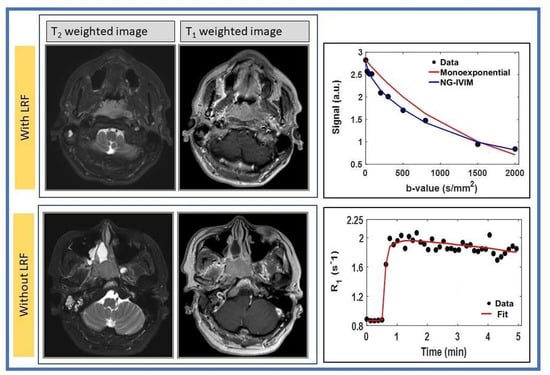
Nongaussian Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion Weighted and Fast Exchange Regime Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced-MRI of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Preliminary Study for Predicting Locoregional Failure
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. MRI Data Acquisition
2.3. DWI Data Acquisition
2.4. DCE Data Acquisition
2.5. DWI Data Analysis
2.6. Fast Exchange Regime Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.7. Regions of Interest (ROIs) Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical
3.2. DWI Data Analysis
3.3. FXR DCE-MRI Analysis
3.4. Survival Analysis: CIA and FG Proportional Subhazards Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, M.P.; Kurzrock, R. Epstein-Barr Virus and Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 803–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.W.; Ma, B.B.; Ng, W.T.; Chan, A.T. Management of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Current Practice and Future Perspective. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3356–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setakornnukul, J.; Thephamongkhol, K. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, A.T.; Hui, E.P.; Ngan, R.K.; Tung, S.Y.; Cheng, A.C.; Ng, W.T.; Lee, V.H.; Ma, B.B.; Cheng, H.C.; Wong, F.C.; et al. Analysis of Plasma Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Nasopharyngeal Cancer After Chemoradiation to Identify High-Risk Patients for Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3091–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, G.-Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, X.-D.; Yang, K.-Y.; Jin, F.; Shi, M.; Chen, Y.-P.; Hu, W.-H.; et al. Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Induction Chemotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Chow, J.C.H.; Lee, N.Y. Treatment De-escalation Strategies for Nasopharyngeal Cancer: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Xia, P.; Quivey, J.M.; Sultanem, K.; Poon, I.; Akazawa, C.; Akazawa, P.; Weinberg, V.; Fu, K.K. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An update of the UCSF experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2002, 53, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Harris, J.; Garden, A.S.; Straube, W.; Glisson, B.; Xia, P.; Bosch, W.; Morrison, W.H.; Quivey, J.; Thorstad, W.; et al. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy with or Without Chemotherapy for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Phase II Trial 0225. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.W.; Ng, W.T.; Chan, L.L.; Hung, W.M.; Chan, C.C.; Sze, H.C.; Chan, O.S.; Chang, A.T.; Yeung, R.M. Evolution of treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer—Success and setback in the intensity-modulated radiotherapy era. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Xiao, J.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, K. The effectiveness of intensity-modulated radiation therapy versus 2D-RT for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, S.C.; Riaz, N.; Lee, N. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 24, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.-B.; Mao, Y.-P.; Liu, L.-Z.; Tang, L.-L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, A.-H.; Cui, C.-Y.; Li, L.; Ma, J. How Does Magnetic Resonance Imaging Influence Staging According to AJCC Staging System for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Compared With Computed Tomography? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 72, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E.; Lallemand, D.; Grenier, P.; Cabanis, E.; Laval-Jeantet, M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: Application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 1986, 161, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.-F.; Chen, L.; Mao, Y.-P.; Shen, J.-X.; Zhang, F.; Peng, H.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Prognostic value of the primary lesion apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study of 541 cases. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, D.; Xu, L.; Hong, L.; Xu, Y.; Pan, J. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for early response assessment of chemoradiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 32, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, B.K.H.; King, A.; Bhatia, K.; Ahuja, A.; Kam, M.; Ma, B.; Ai, Q.; Mo, F.; Yuan, J.; Yeung, D. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Can Pretreatment DWI Predict Local Failure Based on Long-Term Outcome? Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Hazle, J.D.; Mohamed, A.S.R.; Frank, S.J.; Hobbs, B.P.; Colen, R.R.; Gunn, G.B.; Wang, J.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Garden, A.S.; et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging kinetics during chemoradiotherapy for human papillomavirus-associated squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx: Preliminary results from a prospective pilot study. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, D.A.; Medina, A.L.; Iglesias, M.M.; Gomez, F.S.; Dave, A.; Hatzoglou, V.; Paudyal, R.; Calzado, A.; Deasy, J.O.; Shukla-Dave, A.; et al. Multimodality functional imaging using DW-MRI and 18F-FDG-PET/CT during radiation therapy for human papillomavirus negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Meixoeiro Hospital of Vigo Experience. World J. Radiol. 2017, 9, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.F.; Stambuk, H.E.; Koutcher, J.A.; Shukla-Dave, A. Non-Gaussian Analysis of Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Feasibility Study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 31, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagher-Ebadian, H.; Jain, R.; Nejad-Davarani, S.P.; Mikkelsen, T.; Lu, M.; Jiang, Q.; Scarpace, L.; Arbab, A.S.; Narang, J.; Soltanian-Zadeh, H.; et al. Model selection for DCE-T1 studies in glioblastoma. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paudyal, R.; Riaz, N.; Hatzoglou, V.; Lee, N.; Shukla-Dave, A. Non-gaussian IVIM-DWI for HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer patients who received marked dose de-escalation in chemo-radiotherapy: Intra-treatment imaging response evaluation. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 2019, 27, 2358. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, N.; Sherman, E.; Pei, X.; Schoder, H.; Grkovski, M.; Paudyal, R.; Katabi, N.; Selenica, P.; Yamaguchi, T.N.; Ma, D.; et al. Precision Radiotherapy: Reduction in Radiation for Oropharyngeal Cancer in the 30 ROC Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofts, P.S.; Brix, G.; Buckley, D.L.; Evelhoch, J.L.; Henderson, E.; Knopp, M.V.; Larsson, H.B.; Lee, T.-Y.; Mayr, N.A.; Parker, G.J.; et al. Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced t1-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: Standardized quantities and symbols. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1999, 10, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, W.; Yao, Y.; Du, Z.; Deng, X.; Chan, Q. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A preliminary study of the correlations between quantitative parameters and clinical stage. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 39, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla-Dave, A.; Lee, N.Y.; Jansen, J.F.; Thaler, H.T.; Stambuk, H.E.; Fury, M.G.; Patel, S.G.; Moreira, A.L.; Sherman, E.; Karimi, S.; et al. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Predictor of Outcome in Head-and-Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients With Nodal Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 82, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aftab, O.; Liao, S.; Zhang, R.; Tang, N.; Luo, M.; Zhang, B.; Shahi, S.; Rai, R.; Ali, J.; Jiang, W. Efficacy and safety of intensity-modulated radiotherapy alone versus intensity-modulated radiotherapy plus chemotherapy for treatment of intermediate-risk nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Loevner, L.; Quon, H.; Kilger, A.; Sherman, E.; Weinstein, G.; Chalian, A.; Poptani, H. Prediction of Response to Chemoradiation Therapy in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Head and Neck Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 31, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chawla, S.; Loevner, L.; Kim, S.; Hwang, W.-T.; Wang, S.; Verma, G.; Mohan, S.; Livolsi, V.; Quon, H.; Poptani, H.; et al. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI–Derived Intracellular Water Lifetime (τi): A Prognostic Marker for Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 39, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behera, M.; Fowler, E.E.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Land, W.H.; Mayfield, W.; Chen, Z.; Khuri, F.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Heine, J.J. Statistical learning methods as a preprocessing step for survival analysis: Evaluation of concept using lung cancer data. Biomed. Eng. Online 2011, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lahiji, A.P.; Jackson, T.; Nejadnik, H.; Von Eyben, R.; Rubin, D.; Spunt, S.L.; Quon, A.; Daldrup-Link, H. Association of Tumor [18F]FDG Activity and Diffusion Restriction with Clinical Outcomes of Rhabdomyosarcomas. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 21, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, J.P.; Gray, R.J. A Proportional Hazards Model for the Subdistribution of a Competing Risk. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, R.; Oh, J.H.; Riaz, N.; Venigalla, P.; Li, J.; Hatzoglou, V.; Leeman, J.; Nunez, D.A.; Lu, Y.; Deasy, J.O.; et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI during chemoradiation therapy to characterize and monitor treatment response in human papillomavirus head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jansen, J.F.; Mazaheri, Y.; Stambuk, H.E.; Koutcher, J.A.; Shukla-Dave, A. Extension of the intravoxel incoherent motion model to non-gaussian diffusion in head and neck cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paudyal, R.; Bagher-Ebadian, H.; Nagaraja, T.N.; Fenstermacher, J.D.; Ewing, J.R. Modeling of Look-Locker estimates of the magnetic resonance imaging estimate of longitudinal relaxation rate in tissue after contrast administration. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McConnell, H.M. Reaction Rates by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 28, 430–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paudyal, R.; Poptani, H.; Cai, K.; Zhou, R.; Glickson, J.D. Impact of transvascular and cellular-interstitial water exchange on dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging estimates of blood to tissue transfer constant and blood plasma volume. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 37, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, R.K.; Reyngold, M.; Paudyal, R.; Oh, J.H.; Konar, A.S.; LoCastro, E.; Goodman, K.A.; Shukla-Dave, A. Diffusion-Weighted and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Derived Imaging Metrics for Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Preliminary Findings. Tomography 2020, 6, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ; U. S. National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1997.
- LoCastro, E.; Paudyal, R.; Mazaheri, Y.; Hatzoglou, V.; Oh, J.H.; Lu, Y.; Konar, A.S.; Eigen, K.V.; Ho, A.; Ewing, J.R.; et al. Computational Modeling of Interstitial Fluid Pressure and Velocity in Head and Neck Cancer Based on Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Feasibility Analysis. Tomography 2020, 6, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrias, G.; Raeside, M.C.; Agostini, A.; Huicochea-Castellanos, S.; Aramburu-Nunez, D.; Paudyal, R.; Shukla-Dave, A.; Smelianskaia, O.; Capanu, M.; Zheng, J.; et al. Pilot study of rapid MR pancreas screening for patients with BRCA mutation. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudyal, R.; Lu, Y.; Hatzoglou, V.; Moreira, A.; Stambuk, H.E.; Oh, J.H.; Cunanan, K.M.; Nunez, D.A.; Mazaheri, Y.; Gonen, M.; et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI model selection for predicting tumor aggressiveness in papillary thyroid cancers. NMR Biomed. 2019, 33, e4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youden, W.J. Index for Rating Diagnostic Tests. Biometrics 1950, 6, 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, A.; Löck, S. Competing risks in survival data analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 130, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Team R Core. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, N.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Xing, F.; Chen, L.; Wu, G. Treatment Response Prediction of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Based on Histogram Analysis of Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, S.; Kim, S.; Dougherty, L.; Wang, S.; Loevner, L.A.; Quon, H.; Poptani, H. Pretreatment Diffusion-Weighted and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI for Prediction of Local Treatment Response in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Head and Neck. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, A.D.; Chow, K.-K.; Yu, K.-H.; Mo, F.K.F.; Yeung, D.K.W.; Yuan, J.; Bhatia, K.S.; Vlantis, A.C.; Ahuja, A.T. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Diagnostic Performance of Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging for the Prediction of Treatment Response. Radiology 2013, 266, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, J.; Dong, D.; Gu, D.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lian, Z.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Pei, S.; et al. Radiomics Features of Multiparametric MRI as Novel Prognostic Factors in Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4259–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, G.; Wang, T.; Yang, K.-Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Han, J.; Wu, G. A prospective, randomized study comparing outcomes and toxicities of intensity-modulated radiotherapy vs. conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 104, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Gu, D.; Tian, J.; Zhang, B.; Dong, D.; Mo, X.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Pei, S.; et al. Radiomic Nomogram: Pretreatment Evaluation of Local Recurrence in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma based on MR Imaging. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Z.-G.; Tan, H.Q.; Zhang, F.; Tan, L.K.R.; Lin, L.; Lenkowicz, J.; Wang, H.; Ong, E.H.W.; Kusumawidjaja, G.; Phua, J.H.; et al. Comparison of radiomics tools for image analyses and clinical prediction in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, D.A.; Heidemann, R.M. High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.; Le Bihan, D. Single-shot diffusion imaging at 2.0 tesla. J. Magn. Reson. (1969) 1990, 86, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Characteristics | Patients with LRF (n = 6) | Patients without LRF (n = 22) |
|---|---|---|
| Male/Female (%) | 4/2 (14/7) | 16/7 (55/24) |
| Age: median(range) | 45 (21–64 years) | 45 (21–64 years) |
| Stage III and IV (AJCC, %) | 60/40 | 71/29 |
| EBV-associated (%) | 40 | 83 |
| Model | Metric | With LRF | Without LRF | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monoexponential | ADC × 10−3 (mm2/s) | 0.66 ± 0.19 | 0.76 ± 0.15 | 0.31 |
| NG-IVIM | D × 10−3 (mm2/s) | 0.74 ± 0.23 | 0.87 ± 0.22 | 0.31 |
| D* × 10−3 (mm2/s) | 2.30 ± 0.25 | 2.40 ± 0.18 | 0.48 | |
| f | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 0.08 | |
| K | 0.94 ± 0.25 | 0.82 ± 0.15 | 0.23 |
| Metric | With LRF | Without LRF | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ktrans (min−1) | 0.29 ± 0.11 | 0.39 ± 0.16 | 0.14 |
| ve | 0.23 ± 0.13 | 0.44 ± 0.21 | 0.03 |
| τi (s) | 0.91 ± 0.15 | 0.71 ± 0.27 | 0.11 |
| Method | Parameter | Cumulative Incidence Analysis | Competing Risks Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gray’s Test (p-Value) | Subdistribution Hazard Ratio (SHR) | p-Value | 95% CI | ||
| DWI | ADC × 10−3 (mm2/s) | ≤0.68 vs. >0.68 p = 0.046 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.00–4.37 |
| D × 10−3 (mm2/s) | ≤0.74 vs. >0.74 p = 0.046 | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.00–4.05 | |
| D* × 10−3 (mm2/s) | ≤2.25 vs. >2.25 p = 0.115 | 0.29 | 0.45 | 0.011–7.40 | |
| f | ≤0.18 vs. >0.18 p = 0.006 | 93.06 | 0.034 | 1.42–6082.28 | |
| K | ≤0.86 vs. >0.86 p = 0.226 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.0–34,096.0 | |
| DCE | Ktrans (min−1) | ≤0.35 vs. >0.35 p = 0.169 | 1.02 | 0.98 | 0.03–33.17 |
| ve | ≤0.21 vs. >0.21 p = 0.159 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.00–13.62 | |
| τi (s) | ≤0.89 vs. >0.89 0.098 | 99.87 | 0.07 | 0.66–15,080.66 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paudyal, R.; Chen, L.; Oh, J.H.; Zakeri, K.; Hatzoglou, V.; Tsai, C.J.; Lee, N.; Shukla-Dave, A. Nongaussian Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion Weighted and Fast Exchange Regime Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced-MRI of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Preliminary Study for Predicting Locoregional Failure. Cancers 2021, 13, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051128
Paudyal R, Chen L, Oh JH, Zakeri K, Hatzoglou V, Tsai CJ, Lee N, Shukla-Dave A. Nongaussian Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion Weighted and Fast Exchange Regime Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced-MRI of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Preliminary Study for Predicting Locoregional Failure. Cancers. 2021; 13(5):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051128
Chicago/Turabian StylePaudyal, Ramesh, Linda Chen, Jung Hun Oh, Kaveh Zakeri, Vaios Hatzoglou, C. Jillian Tsai, Nancy Lee, and Amita Shukla-Dave. 2021. "Nongaussian Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion Weighted and Fast Exchange Regime Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced-MRI of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Preliminary Study for Predicting Locoregional Failure" Cancers 13, no. 5: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051128
APA StylePaudyal, R., Chen, L., Oh, J. H., Zakeri, K., Hatzoglou, V., Tsai, C. J., Lee, N., & Shukla-Dave, A. (2021). Nongaussian Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion Weighted and Fast Exchange Regime Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced-MRI of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Preliminary Study for Predicting Locoregional Failure. Cancers, 13(5), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051128