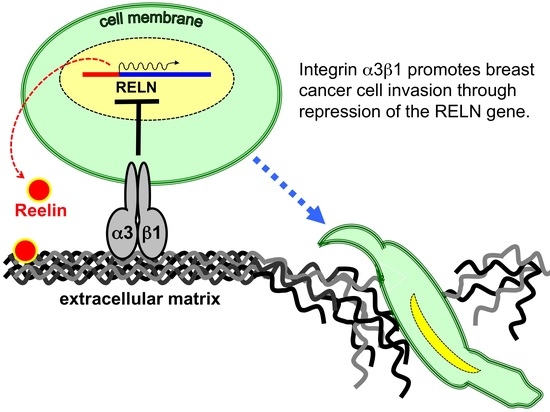
Integrin α3β1 Represses Reelin Expression in Breast Cancer Cells to Promote Invasion
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. RNAi-Mediated Suppression of Integrin α3β1 Increases RELN Gene Expression in Breast Cancer Cells
2.2. Modulation of RELN Expression in Breast Cancer Cells Alters Invasiveness
2.3. Reelin that Is Secreted by α3β1-Deficient MDA-MB-231 Cells Inhibits Cell Invasion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. siRNA- and shRNA-Mediated Gene Suppression
4.3. Stable Overexpression of Recombinant RELN
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. RELN Promoter Transfection and Luciferase Assay
4.7. Matrigel Invasion Assay
4.8. Flow Cytometry
4.9. Preparation of Laminin-332-Rich ECM from SCC-25 Cells
4.10. Treatment of Cells with Anti-α3β1 Blocking Antibody
4.11. Bioinformatics
4.12. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeSantis, C.E.; Ma, J.; Gaudet, M.M.; Newman, L.A.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niland, S.; Eble, J.A. Hold on or Cut? Integrin- and MMP-Mediated Cell–Matrix Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, L.; Roy, D. Candidate prognostic markers in breast cancer: Focus on extracellular proteases and their inhibitors. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2014, 6, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. The extracellular matrix: A dynamic niche in cancer progression. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Di, G. Role of tumor microenvironment in triple-negative breast cancer and its prognostic significance. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 29, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.E.A.; Elhassan, N.M. Cytoskeletal and extracellular matrix proteins as markers for metastatic triple negative breast cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 5767–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Jung, S.P.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.E.; Nam, S.J.; Bae, J.W. Role of secreted type I collagen derived from stromal cells in two breast cancer cell lines. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subbaram, S.; DiPersio, C.M. Integrin α3β1 as a breast cancer target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercurio, A.M.; Bachelder, R.E.; Chung, J.; O’Connor, K.L.; Rabinovitz, I.; Shaw, L.M.; Tani, T. Integrin Laminin Receptors and Breast Carcinoma Progression. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2001, 6, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, J.; Kusuma, N.; Anderson, R.L.; Parker, B.S.; Bidwell, B.; Zamurs, L.; Nice, E.; Pouliot, N. Evidence for a Role of Tumor-Derived Laminin-511 in the Metastatic Progression of Breast Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 2135–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, Allosteric Signaling Machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphries, J.D.; Byron, A.; Humphries, M.J. Integrin ligands at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 3901–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, K.; Svenson, K.B.; Longmate, W.M.; Gkirtzimanaki, K.; Sadej, R.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Eliopoulos, A.G.; Berditchevski, F.; DiPersio, C.M. Suppression of Integrin α3β1 in Breast Cancer Cells Reduces Cyclooxygenase-2 Gene Expression and Inhibits Tumorigenesis, Invasion, and Cross-Talk to Endothelial Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6359–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subbaram, S.; Lyons, S.P.; Svenson, K.B.; Hammond, S.L.; McCabe, L.G.; Chittur, S.V.; DiPersio, C.M. Integrin α3β1 controls mRNA splicing that determines Cox-2 mRNA stability in breast cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Arcangelo, G.; Nakajima, K.; Miyata, T.; Ogawa, M.; Mikoshiba, K.; Curran, T. Reelin Is a Secreted Glycoprotein Recognized by the CR-50 Monoclonal Antibody. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Arcangelo, G. Reelin in the Years: Controlling Neuronal Migration and Maturation in the Mammalian Brain. Adv. Neurosci. 2014, 2014, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchi, C.C.; Wannenes, F.; Persico, A.M.; Ciafré, S.A.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Farace, M.G.; Keller, F. Reelin Is a Serine Protease of the Extracellular Matrix. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trommsdorff, M.; Gotthardt, M.; Hiesberger, T.; Shelton, J.; Stockinger, W.; Nimpf, J.; Hammer, R.E.; Richardson, J.A.; Herz, J. Reeler/Disabled-like Disruption of Neuronal Migration in Knockout Mice Lacking the VLDL Receptor and ApoE Receptor 2. Cell 1999, 97, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howell, B.W.; Herrick, T.M.; Cooper, J.A.A. Reelin-induced tryosine phosphorylation of Disabled 1 during neuronal positioning. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulabon, L.; Olson, E.C.; Taglienti, M.G.; Eisenhuth, S.; McGrath, B.; Walsh, C.A.; Kreidberg, J.A.; Anton, E.S. Reelin binds α3β1 integrin and inhibits neuronal migration. Neuron 2000, 27, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khialeeva, E.; Lane, T.F.; Carpenter, E.M. Disruption of reelin signaling alters mammary gland morphogenesis. Development 2011, 138, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, T.; Cosimo, E.; Yu, X.; Smith, P.R.; Simon, R.; Cottrell, L.; Pringle, M.-A.; Bell, A.K.; Lattanzio, L.; Sauter, G.; et al. Loss of Reelin Expression in Breast Cancer Is Epigenetically Controlled and Associated with Poor Prognosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, N.; Dohi, O.; Takada, H.; Yasui, K.; Sakakura, C.; Mitsufuji, S.; Naito, Y.; Taniwaki, M.; Yoshikawa, T. Epigenetic silencing of RELN in gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 36, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-M.; Kelly, D.; Griffith, M.; Omura, N.; Li, A.; Li, C.-P.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Multiple genes are hypermethylated in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neman, J.; Termini, J.; Wilczynski, S.; Vaidehi, N.; Choy, C.; Kowolik, C.M.; Li, H.; Hambrecht, A.C.; Roberts, E.; Jandial, R. Human breast cancer metastases to the brain display GABAergic properties in the neural niche. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jandial, R.; Choy, C.; Levy, D.M.; Chen, M.Y.; Ansari, K.I. Astrocyte-induced Reelin expression drives proliferation of Her2+ breast cancer metastases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2017, 34, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sharma, R.P.; Costa, R.H.; Costa, E.; Grayson, D.R. On the epigenetic regulation of the human reelin promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 2930–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayner, E.A.; Carter, W.G. Identification of multiple cell adhesion receptors for collagen and fibronectin in human fibrosarcoma cells possessing unique alpha and common beta subunits. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koie, M.; Okumura, K.; Hisanaga, A.; Kamei, T.; Sasaki, K.; Deng, M.; Baba, A.; Kohno, T.; Hattori, M. Cleavage within Reelin Repeat 3 Regulates the Duration and Range of the Signaling Activity of Reelin Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12922–12930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Kobayashi, D.; Kohno, T.; Kidani, Y.; Prox, J.; Becker-Pauly, C.; Hattori, M. Determination of cleavage site of Reelin between its sixth and seventh repeat and contribution of meprin metalloproteases to the cleavage. J. Biochem. 2015, 159, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, N.; Fukushima, N.; Chang, R.; Matsubayashi, H.; Goggins, M. Differential and Epigenetic Gene Expression Profiling Identifies Frequent Disruption of the RELN Pathway in Pancreatic Cancers. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 548–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Erfani, S.; Liu, Z.; Jia, C.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Deng, X.; Alfáro, J.E.; Chen, L.; Napier, D.; et al. CD151-α3β1 integrin complexes are prognostic markers of glioblastoma and cooperate with EGFR to drive tumor cell motility and invasion. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29675–29693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soares, M.Q.S.; Mendonça, J.A.; Morais, M.O.; Leles, C.R.; Batista, A.C.; Mendonça, E.F. E-Cadherin, β-Catenin, and A2β1 and A3β1 integrin expression in primary oral squamous cell carcinoma and its regional metastasis. Histol. Histopathol. 2015, 30, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stipp, C.S. Laminin-binding integrins and their tetraspanin partners as potential antimetastatic targets. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2010, 12, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cagnet, S.; Faraldo, M.M.; Kreft, M.; Sonnenberg, A.; Raymond, K.; Glukhova, M.A. Signaling events mediated by α3β1 integrin are essential for mammary tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2013, 33, 4286–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramovs, V.; Garcia, A.K.; Kreft, M.; Sonnenberg, A. Integrin α3β1 is a key regulator of several pro-tumorigenic pathways during skin carcinogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmate, W.M. Keeping a Secretome: Emerging Roles for Epithelial Integrins in Controlling a Stroma-Supportive Secretome. J. Dermatol. Ski. Sci. 2020, 2, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ramovs, V.; Te Molder, L.; Sonnenberg, A. The opposing roles of laminin-binding integrins in cancer. Matrix Biol. 2017, 57–58, 213–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmate, W.M.; Lyons, S.P.; DeFreest, L.; Van De Water, L.; DiPersio, C.M. Opposing Roles of Epidermal Integrins α3β1 and α9β1 in Regulation of mTLD/BMP-1–Mediated Laminin-γ2 Processing during Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, K.; Szekeres, C.; Milano, V.; Svenson, K.B.; Nilsen-Hamilton, M.; Kreidberg, J.A.; DiPersio, C.M. 3 1 integrin in epidermis promotes wound angiogenesis and keratinocyte-to-endothelial-cell crosstalk through the induction of MRP3. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1778–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramovs, V.; Garcia, A.K.; Song, J.-Y.; De Rink, I.; Kreft, M.; Goldschmeding, R.; Sonnenberg, A. Integrin α3β1 in hair bulge stem cells modulates CCN2 expression and promotes skin tumorigenesis. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3, e202000645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missan, D.S.; Chittur, S.V.; DiPersio, C.M. Regulation of fibulin-2 gene expression by integrin α3β1 contributes to the invasive phenotype of transformed keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longmate, W.M.; Monichan, R.; Chu, M.-L.; Tsuda, T.; Mahoney, M.G.; DiPersio, C.M. Reduced Fibulin-2 Contributes to Loss of Basement Membrane Integrity and Skin Blistering in Mice Lacking Integrin α3β1 in the Epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Koblinski, J.; Johnson, J.; Liu, Y.; Ericsson, A.; Davis, J.W.; Shi, Z.; Ravosa, M.J.; Crawford, S.; Frazier, S.; et al. Urinary-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor/α3β1 Integrin Signaling, Altered Gene Expression, and Oral Tumor Progression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiPersio, C.M.; Shao, M.; Di Costanzo, L.; Kreidberg, J.A.; Hynes, R.O. Mouse keratinocytes immortalized with large T antigen acquire alpha3beta1 integrin-dependent secretion of MMP-9/gelatinase B. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 2909–2921. [Google Scholar]
- Mariani, J.; Crepel, F.; Mikoshiba, K.; Changeux, J.P.; Sotelo, C. Anatomical, Physiological and biochemical studies of the cerebellum from reeler mutant mouse. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1977, 281, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffinet, A.M. The embryonic development of the cerebellum in normal and reeler mutant mice. Brain Struct. Funct. 1983, 168, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffinet, A.M. Events governing organization of postmigratory neurons: Studies on brain development in normal and reeler mice. Brain Res. Rev. 1984, 7, 261–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Kubo, K.-I.; Nakajima, K. Reelin and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khialeeva, E.; Carpenter, E.M. Nonneuronal roles for the reelin signaling pathway. Dev. Dyn. 2017, 246, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longmate, W.M.; DiPersio, C.M. Integrin Regulation of Epidermal Functions in Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarker, F.A.; Prior, V.G.; Bax, S.; O’Neill, G.M. Forcing a growth factor response—Tissue-stiffness modulation of integrin signaling and crosstalk with growth factor receptors. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs242461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margadant, C.; Sonnenberg, A. Integrin–TGF-β crosstalk in fibrosis, cancer and wound healing. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, Z.; Marshall, J.F. The role of integrins in TGFβ activation in the tumour stroma. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, K.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. TGF-β1 promotes cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing reelin expression. Gene 2019, 688, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal, N.E.; Afagh, A.; Kanit, N.; Said, H.M. TGF-β1 promotes cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing REELIN expression. Gene 2020, 724, 143923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, G.; Cao, X.; Liu, Z. Reelin Is Involved in Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Induced Cell Migration in Esophageal Carcinoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longmate, W.M.; Varney, S.; Power, D.; Miskin, R.P.; Anderson, K.E.; DeFreest, L.; Van De Water, L.; DiPersio, C.M. Integrin α3β1 on Tumor Keratinocytes Is Essential to Maintain Tumor Growth and Promotes a Tumor-Supportive Keratinocyte Secretome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 142–151.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPersio, C.M.; Shah, S.; Hynes, R.O. alpha 3A beta 1 integrin localizes to focal contacts in response to diverse extracellular matrix proteins. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 2321–2336. [Google Scholar]
- Boelz, S.; Neu-Yilik, G.; Gehring, N.H.; Hentze, M.W.; Kulozik, A.E. A chemiluminescence-based reporter system to monitor nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rheinwald, J.G.; Beckett, M.A. Tumorigenic keratinocyte lines requiring anchorage and fibroblast support cultured from human squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ndoye, A.; Miskin, R.P.; DiPersio, C.M. Integrin α3β1 Represses Reelin Expression in Breast Cancer Cells to Promote Invasion. Cancers 2021, 13, 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020344
Ndoye A, Miskin RP, DiPersio CM. Integrin α3β1 Represses Reelin Expression in Breast Cancer Cells to Promote Invasion. Cancers. 2021; 13(2):344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020344
Chicago/Turabian StyleNdoye, Abibatou, Rakshitha Pandulal Miskin, and C. Michael DiPersio. 2021. "Integrin α3β1 Represses Reelin Expression in Breast Cancer Cells to Promote Invasion" Cancers 13, no. 2: 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020344
APA StyleNdoye, A., Miskin, R. P., & DiPersio, C. M. (2021). Integrin α3β1 Represses Reelin Expression in Breast Cancer Cells to Promote Invasion. Cancers, 13(2), 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020344