Radio-Iodide Treatment: From Molecular Aspects to the Clinical View
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Radioactive Iodide (RAI) Therapy
2. Iodide Accumulation in Normal, Tumor, and Metastatic Thyroid Cells
2.1. Physiology of the Thyroid Epithelial Cell
2.2. Thyroid Tumor Cell
2.3. Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Cells
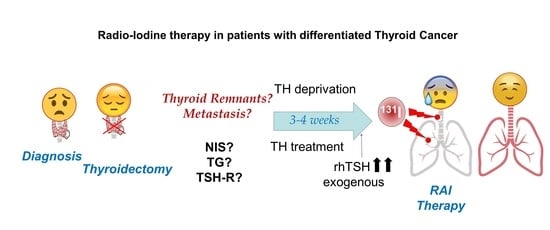
3. Thyroid Hormone Deprivation vs. Recombinant Human TSH: Pros and Cons
3.1. Which TSH Stimulation Treatment Obtains Higher Radioiodide Accumulation and Organification in Tumor Cells?
3.2. Which TSH Stimulation Treatment Obtains Longer Radioiodine Residence Time in Tumor Cells?
3.3. Do Different TSH Stimulation Treatments Affect Negative Scans in Diagnosis?
3.4. What TSH Stimulation Treatment Could Be Better for DTC Metastases?
4. Stunning Phenomenon in RAI Therapy
5. Imaging Techniques in Thyroid Cancer
6. Socio-Economic Facts
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hertz, S.; Roberts, A. Radioactive Iodine as an Indicator in Thyroid Physiology. V. The Use of Radioactive Iodine in the Differential Diagnosis of Two Types of Graves’ Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1942, 21, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidlin, S.M.; Marinelli, L.D.; Oshry, E. Radioactive Iodine Therapy; Effect on Functioning Metastases of Adenocarcinoma of the Thyroid. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1946, 132, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronich, N.; Lavi, I.; Rennert, G.; Saliba, W. Cancer Risk after Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Hyperthyroidism: A Cohort Study. Thyroid 2020, 30, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, M.E.; Folkes, L.K.; O’Neill, P. Biological consequences of radiation-induced DNA damage: Relevance to radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.M.; Pang, A.X. Iodine-131 treatment of thyroid cancer cells leads to suppression of cell proliferation followed by induction of cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by regulation of B-cell translocation gene 2-mediated JNK/NF-kappaB pathways. Braz. J. Med Biol. Res. Rev. Bras. Pesqui. Med. Biol. 2017, 50, e5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyckesvard, M.N.; Kapoor, N.; Ingeson-Carlsson, C.; Carlsson, T.; Karlsson, J.O.; Postgard, P.; Himmelman, J.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.; Hammarsten, O.; Nilsson, M. Linking loss of sodium-iodide symporter expression to DNA damage. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 344, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouget, J.P.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Ravanat, J.L. Targeted and Off-Target (Bystander and Abscopal) Effects of Radiation Therapy: Redox Mechanisms and Risk/Benefit Analysis. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2018, 29, 1447–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylli, D.; Van Nostrand, D.; Wartofsky, L. Conventional Radioiodine Therapy for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, R.M.; Ahuja, S.; Avram, A.M.; Bernet, V.J.; Bourguet, P.; Daniels, G.H.; Dillehay, G.; Draganescu, C.; Flux, G.; Fuhrer, D.; et al. Controversies, Consensus, and Collaboration in the Use of 131I Therapy in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Joint Statement from the American Thyroid Association, the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, and the European Thyroid Association. Thyroid 2019, 29, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Micali, S.; Maggisano, V.; Cesinaro, A.; Celano, M.; Territo, A.; Reggiani Bonetti, L.; Sponziello, M.; Migaldi, M.; Navarra, M.; Bianchi, G.; et al. Sodium/iodide symporter is expressed in the majority of seminomas and embryonal testicular carcinomas. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 216, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riesco-Eizaguirre, G.; Leoni, S.G.; Mendiola, M.; Estevez-Cebrero, M.A.; Gallego, M.I.; Redondo, A.; Hardisson, D.; Santisteban, P.; De la Vieja, A. NIS mediates iodide uptake in the female reproductive tract and is a poor prognostic factor in ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1199-1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tazebay, U.H.; Wapnir, I.L.; Levy, O.; Dohan, O.; Zuckier, L.S.; Zhao, Q.H.; Deng, H.F.; Amenta, P.S.; Fineberg, S.; Pestell, R.G.; et al. The mammary gland iodide transporter is expressed during lactation and in breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Vieja, A.; Santisteban, P. Role of iodide metabolism in physiology and cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, R225–R245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravera, S.; Reyna-Neyra, A.; Ferrandino, G.; Amzel, L.M.; Carrasco, N. The Sodium/Iodide Symporter (NIS): Molecular Physiology and Preclinical and Clinical Applications. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 261–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spitzweg, C.; Morris, J.C. Gene therapy for thyroid cancer: Current status and future prospects. Thyroid 2004, 14, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.K.; Cheon, G.J. Radioiodine therapy in differentiated thyroid cancer: The first targeted therapy in oncology. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 29, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, B.C. Sodium iodide symporter for nuclear molecular imaging and gene therapy: From bedside to bench and back. Theranostics 2012, 2, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De La Vieja, A.; Dohan, O.; Levy, O.; Carrasco, N. Molecular analysis of the sodium/iodide symporter: Impact on thyroid and extrathyroid pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1083–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousset, B.; Dupuy, C.; Miot, F.; Dumont, J. Chapter 2 Thyroid Hormone Synthesis And Secretion. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Kaltsas, G., Koch, C., Kopp, P., et al., Eds.; MDText. com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; DeGrado, T.R. [18F]Tetrafluoroborate ([18F]TFB) and its analogs for PET imaging of the sodium/iodide symporter. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3918–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portulano, C.; Paroder-Belenitsky, M.; Carrasco, N. The Na+/I− symporter (NIS): Mechanism and medical impact. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 106–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riesco-Eizaguirre, G.; Santisteban, P. New insights in thyroid follicular cell biology and its impact in thyroid cancer therapy. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 957–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, G.; Levy, O.; Carrasco, N. Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature 1996, 379, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, O.; De la Vieja, A.; Ginter, C.S.; Riedel, C.; Dai, G.; Carrasco, N. N-linked glycosylation of the thyroid Na+/I− symporter (NIS). Implications for its secondary structure model. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 22657–22663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paroder-Belenitsky, M.; Maestas, M.J.; Dohan, O.; Nicola, J.P.; Reyna-Neyra, A.; Follenzi, A.; Dadachova, E.; Eskandari, S.; Amzel, L.M.; Carrasco, N. Mechanism of anion selectivity and stoichiometry of the Na+/I− symporter (NIS). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17933–17938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Jeso, B.; Arvan, P. Thyroglobulin From Molecular and Cellular Biology to Clinical Endocrinology. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 2–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Deken, X.; Wang, D.; Many, M.C.; Costagliola, S.; Libert, F.; Vassart, G.; Dumont, J.E.; Miot, F. Cloning of two human thyroid cDNAs encoding new members of the NADPH oxidase family. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23227–23233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, J.C.; Visser, T.J. Genetics and phenomics of hypothyroidism and goiter due to iodotyrosine deiodinase (DEHAL1) gene mutations. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 322, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, W.E.; Friesema, E.C.; Visser, T.J. Minireview: Thyroid hormone transporters: The knowns and the unknowns. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Jimenez, C.; Santisteban, P. TSH signalling and cancer. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2007, 51, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riedel, C.; Levy, O.; Carrasco, N. Post-transcriptional regulation of the sodium/iodide symporter by thyrotropin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 21458–21463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M.; Chiamolera, M.I.; Pazos-Moura, C.C.; Wondisford, F.E. Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1387–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, B.; Bartalena, L.; Cooper, D.S.; Hegedus, L.; Laurberg, P.; Kahaly, G.J. The 2015 European Thyroid Association Guidelines on Diagnosis and Treatment of Endogenous Subclinical Hyperthyroidism. Eur. Thyroid J. 2015, 4, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medici, M.; Visser, T.J.; Peeters, R.P. Genetics of thyroid function. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 31, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, S.G.; Kimura, E.T.; Santisteban, P.; De la Vieja, A. Regulation of thyroid oxidative state by thioredoxin reductase has a crucial role in thyroid responses to iodide excess. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolff, J.; Chaikoff, I.L. Plasma inorganic iodide as a homeostatic regulator of thyroid function. J. Biol. Chem. 1948, 174, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.M.; Braverman, L.E. Consequences of excess iodine. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eng, P.H.; Cardona, G.R.; Fang, S.L.; Previti, M.; Alex, S.; Carrasco, N.; Chin, W.W.; Braverman, L.E. Escape from the acute Wolff-Chaikoff effect is associated with a decrease in thyroid sodium/iodide symporter messenger ribonucleic acid and protein. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 3404–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, S.G.; Sastre-Perona, A.; De la Vieja, A.; Santisteban, P. Selenium Increases Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone-Induced Sodium/Iodide Symporter Expression Through Thioredoxin/Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1-Dependent Regulation of Paired Box 8 Binding Activity. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2016, 24, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hichri, M.; Vassaux, G.; Guigonis, J.M.; Juhel, T.; Graslin, F.; Guglielmi, J.; Pourcher, T.; Cambien, B. Proteomic Analysis of Iodinated Contrast Agent-Induced Perturbation of Thyroid Iodide Uptake. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vassaux, G.; Zwarthoed, C.; Signetti, L.; Guglielmi, J.; Compin, C.; Guigonis, J.M.; Juhel, T.; Humbert, O.; Benisvy, D.; Pourcher, T.; et al. Iodinated Contrast Agents Perturb Iodide Uptake by the Thyroid Independently of Free Iodide. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, B.; Santisteban, P. PI3K is involved in the IGF-I inhibition of TSH-induced sodium/iodide symporter gene expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kogai, T.; Sajid-Crockett, S.; Newmarch, L.S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Brent, G.A. Phosphoinositide-3-kinase inhibition induces sodium/iodide symporter expression in rat thyroid cells and human papillary thyroid cancer cells. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 199, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaballos, M.A.; Garcia, B.; Santisteban, P. Gbetagamma dimers released in response to thyrotropin activate phosphoinositide 3-kinase and regulate gene expression in thyroid cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1183–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacroix, L.; Nocera, M.; Mian, C.; Caillou, B.; Virion, A.; Dupuy, C.; Filetti, S.; Bidart, J.M.; Schlumberger, M. Expression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase flavoprotein DUOX genes and proteins in human papillary and follicular thyroid carcinomas. Thyroid 2001, 11, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, V.; Bidart, J.M.; Caillou, B.; Mahe, C.; Lacroix, L.; Filetti, S.; Schlumberger, M. Expression of the Na+/I− symporter gene in human thyroid tumors: A comparison study with other thyroid-specific genes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 3228–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, A.M.; Chitikova, Z.; Pusztaszeri, M.; Berczy, M.; Delucinge-Vivier, C.; Triponez, F.; Meyer, P.; Philippe, J.; Dibner, C. Identification of CHEK1, SLC26A4, c-KIT, TPO and TG as new biomarkers for human follicular thyroid carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 45776–45788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastos, A.U.; Oler, G.; Nozima, B.H.; Moyses, R.A.; Cerutti, J.M. BRAF V600E and decreased NIS and TPO expression are associated with aggressiveness of a subgroup of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bidart, J.M.; Mian, C.; Lazar, V.; Russo, D.; Filetti, S.; Caillou, B.; Schlumberger, M. Expression of pendrin and the Pendred syndrome (PDS) gene in human thyroid tissues. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 2028–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kondo, T.; Nakamura, N.; Suzuki, K.; Murata, S.; Muramatsu, A.; Kawaoi, A.; Katoh, R. Expression of human pendrin in diseased thyroids. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2003, 51, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dohan, O.; Baloch, Z.; Banrevi, Z.; Livolsi, V.; Carrasco, N. Rapid communication: Predominant intracellular overexpression of the Na+/I− symporter (NIS) in a large sampling of thyroid cancer cases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2697–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.P.; Dupuy, C. Role of the NADPH Oxidases DUOX and NOX4 in Thyroid Oxidative Stress. Eur. Thyroid J. 2013, 2, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caballero, Y.; Lopez-Tomassetti, E.M.; Favre, J.; Santana, J.R.; Cabrera, J.J.; Hernandez, J.R. The value of thyroperoxidase as a prognostic factor for differentiated thyroid cancer—A long-term follow-up study. Thyroid Res. 2015, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faggiano, A.; Caillou, B.; Lacroix, L.; Talbot, M.; Filetti, S.; Bidart, J.M.; Schlumberger, M. Functional characterization of human thyroid tissue with immunohistochemistry. Thyroid 2007, 17, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skubis-Zegadlo, J.; Nikodemska, A.; Przytula, E.; Mikula, M.; Bardadin, K.; Ostrowski, J.; Wenzel, B.E.; Czarnocka, B. Expression of pendrin in benign and malignant human thyroid tissues. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavares, C.; Coelho, M.J.; Eloy, C.; Melo, M.; da Rocha, A.G.; Pestana, A.; Batista, R.; Ferreira, L.B.; Rios, E.; Selmi-Ruby, S.; et al. NIS expression in thyroid tumors, relation with prognosis clinicopathological and molecular features. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesco-Eizaguirre, G.; Rodriguez, I.; De la Vieja, A.; Costamagna, E.; Carrasco, N.; Nistal, M.; Santisteban, P. The BRAFV600E oncogene induces transforming growth factor beta secretion leading to sodium iodide symporter repression and increased malignancy in thyroid cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8317–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dohan, O.; De la Vieja, A.; Paroder, V.; Riedel, C.; Artani, M.; Reed, M.; Ginter, C.S.; Carrasco, N. The sodium/iodide Symporter (NIS): Characterization, regulation, and medical significance. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 48–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zwarthoed, C.; Chatti, K.; Guglielmi, J.; Hichri, M.; Compin, C.; Darcourt, J.; Vassaux, G.; Benisvy, D.; Pourcher, T.; Cambien, B. Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography for Preclinical Assessment of Thyroid Radioiodide Uptake Following Various Combinations of Preparative Measures. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, R.; Ferretti, E.; Tosi, E.; Arturi, F.; Giannasio, P.; Mattei, T.; Scipioni, A.; Presta, I.; Morisi, R.; Gulino, A.; et al. Modulation of thyroid-specific gene expression in normal and nodular human thyroid tissues from adults: An in vivo effect of thyrotropin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 5692–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohye, H.; Sugawara, M. Dual oxidase, hydrogen peroxide and thyroid diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 235, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameziane El Hassani, R.; Buffet, C.; Leboulleux, S.; Dupuy, C. Oxidative stress in thyroid carcinomas: Biological and clinical significance. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, R131–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azouzi, N.; Cailloux, J.; Cazarin, J.M.; Knauf, J.A.; Cracchiolo, J.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Hartl, D.; Polak, M.; Carre, A.; El Mzibri, M.; et al. NADPH Oxidase NOX4 Is a Critical Mediator of BRAF(V600E)-Induced Downregulation of the Sodium/Iodide Symporter in Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2017, 26, 864–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riesco-Eizaguirre, G.; Gutierrez-Martinez, P.; Garcia-Cabezas, M.A.; Nistal, M.; Santisteban, P. The oncogene BRAF V600E is associated with a high risk of recurrence and less differentiated papillary thyroid carcinoma due to the impairment of Na+/I− targeting to the membrane. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.L.; Grewal, R.K.; Leboeuf, R.; Sherman, E.J.; Pfister, D.G.; Deandreis, D.; Pentlow, K.S.; Zanzonico, P.B.; Haque, S.; Gavane, S.; et al. Selumetinib-enhanced radioiodine uptake in advanced thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell 2014, 159, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.S.; Park, Y.J. Expression of Sodium-Iodide Symporter Depending on Mutational Status and Lymphocytic Thyroiditis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Int. J. Thyroidol. 2018, 11, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, J.N.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, Q.; Yun, B.; Liu, J.Q.; Cai, X.Y. Expression of sodium/iodide transporters and thyroid stimulating hormone receptors in thyroid cancer patients and its correlation with iodine nutrition status and pathology. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet, C.; Wassermann, J.; Hecht, F.; Leenhardt, L.; Dupuy, C.; Groussin, L.; Lussey-Lepoutre, C. Redifferentiation of radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancers. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liang, J. Radioactive Iodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Redifferentiation Therapy. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 34, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubas, J.; Ovesen, T.; Rusan, M. A Systematic Review of Phase II Targeted Therapy Clinical Trials in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Liu, T.P.; Yang, P.S.; Cheng, S.P. Characteristics of lymphocyte-infiltrating papillary thyroid cancer. J. Cancer Res. Pract. 2017, 4, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arturi, F.; Russo, D.; Giuffrida, D.; Schlumberger, M.; Filetti, S. Sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) gene expression in lymph-node metastases of papillary thyroid carcinomas. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 143, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castro, M.R.; Bergert, E.R.; Goellner, J.R.; Hay, I.D.; Morris, J.C. Immunohistochemical analysis of sodium iodide symporter expression in metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: Correlation with radioiodine uptake. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5627–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, H.I.; Park, S.Y.; Choe, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.W. Preoperative serum thyroglobulin predicts initial distant metastasis in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verburg, F.A.; Hanscheid, H.; Luster, M. Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy for metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 31, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, D.; Panarotto, M.B.; Durmo, R.; Rodella, C.; Bertagna, F.; Giubbini, R. Clinical and prognostic role of detection timing of distant metastases in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocrine 2019, 63, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, U.; Harmer, C.; Yap, B.; Wadsley, J.; Clarke, S.; Moss, L.; Nicol, A.; Clark, P.M.; Farnell, K.; McCready, R.; et al. Ablation with low-dose radioiodine and thyrotropin alfa in thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlumberger, M.; Catargi, B.; Borget, I.; Deandreis, D.; Zerdoud, S.; Bridji, B.; Bardet, S.; Leenhardt, L.; Bastie, D.; Schvartz, C.; et al. Strategies of radioiodine ablation in patients with low-risk thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sellitti, D.F.; Suzuki, K. Intrinsic regulation of thyroid function by thyroglobulin. Thyroid 2014, 24, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bal, C.; Chandra, P.; Kumar, A.; Dwivedi, S. A randomized equivalence trial to determine the optimum dose of iodine-131 for remnant ablation in differentiated thyroid cancer. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2012, 33, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior-Sanchez, I.; Muñoz-Jimenez, C.; Moreno-Moreno, P.; Rebollo-Roman, A.; Barrera-Martín, A.; Moreno-Ortega, E.; Vallejo-Casas, J.A.; Galvez-Moreno, M.A. Our experience with low doses of radioactive iodine (30 mCi) in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. In Proceedings of the 18th European Congress of Endocrinology, Munich, Germany, 28–31 May 2016; p. EP1139. [Google Scholar]
- Albano, D.; Bonacina, M.; Durmo, R.; Bertagna, F.; Giubbini, R. Efficacy of low radioiodine activity versus intermediate-high activity in the ablation of low-risk differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocrine 2020, 68, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Ishizaki, U.; Ono, T.; Horiuchi, K.; Kanaya, K.; Sakai, S.; Okamoto, T. Low-dose radioiodine therapy for patients with intermediate- to high-risk differentiated thyroid cancer. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2020, 34, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanscheid, H.; Lassmann, M.; Luster, M.; Thomas, S.R.; Pacini, F.; Ceccarelli, C.; Ladenson, P.W.; Wahl, R.L.; Schlumberger, M.; Ricard, M.; et al. Iodine biokinetics and dosimetry in radioiodine therapy of thyroid cancer: Procedures and results of a prospective international controlled study of ablation after rhTSH or hormone withdrawal. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 648–654. [Google Scholar]
- Taieb, D.; Sebag, F.; Farman-Ara, B.; Portal, T.; Baumstarck-Barrau, K.; Fortanier, C.; Bourrelly, M.; Mancini, J.; De Micco, C.; Auquier, P.; et al. Iodine biokinetics and radioiodine exposure after recombinant human thyrotropin-assisted remnant ablation in comparison with thyroid hormone withdrawal. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3283–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elisei, R.; Schlumberger, M.; Driedger, A.; Reiners, C.; Kloos, R.T.; Sherman, S.I.; Haugen, B.; Corone, C.; Molinaro, E.; Grasso, L.; et al. Follow-up of low-risk differentiated thyroid cancer patients who underwent radioiodine ablation of postsurgical thyroid remnants after either recombinant human thyrotropin or thyroid hormone withdrawal. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuttle, R.M.; Brokhin, M.; Omry, G.; Martorella, A.J.; Larson, S.M.; Grewal, R.K.; Fleisher, M.; Robbins, R.J. Recombinant human TSH-assisted radioactive iodine remnant ablation achieves short-term clinical recurrence rates similar to those of traditional thyroid hormone withdrawal. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campenni, A.; Amato, E.; Laudicella, R.; Alibrandi, A.; Cardile, D.; Pignata, S.A.; Trimarchi, F.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Auditore, L.; Baldari, S. Recombinant human thyrotropin (rhTSH) versus Levo-thyroxine withdrawal in radioiodine therapy of differentiated thyroid cancer patients: Differences in abdominal absorbed dose. Endocrine 2019, 65, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M. Management of differentiated thyroid cancer with rising thyroglobulin and negative diagnostic radioiodine whole body scan. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 22, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elboga, U.; Karaoglan, H.; Sahin, E.; Kalender, E.; Demir, H.D.; Basibuyuk, M.; Zeki Celen, Y.; Yilmaz, M.; Ozkaya, M. F-18 FDG PET/CT imaging in the diagnostic work-up of thyroid cancer patients with high serum thyroglobulin, negative I-131 whole body scan and suppressed thyrotropin: 8-year experience. Eur. Rev. Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 396–401. [Google Scholar]
- Riesco-Eizaguirre, G.; Galofre, J.C.; Grande, E.; Zafon Llopis, C.; Ramon y Cajal Asensio, T.; Navarro Gonzalez, E.; Jimenez-Fonseca, P.; Santamaria Sandi, J.; Gomez Saez, J.M.; Capdevila, J. Spanish consensus for the management of patients with advanced radioactive iodine refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2016, 63, e17-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakani, A.; Saghari, M.; Eftekhari, M.; Fard-Esfahani, A.; Fallahi, B.; Esmaili, J.; Assadi, M. Evaluation of radioiodine therapy in differentiated thyroid cancer subjects with elevated serum thyroglobulin and negative whole body scan using 131I with emphasize on the thallium scintigraphy in these subgroups. Eur. Rev. Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; Burman, K.D.; Van Nostrand, D.; Mete, M.; Jonklaas, J.; Wartofsky, L. Potential use of recombinant human thyrotropin in the treatment of distant metastases in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocr. Pract. 2013, 19, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liepe, K. Sensitivity of preparation with rhTSH or thyroid hormone withdrawal using 131I-whole body scans to identify metastases of differentiated thyroid cancer. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 16, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, R.M.; Lopez, N.; Leboeuf, R.; Minkowitz, S.M.; Grewal, R.; Brokhin, M.; Omry, G.; Larson, S. Radioactive iodine administered for thyroid remnant ablation following recombinant human thyroid stimulating hormone preparation also has an important adjuvant therapy function. Thyroid 2010, 20, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tala, H.; Robbins, R.; Fagin, J.A.; Larson, S.M.; Tuttle, R.M. Five-year survival is similar in thyroid cancer patients with distant metastases prepared for radioactive iodine therapy with either thyroid hormone withdrawal or recombinant human TSH. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 2105–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, C.M.; Kim, C.Y.; Son, S.H.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.C. I-131 biokinetics of remnant normal thyroid tissue and residual thyroid cancer in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: Comparison between recombinant human TSH administration and thyroid hormone withdrawal. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2017, 31, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, R.W.; Rall, J.E.; Peacock, W. Limitations in the treatment of cancer of the thyroid with radioactive iodine. Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1951, 64, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundh, C.; Lindencrona, U.; Postgard, P.; Carlsson, T.; Nilsson, M.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. Radiation-induced thyroid stunning: Differential effects of 123I, 131I, 99mTc, and 211At on iodide transport and NIS mRNA expression in cultured thyroid cells. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meller, B.; Gaspar, E.; Deisting, W.; Czarnocka, B.; Baehre, M.; Wenzel, B.E. Decreased radioiodine uptake of FRTL-5 cells after 131I incubation in vitro: Molecular biological investigations indicate a cell cycle-dependent pathway. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postgard, P.; Himmelman, J.; Lindencrona, U.; Bhogal, N.; Wiberg, D.; Berg, G.; Jansson, S.; Nystrom, E.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.; Nilsson, M. Stunning of iodide transport by 131I irradiation in cultured thyroid epithelial cells. J. Nucl. Med. 2002, 43, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Happel, C.; Kranert, W.T.; Ackermann, H.; Binse, I.; Bockisch, B.; Groner, D.; Herrmann, K.; Grunwald, F. Thyroid stunning in radioiodine-131 therapy of benign thyroid diseases. Endocrine 2019, 63, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, M.; Luster, M.; Hanscheid, H.; Reiners, C. Impact of 131I diagnostic activities on the biokinetics of thyroid remnants. J. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morris, L.F.; Waxman, A.D.; Braunstein, G.D. Thyroid stunning. Thyroid 2003, 13, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougall, I.R.; Iagaru, A. Thyroid stunning: Fact or fiction? Semin. Nucl. Med. 2011, 41, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrndic, O.B.; Radivojevic, S.D.; Jovanovic, M.D.; Djukic, S.M.; Teodorovic, L.C.; Simonovic, S.T. Oxidative stress in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: Early effects of radioiodine therapy. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 51, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruhlmann, M.; Sonnenschein, W.; Nagarajah, J.; Binse, I.; Herrmann, K.; Jentzen, W. Pretherapeutic 124I dosimetry reliably predicts intratherapeutic blood kinetics of 131I in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma receiving high therapeutic activities. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2018, 39, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Igarashi, T.; Ashida, H.; Ogiwara, S.; Ohta, T.; Uchiyama, M.; Ojiri, H. Diagnostic value of ultrasonography and TI-201/Tc-99m dual scintigraphy in differentiating between benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Endocrine 2019, 63, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambien, B.; Franken, P.R.; Lamit, A.; Mauxion, T.; Richard-Fiardo, P.; Guglielmi, J.; Crescence, L.; Mari, B.; Pourcher, T.; Darcourt, J.; et al. 99mTcO4−-, auger-mediated thyroid stunning: Dosimetric requirements and associated molecular events. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueh, S.S.; Roach, P.J.; Schembri, G.P. Role of Tc-99m pertechnetate for remnant scintigraphy post-thyroidectomy. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2010, 35, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriagada, A.A.; Albornoz, E.; Opazo, M.C.; Becerra, A.; Vidal, G.; Fardella, C.; Michea, L.; Carrasco, N.; Simon, F.; Elorza, A.A.; et al. Excess iodide induces an acute inhibition of the sodium/iodide symporter in thyroid male rat cells by increasing reactive oxygen species. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liou, G.Y.; Storz, P. Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yap, B.K.; Murby, B. No adverse affect in clinical outcome using low preablation diagnostic 131I activity in differentiated thyroid cancer: Refuting thyroid-stunning effect. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 2433–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Happel, C.; Kranert, W.T.; Groner, D.; Bockisch, B.; Sabet, A.; Vardarli, I.; Gorges, R.; Herrmann, K.; Grunwald, F. Correction for hyperfunctioning radiation-induced stunning (CHRIS) in benign thyroid diseases. Endocrine 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fast, S.; Nielsen, V.E.; Grupe, P.; Bonnema, S.J.; Hegedus, L. Optimizing 131I uptake after rhTSH stimulation in patients with nontoxic multinodular goiter: Evidence from a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filzen, L.M.; Ellingson, L.R.; Paulsen, A.M.; Hung, J.C. Potential Ways to Address Shortage Situations of 99Mo/99mTc. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2017, 45, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubberink, M.; Herzog, H. Quantitative imaging of 124I and 86Y with PET. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38 (Suppl. 1), S10–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pentlow, K.S.; Graham, M.C.; Lambrecht, R.M.; Daghighian, F.; Bacharach, S.L.; Bendriem, B.; Finn, R.D.; Jordan, K.; Kalaigian, H.; Karp, J.S.; et al. Quantitative imaging of iodine-124 with PET. J. Nucl. Med. 1996, 37, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar]
- Spetz, J.; Rudqvist, N.; Forssell-Aronsson, E. Biodistribution and dosimetry of free 211At, 125I− and 131I− in rats. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2013, 28, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Ye, C.; Chen, C.; Xiong, H.; Xie, B.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, L. Glucose transporter GLUT1 expression and clinical outcome in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16875–16886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Chung, J.K.; Min, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; Park, D.J.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, D.S.; Park, S.H.; Cho, B.Y.; Lee, S.; et al. Expression patterns of glucose transporter-1 gene and thyroid specific genes in human papillary thyroid carcinoma. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 48, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakhshayesh Karam, M.; Doroudinia, A.; Joukar, F.; Nadi, K.; Dorudinia, A.; Mehrian, P.; Yousefikoma, A. Hypermetabolic Thyroid Incidentaloma on Positron Emission Tomography: Review of Laboratory, Radiologic, and Pathologic Characteristics. J. Thyroid Res. 2017, 2017, 7176934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruthi, A.; Choudhury, P.S.; Gupta, M.; Taywade, S. Does the intensity of diffuse thyroid gland uptake on F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography scan predict the severity of hypothyroidism? Correlation between maximal standardized uptake value and serum thyroid stimulating hormone levels. Indian J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 30, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosaka, Y.; Tawata, M.; Kurihara, A.; Ohtaka, M.; Endo, T.; Onaya, T. The regulation of two distinct glucose transporter (GLUT1 and GLUT4) gene expressions in cultured rat thyroid cells by thyrotropin. Endocrinology 1992, 131, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prante, O.; Maschauer, S.; Fremont, V.; Reinfelder, J.; Stoehr, R.; Szkudlinski, M.; Weintraub, B.; Hartmann, A.; Kuwert, T. Regulation of uptake of 18F-FDG by a follicular human thyroid cancer cell line with mutation-activated K-ras. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuzu, K.; Segade, F.; Wong, M.; Clark, O.H.; Perrier, N.D.; Bowden, D.W. Glucose transporters in the thyroid. Thyroid 2005, 15, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, F.; Ladenson, P.W.; Schlumberger, M.; Driedger, A.; Luster, M.; Kloos, R.T.; Sherman, S.; Haugen, B.; Corone, C.; Molinaro, E.; et al. Radioiodine ablation of thyroid remnants after preparation with recombinant human thyrotropin in differentiated thyroid carcinoma: Results of an international, randomized, controlled study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taieb, D.; Lussato, D.; Guedj, E.; Roux, F.; Mundler, O. Early sequential changes in serum thyroglobulin after radioiodine ablation for thyroid cancer: Possible clinical implications for recombinant human thyrotropin-aided therapy. Thyroid 2006, 16, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duntas, L.H.; Biondi, B. Short-term hypothyroidism after Levothyroxine-withdrawal in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: Clinical and quality of life consequences. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 156, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Tang, L.; Fu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, H. rhTSH-aided low-activity versus high-activity regimens of radioiodine in residual ablation for differentiated thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2013, 34, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borget, I.; Remy, H.; Chevalier, J.; Ricard, M.; Allyn, M.; Schlumberger, M.; De Pouvourville, G. Length and cost of hospital stay of radioiodine ablation in thyroid cancer patients: Comparison between preparation with thyroid hormone withdrawal and thyrogen. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietlein, M.; Busemeyer, S.; Kobe, C.; Schmidt, M.; Theissen, P.; Schicha, H. Recombinant human TSH versus hypothyroidism. Cost-minimization-analysis in the follow-up care of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Nukl. Nucl. Med. 2010, 49, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luster, M.; Felbinger, R.; Dietlein, M.; Reiners, C. Thyroid hormone withdrawal in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma: A one hundred thirty-patient pilot survey on consequences of hypothyroidism and a pharmacoeconomic comparison to recombinant thyrotropin administration. Thyroid 2005, 15, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Isotope | Detection Technique | Transporter | TG Organification? | Energy Emitted Type | Energy Emitted (KeV) | Half Life | Tissue Penetration/Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 123I | SPECT | NIS | Yes | EC/γ | 159 | 13 h | |
| 124I | PET | NIS | Yes | β+ | 510 | 4.17 d | 5.0 mm |
| 125I | SPECT | NIS | Yes | EC/γ | 27 | 59.4 d | 17 µm |
| 131I | SPECT | NIS | Yes | β-/γ | 364 | 8.02 d | 0.44–2.4 mm |
| 211At | PET | NIS, others | No | EC/α | 27 y 6900 (α) | 7.2 h | 65 µm |
| 99mTcO4− | SPECT | NIS | No | IT/γ | 140 | 6.03 h | |
| 188ReO4− | SPECT | NIS | No | β-/γ | 155 | 17 h | 10.8 mm |
| 18F-BF4− | PET | NIS | No | β+ | 511 | 110 min | |
| 18F-FDG | PET | GLUT | No | β+ | 511 | 110 min | 4.2 mm |
| Stimulators | Inhibitor |
|---|---|
| TSH Selenium | Iodide (I−) |
| Thyroglobulin (TG) | |
| Growth factors and cytokines (IGF1, TGFβ, TNFα, TNFβ, IFNγ, ILα, ILβ and IL-6) | |
| Reactive oxygen species (ROS) | |
| Iodinated contrast agents |
| DTC | mDTC | PDTC and ATC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSH-R | ↓ | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓↓ |
| NIS | ↓ = (PM/cytoplasm) | ↓↓ (PM/cytoplasm) | ND |
| Pendrin | ↓↓ | ND | |
| TG | ↓ | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓↓↓ |
| TPO | ↓ (PM/cytoplasm) | ↓↓ (PM/cytoplasm) | ND |
| Duox2 | = (PM/cytoplasm) | ↓ | ND |
| GLUT1 | = or slightly ↑ | ↑↑ | ↑↑ |
| Benefit | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| TH deprivation for 2–4 weeks |
|
|
| Recombinant human TSH |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De la Vieja, A.; Riesco-Eizaguirre, G. Radio-Iodide Treatment: From Molecular Aspects to the Clinical View. Cancers 2021, 13, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13050995
De la Vieja A, Riesco-Eizaguirre G. Radio-Iodide Treatment: From Molecular Aspects to the Clinical View. Cancers. 2021; 13(5):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13050995
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe la Vieja, Antonio, and Garcilaso Riesco-Eizaguirre. 2021. "Radio-Iodide Treatment: From Molecular Aspects to the Clinical View" Cancers 13, no. 5: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13050995
APA StyleDe la Vieja, A., & Riesco-Eizaguirre, G. (2021). Radio-Iodide Treatment: From Molecular Aspects to the Clinical View. Cancers, 13(5), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13050995