K.; Panaretakis, T.; Mignot, G.; Ullrich, E.; et al. Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Dendritic Cells Induces IL-1beta-Dependent Adaptive Immunity against Tumors. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistigu, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Vacchelli, E.; Chaba, K.; Enot, D.P.; Adam, J.; Vitale, I.; Goubar, A.; Baracco, E.E.; Remédios, C.; et al. Cancer Cell-Autonomous Contribution of Type I Interferon Signaling to the Efficacy of Chemotherapy. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, M.J.; Mentucci, F.M.; Roselli, E.; Araya, P.; Rivarola, V.A.; Rumie Vittar, N.B.; Maccioni, M. Photodynamic Modulation of Type 1 Interferon Pathway on Melanoma Cells Promotes Dendritic Cell Activation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spisek, R.; Charalambous, A.; Mazumder, A.; Vesole, D.H.; Jagannath, S.; Dhodapkar, M.V. Bortezomib Enhances Dendritic Cell (DC)-Mediated Induction of Immunity to Human Myeloma via Exposure of Cell Surface Heat Shock Protein 90 on Dying Tumor Cells: Therapeutic Implications. Blood 2007, 109, 4839–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Hannani, D.; Poirier-Colame, V.; Ladoire, S.; Locher, C.; Sistigu, A.; Prada, N.; Adjemian, S.; Catani, J.P.; Freudenberg, M.; et al. Defective Immunogenic Cell Death of HMGB1-Deficient Tumors: Compensatory Therapy with TLR4 Agonists. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yatim, N.; Cullen, S.; Albert, M.L. Dying Cells Actively Regulate Adaptive Immune Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenay, S.; Reis e Sousa, C. Adaptive Immunity after Cell Death. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montico, B.; Nigro, A.; Casolaro, V.; Dal Col, J. Immunogenic Apoptosis as a Novel Tool for Anticancer Vaccine Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denzler, R.; McGeary, S.E.; Title, A.C.; Agarwal, V.; Bartel, D.P.; Stoffel, M. Impact of MicroRNA Levels, Target-Site Complementarity, and Cooperativity on Competing Endogenous RNA-Regulated Gene Expression. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, W.-J.; Leng, X.-M. Dynamic MiRNA-MRNA Paradigms: New Faces of MiRNAs. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2015, 4, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The Role of MicroRNAs in Human Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrey, E.; Saint-Auret, G.; Bonnamy, B.; Damas, D.; Boyer, O.; Gidrol, X. Pre-MicroRNA and Mature MicroRNA in Human Mitochondria. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of MRNAs and MicroRNAs Is a Novel Mechanism of Genetic Exchange between Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Chen, X. Nuclear MicroRNAs and Their Unconventional Role in Regulating Non-Coding RNAs. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brümmer, A.; Hausser, J. MicroRNA Binding Sites in the Coding Region of MRNAs: Extending the Repertoire of Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation. Bioessays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, J.R.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. Target MRNAs Are Repressed as Efficiently by MicroRNA-Binding Sites in the 5′ UTR as in the 3′ UTR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9667–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helwak, A.; Kudla, G.; Dudnakova, T.; Tollervey, D. Mapping the Human MiRNA Interactome by CLASH Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding. Cell 2013, 153, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasudevan, S.; Tong, Y.; Steitz, J.A. Switching from Repression to Activation: MicroRNAs Can up-Regulate Translation. Science 2007, 318, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. Functional Interactions among MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 34, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirjang, S.; Mansoori, B.; Asghari, S.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Mohammadi, A.; Gjerstorff, M.; Baradaran, B. MicroRNAs in Cancer Cell Death Pathways: Apoptosis and Necroptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 139, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, H.; Hao, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; et al. The Emerging Roles of Autophagy-Related MicroRNAs in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, D.W.; Bracken, C.P.; Goodall, G.J. Experimental Strategies for MicroRNA Target Identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 6845–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, C.; Yu, H.; Shi, C.; Shi, T.; Qin, H.; Cui, Y. MiR-Let-7e Inhibits Invasion and Magration and Regulates HMGB1 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Qiong, G.; Chen, Z.; Deng, S. MicroRNAs-107 Inhibited Autophagy, Proliferation, and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting HMGB1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 8696–8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, C. MiR-1179 Inhibits the Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting HMGB1. Hum. Cell 2019, 32, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, G. MiR-1284 Enhances Sensitivity of Cervical Cancer Cells to Cisplatin via Downregulating HMGB1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chen, J.; He, L. Mir-129-5p Attenuates Irradiation-Induced Autophagy and Decreases Radioresistance of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting HMGB1. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 4122–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Gong, W.; Lu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J. Upregulation of MiR-129-5p Increases the Sensitivity to Taxol through Inhibiting HMGB1-Mediated Cell Autophagy in Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, e8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Meng, W.-Y.; Jie, Y.; Zhao, H. LncRNA MALAT1 Induces Colon Cancer Development by Regulating MiR-129-5p/HMGB1 Axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6750–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Guo, J. MiR-129-5p Inhibits Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells through Targeted Inhibition on HMGB1 Expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 3665–3673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, F.; Teng, L. MiR-129-5p Attenuates Cell Proliferation and Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition via HMGB1 in Gastric Cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cao, J.; Zhong, Q.; Zeng, L.; Cai, C.; Lei, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, F. Long Noncoding RNA PCAT-1 Promotes Invasion and Metastasis via the MiR-129-5p-HMGB1 Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Huang, J.; Ni, J.; Song, D.; Ding, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Li, W. MALAT1 Promotes Osteosarcoma Development by Regulation of HMGB1 via MiR-142–3p and MiR-129–5p. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Jin, H.; Lou, F. The Long Non-Coding RNA TP73-AS1 Interacted With MiR-142 to Modulate Brain Glioma Growth Through HMGB1/RAGE Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 3007–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Qiao, J.; Bao, A. MiR-142-3p Overexpression Increases Chemo-Sensitivity of NSCLC by Inhibiting HMGB1-Mediated Autophagy. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Liu, W.-L. MiR-142-3p Functions as a Potential Tumor Suppressor Directly Targeting HMGB1 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10800–10807. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, T.N.; Mujumdar, N.; Banerjee, S.; Sangwan, V.; Sarver, A.; Vickers, S.; Subramanian, S.; Saluja, A.K. Triptolide Induces the Expression of MiR-142-3p: A Negative Regulator of Heat Shock Protein 70 and Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, F.; Zhang, J.; Ji, M.; Li, P.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Zang, S.; Ma, D.; Sun, X.; Ji, C. MiR-181b Increases Drug Sensitivity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia via Targeting HMGB1 and Mcl-1. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, C. Long Non-Coding RNA UCA1 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration via MicroRNA-193a/HMGB1 Axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Zhou, R.; Fan, X. The Long Non-Coding RNA TP73-AS1 Modulates HCC Cell Proliferation through MiR-200a-Dependent HMGB1/RAGE Regulation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Wang, D.; Xing, J.; Yang, S.; Chu, Q.; Yu, S. MiR-200c Inhibits Metastasis of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting HMGB1. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2014, 34, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.-L.; Liu, W.-L.; Chang, J.-M.; Chen, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.-P.; Kuo, H.-F.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Ding, Y.-S.; Chen, W.-W.; Chong, I.-W. MicroRNA-200c Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Invasion, and Migration of Lung Cancer by Targeting HMGB1. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kang, F.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; He, D. Downregulation of MiR-205 Contributes to Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Targeting HMGB1–RAGE Signaling Pathway. Anticancer Drugs 2019, 30, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, P.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, K. MiR-218 Inhibits HMGB1-Mediated Autophagy in Endometrial Carcinoma Cells during Chemotherapy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 6617–6626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ge, S.; Hu, C.; Yang, N.; Zhang, J. MiRNA-218, a New Regulator of HMGB1, Suppresses Cell Migration and Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; He, X.; Ren, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q. Long Noncoding RNA PCA3 Regulates Prostate Cancer through Sponging MiR-218-5p and Modulating High Mobility Group Box 1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 13097–13109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Cai, M.; Fu, D.; Chen, K.; Sun, M.; Cai, Z.; Cheng, B. Heat Shock Protein 90B1 Plays an Oncogenic Role and Is a Target of MicroRNA-223 in Human Osteosarcoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Xie, G.; Zhu, K.; Li, D. MiR-223/Hsp70/JNK/JUN/MiR-223 Feedback Loop Modulates the Chemoresistance of Osteosarcoma to Cisplatin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Wu, M.; Wang, M.; Jiang, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Ma, N.; Peng, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. MiR-320a Regulates High Mobility Group Box 1 Expression and Inhibits Invasion and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Zhao, T.; Jin, H. Expression of MicroRNA-325-3p and Its Potential Functions by Targeting HMGB1 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 70, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, T.; Polcaro, G.; Ziccardi, P.; Pucci, B.; Muccillo, L.; Galgani, M.; Fucci, A.; Milone, M.R.; Budillon, A.; Santopaolo, M.; et al. Proteomic Screening Identifies Calreticulin as a MiR-27a Direct Target Repressing MHC Class I Cell Surface Exposure in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, T.; Polcaro, G.; Ziccardi, P.; Muccillo, L.; Galgani, M.; Pucci, B.; Rita Milone, M.; Budillon, A.; Santopaolo, M.; Mazzoccoli, G.; et al. The MiR-27a-Calreticulin Axis Affects Drug-Induced Immunogenic Cell Death in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, P.; Qiu, X.; Liang, S.; Guan, B.; Yang, H.; Li, F.; Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Zou, G.; et al. KCNQ1OT1 Facilitates Progression of Non-small-cell Lung Carcinoma via Modulating MiRNA-27b-3p/HSP90AA1 Axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 11304–11314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Huang, J.; Xie, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Kang, R.; Cao, L.; Tang, D.; Duan, X. MIR34A Regulates Autophagy and Apoptosis by Targeting HMGB1 in the Retinoblastoma Cell. Autophagy 2014, 10, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekaran, K.S.; Sathyanarayanan, A.; Karunagaran, D. Downregulation of HMGB1 by MiR-34a Is Sufficient to Suppress Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Human Cervical and Colorectal Cancer Cells. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 13155–13166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Luo, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-34a Directly Targets High-mobility Group Box 1 and Inhibits the Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5611–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Yue, J.; Konno, Y.; Ihira, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Todo, Y.; Watari, H. MicroRNA-361-Mediated Inhibition of HSP90 Expression and EMT in Cervical Cancer Is Counteracted by Oncogenic LncRNA NEAT1. Cells 2020, 9, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Ma, H.; Lv, X. MiR-449a Suppresses Tumor Growth, Migration, and Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Targeting a HMGB1-Mediated NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2019, 27, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wang, Z.; Hao, J.; Zhang, X. MiR-505 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Gastric Cancer Progression through Targeting HMGB1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 8044–8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Qiu, C.; Li, D.; Bai, G.; Liang, J.; Yang, Q. MicroRNA-505 Suppresses Proliferation and Invasion in Hepatoma Cells by Directly Targeting High-Mobility Group Box 1. Life Sci. 2016, 157, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Y.; Bai, G.; Lv, Y.; Liang, J. MiR-505 Enhances Doxorubicin-Induced Cytotoxicity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Repressing the Akt Pathway by Directly Targeting HMGB1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Li, W.; Chang, F.; Liu, J.-N.; Lin, J.-X.; Chen, D.-X. MicroRNA-505 Is Downregulated in Human Osteosarcoma and Regulates Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 39, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Xi, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Circ_0007385 Served as Competing Endogenous for MiR-519d-3p to Suppress Malignant Behaviors and Cisplatin Resistance of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 2196–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Z.; Meng, F.; Jiang, P.; Yue, M.; Li, S. MicroRNA-548b Suppresses Aggressive Phenotypes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Directly Targeting High-Mobility Group Box 1 MRNA. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 5821–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, J.; Wu, D.; Sheng, Z.; Li, M. HSP90: A Novel Target Gene of MiRNA-628-3p in A549 Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Du, S.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W. MicroRNA-665 Inhibits the Oncogenicity of Retinoblastoma by Directly Targeting High-Mobility Group Box 1 and Inactivating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3111–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, M.S.; Park, C.S.; Choi, K.; Ahnn, J.; Kim, J.I.; Eom, S.H.; Kaufman, S.J.; Song, W.K. Calreticulin Couples Calcium Release and Calcium Influx in Integrin-Mediated Calcium Signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.-A.; Groenendyk, J.; Michalak, M. Calreticulin Signaling in Health and Disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Hou, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, Y. MiR-27a-3p Functions as a Tumor Suppressor and Regulates Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation via Targeting HOXB8. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819861971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, H.; Xu, X.; Xiao, W.; Liao, Y.; Xiao, X.; Li, L.; Li, K.; Jia, X.; Feng, H. Silencing of MicroRNA-27a Facilitates Autophagy and Apoptosis of Melanoma Cells through the Activation of the SYK-Dependent MTOR Signaling Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 13262–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z.; Huang, H.-J.; Chen, M.-J.; Ji, J.-S. MicroRNA-27a-3p Inhibits Cell Viability and Migration through down-Regulating DUSP16 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 5143–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cheng, H.; Li, N.; Zhou, N.; Tang, X. Relationship between MicroRNA-27a and Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Gastric Cancer and Its Mechanism in Gastric Cancer Cell Growth and Metastasis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Li, J. Silencing MicroRNA-27a Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion of Human Osteosarcoma Cells through the SFRP1-Dependent Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciocca, D.R.; Calderwood, S.K. Heat Shock Proteins in Cancer: Diagnostic, Prognostic, Predictive, and Treatment Implications. Cell Stress Chaperones 2005, 10, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, R.J. Functions of Heat Shock Proteins in Pathways of the Innate and Adaptive Immune System. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5765–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrido, C.; Gurbuxani, S.; Ravagnan, L.; Kroemer, G. Heat Shock Proteins: Endogenous Modulators of Apoptotic Cell Death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 286, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.E.; Cogno, I.S.; Milla Sanabria, L.S.; Morán, Y.S.; Rivarola, V.A. Heat Shock Proteins in the Context of Photodynamic Therapy: Autophagy, Apoptosis and Immunogenic Cell Death. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Photochem. Assoc. Eur. Soc. Photobiol. 2016, 15, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.-J.; Cheng, J.; Feng, X.; Yu, Y.; Tian, L.; Huang, Q. The Dual Role and Therapeutic Potential of High-Mobility Group Box 1 in Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 64534–64550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T.; Tang, D. HMGB1 in Cancer: Good, Bad, or Both? Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4046–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Ren, W.; Chen, K. MiR-34a Promotes Apoptosis and Inhibits Autophagy by Targeting HMGB1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratti, M.; Lampis, A.; Ghidini, M.; Salati, M.; Mirchev, M.B.; Valeri, N.; Hahne, J.C. MicroRNAs (MiRNAs) and Long Non-Coding RNAs (LncRNAs) as New Tools for Cancer Therapy: First Steps from Bench to Bedside. Target. Oncol. 2020, 15, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acunzo, M.; Romano, G.; Wernicke, D.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA and Cancer--a Brief Overview. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2015, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yu, Y.; Kang, R.; Yang, M.; Xie, M.; Wang, Z.; Tang, D.; Zhao, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Up-Regulated Autophagy by Endogenous High Mobility Group Box-1 Promotes Chemoresistance in Leukemia Cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.F.; Torchilin, V.P. Micelle-like Nanoparticles as SiRNA and MiRNA Carriers for Cancer Therapy. Biomed. Microdevices 2018, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phung, C.D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Choi, J.Y.; Pham, T.T.; Acharya, S.; Timilshina, M.; Chang, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, J.-H.; Ku, S.K.; et al. Reprogramming the T Cell Response to Cancer by Simultaneous, Nanoparticle-Mediated PD-L1 Inhibition and Immunogenic Cell Death. J. Control. Release 2019, 315, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.M.; Chess, R.B. Effect of Pegylation on Pharmaceuticals. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicke, G.L.; Mansoori, G.A.; Jeffery, C.J. Utilizing the Folate Receptor for Active Targeting of Cancer Nanotherapeutics. Nano Rev. 2012, 3, 18496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liang, T.-T. CD59 Receptor Targeted Delivery of MiRNA-1284 and Cisplatin-Loaded Liposomes for Effective Therapeutic Efficacy against Cervical Cancer Cells. AMB Express 2020, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afshar-Kharghan, V. The Role of the Complement System in Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unlu, S.; Tang, S.; Na Wang, E.; Martinez, I.; Tang, D.; Bianchi, M.E.; Iii, H.J.Z.; Lotze, M.T. Damage Associated Molecular Pattern Molecule-Induced MicroRNAs (DAMPmiRs) in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.C.; Ebersberger, S.; Fink, A.F.; Lampe, S.; Weigert, A.; Schmid, T.; Ebersberger, I.; Syed, S.N.; Brüne, B. Apoptotic Tumor Cell-Derived MicroRNA-375 Uses CD36 to Alter the Tumor-Associated Macrophage Phenotype. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, M.; Paone, A.; Calore, F.; Galli, R.; Gaudio, E.; Santhanam, R.; Lovat, F.; Fadda, P.; Mao, C.; Nuovo, G.J.; et al. MicroRNAs Bind to Toll-like Receptors to Induce Prometastatic Inflammatory Response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2110–E2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Xu, L.; White, R.; Sullenger, B.A. Differential Induction of Immunogenic Cell Death and Interferon Expression in Cancer Cells by Structured SsRNAs. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2017, 25, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogino, S.; Nowak, J.A.; Hamada, T.; Phipps, A.I.; Peters, U.; Milner, D.A.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Nishihara, R.; Giannakis, M.; Garrett, W.S.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Exogenous, Endogenous, Tumour and Immune Factors for Precision Medicine. Gut 2018, 67, 1168–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, S.; Nowak, J.A.; Hamada, T.; Milner, D.A.; Nishihara, R. Insights into Pathogenic Interactions Among Environment, Host, and Tumor at the Crossroads of Molecular Pathology and Epidemiology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2019, 14, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| miRNA | miRBase Accession Number | Dysregulation in Cancer vs. Normal Counterparts | Target DAMP | miRNA Binding Site in Target Gene | Cancer Type | Effects | Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-let-7e-5p | MIMAT0000066 | Not evaluated | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Thyroid cancer | ↓ Migration ↓ Invasion | Tumor suppressor | Ding et al., 2019 [39] |
| hsa-miR-107 | MIMAT0000104 | Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Breast cancer | ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation ↓ Autophagy | Tumor suppressor | Ai et al., 2018 [40] |
| hsa-miR-1179 | MIMAT0005824 | Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Gastric cancer | ↓ Proliferation ↓ Invasion | Tumor suppressor | Li et al., 2019 [41] |
| hsa-miR-1284 | MIMAT0005941 | Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | HMGB1 | Not reported | Cervical cancer | ↓ Proliferation ↓ Invasion ↑ Cisplatin-induced apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Chen & Li, 2018 [42] |
| hsa-miR-129-5p | MIMAT0000242 | Not evaluated | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Breast cancer | ↓ Irradiation-induced autophagy ↑ Radiosensitivity | Tumor suppressor | Luo et al., 2015 [43] |
| Not evaluated | Not evaluated | Breast cancer | ↓ Autophagy ↑ Paclitaxel-induced apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Shi et al., 2019 [44] | |||
| Not evaluated | Not reported | Colon cancer | ↓ Proliferation | Tumor suppressor | Wu et al., 2018 [45] | |||
| Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | 3′UTR | Gastric cancer | ↓ Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Feng et al., 2020 [46] | |||
| Downregulation (cell lines) | 3′UTR | Gastric cancer | ↓ Proliferation ↓ Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | Tumor suppressor | Wang et al., 2019 [47] | |||
| Not evaluated | 3′UTR | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ↓ Migration ↓ Invasion | Tumor suppressor | Zhang et al., 2017 [48] | |||
| Downregulation (tissues) | 3′UTR | Osteosarcoma | ↓ Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Liu et al., 2017 [49] | |||
| hsa-miR-142-3p | MIMAT0000434 | Downregulation (tissues) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Glioma | ↓ Proliferation ↓ Invasion | Tumor suppressor | Zhang et al., 2018 [50] |
| Not evaluated | 3′UTR | Non-small-cell lung cancer | ↓ Starvation-induced autophagy ↑ Cisplatin and doxorubicin-chemosensitivity | Tumor suppressor | Chen et al., 2017 [51] | |||
| Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | 3′UTR | Non-small-cell lung cancer | ↓ Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Xiao & Lu, 2015 [52] | |||
| Downregulation (tissues) | 3′UTR | Osteosarcoma | ↓ Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Liu et al., 2017 [49] | |||
| Not evaluated | Hsp70 | 3′UTR | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | ↓ Proliferation | Tumor suppressor | MacKenzie et al., 2013 [53] | ||
| hsa-miR-181b-5p | MIMAT0000257 | Not evaluated | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Acute myeloid leukemia | ↑ Doxorubicin or cytarabine-induced apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Lu et al., 2014 [54] |
| hsa-miR-193a-3p | MIMAT0000459 | Not evaluated | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Lung cancer | ↓ Proliferation ↓ Migration | Tumor suppressor | Wu et al., 2018 [55] |
| hsa-miR-200a-5p | MIMAT0001620 | Downregulation (tissues) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Not determined | Tumor suppressor | Li et al., 2017 [56] |
| hsa-miR-200c-3p | MIMAT0000617 | Not evaluated | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Breast cancer | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration | Tumor suppressor | Chang et al., 2014 [57] |
| Not evaluated | Not evaluated | Lung cancer | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | Tumor suppressor | Liu et al., 2017 [58] | |||
| hsa-miR-205-5p | MIMAT0000266 | Downregulation (tissues). Moreover, it is downregulated in metastatic compared to non-metastatic cancer | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Triple-negative breast cancer | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation | Tumor suppressor | Wang et al., 2019 [59] |
| hsa-miR-218-5p | MIMAT0000275 | Downregulation Paclitaxel-resistant compared to non-drug resistant cells (cell lines) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Endometrial carcinoma | ↓ Autophagy ↑ Paclitaxel-chemosensitivity | Tumor suppressor | Ran et al., 2015 [60] |
| Not evaluated | 3′UTR | Lung cancer | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration | Tumor suppressor | Zhang et al., 2013 [61] | |||
| Non evaluated | 3′UTR | Prostate cancer | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Zhang et al., 2019 [62] | |||
| hsa-miR-223-3p | MIMAT0000280 | Not evaluated | Hsp90 | 3′UTR | Osteosarcoma | ↓ Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis ↑ Cell cycle G0/G1 arrest | Tumor suppressor | Li et al., 2012 [63] |
| hsa-miR-223-5p | MIMAT0004570 | Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | Hsp70 | 3′UTR | Osteosarcoma | ↑ Cisplastin-induced apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Tang et al., 2018 [64] |
| hsa-miR-320a-3p | MIMAT0000510 | Downregulation (tissues) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration | Tumor suppressor | Lv et al., 2017 [65] |
| hsa-miR-325 | MIMAT0000771 | Downregulation (tissues) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Non-small cell lung cancer | ↓ Invasion ↓ Proliferation | Tumor suppressor | Yao et al., 2015 [66] |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | MIMAT0000084 | Upregulation (tissues) | Calreticulin | 3′UTR | Colorectal cancer | ↓ Mitoxantrone and oxaliplain-induced apoptosis ↓ Autophagy ↓ MCH-I expression ↓ Dendritic cell maturation ↓ In situ immune cells infiltration ↑ Tumor growth ↑ Liver metastasis | Onco-miRNA | Colangelo et al., 2016a and b [67,68] |
| hsa-miR-27b-3p | MIMAT0000419 | Not evaluated | Hsp90 | 3′UTR | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ↓ Migration ↓ Invasion | Tumor suppressor | Dong et al., 2019 [69] |
| hsa-miR-34a-3p | MIMAT0004557 | Not evaluated | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Retinoblastoma | ↑ Etoposide and carboplatin-induced apoptosis ↓ Starvation-induced autophagy | Tumor suppressor | Liu et al., 2014 [70] |
| hsa-miR-34a-5p | MIMAT0000255 | Downregulation (cell lines) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | ↑ Apoptosis ↓ Autophagy | Tumor suppressor | Liu et al., 2017 [58] |
| Downregulation (tissues) | 3′UTR | Cervical (CaCx) and colorectal (CRC) cancers | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation | Tumor suppressor | Chandrasekaran et al., 2016 [71] | |||
| Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | 3′UTR | Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation | Tumor suppressor | Li et al., 2017 [72] | |||
| hsa-miR-361-5p | MIMAT0000703 | Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | Hsp90 | 3′UTR | Cervical cancer | ↓ Epithelial-mesenchymal transition ↓ Invasion | Tumor suppressor | Xu et al., 2020 [73] |
| hsa-miR-449a | MIMAT0001541 | Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Non-small cell lung cancer | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation | Tumor suppressor | Wu et al., 2019 [74] |
| hsa-miR-505-3p | MIMAT0002876 | Downregulation (cell lines) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Gastric cancer | ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Tian et al., 2018 [75] |
| Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | 3′UTR | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ↓ Proliferation ↓ Invasion ↓ Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | Tumor suppressor | Lu et al., 2016 [76] | |||
| Not evaluated | Non evaluated | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ↑ Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Lu et al., 2018 [77] | |||
| Downregulation (tissues) | 3′UTR | Osteosarcoma | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation | Tumor suppressor | Liu et al., 2017 [78] | |||
| hsa-miR-519d-3p | MIMAT0002853 | Downregulation (tissues) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Lung cancer | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation | Tumor suppressor | Ye et al., 2020 [79] |
| hsa-miR-548b-3p | MIMAT0003254 | Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Yun et al., 2019 [80] |
| hsa-miR-628-3p | MIMAT0003297 | Not evaluated | Hsp90 | 3′UTR | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | ↓ Migration ↑ Apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Pan et al., 2018 [81] |
| hsa-miR-665 | MIMAT0004952 | Downregulation (tissues and cell lines) | HMGB1 | 3′UTR | Retinoblastoma | ↓ Invasion ↓ Migration ↓ Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis | Tumor suppressor | Wang et al., 2019 [82] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamberti, M.J.; Nigro, A.; Casolaro, V.; Rumie Vittar, N.B.; Dal Col, J. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Modulation by microRNA: Relevance on Immunogenic Cell Death and Cancer Treatment Outcome. Cancers 2021, 13, 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112566
Lamberti MJ, Nigro A, Casolaro V, Rumie Vittar NB, Dal Col J. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Modulation by microRNA: Relevance on Immunogenic Cell Death and Cancer Treatment Outcome. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112566
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamberti, María Julia, Annunziata Nigro, Vincenzo Casolaro, Natalia Belén Rumie Vittar, and Jessica Dal Col. 2021. "Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Modulation by microRNA: Relevance on Immunogenic Cell Death and Cancer Treatment Outcome" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112566
APA StyleLamberti, M. J., Nigro, A., Casolaro, V., Rumie Vittar, N. B., & Dal Col, J. (2021). Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Modulation by microRNA: Relevance on Immunogenic Cell Death and Cancer Treatment Outcome. Cancers, 13(11), 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112566