Ginsenoside Rh1 Induces MCF-7 Cell Apoptosis and Autophagic Cell Death through ROS-Mediated Akt Signaling
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rh1 Showed Anticancer Effects on BC Cells
2.2. Rh1 Induced Cell Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in BC Cells
2.3. Anticancer Effects of Rh1 Are Associated with the Akt Signaling Pathway and ROS Modulation
2.4. Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Induced by Rh1 Is Associated with the ROS-Mediated Akt Pathway
2.5. Rh1 Stimulates Autophagy in BC Cells
2.6. Rh1 Showed a Competitive Effect with an Estrogenic Agent on BC Cells
2.7. Rh1 Exerted Antitumor Activities in a Xenograft Model
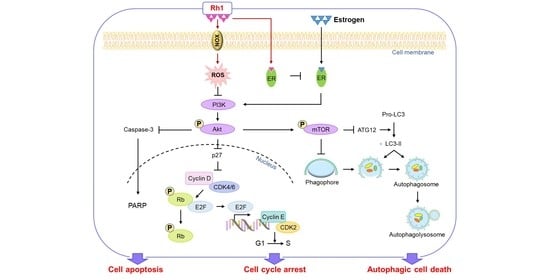
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
4.4. MTT Assay
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Propidium Iodide (PI)/Hoechst 33342 Double Staining
4.7. Generation of pMRX-IP-GFP-LC3-RFP-LC3ΔG-Expressing Cells and Measurement of the Autophagic Flux
4.8. Immunofluorescence Assay
4.9. Clonogenic Assay
4.10. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Levels
4.11. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Cell Cycle
4.12. In Vivo MCF-7 Cell Xenograft Nude Mice Model
4.13. Histological Analysis
4.14. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species in Tumor Tissues through Dihydroethidium (DHE) Staining
4.15. Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, C.; Perestrelo, R.; Silva, P.; Tomás, H.; Câmara, J.S. Breast Cancer Metabolomics: From Analytical Platforms to Multivariate Data Analysis. A Review. Metabolites 2019, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palesh, O.; Scheiber, C.; Kesler, S.; Mustian, K.; Koopman, C.; Schapira, L. Management of side effects during and post-treatment in breast cancer survivors. Breast J. 2018, 24, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Dash, R. Natural Products for the Management and Prevention of Breast Cancer. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8324696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Chang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Induction of reactive oxygen species: An emerging approach for cancer therapy. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Huynh, D.T.N.; Nguyen, T.L.L.; Jeon, H.; Heo, K.-S. Therapeutic effects of ginsenosides on breast cancer growth and metastasis. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2020, 43, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.; Huynh, D.T.N.; Baek, N.; Thuy, N.L.L.; Heo, K.-S. Ginsenoside-Rg2 affects cell growth via regulating ROS-mediated AMPK activation and cell cycle in MCF-7 cells. Phytomedicine 2021, 85, 153549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Deng, J.; Fan, D.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Fu, R.; Wang, S. Ginsenoside Rh4 induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death through activation of the ROS/JNK/p53 pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 148, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, C.; Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Tian, J. TEOA, a triterpenoid from Actinidia eriantha, induces autophagy in SW620 cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress and ROS-dependent mitophagy. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2017, 40, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Bu, W.; Song, J.; Feng, L.; Xu, T.; Liu, D.; Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Ma, B.; et al. Apoptosis induction by alantolactone in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrion-dependent pathway. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2018, 41, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sobhani, N.; D’Angelo, A.; Pittacolo, M.; Roviello, G.; Miccoli, A.; Corona, S.P.; Bernocchi, O.; Generali, D.; Otto, T. Updates on the CDK4/6 Inhibitory Strategy and Combinations in Breast Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Bao, J.-K.; Yang, J.-M. Autophagic pathways as new targets for cancer drug development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rybstein, M.D.; Pedro, J.M.B.-S.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. The autophagic network and cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Rommel, C. PI3K and cancer: Lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoki, M.; Fujishita, T. Oncogenic Roles of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Axis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 407, 153–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.R.; Nam, D.; Yun, H.M.; Lee, S.G.; Jang, H.J.; Sethi, G.; Cho, S.K.; Ahn, K.S. beta-Caryophyllene oxide inhibits growth and induces apoptosis through the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1 pathways and ROS-mediated MAPKs activation. Cancer Lett. 2011, 312, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitulescu, G.M.; Van De Venter, M.; Nitulescu, G.; Ungurianu, A.; Juzenas, P.; Peng, Q.; Olaru, O.T.; Grădinaru, D.; Tsatsakis, A.; Tsoukalas, D.; et al. The Akt pathway in oncology therapy and beyond (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tam, D.N.H.; Truong, D.H.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Quynh, L.N.; Tran, L.; Nguyễn, H.D.; Shamandy, B.E.; Le, T.M.H.; Tran, D.K.; Sayed, D.; et al. Ginsenoside Rh1: A Systematic Review of Its Pharmacological Properties. Planta Medica 2018, 84, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.L.L.; Huynh, D.T.N.; Jin, Y.; Jeon, H.; Heo, K.-S. Protective effects of ginsenoside-Rg2 and -Rh1 on liver function through inhibiting TAK1 and STAT3-mediated inflammatory activity and Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant signaling pathway. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2021, 44, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Xu, X.; Song, A.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits colorectal cancer cell migration and in-vasion in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 4160–4166. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.-S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Le, T.K.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Protopanaxatriol ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and the in vitro invasion/migration of human astroglioma cells. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiyalagan, R.; Wang, C.; Kim, Y.J.; Castro-Aceituno, V.; Ahn, S.; Subramaniyam, S.; Simu, S.Y.; Jiménez-Pérez, Z.E.; Yang, D.C.; Jung, S.-K. Preparation of Polyethylene Glycol-Ginsenoside Rh1 and Rh2 Conjugates and Their Efficacy against Lung Cancer and Inflammation. Molecules 2019, 24, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleem, M.Z.; Nisar, M.A.; Alshwmi, M.; Din, S.R.U.; Gamallat, Y.; Khan, M.; Ma, T. Brevilin A Inhibits STAT3 Signaling and Induces ROS-Dependent Apoptosis, Mitochondrial Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, G.; Luo, W.; Sun, W.; Niu, Y.; Ma, D.-L.; Leung, C.-H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.-J.; Chen, X. Psoralidin induced reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent DNA damage and protective autophagy mediated by NOX4 in breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielke, S.; Meyer, N.; Mari, M.; Abou-El-Ardat, K.; Reggiori, F.; Van Wijk, S.J.L.; Kögel, D.; Fulda, S. Loperamide, pimozide, and STF-62247 trigger autophagy-dependent cell death in glioblastoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Jin, Y.; Lim, W.; Ji, S.; Choi, S.; Jang, S.; Lee, S. A ginsenoside-Rh1, a component of ginseng saponin, activates estrogen receptor in human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 84, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, G.E.; Franke, T.F.; Moroni, M.; Mueller, S.; Morgan, E.; Iann, M.C.; Winder, A.D.; Reiter, R.; Wellstein, A.; Martin, M.B.; et al. Effect of estradiol on estrogen receptor-alpha gene expression and activity can be modulated by the ErbB2/PI 3-K/Akt pathway. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7998–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siraj, F.M.; Natarajan, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. In silico screening of ginsenoside Rh1 with PPAR gamma and in vitro analysis on 3T3-L1 cell line. Mol. Simul. 2015, 41, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Cha, S.-W.; Lee, S.-G. Ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the invasion and migration of THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cells via inactivation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-J.; Cho, K.-H.; Jung, W.-S.; Moon, S.-K.; Park, E.-K.; Kim, N.-H. Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1, crocin, amygdalin, geniposide, puerarin, ginsenoside Re, hesperidin, poncirin, glycyrrhizin, and baicalin by human fecal microflora and its relation to cytotoxicity against tumor cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, K.; Liu, Q.; Wan, J.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Guo, R.-Z.; Alolga, R.N.; Li, P.; Qi, L.-W. Rapid preparation of rare ginsenosides by acid transformation and their structure-activity relationships against cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.W.; Hu, J.J.; Fu, R.Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.N.; Deng, Q.; Luo, Q.S.; et al. Flavonoids inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis and autophagy through downregulation of PI3Kgamma mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K/ULK signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Saralamma, V.V.G.; Kim, S.M.; Ha, S.E.; Raha, S.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, S.J.; Heo, J.D.; Kim, G.S. Pectolinarigenin Induced Cell Cycle Arrest, Autophagy, and Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer Cell via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.M.; Vetrivel, P.; Ha, S.E.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, G.S. Apigetrin induces extrinsic apoptosis, autophagy and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in AGS human gastric cancer cell. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 83, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, J.S.; Ahn, J.; Nam, K.-Y.; Hwang, S.-G.; Song, J.-Y. The small molecule AU14022 promotes colorectal cancer cell death via p53-mediated G2/M-phase arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 4666–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Karantza-Wadsworth, V.; White, E. Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augsburger, F.; Filippova, A.; Rasti, D.; Seredenina, T.; Lam, M.; Maghzal, G.; Mahiout, Z.; Jansen-Dürr, P.; Knaus, U.G.; Doroshow, J.; et al. Pharmacological characterization of the seven human NOX isoforms and their inhibitors. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldieri, E.; Riganti, C.; Polimeni, M.; Gazzano, E.; Lussiana, C.; Campia, I.; Ghigo, D. Classical Inhibitors of NOX NAD(P)H Oxidases Are Not Specific. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yu, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Yi, X.; Wu, Y.L.; Hao, Q.; Kemp, K.T., 2nd; Elshimali, Y.; Iyer, R.; et al. Targeting of PP2Cdelta By a Small Molecule C23 Inhibits High Glucose-Induced Breast Cancer Progression In Vivo. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2019, 30, 1983–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kma, L.; Baruah, T.J. The interplay of ROS and the PI3K/Akt pathway in autophagy regulation. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, S.; Wen, Z.; He, W.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Shi, M. ROS signaling under metabolic stress: Cross-talk between AMPK and AKT pathway. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.-T.; Kwak, D.W.; Lin, S.K.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, O.J. Resveratrol Induces Apoptosis in Chemoresistant Cancer Cells via Modulation of AMPK Signaling Pathway. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2007, 1095, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Cui, J.; Harata-Lee, Y.; Aung, T.N.; Feng, Q.; Raison, J.M.; Kortschak, R.D.; Adelson, D.L. Identification of candidate anti-cancer molecular mechanisms of Compound Kushen Injection using functional genomics. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66003–66019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chumakova, O.V.; Liopo, A.V.; Evers, B.M.; Esenaliev, R.O. Effect of 5-fluorouracil, Optison and ultrasound on MCF-7 cell viability. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neve, R.M.; Chin, K.; Fridlyand, J.; Yeh, J.; Baehner, F.L.; Fevr, T.; Clark, L.; Bayani, N.; Coppe, J.P.; Tong, F.; et al. A col-lection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowsheen, S.; Cooper, T.; Bonner, J.A.; LoBuglio, A.F.; Yang, E.S. HER2 Overexpression Renders Human Breast Cancers Sensitive to PARP Inhibition Independently of Any Defect in Homologous Recombination DNA Repair. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4796–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahbandi, A.; Rao, S.G.; Anderson, A.Y.; Frey, W.D.; Olayiwola, J.O.; Ungerleider, N.A.; Jackson, J.G. BH3 mimetics selectively eliminate chemotherapy-induced senescent cells and improve response in TP53 wild-type breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 3097–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, D.T.N.; Baek, N.; Sim, S.; Myung, C.-S.; Heo, K.-S. Minor Ginsenoside Rg2 and Rh1 Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Liver and Kidney Damages via Downregulating Activation of TLR4-STAT1 and Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Lu, J.; Abe, H.; Huang, K.; Manabe, M.; Kodama, H. Inhibitory Effects of Ginsenosides from the Root of Panax ginseng on Stimulus-Induced Superoxide Generation, Tyrosyl or Serine/Threonine Phosphorylation, and Translocation of Cytosolic Compounds to Plasma Membrane in Human Neutrophils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Yang, Z.; Ye, Y. Structure and biological activity of protopanaxatriol-type saponins from the roots of Panax no-toginseng. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, D.T.N.; Jin, Y.; Myung, C.-S.; Heo, K.-S. Inhibition of p90RSK is critical to abolish Angiotensin II-induced rat aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, N.A.P.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; Van Bree, C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huynh, D.T.N.; Jin, Y.; Myung, C.-S.; Heo, K.-S. Ginsenoside Rh1 Induces MCF-7 Cell Apoptosis and Autophagic Cell Death through ROS-Mediated Akt Signaling. Cancers 2021, 13, 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081892
Huynh DTN, Jin Y, Myung C-S, Heo K-S. Ginsenoside Rh1 Induces MCF-7 Cell Apoptosis and Autophagic Cell Death through ROS-Mediated Akt Signaling. Cancers. 2021; 13(8):1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081892
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuynh, Diem Thi Ngoc, Yujin Jin, Chang-Seon Myung, and Kyung-Sun Heo. 2021. "Ginsenoside Rh1 Induces MCF-7 Cell Apoptosis and Autophagic Cell Death through ROS-Mediated Akt Signaling" Cancers 13, no. 8: 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081892
APA StyleHuynh, D. T. N., Jin, Y., Myung, C. -S., & Heo, K. -S. (2021). Ginsenoside Rh1 Induces MCF-7 Cell Apoptosis and Autophagic Cell Death through ROS-Mediated Akt Signaling. Cancers, 13(8), 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081892