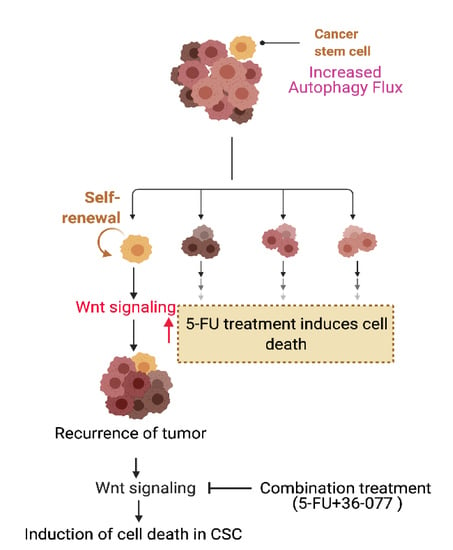
PIK3C3 Inhibition Promotes Sensitivity to Colon Cancer Therapy by Inhibiting Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. Retroviral Infection in Caco2 and HCT116 Cells
2.3. Autophagy Flux Measurement
2.4. Synthesis of the VPS34/PIK3C3 Inhibitor (36-077): 1-Cyclopropyl-3-(2-(methylthio) pyrimidin-4-yl) propan-2-one (3)
2.5. (Z)-1-cyclopropyl-4-(dimethylamino)-3-(2-(methylthio) pyrimidin-4-yl) but-3-en-2-one (4)
2.6. 4′-(Cyclopropylmethyl)-2-(methylthio)-[4,5′-bipyrimidin]-2′-amine (5)
2.7. 4′-(Cyclopropylmethyl)-2-(methylsulfinyl)-[4,5′-bipyrimidin]-2′-amine (6)
2.8. 4′-(Cyclopropylmethyl)-N2-(pyridin-4-yl)-[4,5′-bipyrimidine]-2,2′-diamine (7)
2.9. APCMin/+Colon Tumoroid Culture
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Immunofluorescence
2.12. Promoter Activity
2.13. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR Analysis
2.14. Isolation of Side Population (SP) Cells
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemotherapy Induces Autophagy in Colon Cancer
3.2. Chemotherapy-Induced Autophagy Is Specific to Cancer Stem Cells
3.3. 36-077, a PIK3C3/VPS34 Inhibitor, Is a Highly Specific and Potent Autophagy Inhibitor
3.4. Co-Treatment with 36-077 Improves Therapeutic Efficacy of 5-FU Treatment
3.5. Co-Treatment of 5-FU and 36-077 Inhibits GSK-3β/Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
3.6. Combination Treatment of 5-FU+36-077 Inhibits Survival of Cancer Stem Cells
3.7. 36-077 Treatment Increased the Therapeutic Efficacy of 5-FU by Inhibiting the WNT Signeling in CSC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Fedewa, S.A.; Anderson, W.F.; Miller, K.D.; Ma, J.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Jemal, A. Colorectal Cancer Incidence Patterns in the United States, 1974–2013. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, K.D.; Nogueira, L.; Mariotto, A.B.; Rowland, J.H.; Yabroff, K.R.; Alfano, C.M.; Jemal, A.; Kramer, J.L.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguiar Junior, S.; Oliveira, M.M.; Silva, D.; Mello, C.A.L.; Calsavara, V.F.; Curado, M.P. Survival of Patients with Colorectal Cancer in a Cancer Center. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2020, 57, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouillard, A.; Bouvier, A.M.; Boussari, O.; Romain, G.; Manfredi, S.; Lepage, C.; Faivre, J.; Jooste, V. Net survival in recurrence-free colon cancer patients. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 61, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, J.N.; Bao, S. Chemotherapy and cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batlle, E.; Clevers, H. Cancer stem cells revisited. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Settleman, J. EMT, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Francesco, E.M.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Cancer stem cells (CSCs): Metabolic strategies for their identification and eradication. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 1611–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, M.; Law, S. Role of tumor microenvironment in cancer stem cell chemoresistance and recurrence. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 103, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N. Autophagy: Process and function. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kroemer, G.; Marino, G.; Levine, B. Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.J.; Chee, C.E.; Huang, S.; Sinicrope, F.A. The role of autophagy in cancer: Therapeutic implications. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorburn, A.; Thamm, D.H.; Gustafson, D.L. Autophagy and cancer therapy. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chude, C.I.; Amaravadi, R.K. Targeting Autophagy in Cancer: Update on Clinical Trials and Novel Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dyczynski, M.; Yu, Y.; Otrocka, M.; Parpal, S.; Braga, T.; Henley, A.B.; Zazzi, H.; Lerner, M.; Wennerberg, K.; Viklund, J.; et al. Targeting autophagy by small molecule inhibitors of vacuolar protein sorting 34 (Vps34) improves the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to Sunitinib. Cancer Lett. 2018, 435, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.Z.; Parpal, S.; Van Moer, K.; Xiao, M.; Yu, Y.; Viklund, J.; De Milito, A.; Hasmim, M.; Andersson, M.; Amaravadi, R.K.; et al. Inhibition of Vps34 reprograms cold into hot inflamed tumors and improves anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wu, X.; Qian, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J. PIK3C3 regulates the expansion of liver CSCs and PIK3C3 inhibition counteracts liver cancer stem cell activity induced by PI3K inhibitor. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.Y.; Anand, S.V.; Tangella, K.; Ramkumar, D.; Saif, T.A. Isolation of Primary Human Colon Tumor Cells from Surgical Tissues and Culturing Them Directly on Soft Elastic Substrates for Traction Cytometry. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, e52532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fatehullah, A.; Tan, S.H.; Barker, N. Organoids as an in vitro model of human development and disease. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, R.; Kumar, B.; Pan, K.; Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B. HDAC-4 regulates claudin-2 expression in EGFR-ERK1/2 dependent manner to regulate colonic epithelial cell differentiation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 87718–87736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, R.; Chaturvedi, R.; Olivares-Villagomez, D.; Habib, T.; Asim, M.; Shivesh, P.; Polk, D.B.; Wilson, K.T.; Washington, M.K.; Van Kaer, L.; et al. Targeted colonic claudin-2 expression renders resistance to epithelial injury, induces immune suppression, and protects from colitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 1340–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Ro, E.J.; Yoon, J.S.; Mizutani, T.; Kang, D.W.; Park, J.C.; Il Kim, T.; Clevers, H.; Choi, K.Y. 5-FU promotes stemness of colorectal cancer via p53-mediated WNT/beta-catenin pathway activation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaizuka, T.; Morishita, H.; Hama, Y.; Tsukamoto, S.; Matsui, T.; Toyota, Y.; Kodama, A.; Ishihara, T.; Mizushima, T.; Mizushima, N. An Autophagic Flux Probe that Releases an Internal Control. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.V.; Vanner, R.; Dirks, P.; Eaves, C.J. Cancer stem cells: An evolving concept. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, B.; Blanpain, C. Unravelling cancer stem cell potential. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, M.H.; Karasic, T.B.; Vasilevskaya, I.; Redlinger, M.; Loaiza-Bonilla, A.; Teitelbaum, U.R.; Giantonio, B.J.; Damjanov, N.; Reiss, K.A.; Rosen, M.A.; et al. Phase II trial of the autophagy inhibitor hydroxychloroquine with FOLFOX and bevacizumab in front line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. S15), 3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Deng, L.; Wang, H. Combination of an Autophagy Inducer and an Autophagy Inhibitor: A Smarter Strategy Emerging in Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronan, B.; Flamand, O.; Vescovi, L.; Dureuil, C.; Durand, L.; Fassy, F.; Bachelot, M.F.; Lamberton, A.; Mathieu, M.; Bertrand, T.; et al. A highly potent and selective Vps34 inhibitor alters vesicle trafficking and autophagy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, G.; Birsen, R.; Cazelles, C.; Belhadj, M.; Cantero-Aguilar, L.; Kosmider, O.; Fontenay, M.; Azar, N.; Mayeux, P.; Chapuis, N.; et al. Antileukemic activity of the VPS34-IN1 inhibitor in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Boyle, J.W.; Ko, C.N.; Zeng, W.; Wong, V.K.W.; Wan, J.B.; Chan, P.W.H.; Ma, D.L.; Leung, C.H. Aurone derivatives as Vps34 inhibitors that modulate autophagy. Acta Pharm Sin. B 2019, 9, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, A.; Harrington, E.; Cornella-Taracido, I.; Furet, P.; Knapp, M.S.; Glick, M.; Triantafellow, E.; Dowdle, W.E.; Wiedershain, D.; Maniara, W.; et al. Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitors of VPS34 Provide Chemical Tools to Modulate Autophagy in Vivo. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schatoff, E.M.; Leach, B.I.; Dow, L.E. Wnt Signaling and Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2017, 13, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, M.J.; de los Santos, R.; Albert, I.N.; Rubinfeld, B.; Polakis, P. Downregulation of beta-catenin by human Axin and its association with the APC tumor suppressor, beta-catenin and GSK3 beta. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aberle, H.; Bauer, A.; Stappert, J.; Kispert, A.; Kemler, R. Beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 3797–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lade, A.G.; Monga, S.P. Beta-catenin signaling in hepatic development and progenitors: Which way does the WNT blow? Dev. Dyn. 2011, 240, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, B.T.; Tamai, K.; He, X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schepers, A.; Clevers, H. Wnt signaling, stem cells, and cancer of the gastrointestinal tract. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a007989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.; Ahmed, M.; Lorenzi, F.; Nateri, A.S. Spheroid-Formation (Colonosphere) Assay for in Vitro Assessment and Expansion of Stem Cells in Colon Cancer. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2016, 12, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Ginestier, C.; Iovino, F.; Wicinski, J.; Cervera, N.; Finetti, P.; Hur, M.H.; Diebel, M.E.; Monville, F.; Dutcher, J.; et al. Breast cancer cell lines contain functional cancer stem cells with metastatic capacity and a distinct molecular signature. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Ramena, G.; Elble, R.C. The role of cancer stem cells in relapse of solid tumors. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2012, 4, 1528–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, Z.; Adams, J.J.; Blazer, L.L.; Gakhal, A.K.; Jarvik, N.; Steinhart, Z.; Robitaille, M.; Mascall, K.; Pan, J.; Angers, S.; et al. A synthetic anti-Frizzled antibody engineered for broadened specificity exhibits enhanced anti-tumor properties. MAbs 2018, 10, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takebe, N.; Miele, L.; Harris, P.J.; Jeong, W.; Bando, H.; Kahn, M.; Yang, S.X.; Ivy, S.P. Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.M.; Ryter, S.W.; Levine, B. Autophagy in human health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Pietrocola, F.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Amaravadi, R.K.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Cecconi, F.; Codogno, P.; Debnath, J.; Gewirtz, D.A.; Karantza, V.; et al. Autophagy in malignant transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 856–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avalos, Y.; Canales, J.; Bravo-Sagua, R.; Criollo, A.; Lavandero, S.; Quest, A.F. Tumor suppression and promotion by autophagy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 603980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; White, E. Role of autophagy in cancer: Management of metabolic stress. Autophagy 2007, 3, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.G.; Macleod, K.F. Autophagy, cancer stem cells and drug resistance. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Mathew, R.; Fan, J.; Strohecker, A.M.; Karsli-Uzunbas, G.; Kamphorst, J.J.; Chen, G.; Lemons, J.M.; Karantza, V.; et al. Activated Ras requires autophagy to maintain oxidative metabolism and tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiffry, J.; Thavornwatanayong, T.; Rao, D.; Fogel, E.J.; Saytoo, D.; Nahata, R.; Guzik, H.; Chaudhary, I.; Augustine, T.; Goel, S.; et al. Oncolytic Reovirus (pelareorep) Induces Autophagy in KRAS-mutated Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.; Cacheux, W.; Bara, M.A.; L’Hermitte, A.; Lepage, P.; Fraudeau, M.; Trentesaux, C.; Lemarchand, J.; Durand, A.; Crain, A.M.; et al. Intestinal inhibition of Atg7 prevents tumour initiation through a microbiome-influenced immune response and suppresses tumour growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Hernandez, M.; Arias, A.; Martinez-Garcia, D.; Perez-Tomas, R.; Quesada, R.; Soto-Cerrato, V. Targeting Autophagy for Cancer Treatment and Tumor Chemosensitization. Cancers 2019, 11, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amaravadi, R.K.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Yin, X.M.; Weiss, W.A.; Takebe, N.; Timmer, W.; DiPaola, R.S.; Lotze, M.T.; White, E. Principles and current strategies for targeting autophagy for cancer treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, M.R.; Ye, X.; Supko, J.G.; Desideri, S.; Grossman, S.A.; Brem, S.; Mikkelson, T.; Wang, D.; Chang, Y.C.; Hu, J.; et al. A phase I/II trial of hydroxychloroquine in conjunction with radiation therapy and concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquier, B. SAR405, a PIK3C3/Vps34 inhibitor that prevents autophagy and synergizes with MTOR inhibition in tumor cells. Autophagy 2015, 11, 725–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rennoll, S.; Yochum, G. Regulation of MYC gene expression by aberrant Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 29–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhawan, P.; Ahmad, R.; Srivastava, A.S.; Singh, A.B. Cancer stem cells and colorectal cancer: An overview. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1592–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, K.; Moroishi, T.; de Jong, P.R.; Krawczyk, M.; Grebbin, B.M.; Luo, H.; Xu, R.H.; Golob-Schwarzl, N.; Schweiger, C.; Wang, K.; et al. YAP-IL-6ST autoregulatory loop activated on APC loss controls colonic tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petherick, K.J.; Williams, A.C.; Lane, J.D.; Ordonez-Moran, P.; Huelsken, J.; Collard, T.J.; Smartt, H.J.; Batson, J.; Malik, K.; Paraskeva, C.; et al. Autolysosomal beta-catenin degradation regulates Wnt-autophagy-p62 crosstalk. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nager, M.; Sallan, M.C.; Visa, A.; Pushparaj, C.; Santacana, M.; Macia, A.; Yeramian, A.; Canti, C.; Herreros, J. Inhibition of WNT-CTNNB1 signaling upregulates SQSTM1 and sensitizes glioblastoma cells to autophagy blockers. Autophagy 2018, 14, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, B.; Ahmad, R.; Sharma, S.; Gowrikumar, S.; Primeaux, M.; Rana, S.; Natarajan, A.; Oupicky, D.; Hopkins, C.R.; Dhawan, P.; et al. PIK3C3 Inhibition Promotes Sensitivity to Colon Cancer Therapy by Inhibiting Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092168
Kumar B, Ahmad R, Sharma S, Gowrikumar S, Primeaux M, Rana S, Natarajan A, Oupicky D, Hopkins CR, Dhawan P, et al. PIK3C3 Inhibition Promotes Sensitivity to Colon Cancer Therapy by Inhibiting Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers. 2021; 13(9):2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092168
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Balawant, Rizwan Ahmad, Swagat Sharma, Saiprasad Gowrikumar, Mark Primeaux, Sandeep Rana, Amarnath Natarajan, David Oupicky, Corey R. Hopkins, Punita Dhawan, and et al. 2021. "PIK3C3 Inhibition Promotes Sensitivity to Colon Cancer Therapy by Inhibiting Cancer Stem Cells" Cancers 13, no. 9: 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092168
APA StyleKumar, B., Ahmad, R., Sharma, S., Gowrikumar, S., Primeaux, M., Rana, S., Natarajan, A., Oupicky, D., Hopkins, C. R., Dhawan, P., & Singh, A. B. (2021). PIK3C3 Inhibition Promotes Sensitivity to Colon Cancer Therapy by Inhibiting Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers, 13(9), 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092168