Receptor Activator of NF-κB (RANK) Confers Resistance to Chemotherapy in AML and Associates with Dismal Disease Course
Abstract
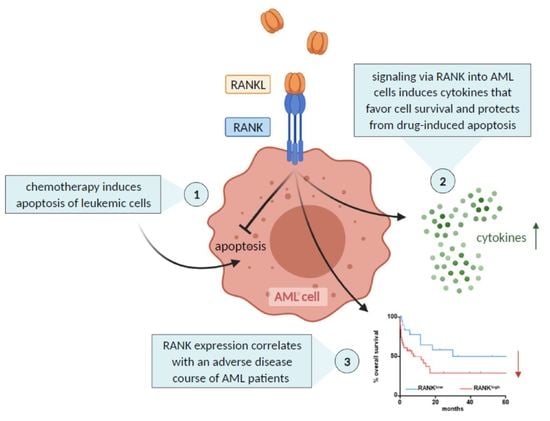
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Quantitative PCR
2.4. Analysis of the RANK Expression on the Cell Surface
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Measurement of Transmembrane Potential and Activation of Caspase-3
2.7. Measurement of Cytokine Induction
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. RANK Is Expressed by AML Cells
3.2. RANK Induces Cytokines Involved in Pathophysiology and Promotes Metabolic Activity of AML Cells
3.3. RANK Mediates Chemotherapy Resistance of AML Cells
3.4. RANK Expression Is Associated with Dismal Survival of AML Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamamoto, J.F.; Goodman, M.T. Patterns of leukemia incidence in the United States by subtype and demographic characteristics, 1997–2002. Cancer Causes Control 2008, 19, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kouchkovsky, I.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute myeloid leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2016 update. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southam, C.M.; Craver, L.F.; Dargeon, H.W.; Burchenal, J.H. A study of the natural history of acute leukemia with special reference to the duration of the disease and the occurrence of remissions. Cancer 1951, 4, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, D.; Bateman, C.J.T.; Vartan, C.P.; Whitehouse, J.M.; Malpas, J.S.; Fairley, G.H.; Scott, R.B. Combination Chemotherapy using L-Asparaginase, Daunorubicin, and Cytosine Arabinoside in Adults with Acute Myelogenous Leukaemia. Br. Med. J. 1970, 4, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wheatley, K.; Burnett, A.K.; Goldstone, A.H.; Gray, R.G.; Hann, I.M.; Harrison, C.J.; Rees, J.K.; Stevens, R.F.; Walker, H. A simple, robust, validated and highly predictive index for the determination of risk-directed therapy in acute myeloid leukaemia derived from the MRC AML 10 trial. United Kingdom Medical Research Council’s Adult and Childhood Leukaemia Working Parties. Br. J. Haematol. 1999, 107, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzel, C.; Sun, Z.; Cripe, L.D.; Fernandez, H.F.; Douer, D.; Rowe, J.M.; Paietta, E.M.; Ketterling, R.; O’Connell, M.J.; Wiernik, P.H.; et al. Very poor long-term survival in past and more recent studies for relapsed AML patients: The ECOG-ACRIN experience. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SEER: Cancer Stat Facts: Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html (accessed on 18 October 2021).
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.W.; et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H. Emerging agents and regimens for AML. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, N.J.; Konopleva, M.; Kadia, T.M.; Borthakur, G.; Ravandi, F.; Dinardo, C.D.; Daver, N. Advances in the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: New Drugs and New Challenges. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 506–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.; Lacey, D.L.; Dunstan, C.R.; Solovyev, I.; Colombero, A.; Timms, E.; Tan, H.-L.; Elliott, G.; Kelley, M.J.; Sarosi, I.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor family member RANK mediates osteoclast differentiation and activation induced by osteoprotegerin ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3540–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Neubauer, A.; Heufelder, A.E. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin: Potential implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of malignant bone diseases. Cancer 2001, 92, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiedel, B.J.; Scheible, C.A.; Nuebling, T.; Kopp, H.-G.; Wirths, S.; Azuma, M.; Schneider, P.; Jung, G.; Grosse-Hovest, L.; Salih, H.R. RANKL Expression, Function, and Therapeutic Targeting in Multiple Myeloma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajakumar, S.A.; Papp, E.; Lee, K.K.; Grandal, I.; Merico, D.; Liu, C.C.; Allo, B.; Zhang, L.; Grynpas, M.D.; Minden, M.D.; et al. B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells mediate RANK-RANKL–dependent bone destruction. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiedel, B.J.; Nuebling, T.; Steinbacher, J.; Malinovska, A.; Wende, C.M.; Azuma, M.; Schneider, P.; Grosse-Hovest, L.; Salih, H.R. Receptor activator for NF-κB ligand in acute myeloid leukemia: Expression, function, and modulation of NK cell immunosurveillance. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, M.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, B.; Ko, Y.J.; Jang, Y.; Moon, Y.H.; Hyun, H.; Lim, W. RANKL immunisation inhibits prostate cancer metastasis by modulating EMT through a RANKL-dependent pathway. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, M.; Fabi, A.; Cognetti, F.; Gorini, S.; Caprio, M.; Fabbri, A. RANKL/RANK/OPG system beyond bone remodeling: Involvement in breast cancer and clinical perspectives. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, F.; Dang, L.; Liang, C.; Lu, A.; Zhang, G. RANKL/RANK System-Based Mechanism for Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis and Related Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, D.; Schiavon, G.; Vincenzi, B.; Gaeta, L.; Pantano, F.; Russo, A.; Ortega, C.; Porta, C.; Galluzzo, S.; Armento, G.; et al. Receptor activator of NF-kB (RANK) expression in primary tumors associates with bone metastasis occurrence in breast cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clar, K.L.; Hinterleitner, C.; Schneider, P.; Salih, H.R.; Maurer, S. Inhibition of NK Reactivity Against Solid Tumors by Platelet-Derived RANKL. Cancers 2019, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, W.; Zhang, W.; Strasner, A.; Grivennikov, S.; Cheng, J.Q.; Hoffman, R.M.; Karin, M. Tumour-infiltrating regulatory T cells stimulate mammary cancer metastasis through RANKL–RANK signalling. Nature 2011, 470, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tandler, C.; Schmidt, M.; Heitmann, J.S.; Hierold, J.; Schmidt, J.; Schneider, P.; Dörfel, D.; Walz, J.; Salih, H.R. Neutralization of B-Cell Activating Factor (BAFF) by Belimumab Reinforces Small Molecule Inhibitor Treatment in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2020, 12, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, P.; Willen, L.; Smulski, C.R. Tools and Techniques to Study Ligand–Receptor Interactions and Receptor Activation by TNF Superfamily Members. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 545, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechele, C.; Baessler, T.; Wirths, S.; Schmohl, J.U.; Schmiedel, B.J.; Salih, H.R. Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR) ligand modulates cytokine release and NK cell reactivity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Leukemia 2011, 26, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuebling, T.; Schumacher, C.E.; Hofmann, M.; Hagelstein, I.; Schmiedel, B.J.; Maurer, S.; Federmann, B.; Rothfelder, K.; Roerden, M.; Dörfel, D.; et al. The Immune Checkpoint Modulator OX40 and Its Ligand OX40L in NK-Cell Immunosurveillance and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mihalcik, S.A.; Tschumper, R.C.; Jelinek, D.F. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms of BAFF-receptor dysregulation in human B lineage malignancies. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 4884–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, P.; Holler, N.; Bodmer, J.-L.; Hahne, M.; Frei, K.; Fontana, A.; Tschopp, J. Conversion of Membrane-bound Fas(CD95) Ligand to Its Soluble Form Is Associated with Downregulation of Its Proapoptotic Activity and Loss of Liver Toxicity. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucka, K.; Wajant, H. Receptor Oligomerization and Its Relevance for Signaling by Receptors of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.R.; Tallman, M.S.; Abboud, C.N.; Altman, J.K.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Arber, D.A.; Bhatt, V.; Bixby, D.; Blum, W.; Coutre, S.E.; et al. Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Version 3.2017, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2017, 15, 926–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamasaki, S.; Kawakami, A.; Eguchi, K.; Sasaki, H.; Sakai, H. Protein expression and functional difference of membrane-bound and soluble receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand: Modulation of the expression by osteotropic factors and cytokines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, L.; Wong, B.R.; Josien, R.; Becherer, J.D.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Schlondorff, J.; Tempst, P.; Choi, Y.; Blobel, C.P. Evidence for a role of a tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-converting enzyme-like protease in shedding of TRANCE, a TNF family member involved in osteoclastogenesis and dendritic cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13613–13618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hikita, A.; Yana, I.; Wakeyama, H.; Nakamura, M.; Kadono, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Seiki, M.; Tanaka, S. Negative regulation of osteoclastogenesis by ectodomain shedding of receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 36846–36855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanada, R.; Leibbrandt, A.; Hanada, T.; Kitaoka, S.; Furuyashiki, T.; Fujihara, H.; Trichereau, J.; Paolino, M.; Qadri, F.; Plehm, R.; et al. Central control of fever and female body temperature by RANKL/RANK. Nature 2009, 462, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Estey, E.; Wen, S.; Pierce, S.; Kantarjian, H.; Albitar, M.; Kurzrock, R. The prognostic significance of cytokine levels in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer 2008, 113, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornblau, S.M.; McCue, D.; Singh, N.; Chen, W.; Estrov, Z.; Coombes, K.R. Recurrent expression signatures of cytokines and chemokines are present and are independently prognostic in acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplasia. Blood 2010, 116, 4251–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binder, S.; Luciano, M.; Horejs-Hoeck, J. The cytokine network in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): A focus on pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 43, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Correa, B.; Bergua, J.M.; Campos, C.; Gayoso, I.; Arcos, M.J.; Bañas, H.; Morgado, S.; Casado, J.G.; Solana, R.; Tarazona, R. Cytokine profiles in acute myeloid leukemia patients at diagnosis: Survival is inversely correlated with IL-6 and directly correlated with IL-10 levels. Cytokine 2013, 61, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Wang, B.; You, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhan, W.; Chen, P.; Qin, T.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H. Stromal cells promote chemoresistance of acute myeloid leukemia cells via activation of the IL-6/STAT3/OXPHOS axis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, V.; Miller, R.; Vue, G.S.; Pezeshkian, M.B.; Maywood, M.; Ast, A.M.; Drusbosky, L.M.; Pompeu, Y.; Salgado, A.D.; Lipten, S.D.; et al. Interleukin-8 blockade prevents activated endothelial cell mediated proliferation and chemoresistance of acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2019, 84, 106180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, C.; Ikezoe, T.; Pan, B.; Xu, K.; Yokoyama, A. MicroRNA-9 plays a role in interleukin-10-mediated expression of E-cadherin in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagoya, Y.; Yoshimi, A.; Kataoka, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Kumano, K.; Arai, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Saito, T.; Iwakura, Y.; Kurokawa, M. Positive feedback between NF-κB and TNF-α promotes leukemia-initiating cell capacity. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baessler, T.; Charton, J.E.; Schmiedel, B.J.; Grünebach, F.; Krusch, M.; Wacker, A.; Rammensee, H.-G.; Salih, H.R. CD137 ligand mediates opposite effects in human and mouse NK cells and impairs NK-cell reactivity against human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 2010, 115, 3058–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levings, M.K.; Sangregorio, R.; Sartirana, C.; Moschin, A.L.; Battaglia, M.; Orban, P.C.; Roncarolo, M.G. Human CD25+CD4+ T suppressor cell clones produce transforming growth factor beta, but not interleukin 10, and are distinct from type 1 T regulatory cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuyaerts, S.; Van Meirvenne, S.; Bonehill, A.; Heirman, C.; Corthals, J.; Waldmann, H.; Breckpot, K.; Thielemans, K.; Aerts, J.L. Expression of human GITRL on myeloid dendritic cells enhances their immunostimulatory function but does not abrogate the suppressive effect of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.C.; Choi, Y. Biology of the RANKL-RANK-OPG System in Immunity, Bone, and Beyond. Front Immunol. 2014, 5, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gyrd-Hansen, M.; Meier, P. IAPs: From caspase inhibitors to modulators of NF-kappaB, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Edelstein, L.C.; Gelinas, C. The Rel/NF-κB Family Directly Activates Expression of the Apoptosis Inhibitor Bcl-xL. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 2687–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayet, B.; Gélinas, C. Aberrant rel/nfkb genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6938–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melgar, K.; Walker, M.M.; Jones, L.M.; Bolanos, L.C.; Hueneman, K.; Wunderlich, M.; Jiang, J.K.; Wilson, K.M.; Zhang, X.; Sutter, P.; et al. Overcoming adaptive therapy resistance in AML by targeting immune response pathways. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnant, M.; Pfeiler, G.; Steger, G.G.; Egle, D.; Greil, R.; Fitzal, F.; Wette, V.; Balic, M.; Haslbauer, F.; Melbinger-Zeinitzer, E.; et al. Adjuvant denosumab in postmenopausal patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (ABCSG-18): Disease-free survival results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrmann, L.; Wellbrock, J.; Fiedler, W. Acute Myeloid Leukemia and the Bone Marrow Niche—Take a Closer Look. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meads, M.B.; Gatenby, R.A.; Dalton, W.S. Environment-mediated drug resistance: A major contributor to minimal residual disease. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| UPN | RANK | FAB | Age | Sex | PBB | Karyotype | WBC | Hb | Plt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [%] | [SFI] | [Years] | [%] | [G/L] | [G/dL] | [G/L] | ||||
| 1 | 1.7 | 1.0 | M0 | 46 | M | 97 | 46,XY | 60.6 | 7.0 | 39 |
| 2 | 11.9 | 1.5 | M0 | 83 | M | 90 | 48,XY,+X,+13 | 191.6 | 8.9 | 59 |
| 3 | 3.1 | 1.8 | M0 | 68 | M | 93 | ND | 52.8 | 10.5 | 114 |
| 4 | 4.9 | 1.6 | M0 | 65 | M | 85 | 46,XY | 186.3 | 9 | 11 |
| 5 | 20.2 | 1.3 | M0 | 90 | F | 97 | complex | 14.5 | 8.1 | 586 |
| 6 | 11.0 | 1.2 | M1 | 40 | M | 100 | complex | 81.3 | 10.8 | 51 |
| 7 | 13.5 | 1.7 | M1 | 69 | M | 86 | 46,XY | 84.1 | 6.7 | 322 |
| 8 | 4.8 | 1.0 | M1 | 21 | F | 95 | 46,XX; 46,XX,del(9)(q13q22) | 84.0 | 7.1 | 30 |
| 9 | 2.6 | 1.1 | M1 | 56 | F | 56 | 46,XX | 52.0 | 12.1 | 9 |
| 10 | 3.0 | 1.1 | M1 | 77 | M | 87 | 46,XY | 116.0 | 7.3 | 57 |
| 11 | 9.0 | 1.5 | M1 | 50 | F | 93 | 46,XX | 267.8 | 8.0 | 18 |
| 12 | 1.3 | 1.1 | M1 | 64 | F | 98 | ND | 222.2 | 9.2 | 44 |
| 13 | 1.6 | 1.1 | M2 | 88 | M | 29 | ND | 45.4 | 8.9 | 81 |
| 14 | 18.0 | 1.1 | M2 | 68 | M | 96 | 46,XY | 85.5 | 9.5 | 146 |
| 15 | 9.3 | 1.2 | M2 | 64 | M | 82 | complex | 338.5 | 8.1 | 19 |
| 16 | 5.9 | 1.1 | M2 | 60 | M | 95 | 46,XY,+14 | 42.0 | 10.1 | 57 |
| 17 | 41.3 | 1.1 | M2 | 71 | F | 89 | 47,XX,+11 | 16.4 | 8.6 | 18 |
| 18 | 3.8 | 2.6 | M2 | 79 | F | 69 | 46,XX | 21.5 | 7.0 | 14 |
| 19 | 3.5 | 1.1 | M2 | 67 | F | 94 | complex | 112.7 | 10.6 | 137 |
| 20 | 21.5 | 1.3 | M3 | 46 | M | 87 | 46,XY,t(15;17)(q22;q11~21) | 8.42 | 9.9 | 40 |
| 21 | 23.6 | 1.5 | M3 | 65 | M | 70 | 46,XY,t(15;17)(q22;q12) | 7.0 | 9.7 | 27 |
| 22 | 6.0 | 1.1 | M3 | 29 | M | 93 | 46,XY,t(15;17)(q22;q12) | 21.6 | 7.1 | 61 |
| 23 | 9.3 | 1.0 | M3 | 58 | F | 96 | 46,XX,t(15;17)(q22;q12) | 42.1 | 8.4 | 17 |
| 24 | 7.9 | 1.0 | M3 | 46 | F | 42 | 46,XX,t(15;17)(q24.1;q21.2) | 21.6 | 7.1 | 14 |
| 25 | 2.5 | 1.0 | M4 | 30 | F | 90 | complex | 214.0 | 6.4 | 10 |
| 26 | 58.3 | 1.7 | M4 | 64 | F | 91 | 46,XX | 61.5 | 7.2 | 100 |
| 27 | 5.6 | 1.1 | M4 | 71 | M | 97 | 47,XY,+11 | 87.1 | 7.5 | 23 |
| 28 | 9.4 | 1.0 | M4 | 76 | F | 94 | complex | 140.9 | 12.0 | 70 |
| 29 | 9.3 | 1.2 | M4 | 85 | M | 92 | ND | 183.2 | 8.9 | 64 |
| 30 | 11.2 | 1.1 | M4 | 45 | F | 97 | 46,XX,t(1;3)(p36;q21)(22) | 448.3 | 6.6 | 36 |
| 31 | 1.9 | 1.0 | M4 | 62 | M | 91 | complex | 104.7 | 6.5 | 34 |
| 32 | 17.2 | 2.1 | M4 | 83 | F | 95 | 46,XX,add(14)(p11); 46,XX | 155.8 | 11.6 | 144 |
| 33 | 25.1 | 1.2 | M4 | 36 | M | 95 | 46,XY | 207.4 | 6.1 | 55 |
| 34 | 60.0 | 1.9 | M4 | 67 | F | 86 | ND | 315.9 | 8.2 | 34 |
| 35 | 42.5 | 1.6 | M4 | 57 | M | 87 | ND | 333.7 | 9.4 | 293 |
| 36 | 40.9 | 1.3 | M4 | 54 | F | 91 | 46,XX | 17.2 | 10.6 | 167 |
| 37 | 2.7 | 1.0 | M4 | 57 | M | 14 | 45,XY,inv(3)(q21.3q26.2),−7 | 26.2 | 10.4 | 252 |
| 38 | 57.0 | 1.6 | M5 | 69 | F | 95 | ND | 274.9 | 7.1 | 47 |
| 39 | 3.5 | 1.1 | M5 | 72 | M | 97 | 47,XY,+8; 46,XY | 90.3 | 8.9 | 79 |
| 40 | 22.3 | 1.5 | M5 | 65 | M | 91 | ND | 151.0 | 7.9 | 151 |
| 41 | 70.2 | 1.3 | M5 | 76 | M | 93 | complex | 169.3 | 9.9 | 26 |
| 42 | 35.7 | 1.2 | M5 | 54 | M | 89 | 46,XY,del(9)(q13q22) | 97.1 | 8.1 | 73 |
| 43 | 74.3 | 2.0 | M5 | 37 | F | 85 | ND | 126.8 | 9.7 | 41 |
| 44 | 81.8 | 1.2 | M5 | 81 | M | 93 | 46,XY | 61.3 | 11.7 | 72 |
| 45 | 14.3 | 1.2 | M5 | 23 | M | 92 | 48,XY,+8,+13; 46,XY | 153.5 | 6.7 | 44 |
| 46 | 28.7 | 1.2 | M5 | 35 | F | 83 | 46,XX | 45.4 | 8.9 | 81 |
| 47 | 65.7 | 1.5 | M5 | 53 | M | 85 | 46,XY | 105.6 | 8.1 | 35 |
| 48 | 49.5 | 1.5 | M5 | 48 | M | 95 | 46,XY | 54.6 | 6.8 | 190 |
| 49 | 22.0 | 1.3 | M5 | 70 | M | 90 | 46,XY | 190.9 | 7.1 | 65 |
| 50 | 48.9 | 1.4 | M5 | 32 | M | 98 | complex | 179.3 | 3.3 | 80 |
| 51 | 24.1 | 1.5 | M5 | 71 | M | 94 | complex | 161.1 | 8.6 | 61 |
| 52 | 68.4 | 1.8 | M5 | 68 | M | 95 | 46,XY | 148.7 | 9.1 | 134 |
| 53 | 13.9 | 1.0 | M5 | 41 | F | 92 | 46,XX | 59.9 | 8.9 | 34 |
| 54 | 67.7 | 2.7 | ND | 49 | M | 96 | ND | 316.0 | 7.1 | 80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clar, K.L.; Weber, L.M.; Schmied, B.J.; Heitmann, J.S.; Marconato, M.; Tandler, C.; Schneider, P.; Salih, H.R. Receptor Activator of NF-κB (RANK) Confers Resistance to Chemotherapy in AML and Associates with Dismal Disease Course. Cancers 2021, 13, 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13236122
Clar KL, Weber LM, Schmied BJ, Heitmann JS, Marconato M, Tandler C, Schneider P, Salih HR. Receptor Activator of NF-κB (RANK) Confers Resistance to Chemotherapy in AML and Associates with Dismal Disease Course. Cancers. 2021; 13(23):6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13236122
Chicago/Turabian StyleClar, Kim L., Lisa M. Weber, Bastian J. Schmied, Jonas S. Heitmann, Maddalena Marconato, Claudia Tandler, Pascal Schneider, and Helmut R. Salih. 2021. "Receptor Activator of NF-κB (RANK) Confers Resistance to Chemotherapy in AML and Associates with Dismal Disease Course" Cancers 13, no. 23: 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13236122
APA StyleClar, K. L., Weber, L. M., Schmied, B. J., Heitmann, J. S., Marconato, M., Tandler, C., Schneider, P., & Salih, H. R. (2021). Receptor Activator of NF-κB (RANK) Confers Resistance to Chemotherapy in AML and Associates with Dismal Disease Course. Cancers, 13(23), 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13236122