Feasibility, Safety and Impact on Overall Survival of Awake Resection for Newly Diagnosed Supratentorial IDH-Wildtype Glioblastomas in Adults
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Variables and Data Sources
2.4. Extent of Resection
2.5. Surgical Procedures
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Tumor Characteristics
3.2. Awake Surgery Procedure
3.3. Extent of Resection
3.4. Postoperative Outcomes
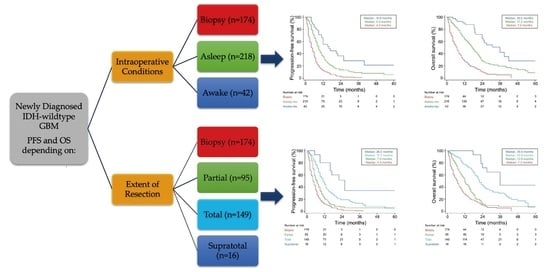
3.5. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Results
4.2. Interpretation
4.3. Generalizability
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.-C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.-F.; de Tribolet, N.; Weller, M. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from te-mozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molinaro, A.M.; Hervey-Jumper, S.; Morshed, R.A.; Young, J.; Han, S.J.; Chunduru, P.; Zhang, Y.; Phillips, J.J.; Shai, A.; Lafontaine, M.; et al. Association of maximal extent of resection of contrast-enhanced and non–contrast-enhanced tumor with survival within molecular subgroups of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambless, L.B.; Kistka, H.M.; Parker, S.L.; Hassam-Malani, L.; McGirt, M.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Mohammad, L. The relative value of postoperative versus preoperative Karnofsky Performance Scale scores as a predictor of survival after surgical resection of glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 121, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanai, N.; Polley, M.Y.; McDermott, M.W.; Parsa, A.T.; Berger, M.S. An extent of resection threshold for newly diagnosed glioblastomas. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.; Abbatematteo, J.; De Leo, E.K.; Kubilis, P.S.; Vaziri, S.; Bova, F.; Sayour, E.; Mitchell, D.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A. The effects of new or worsened postoperative neurological deficits on survival of patients with glioblastoma. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.J.; Brennan, M.C.; Li, M.; Church, E.W.; Brandmeir, N.J.; Rakszawski, K.L.; Patel, A.S.; Rizk, E.B.; Suki, D.; Sawaya, R.; et al. Association of the extent of resection with survival in glioblastoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reulen, H.-J.; Poepperl, G.; Goetz, C.; Gildehaus, F.J.; Schmidt, M.R.; Tatsch, K.; Pietsch, T.; Kraus, T.F.J.; Rachinger, W. Long-term outcome of patients with WHO Grade III and IV gliomas treated by fractionated intracavitary radioimmunotherapy. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moiraghi, A.; Prada, F.; Delaidelli, A.; Guatta, R.; May, A.; Bartoli, A.; Saini, M.; Perin, A.; Wälchli, T.; Momjian, S.; et al. Navigated intraoperative 2-dimensional ultrasound in high-grade glioma surgery: Impact on extent of resection and patient outcome. Oper. Neurosurg. 2019, 18, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ALA-Glioma Study Group; Stummer, W.; Reulen, H.-J.; Meinel, T.; Pichlmeier, U.; Schumacher, W.; Tonn, J.-C.; Rohde, V.; Oppel, F.; Turowski, B.; et al. Extent of resection and survival in glioblastoma multiforme: Identification of and adjustment for bias. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubben, P.L.; ter Meulen, K.J.; Schijns, O.E.M.G.; ter Laak-Poort, M.P.; van Overbeeke, J.J.; van Santbrink, H. Intraoperative MRI-guided resection of glioblastoma multiforme: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiraghi, A.; Pallud, J. Intraoperative ultrasound techniques for cerebral gliomas resection: Usefulness and pitfalls. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGirt, M.J.; Mukherjee, D.; Chaichana, K.L.; Than, K.D.; Weingart, J.D.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A. Association of surgically acquired motor and language deficits on overall survival after resection of glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurgery 2009, 65, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stummer, W.; Pichlmeier, U.; Meinel, T.; Wiestler, O.D.; Zanella, F.; Reulen, H.-J. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: A randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsevman, G.A.; Turner, R.C.; Urhie, O.; Voelker, J.L.; Bhatia, S. Utility of sodium fluorescein for achieving resection targets in glioblastoma: Increased gross- or near-total resections and prolonged survival. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 132, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incekara, F.; Smits, M.; Dirven, L.; Bos, E.M.; Balvers, R.K.; Haitsma, I.K.; Schouten, J.W.; Vincent, A.J.P.E. Intraoperative B-Mode Ultrasound Guided Surgery and the Extent of Glioblastoma Resection: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witt Hamer, P.C.; Robles, S.G.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Duffau, H.; Berger, M.S. Impact of intraoperative stimulation brain mapping on glioma surgery outcome: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hervey-Jumper, S.L.; Li, J.; Osorio, J.A.; Lau, D.; Molinaro, A.M.; Benet, A.; Berger, M.S. Surgical assessment of the insula. Part 2: Validation of the Berger-Sanai zone classification system for predicting extent of glioma resection. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roux, A.; Dezamis, E.; Trancart, B.; Pallud, J. How I do it: Trans-cortical approach for insular diffuse glioma. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 3025–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, J.; Beland, B.; Kelly, J. Supramaximal resection: A systematic review of its safety, efficacy and feasibility in glioblastoma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 72, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquenazi, Y.; Friedman, E.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.-J.; Hsu, S.; Tandon, N. The survival advantage of “Supratotal” resection of glioblastoma using selective cortical mapping and the subpial technique. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, J.K.W.; Viëtor, C.L.; Rizopoulos, D.; Schouten, J.W.; Klimek, M.; Dirven, C.M.F.; Vincent, A.J.-P.E. Awake craniotomy versus craniotomy under general anesthesia without surgery adjuncts for supratentorial glioblastoma in eloquent areas: A retrospective matched case-control study. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigiotto, L.; Annicchiarico, L.; Corsini, F.; Vitali, L.; Falchi, R.; Dalpiaz, C.; Rozzanigo, U.; Barbareschi, M.; Avesani, P.; Papagno, C.; et al. Effects of supra-total resection in neurocognitive and oncological outcome of high-grade gliomas comparing asleep and awake surgery. J. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 148, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.; Choi, J.; Khalafallah, A.M.; Price, C.; Bettegowda, C.; Lim, M.; Gallia, G.; Weingart, J.; Brem, H.; Mukherjee, D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of supratotal versus gross total resection for glioblastoma. J. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 148, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K. The 2016 world health or-ganization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brat, D.J.; Aldape, K.; Colman, H.; Holland, E.C.; Louis, D.N.; Jenkins, R.B. cIMPACT-NOW update 3: Recommended diagnostic criteria for “Diffuse astrocytic glioma, IDH-wildtype, with molecular features of glioblastoma, WHO grade IV”. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, M.; Gay, L.; Ambrogi, F.; Nibali, M.C.; Sciortino, T.; Puglisi, G.; Leonetti, A.; Mocellini, C.; Caroli, M.; Cordera, S.; et al. Association of supratotal resection with progression-free survival, malignant transformation, and overall survival in lower-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncology 2021, 23, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordanova, Y.N.; Moritz-Gasser, S.; Duffau, H. Awake surgery for WHO Grade II gliomas within “noneloquent” areas in the left dominant hemisphere: Toward a “supratotal” resection. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallud, J.; Dezamis, E. Functional and oncological outcomes following awake surgical resection using intraoperative corti-co-subcortical functional mapping for supratentorial gliomas located in eloquent areas. Neurochirurgie 2017, 63, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.U.; Lee, E.Q.; Aoyama, H.; Barani, I.J.; Barboriak, D.P.; Baumert, B.G.; Bendszus, M.; Brown, P.D.; Camidge, D.R.; Chang, S.M.; et al. Response assessment criteria for brain metastases: Proposal from the RANO group. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e270–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanello, M.; Roux, A.; Zah-Bi, G.; Trancart, B.; Parraga, E.; Edjlali, M.; Tauziede-Espariat, A.; Sauvageon, X.; Sharshar, T.; Oppenheim, C.; et al. Predictors of early postoperative epileptic seizures after awake surgery in supratentorial diffuse gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 134, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallud, J.; Rigaux-Viode, O.; Corns, R.; Muto, J.; Lopez, C.L.; Mellerio, C.; Sauvageon, X.; Dezamis, E. Direct electrical bipolar electrostimulation for functional cortical and subcortical cerebral mapping in awake craniotomy. Practical considerations. Neurochirurgie 2017, 63, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallud, J.; Mandonnet, E.; Corns, R.; Dezamis, E.; Parraga, E.; Zanello, M.; Spena, G. Technical principles of direct bipolar electrostimulation for cortical and subcortical mapping in awake craniotomy. Neurochirurgie 2017, 63, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallud, J.; Varlet, P.; Devaux, B.; Geha, S.; Badoual, M.; Deroulers, C.; Page, P.; Dezamis, E.; Daumas-Duport, C.; Roux, F.X. Diffuse low-grade oligodendrogliomas extend beyond MRI-defined abnormalities. Neurochirurgie 2010, 74, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanello, M.; Roux, A.; Debacker, C.; Peeters, S.; Edjlali-Goujon, M.; Dhermain, F.; Dezamis, E.; Oppenheim, C.; Lechapt-Zalcman, E.; Harislur, M.; et al. Postoperative intracerebral haematomas following stereotactic biopsies: Poor planning or poor execution? Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incekara, F.; van der Voort, S.R.; Dubbink, H.J.; Atmodimedjo, P.N.; Nandoe Tewarie, R.; Lycklama, G. Topographical mapping of 436 newly diagnosed IDH wildtype glioblastoma with vs. without MGMT promoter methylation. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, A.; Roca, P.; Edjlali, M.; Sato, K.; Zanello, M.; Dezamis, E.; Gori, P.; Lion, S.; Fleury, A.; Dhermain, F.; et al. MRI atlas of IDH wild-type supratentorial glioblastoma: Probabilistic maps of phenotype, management, and outcomes. Radiology 2019, 293, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incekara, F.; Smits, M.; van der Voort, S.R.; Dubbink, H.J.; Atmodimedjo, P.N.; Kros, J.M. The association between the extent of glioblastoma resection and survival in light of MGMT promoter methylation in 326 patients with newly diagnosed IDH-wildtype glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.H.; Mahavadi, A.; Di, L.; Sanjurjo, A.; Eichberg, D.G.; Borowy, V.; Figueroa, J.; Luther, E.; De La Fuente, M.I.; Semonche, A.; et al. Survival benefit of lobectomy for glioblastoma: Moving towards radical supramaximal resection. J. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 148, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessina, F.; Navarria, P.; Cozzi, L.; Ascolese, A.M.; Simonelli, M.; Santoro, A. Maximize surgical resection beyond con-trast-enhancing boundaries in newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme: Is it useful and safe? A single institution retrospective experience. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 135, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, J.K.W.; Arends, L.; Klimek, M.; Dirven, C.M.F.; Vincent, A.J.-P.E. Impact of intraoperative stimulation mapping on high-grade glioma surgery outcome: A meta-analysis. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clavreul, A.; Aubin, G.; Delion, M.; Lemée, J.-M.; Ter Minassian, A.; Menei, P. What effects does awake craniotomy have on functional and survival outcomes for glioblastoma patients? J. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 151, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boetto, J.; Bertram, L.; Moulinié, G.; Herbet, G.; Moritz-Gasser, S.; Duffau, H. Low rate of intraoperative seizures during awake craniotomy in a prospective cohort with 374 supratentorial brain lesions: Electrocorticography is not mandatory. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallud, J.; Roux, A.; Mellerio, C. Glioma resection unmasks eloquent brain areas. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchcinski, G.; Mellerio, C.; Pallud, J.; Dezamis, E.; Turc, G.; Rigaux-Viode, O.; Malherbe, C.; Roca, P.; Leclerc, X.; Varlet, P.; et al. Three-tesla functional MR language mapping: Comparison with direct cortical stimulation in gliomas. Neurology 2015, 84, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mampre, D.; Ehresman, J.; Pinilla-Monsalve, G.D.; Osorio, M.A.G.; Olivi, A.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Chaichana, K.L. Extending the resection beyond the contrast-enhancement for glioblastoma: Feasibility, efficacy, and outcomes. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 32, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.M.; Suki, D.; Hess, K.R.; Sawaya, R. The influence of maximum safe resection of glioblastoma on survival in 1229 patients: Can we do better than gross-total resection? J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karschnia, P.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; van den Bent, M.; Cahill, D.P.; Bello, L.; Narita, Y. Evidence-based recommendations on cate-gories for extent of resection in diffuse glioma. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, D.; Freedman, R.; Cope, L.; Sacks, P.; Abbatematteo, J.; Kubilis, P.; Bova, F.; Rahman, M. Impact of extent of resection on incidence of postoperative complications in patients with glioblastoma. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Holou, W.N.; Hodges, T.R.; Everson, R.G.; Freeman, J.; Zhou, S.; Suki, D. Perilesional resection of glioblastoma is inde-pendently associated with improved outcomes. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eseonu, C.I.; Rincon-Torroella, J.; Refaey, K.; Lee, B.Y.M.; Nangiana, J.; Vivas-Buitrago, T.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A. Awake Craniotomy vs Craniotomy Under General Anesthesia for Perirolandic Gliomas: Evaluating Perioperative Complications and Extent of Resection. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, S.T.; Han, S.J.; Li, J.; Berger, M.S. Resection of primary motor cortex tumors: Feasibility and surgical outcomes. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, J.; Dezamis, E.; Rigaux-Viode, O.; Peeters, S.; Roux, A.; Zanello, M.; Mellerio, C.; Sauvageon, X.; Varlet, P.; Oppenheim, C.; et al. Functional-based resection does not worsen quality of life in patients with a diffuse low-grade glioma involving eloquent brain regions: A prospective cohort study. World Neurosurg. 2018, 113, e200–e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, R.; Kinoshita, M.; Okita, H.; Yahata, T.; Nakada, M. Awake surgery for glioblastoma can preserve independence level, but is dependent on age and the preoperative condition. J. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 144, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Awake Resection Subgroup | Asleep Resection Subgroup | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | Sex | Age | RTOG-RPA Class | Side | Lobe | Volume | Neurosurgeon | Sex | Age | RTOG-RPA Class | Side | Lobe | Volume | Neurosurgeon |
| Complete match | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | F | 48 | 3–4 | L | F | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 49 | 3–4 | L | F | > | Expert Asleep |
| 5 | F | 63 | 3–4 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 65 | 3–4 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 7 | F | 72 | 5–5 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 68 | 5–5 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 8 | F | 50 | 3–4 | R | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 55 | 3–4 | R | T | < | Expert Asleep |
| 10 | F | 65 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 70 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 11 | F | 40 | 3–4 | L | P | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 47 | 3–4 | L | P | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 13 | M | 46 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 44 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 14 | M | 51 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 51 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 16 | M | 62 | 3–4 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 57 | 3–4 | L | F | < | Expert Asleep |
| 17 | M | 66 | 5–5 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 63 | 5–5 | L | F | < | Expert Asleep |
| 18 | M | 68 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 71 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 20 | M | 47 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 45 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Asleep |
| 21 | M | 50 | 3–4 | L | T | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 47 | 3–4 | L | T | > | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 22 | M | 66 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 68 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Asleep |
| 24 | M | 45 | 3–4 | L | P | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 46 | 3–4 | L | P | < | Expert Asleep |
| 26 | M | 44 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 46 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 27 | M | 62 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 69 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 28 | M | 59 | 5–5 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 63 | 5–5 | L | F | < | Expert Asleep |
| 29 | M | 56 | 3–4 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 57 | 3–4 | L | F | < | Expert Asleep |
| 31 | M | 51 | 5–5 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 53 | 5–5 | L | T | < | Expert Asleep |
| 33 | M | 55 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 50 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Asleep |
| 34 | M | 26 | 3–4 | R | F | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 32 | 3–4 | R | F | > | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 40 | M | 49 | 3–4 | L | P | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 46 | 3–4 | L | P | < | Expert Asleep |
| 41 | M | 54 | 3–4 | R | P | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 56 | 3–4 | R | P | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| Incomplete match in one criterion £ | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | F | 46 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 46 | 3–4 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 4 | F | 54 | 3–4 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 45 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Asleep |
| 9 | F | 59 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 64 | 3–4 | L | T | < | General |
| 19 | M | 40 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 40 | 3–4 | L | T | < | General |
| 25 | M | 66 | 5–5 | L | T | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 61 | 5–5 | L | T | < | Expert Asleep |
| 32 | M | 51 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 47 | 3–4 | L | T | > | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 39 | M | 29 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 34 | 3–4 | R | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 42 | M | 50 | 5–5 | L | P | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 49 | 5–5 | R | P | > | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| Incomplete match in two criteria £ | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | F | 33 | 3–4 | L | T | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 40 | 3–4 | R | T | > | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 6 | F | 65 | 5–5 | R | F | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 58 | 3–4 | R | F | < | Expert Asleep |
| 12 | F | 61 | 5–5 | L | P | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 60 | 3–4 | L | P | < | Expert Asleep |
| 15 | M | 54 | 5–5 | R | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 55 | 3–4 | R | F | < | General |
| 23 | M | 42 | 3–4 | L | P | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 42 | 3–4 | B | P | < | Expert Asleep |
| 35 | M | 63 | 3–4 | L | P | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 51 | 3–4 | L | P | > | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 37 | F | 57 | 3–4 | L | I | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 60 | 3–4 | R | I | > | Expert Awake-Asleep |
| 38 | M | 49 | 3–4 | L | F | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 47 | 3–4 | R | F | > | General |
| Incomplete match in three criteria £ | ||||||||||||||
| 30 | M | 56 | 5–5 | L | F | < | Expert Awake-Asleep | M | 55 | 3–4 | R | F | < | General |
| 36 | F | 39 | 3–4 | L | F | > | Expert Awake-Asleep | F | 27 | 3–4 | L | F | < | General |
| Characteristics | Whole Series | Asleep Resection Subgroup | Awake Resection Subgroup | Biopsy Subgroup | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (%) | 453 (100) | 222 (49.0) | 42 (9.3) | 189 (41.7) | |
| Age ≤60 years (%) >60 years (%) Mean ± SD | 177 (39.1) 276 (60.9) 63.0 ± 12.6 | 94 (42.3) 128 (57.7) 62.1 ± 11.7 | 30 (71.4) 12 (28.6) 52.6 ± 10.6 | 53 (28.0) 136 (72.0) 66.4 ± 12.6 | <0.0001 <0.0001 |
| Sex Female (%) Male (%) | 202 (44.6) 251 (55.4) | 107 (48.2) 115 (51.8) | 17 (40.5) 25 (59.5) | 78 (41.3) 111 (58.7) | 0.3162 |
| Time to diagnosis Mean ± SD | 1.6 ± 2.0 | 1.5 ± 1.8 | 1.7 ± 1.5 | 1.7 ± 2.2 | 0.1032 |
| Volume (cm3) Mean ± SD | 44.8 ± 50.2 | 52.1 ± 53.6 | 23.9 ± 29.3 | 40.8 ± 48.2 | <0.0001 |
| Side Right (%) Left (%) Bilateral (%) | 189 (41.7) 202 (44.6) 62 (13.7) | 124 (55.9) 80 (36.0) 18 (8.1) | 9 (21.4) 33 (78.6) 0 (0.0) | 56 (29.6) 89 (47.1) 44 (23.3) | <0.0001 |
| Location Frontal (%) Temporal (%) Parietal (%) Insular (%) Occipital (%) Basal Ganglia (%) Limbic (%) | 170 (37.5) 137 (30.2) 89 (19.7) 21 (4.6) 17 (3.8) 17 (3.8) 2 (0.4) | 65 (29.3) 92 (41.4) 46 (20.7) 7 (3.2) 12 (5.4) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) | 18 (42.9) 14 (33.3) 9 (21.4) 1 (2.4) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) | 87 (46.0) 31 (16.4) 34 (18.0) 13 (6.9) 5 (2.7) 17 (9.0) 2 (1.0) | <0.0001 |
| Presenting Symptom Asymptomatic (%) Epileptic seizures (%) Elevated intracranial pressure (%) Focal neurologic deficit (%) | 8 (1.8) 144 (31.8) 69 (15.2) 232 (51.2) | 5 (2.3) 66 (29.7) 46 (20.7) 105 (47.3) | 1 (2.4) 27 (64.2) 3 (7.1) 11 (26.2) | 2 (1.1) 51 (27.0) 20 (10.6) 116 (61.4) | <0.0001 |
| Elevated intracranial pressure No (%) Yes (%) | 315 (69.5) 138 (30.5) | 127 (57.2) 95 (42.8) | 38 (90.5) 4 (9.5) | 150 (79.4) 39 (20.6) | <0.0001 |
| Epileptic seizures at surgery No (%) Yes (%) | 281 (62.0) 172 (38.0) | 142 (64.0) 80 (36.0) | 10 (23.8) 32 (76.2) | 129 (68.5) 60 (31.5) | <0.0001 |
| Focal neurologic deficit at surgery No (%) Yes (%) | 133 (29.4) 320 (70.6) | 69 (31.1) 153 (68.9) | 22 (52.4) 20 (47.6) | 42 (22.2) 147 (77.8) | 0.0006 |
| KPS score >70 (%) ≤70 (%) Mean ± SD | 267 (58.9) 186 (41.1) 75.5 ± 15.8 | 139 (62.6) 83 (37.4) 76.7 ± 4.8 | 37 (88.1) 5 (11.9) 85.5 ± 10.9 | 91 (48.2) 98 (51.8) 71.8 ± 16.6 | <0.0001 <0.0001 |
| RTOG-RPA Class Class 3-4 (%) Class 5-6 (%) | 207 (45.7) 246 (54.3) | 141 (63.5) 81 (36.5) | 32 (76.2) 10 (23.8) | 34 (18.0) 155 (82.0) | <0.0001 |
| MGMT promoter methylation status No (%) Yes (%) Not available (%) | 76 (16.8) 60 (13.2) 317 (70.0) | 61 (27.5) 40 (18.0) 121 (54.5) | 5 (11.9) 7 (16.7) 30 (71.4) | 10 (5.3) 13 (6.9) 166 (87.8) | <0.0001 |
| Neurosurgeon Expert both in awake and asleep surgery Expert only in asleep surgery General | 223 (49.2) 116 (25.6) 114 (25.2) | 89 (40.1) 52 (23.4) 81 (36.5) | 42 (100) 0 (0) 0 (0) | 92 (48.7) 64 (33.9) 33 (17.5) | <0.0001 |
| Extent of resection Mean resection ± SD Mean residual ± SD Partial (%) Total (%) Supratotal (%) | 98 (21.6) 150 (33.1) 16 (3.5) | 92.9 ± 15.1 7.3 ± 15.6 89 (40.1) 126 (56.8) 7 (3.1) | 93.9 ± 18.7 6.3 ± 19.2 9 (21.4) 24 (57.2) 9 (21.4) | 0.0313 0.0306 <0.0001 | |
| Surgery-related Complications Surgical site hematoma (%) Surgical site infection (%) Systemic infection (%) Seizures worsening (%) Focal neurologic deficit worsening (%) Thrombosis (%) | 10 (2.2) 9 (2.0) 10 (2.2) 20 (4.4) 69 (15.2) 9 (2.0) | 3 (1.4) 8 (3.6) 7 (3.2) 11 (5.0) 42 (18.9) 6 (2.7) | 1 (2.4) 1 (0.2) 2 (4.8) 0 (0.0) 8 (19.0) 0 (0.0) | 6 (3.2) 0 (0.0) 1 (0.5) 9 (4.8) 19 (10.1) 3 (1.6) | 0.4490 0.0330 0.0975 0.1358 0.0299 0.4514 |
| One-Month Postoperative Death (%) No (%) Yes (%) | 437 (96.5) 16 (3.5) | 219 (98.6) 3 (1.4) | 42 (100) 0 (0.0) | 176 (93.1) 13 (6.9) | 0.0025 |
| Postoperative Oncological Treatment Standard Radiochemotherapy Protocol Radiotherapy alone (%) Temozolomide alone (%) Radiotherapy followed by Temozolomide (%) Other chemotherapy Supportive care (%) Lost to Follow-Up (%) | 275 (60.7) 45 (9.9) 27 (6.0) 26 (5.7) 2 (0.5) 59 (13.0) 19 (4.2) | 165 (74.3) 18 (8.1) 8 (3.6) 15 (6.8) 0 (0.0) 12 (5.4) 4 (1.8) | 38 (90.4) 2 (4.8) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 2 (4.8) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) | 72 (38.1) 25 (13.2) 19 (10.1) 11 (5.8) 0 (0.0) 47 (24.9) 15 (7.9) | <0.0001 |
| Time to Oncological Treatment Weeks ± SD | 5.5 ± 2.5 | 5.9 ± 2.5 | 4.2 ± 2.5 | 5.2 ± 2.2 | 0.0008 |
| Molinaro’s Classes (1-4) 1 2 3 4 Biopsy only (excluded) | 7 (1.5) 114 (25.2) 121 (26.7) 22 (4.9) 189 (41.7) | 6 (2.7) 104 (46.9) 96 (43.2) 16 (7.2) 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.4) 10 (23.8) 25 (59.5) 6 (14.3) 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 189 (100) | 0.0325 |
| Progression-Free Survival Median (months) [95% CI] | 7.0 [6.5–8.0] | 9.0 [8.0–10.0] | 16.0 [11.1–26.0] | 4.7 [4.0–6.0] | <0.0001 |
| Overall Survival Median (months) [95% CI] | 13.6 [12.0–16.0] | 17.2 [15.1–19.4] | 36.0 [24.0–42.0] | 7.0 [5.0–8.0] | <0.0001 |
| Parameter | Progression-Free Survival | Overall Survival | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted Hazard Ratio | Adjusted Hazard Ratio | Unadjusted Hazard Ratio | Adjusted Hazard Ratio | |||||||||
| uHR | CI95% | p-Value | aHR | CI95% | p-Value | uHR | CI95% | p-Value | aHR | CI95% | p-Value | |
| Age ≤60 years >60 years | 1 (ref) 1.25 | 0.99–1.58 | 0.0638 | 1 (ref) 1.76 | 1.40–2.21 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Sex Female Male | 1 (ref) 1.07 | 0.87–1.31 | 0.4992 | 1 (ref) 1.06 | 0.76–1.32 | 0.6101 | ||||||
| Volume ≤28 cm3 >28 cm3 | 1 (ref) 1.13 | 0.92–1.38 | 0.2305 | 1 (ref) 1.34 | 1.08–1.67 | 0.0074 | ||||||
| Location Frontal Temporal Parietal Insular Occipital Deep seated | 1 (ref) 0.95 0.76 1.41 0.82 2.12 | 0.72–1.25 0.54–1.08 0.77–2.57 0.44–1.54 0.97–4.61 | 0.7175 0.1246 0.2640 0.5437 0.0586 | 1 (ref) 0.79 0.80 2.07 0.57 2.29 | 0.61–1.03 0.59–1.10 1.27–3.37 0.30–1.04 1.34–3.94 | 0.0793 0.1763 0.0033 0.0687 0.0025 | ||||||
| KPS score ≤70 >70 | 1 (ref) 0.56 | 0.45–0.69 | <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.49 | 0.39–0.61 | <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.66 | 0.52–0.85 | 0.0013 | |||
| RTOG-RPA classes * 3-4 5-6 | 1 (ref) 1.43 | 1.13–1.82 | 0.0031 | 1 (ref) 3.43 | 2.13–5.52 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| MGMT promoter Non methylated Methylated Not available | 1 (ref) 0.64 1.01 | 0.45–0.92 0.78–1.32 | 0.0159 0.9109 | 1 (ref) 0.54 1.01 | 0.36–0.79 0.77–1.32 | 0.0017 0.9293 | 1 (ref) 0.55 1.04 | 0.37–0.82 0.48–1.87 | 0.0031 0.4043 | |||
| Neurosurgeon General Expert in Glioma | 1 (ref) 0.71 | 0.42–1.19 | 0.1946 | 1 (ref) 0.89 | 0.71–1.12 | 0.3176 | ||||||
| Extent of resection Biopsy Supratotal Total Partial | 1 (ref) 0.17 0.38 0.62 | 0.08–0.33 0.29–0.48 0.48–0.81 | <0.0001 <0.0001 0.0005 | 1 (ref) 0.31 0.52 0.81 | 015–0.65 0.40–0.68 0.61–1.06 | 0.0019 <0.0001 0.13 | 1 (ref) 0.13 0.30 0.63 | 0.06–0.29 0.23–0.39 0.48–0.83 | <0.0001 <0.0001 0.0013 | 1 (ref) 0.27 0.43 0.72 | 0.12–0.62 0.32–0.57 0.54–0.98 | 0.0021 <0.0001 0.0366 |
| Surgery Asleep Awake | 1 (ref) 0.39 | 0.26–0.59 | <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.61 | 0.40–0.93 | 0.0157 | 1 (ref) 0.33 | 0.21–0.52 | <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.54 | 0.33–0.89 | 0.0156 |
| Treatment Abstention Other treatment Stupp protocol | 1 (ref) 0.19 0.06 | 0.13–0.28 0.04–0.09 | <0.0001 <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.21 0.08 | 0.14–0.30 0.05–0.12 | <0.0001 <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.38 0.16 | 0.22–0.67 0.12–0.21 | 0.0006 <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.39 0.22 | 0.22–0.68 0.16–0.29 | 0.0010 <0.0001 |
| Molinaro’s classes * Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 | 1 (ref) 0.15 0.11 0.12 | 0.04–0.63 0.02–0.47 0.03–0.57 | 0.0097 0.0030 0.0072 | 1 (ref) 0.12 0.06 0.05 | 0.05–0.31 0.02–0.16 0.02–0.16 | <0.0001 <0.0001 <0.0001 | ||||||
| Parameter | Progression-Free Survival | Overall Survival | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted Hazard Ratio | Adjusted Hazard Ratio | Unadjusted Hazard Ratio | Adjusted Hazard Ratio | |||||||||
| uHR | CI95% | p-Value | aHR | CI95% | p-Value | uHR | CI95% | p-Value | aHR | CI95% | p-Value | |
| Age ≤60 years >60 years | 1 (ref) 1.12 | 0.79–1.56 | 0.5228 | 1 (ref) 1.92 | 1.40–2.65 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Sex Female Male | 1 (ref) 1.05 | 0.75–1.48 | 0.7716 | 1 (ref) 1.01 | 0.73–1.37 | 0.9856 | ||||||
| Volume ≤ 28 cm3 > 28 cm3 | 1 (ref) 1.17 | 0.95–1.54 | 0.4556 | 1 (ref 1.28 | 1.02–1.54 | 0.0138 | ||||||
| Location Frontal Temporal Parietal Insular Occipital Deep seated | 1 (ref) 1.03 0.73 2.12 0.88 2.77 | 0.70–1.53 0.44–1.22 0.95–4.69 0.39–1.95 0.85–9.02 | 0.8586 0.2351 0.0648 0.7545 0.0911 | 1 (ref) 0.79 0.73 2.10 0.39 3.55 | 0.56–1.15 0.45–1.17 1.04–4.25 0.15–0.99 1.51–8.33 | 0.2285 0.1879 0.0390 0.0479 0.0036 | ||||||
| KPS score ≤70 >70 | 1 (ref) 0.59 | 0.39–0.86 | 0.0067 | 1 (ref) 0.41 | 0.29–0.56 | <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.51 | 0.35–0.74 | 0.0003 | |||
| RTOG-RPA classes * 3-4 5-6 | 1 (ref) 1.46 | 1.03–2.06 | 0.0321 | 1 (ref) 2.79 | 2.03–3.84 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| MGMT promoter Non methylated Methylated Not available | 1 (ref) 0.43 0.72 | 0.24–0.74 0.49–1.07 | 0.0027 0.1080 | 1 (ref) 0.46 0.62 | 0.27–0.81 0.41–1.26 | 0.0073 0.2820 | 1 (ref) 0.42 0.97 | 0.24–0.74 0.66–1.40 | 0.0027 0.8599 | 1 (ref) 0.42 1.18 | 0.23–0.75 0.78–1.60 | 0.0037 0.5422 |
| Extent of resection Biopsy Supratotal Total Partial | 1 (ref) 0.26 0.53 0.83 | 0.12–0.53 0.36–0.78 0.49–1.37 | 0.0002 0.0012 0.4646 | 1 (ref) 0.35 0.62 0.81 | 0.15–0.81 0.39–0.98 0.46–1.43 | 0.0145 0.0433 0.4698 | 1 (ref) 0.14 0.30 0.56 | 0.06–0.30 0.21–0.43 0.35–0.89 | <0.0001 <0.0001 0.0142 | 1 (ref) 0.31 0.46 0.67 | 0.13–0.76 0.29–0.71 0.39–1.14 | 0.0098 0.0005 0.1375 |
| Surgery Asleep Awake | 1 (ref) 0.50 | 0.32–0.78 | 0.0019 | 1 (ref) 0.63 | 0.39–0.98 | 0.0397 | 1 (ref) 0.34 | 0.21–0.54 | <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.50 | 0.29–0.85 | 0.0115 |
| Treatment Abstention Other Treatment Stupp protocol | 1 (ref) 0.57 0.23 | 0.25–1.29 0.14–0.39 | 0.1792 <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.57 0.25 | 0.25–1.29 0.15–0.41 | 0.1973 <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.41 0.16 | 0.19–0.86 0.11–0.22 | 0.0184 <0.0001 | 1 (ref) 0.53 0.23 | 0.24–1.55 0.15–0.34 | 0.1099 <0.0001 |
| Molinaro’s classes * Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 | 1 (ref) 0.08 0.06 0.08 | 0.02–0.39 0.01–0.27 0.02–0.40 | 0.0016 0.0003 0.0024 | 1 (ref) 0.12 0.06 0.07 | 0.03–0.43 0.02–0.21 0.02–0.28 | 0.0011 <0.0001 0.0002 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moiraghi, A.; Roux, A.; Peeters, S.; Pelletier, J.-B.; Baroud, M.; Trancart, B.; Oppenheim, C.; Lechapt, E.; Benevello, C.; Parraga, E.; et al. Feasibility, Safety and Impact on Overall Survival of Awake Resection for Newly Diagnosed Supratentorial IDH-Wildtype Glioblastomas in Adults. Cancers 2021, 13, 2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13122911
Moiraghi A, Roux A, Peeters S, Pelletier J-B, Baroud M, Trancart B, Oppenheim C, Lechapt E, Benevello C, Parraga E, et al. Feasibility, Safety and Impact on Overall Survival of Awake Resection for Newly Diagnosed Supratentorial IDH-Wildtype Glioblastomas in Adults. Cancers. 2021; 13(12):2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13122911
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoiraghi, Alessandro, Alexandre Roux, Sophie Peeters, Jean-Baptiste Pelletier, Marwan Baroud, Bénédicte Trancart, Catherine Oppenheim, Emmanuèle Lechapt, Chiara Benevello, Eduardo Parraga, and et al. 2021. "Feasibility, Safety and Impact on Overall Survival of Awake Resection for Newly Diagnosed Supratentorial IDH-Wildtype Glioblastomas in Adults" Cancers 13, no. 12: 2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13122911
APA StyleMoiraghi, A., Roux, A., Peeters, S., Pelletier, J. -B., Baroud, M., Trancart, B., Oppenheim, C., Lechapt, E., Benevello, C., Parraga, E., Varlet, P., Chrétien, F., Dezamis, E., Zanello, M., & Pallud, J. (2021). Feasibility, Safety and Impact on Overall Survival of Awake Resection for Newly Diagnosed Supratentorial IDH-Wildtype Glioblastomas in Adults. Cancers, 13(12), 2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13122911