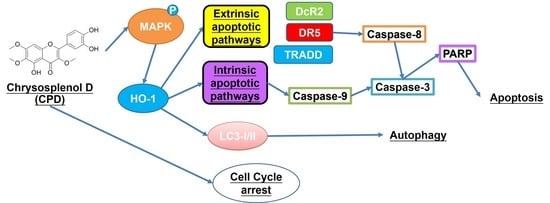
Chrysosplenol D Triggers Apoptosis through Heme Oxygenase-1 and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Clonogenic Assay
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Chromatin Condensation Assay
2.8. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide Double Staining
2.9. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Analysis
2.10. In Situ Immunofluorescence Assay
2.11. Autophagosome Detection Assay
2.12. Specific Inhibitor Treatments
2.13. RNA Interference Experiments
2.14. The Cancer Genome Atlas Database Analysis
2.15. Gene Expression Omnibus Dataset Analysis
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chrysosplenol D Exhibits Antiproliferative Activity and Causes Cell Cycle Arrest in the G2/M Phase in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) Cell Lines
3.2. Apoptotic Effect of Chrysosplenol D on OSCC Cell Lines
3.3. Activation of Autophagy and the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Pathway by Chrysosplenol D in OSCC
3.4. HO-1 Is Involved in Chrysosplenol D-Activated Apoptotic Cell Death in OSCC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, H.; Langerman, A.; Zhang, Y.; Khalid, O.; Hu, S.; Cao, C.X.; Lingen, M.W.; Wong, D.T.W. Quantitative proteomic analysis of microdissected oral epithelium for cancer biomarker discovery. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, R.; Sinha, D.N.; Mehrotra, R. Relationship between type of smokeless tobacco & risk of cancer: A systematic review. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, 56–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.; Sauvaget, C.; de Camargo Cancela, M.; Sankaranarayanan, R. Epidemiology of cancer from the oral cavity and oropharynx. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 23, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; David, M.; Ellis, O.; Hubert Low, T.H.; Palme, C.E.; Clark, J.; Batstone, M. Treatment for oral squamous cell carcinoma: Impact of surgeon volume on survival. Oral Oncol. 2019, 96, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharat, S.A.; Momin, M.; Bhavsar, C. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Current Treatment Strategies and Nanotechnology-Based Approaches for Prevention and Therapy. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2016, 33, 363–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, Y.C.; Hwang, J.H.; Ahn, K.M. Overall and disease-specific survival outcomes following primary surgery for oral squamous cell carcinoma: Analysis of consecutive 67 patients. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 45, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, A.M.; Ryter, S.W.; Levine, B. Autophagy in human health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1845–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Noda, T.; Yoshimori, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishii, T.; George, M.D.; Klionsky, D.J.; Ohsumi, M.; Ohsumi, Y. A protein conjugation system essential for autophagy. Nature 1998, 395, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhammer, F.A.; Hochegger, K.; Froschl, G.; Tiefenbacher, R.; Pavelka, M. Chromatin condensation during apoptosis is accompanied by degradation of lamin A+B, without enhanced activation of cdc2 kinase. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 126, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lai, Y.; Hua, Z.C. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: Disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chipuk, J.E.; Bouchier-Hayes, L.; Green, D.R. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: The innocent bystander scenario. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Yuan, J. Caspases in apoptosis and beyond. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6194–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowe, S.W.; Lin, A.W. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, E.Y.; Ryan, K.M. Autophagy and cancer—Issues we need to digest. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S. Autophagy, mitochondrial quality control, and oncogenesis. Autophagy 2006, 2, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karantza-Wadsworth, V.; White, E. Role of autophagy in breast cancer. Autophagy 2007, 3, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; White, E. Role of autophagy in cancer: Management of metabolic stress. Autophagy 2007, 3, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graeber, T.G.; Osmanian, C.; Jacks, T.; Housman, D.E.; Koch, C.J.; Lowe, S.W.; Giaccia, A.J. Hypoxia-mediated selection of cells with diminished apoptotic potential in solid tumours. Nature 1996, 379, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, K.; Mathew, R.; Beaudoin, B.; Bray, K.; Anderson, D.; Chen, G.; Mukherjee, C.; Shi, Y.; Gelinas, C.; Fan, Y.; et al. Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fulda, S.; Debatin, K.M. Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4798–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashkenazi, A. Targeting the extrinsic apoptosis pathway in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, L.Y. Heme oxygenase-1: Emerging target of cancer therapy. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, B.; Chen, G.; Xu, L.; Zhou, H. Expression and function of heme oxygenase-1 in human gastric cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2012, 237, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degese, M.S.; Mendizabal, J.E.; Gandini, N.A.; Gutkind, J.S.; Molinolo, A.; Hewitt, S.M.; Curino, A.C.; Coso, O.A.; Facchinetti, M.M. Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and its correlation with clinical data. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.F.; Yeh, C.T.; Sun, Y.J.; Chiang, M.T.; Lan, W.M.; Li, F.A.; Lee, W.H.; Chau, L.Y. Signal peptide peptidase-mediated nuclear localization of heme oxygenase-1 promotes cancer cell proliferation and invasion independent of its enzymatic activity. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2410–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, N.A.; Alonso, E.N.; Fermento, M.E.; Mascaro, M.; Abba, M.C.; Colo, G.P.; Arevalo, J.; Ferronato, M.J.; Guevara, J.A.; Nunez, M.; et al. Heme Oxygenase-1 Has an Antitumor Role in Breast Cancer. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 2030–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagawa, T.; Omura, K.; Harada, H.; Nakaso, K.; Iwasa, S.; Koyama, Y.; Onizawa, K.; Yusa, H.; Yoshida, H. Heme oxygenase-1 expression predicts cervical lymph node metastasis of tongue squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2004, 40, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bridgford, J.L.; Xie, S.C.; Cobbold, S.A.; Pasaje, C.F.A.; Herrmann, S.; Yang, T.; Gillett, D.L.; Dick, L.R.; Ralph, S.A.; Dogovski, C.; et al. Artemisinin kills malaria parasites by damaging proteins and inhibiting the proteasome. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slezakova, S.; Ruda-Kucerova, J. Anticancer Activity of Artemisinin and its Derivatives. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 5995–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, J.F.; Luthria, D.L.; Sasaki, T.; Heyerick, A. Flavonoids from Artemisia annua L. as antioxidants and their potential synergism with artemisinin against malaria and cancer. Molecules 2010, 15, 3135–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lang, S.J.; Schmiech, M.; Hafner, S.; Paetz, C.; Werner, K.; El Gaafary, M.; Schmidt, C.Q.; Syrovets, T.; Simmet, T. Chrysosplenol d, a Flavonol from Artemisia annua, Induces ERK1/2-Mediated Apoptosis in Triple Negative Human Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Weng, X.G.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.C.; et al. Flavonoids casticin and chrysosplenol D from Artemisia annua L. inhibit inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 286, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, J.; Ying, G.G.; Wang, G.W.; Zhang, L. Quercetin inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via Bcl-2 and Bax regulation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, B.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Kaempferol induces apoptosis in human HCT116 colon cancer cells via the Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated-p53 pathway with the involvement of p53 Upregulated Modulator of Apoptosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 177, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, Y.; Mao, Q.Q.; Li, X.; Chen, M.W.; Su, J.; Tian, L.; Mao, N.Q.; Long, L.Z.; Quan, M.F.; et al. Casticin induces caspase-mediated apoptosis via activation of mitochondrial pathway and upregulation of DR5 in human lung cancer cells. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franken, N.A.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; van Bree, C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, T.; Yang, P.C. Western blot: Technique, theory, and trouble shooting. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 4, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estandarte, A.K.; Botchway, S.; Lynch, C.; Yusuf, M.; Robinson, I. The use of DAPI fluorescence lifetime imaging for investigating chromatin condensation in human chromosomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamuru, S.; Attene-Ramos, M.S.; Xia, M. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1473, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.C.; Hsieh, M.C.; Lin, S.H.; Lin, C.C.; Hsi, Y.T.; Lo, Y.S.; Chuang, Y.C.; Hsieh, M.J.; Chen, M.K. Coronarin D induces reactive oxygen species-mediated cell death in human nasopharyngeal cancer cells through inhibition of p38 MAPK and activation of JNK. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108006–108019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhon, I.; Reggiori, F. Assays to Monitor Autophagy Progression in Cell Cultures. Cells 2017, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saraste, A.; Pulkki, K. Morphologic and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 45, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, J.D.; Grubb, D.R.; Lawen, A. The mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; an update. Apoptosis 2003, 8, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Hsieh, M.J.; Chen, P.N.; Weng, C.J.; Yang, S.F.; Lin, C.W. Erianin Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bu, S. Curcumin Induces Autophagy, Apoptosis, and Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Evid.-Based Complementary Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 5787218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, W.X.; Yan, F.; Xue, Q.; Wu, G.J.; Qin, W.J.; Wang, F.L.; Qin, J.; Tian, C.J.; Yuan, J.L. Heme oxygenase-1 is a predictive biomarker for therapeutic targeting of advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with sorafenib or sunitinib. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 2081–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.X.; Cui, C.B.; Cai, B.; Wang, H.Y.; Yao, X.S. Flavonoids from Vitex trifolia L. inhibit cell cycle progression at G2/M phase and induce apoptosis in mammalian cancer cells. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 7, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.H.; Ye, S.; Li, X.J.; Lee, K.B.; Park, M.H.; Kim, S.M. Combination treatment with paclitaxel and doxorubicin inhibits growth of human esophageal squamous cancer cells by inactivation of Akt. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, Z.A.; Westfall, M.D.; Pietenpol, J.A. Cell-cycle dysregulation and anticancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 24, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, U.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Turner, N.C.; Knudsen, E.S. The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent kinases in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Y.; Hannon, G.J.; Zhang, H.; Casso, D.; Kobayashi, R.; Beach, D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature 1993, 366, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.A.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Patten, A.K.; Massague, J.; Pavletich, N.P. Crystal structure of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent-kinase inhibitor bound to the cyclin A-Cdk2 complex. Nature 1996, 382, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.J.; Wang, C.W.; Lin, J.T.; Chuang, Y.C.; Hsi, Y.T.; Lo, Y.S.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, M.K. Celastrol, a plant-derived triterpene, induces cisplatin-resistance nasopharyngeal carcinoma cancer cell apoptosis though ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2019, 58, 152805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivandzade, F.; Bhalerao, A.; Cucullo, L. Analysis of the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Using the Cationic JC-1 Dye as a Sensitive Fluorescent Probe. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; El-Deiry, W.S. TRAIL and apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8628–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, D.R. Apoptotic pathways: Paper wraps stone blunts scissors. Cell 2000, 102, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeBlanc, H.N.; Ashkenazi, A. Apo2L/TRAIL and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, G.; Ni, J.; Wei, Y.F.; Yu, G.; Gentz, R.; Dixit, V.M. An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science 1997, 277, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattingre, S.; Tassa, A.; Qu, X.; Garuti, R.; Liang, X.H.; Mizushima, N.; Packer, M.; Schneider, M.D.; Levine, B. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005, 122, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gump, J.M.; Thorburn, A. Autophagy and apoptosis: What is the connection? Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moscat, J.; Diaz-Meco, M.T. p62 at the crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell 2009, 137, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathew, R.; Karp, C.M.; Beaudoin, B.; Vuong, N.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.Y.; Bray, K.; Reddy, A.; Bhanot, G.; Gelinas, C.; et al. Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis through elimination of p62. Cell 2009, 137, 1062–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marino, G.; Niso-Santano, M.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Kroemer, G. Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, N.; Itoh, T.; Omori, H.; Fukuda, M.; Noda, T.; Yoshimori, T. The Atg16L complex specifies the site of LC3 lipidation for membrane biogenesis in autophagy. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 2092–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fresno Vara, J.A.; Casado, E.; de Castro, J.; Cejas, P.; Belda-Iniesta, C.; Gonzalez-Baron, M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004, 30, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.H.; Hong, K.O.; Jin, B.; Lee, W.; Jung, Y.C.; Lee, H.; Shin, J.A.; Cho, S.D.; Hong, S.D. Contribution of p38 MAPK Pathway to Norcantharidin-Induced Programmed Cell Death in Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, C. Genipin Induces Autophagy and Suppresses Cell Growth of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma via PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, H.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lo, Y.S.; Hsieh, M.J.; Chen, M.K. Apoptotic effects of dehydrocrenatidine via JNK and ERK pathway regulation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitti, M.; Piras, S.; Marinari, U.M.; Moretta, L.; Pronzato, M.A.; Furfaro, A.L. HO-1 Induction in Cancer Progression: A Matter of Cell Adaptation. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunamura, M.; Duda, D.G.; Ghattas, M.H.; Lozonschi, L.; Motoi, F.; Yamauchi, J.; Matsuno, S.; Shibahara, S.; Abraham, N.G. Heme oxygenase-1 accelerates tumor angiogenesis of human pancreatic cancer. Angiogenesis 2003, 6, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berberat, P.O.; Dambrauskas, Z.; Gulbinas, A.; Giese, T.; Giese, N.; Kunzli, B.; Autschbach, F.; Meuer, S.; Buchler, M.W.; Friess, H. Inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 increases responsiveness of pancreatic cancer cells to anticancer treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- So, K.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, K.T.; Lee, H.Y.; Oh, S.H. MAPK/JNK1 activation protects cells against cadmium-induced autophagic cell death via differential regulation of catalase and heme oxygenase-1 in oral cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 332, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, M.H.; Yang, W.E.; Yang, Y.C.; Ku, C.C.; Lee, W.J.; Tsai, M.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, S.F. Dual Targeting of the p38 MAPK-HO-1 Axis and cIAP1/XIAP by Demethoxycurcumin Triggers Caspase-Mediated Apoptotic Cell Death in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, M.-J.; Lin, C.-C.; Lo, Y.-S.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Ho, H.-Y.; Chen, M.-K. Chrysosplenol D Triggers Apoptosis through Heme Oxygenase-1 and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4327. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174327
Hsieh M-J, Lin C-C, Lo Y-S, Chuang Y-C, Ho H-Y, Chen M-K. Chrysosplenol D Triggers Apoptosis through Heme Oxygenase-1 and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4327. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174327
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, Ming-Ju, Chia-Chieh Lin, Yu-Sheng Lo, Yi-Ching Chuang, Hsin-Yu Ho, and Mu-Kuan Chen. 2021. "Chrysosplenol D Triggers Apoptosis through Heme Oxygenase-1 and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4327. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174327
APA StyleHsieh, M. -J., Lin, C. -C., Lo, Y. -S., Chuang, Y. -C., Ho, H. -Y., & Chen, M. -K. (2021). Chrysosplenol D Triggers Apoptosis through Heme Oxygenase-1 and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 13(17), 4327. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174327