The Prognostic Value of the Circulating Tumor Cell-Based Four mRNA Scoring System: A New Non-Invasive Setting for the Management of Bladder Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
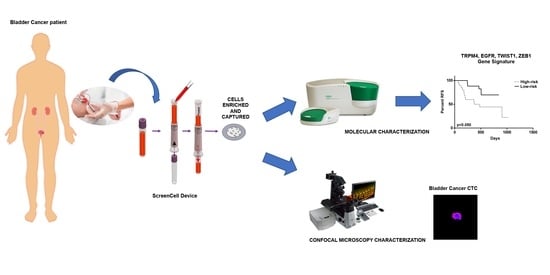
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of Previously Published Biomarker Candidates
2.2. Study Patients
2.3. Patient Samples
2.4. RNA Extraction
2.5. Reverse Transcription
2.6. Digital Droplet PCR (ddPCR)
2.7. Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy
2.8. InCTC Assay
2.9. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis
2.10. Prognostic Signature
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Previously Described BC Biomarker Candidates
3.2. Isolation and Gene Expression Profiling of CTCs from BC Patients
3.3. Biomarkers Predictive of Recurrence
3.4. Identification of a Four-mRNA Based Signature
3.5. The Risk Score Based on Four-mRNA Signature Predicted the RFS of BC Patients: Validation of the Prognostic Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Svatek, R.S.; Hollenbeck, B.K.; Holmäng, S.; Lee, R.; Kim, S.P.; Stenzl, A.; Lotan, Y. The Economics of Bladder Cancer: Costs and Considerations of Caring for This Disease. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN Sources and Methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jordan, B.; Meeks, J.J. T1 Bladder Cancer: Current Considerations for Diagnosis and Management. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2019, 16, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Wu, C.; Cheng, F. Traditional Classification and Novel Subtyping Systems for Bladder Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedegaard, J.; Lamy, P.; Nordentoft, I.; Algaba, F.; Høyer, S.; Ulhøi, B.P.; Vang, S.; Reinert, T.; Hermann, G.G.; Mogensen, K.; et al. Comprehensive Transcriptional Analysis of Early-Stage Urothelial Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, A.G.; Groeneveld, C.S.; Jordan, B.; Lin, X.; McLaughlin, K.A.; Das, A.; Fall, L.A.; Fantini, D.; Taxter, T.J.; Mogil, L.S.; et al. Identification of Differential Tumor Subtypes of T1 Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Roh, Y.-G.; Park, K.; Kang, T.-H.; Kim, W.-J.; Lee, J.-S.; Leem, S.-H.; Chu, I.-S. Expression Signature Defined by FOXM1–CCNB1 Activation Predicts Disease Recurrence in Non–Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warrick, J.I.; Sjödahl, G.; Kaag, M.; Raman, J.D.; Merrill, S.; Shuman, L.; Chen, G.; Walter, V.; DeGraff, D.J. Intratumoral Heterogeneity of Bladder Cancer by Molecular Subtypes and Histologic Variants. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, Y.-G.; Mun, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K.; Park, W.Y.; Jeong, M.-S.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, W.-T.; Choi, Y.H.; Chu, I.-S.; Leem, S.-H. Fanconi Anemia Pathway Activation by FOXM1 Is Critical to Bladder Cancer Recurrence and Anticancer Drug Resistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, J.-Y.; Baek, S.-W.; Park, W.Y.; Kim, W.-T.; Kim, S.-K.; Roh, Y.-G.; Jeong, M.-S.; Yang, G.-E.; Lee, J.-H.; Chung, J.W.; et al. E2F1 Promotes Progression of Bladder Cancer by Modulating RAD54L Involved in Homologous Recombination Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConkey, D.J. Molecular Biology of Bladder Cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 35, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Shen, L.; Luo, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells: Biology and Clinical Significance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Yang, H.; Shin, Y.K. Relevance of Circulating Tumor Cells as Predictive Markers for Cancer Incidence and Relapse. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, A.; Campo, D.; Porras, T.B.; Kaur, P.; Forte, V.A.; Tripathy, D.; Lu, J.; Kang, I.; Press, M.F.; Jeong, Y.J.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Transcriptomics as Biopsy Surrogates in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2882–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zheng, Y. Circulating Tumor Cell Count: A Reliable Biomarker for Treatment Selection in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xiang, X.; Han, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Yang, L.; Guo, S.; Soo, R.; et al. Blood-Based Liquid Biopsy: Insights into Early Detection and Clinical Management of Lung Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2022, 524, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of Circulating Tumor Cells to Tumor Response, Progression-Free Survival, and Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Mathiot, C.; Delaloge, S.; Brain, E.; Giachetti, S.; de Cremoux, P.; Marty, M.; Pierga, J.-Y. Single Circulating Tumor Cell Detection and Overall Survival in Nonmetastatic Breast Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harouaka, R.; Kang, Z.; Zheng, S.-Y.; Cao, L. Circulating Tumor Cells: Advances in Isolation and Analysis, and Challenges for Clinical Applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Bono, J.S.; Scher, H.I.; Montgomery, R.B.; Parker, C.; Miller, M.C.; Tissing, H.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.W.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Raghavan, D. Circulating Tumor Cells Predict Survival Benefit from Treatment in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, W.; Deng, Q.; Tang, S.; Wang, P.; Xu, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, M. The Prognostic and Diagnostic Value of Circulating Tumor Cells in Bladder Cancer and Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of 30 Published Studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59527–59538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Du, H.; Li, G. Significant Prognostic Value of Circulating Tumor Cells in Esophageal Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15815–15826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolazzo, C.; Busetto, G.M.; Gradilone, A.; Sperduti, I.; del Giudice, F.; Loreni, F.; Cortesi, E.; de Berardinis, E.; Gazzaniga, P.; Raimondi, C. Circulating Tumor Cells Identify Patients with Super-High-Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Updated Outcome Analysis of a Prospective Single-Center Trial. Oncologist 2019, 24, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, P.; de Berardinis, E.; Raimondi, C.; Gradilone, A.; Busetto, G.M.; de Falco, E.; Nicolazzo, C.; Giovannone, R.; Gentile, V.; Cortesi, E.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells Detection Has Independent Prognostic Impact in High-Risk Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1978–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haga, N.; Tsubouchi, K.; Maruta, H.; Koguchi, T.; Hoshi, S.; Ogawa, S.; Akaihata, H.; Hata, J.; Kojima, Y. Increase in Circulating Tumor Cells in Invasive Bladder Cancer After Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 4299–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, N.; Onagi, A.; Koguchi, T.; Hoshi, S.; Ogawa, S.; Akaihata, H.; Hata, J.; Hiraki, H.; Honda, R.; Tanji, R.; et al. Perioperative Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Radical or Partial Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engilbertsson, H.; Aaltonen, K.E.; Björnsson, S.; Kristmundsson, T.; Patschan, O.; Rydén, L.; Gudjonsson, S. Transurethral Bladder Tumor Resection Can Cause Seeding of Cancer Cells into the Bloodstream. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumura, H.; Satoh, T.; Ishiyama, H.; Tabata, K.; Takenaka, K.; Sekiguchi, A.; Nakamura, M.; Kitano, M.; Hayakawa, K.; Iwamura, M. Perioperative Search for Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients Undergoing Prostate Brachytherapy for Clinically Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maggi, F.; Amantini, C.; Nabissi, M.; Marinelli, O.; Santoni, G.; Morelli, M.B. Typical and Atypical Circulating Tumour Cells in Bladder Cancer. Why Improve Our Knowledge? Clin. Oncol. 2019, 2, 1008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Tytell, J.D.; Ingber, D.E. Mechanotransduction at a Distance: Mechanically Coupling the Extracellular Matrix with the Nucleus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F.; Sun, J.; Jia, Q.; Zhou, W.; Singh, R.; Khanna, N.; Belmont, A.S.; Wang, N. Transcription Upregulation via Force-Induced Direct Stretching of Chromatin. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buxboim, A.; Swift, J.; Irianto, J.; Spinler, K.R.; Dingal, P.C.D.P.; Athirasala, A.; Kao, Y.-R.C.; Cho, S.; Harada, T.; Shin, J.-W.; et al. Matrix Elasticity Regulates Lamin-A,C Phosphorylation and Turnover with Feedback to Actomyosin. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinac, B. The Ion Channels to Cytoskeleton Connection as Potential Mechanism of Mechanosensitivity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Formigli, L.; Meacci, E.; Sassoli, C.; Squecco, R.; Nosi, D.; Chellini, F.; Naro, F.; Francini, F.; Zecchi-Orlandini, S. Cytoskeleton/Stretch-Activated Ion Channel Interaction Regulates Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 211, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Chien, S.; Lv, Y. Suspension State Promotes Metastasis of Breast Cancer Cells by Up-Regulating Cyclooxygenase-2. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3722–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, T.; Zhang, W.; Guo, H.; Pan, X.; Chen, X.; He, Q.; Yang, B.; Ding, L. The Regulatory and Modulatory Roles of TRP Family Channels in Malignant Tumors and Relevant Therapeutic Strategies. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 12, 1761–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amantini, C.; Morelli, M.B.; Nabissi, M.; Piva, F.; Marinelli, O.; Maggi, F.; Bianchi, F.; Bittoni, A.; Berardi, R.; Giampieri, R.; et al. Expression Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients: Biomarkers Predicting Overall Survival. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolazzo, C.; Colangelo, L.; Corsi, A.; Carpino, G.; Gradilone, A.; Sonato, C.; Raimondi, C.; Gaudio, E.; Gazzaniga, P.; Gianni, W. Liquid Biopsy in Rare Cancers: Lessons from Hemangiopericytoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2018, 2018, 9718585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Msaouel, P.; Koutsilieris, M. Diagnostic Value of Circulating Tumor Cell Detection in Bladder and Urothelial Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING V11: Protein–Protein Association Networks with Increased Coverage, Supporting Functional Discovery in Genome-Wide Experimental Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, Q.; Chu, X.; Cheung, J.Y.; Conrad, K.; Stahl, R.; Barber, D.L.; Mignery, G.; Miller, B.A. Erythropoietin-Modulated Calcium Influx through TRPC2 Is Mediated by Phospholipase Cgamma and IP3R. Am. J. Physiol.—Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C1667–C1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patterson, R.L.; van Rossum, D.B.; Nikolaidis, N.; Gill, D.L.; Snyder, S.H. Phospholipase C-γ: Diverse Roles in Receptor-Mediated Calcium Signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Shi, Z. Phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCG1) Overexpression Is Associated with Tumor Growth and Poor Survival in IDH Wild-Type Lower-Grade Gliomas in Adult Patients. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.B.; Amantini, C.; Rossi de Vermandois, J.A.; Gubbiotti, M.; Giannantoni, A.; Mearini, E.; Maggi, F.; Nabissi, M.; Marinelli, O.; Santoni, M.; et al. Correlation between High PD-L1 and EMT/Invasive Genes Expression and Reduced Recurrence-Free Survival in Blood-Circulating Tumor Cells from Patients with Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-C.; Chen, K.-C.; Peng, R.Y.; Su, C.-H.; Hsieh-Li, H.M. Human Urinary Bladder Cancer T24 Cells Are Susceptible to the Antrodia Camphorata Extracts. Cancer Lett. 2006, 243, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, Y.; Harraz, A.M. A Review Comparing Experience and Results with Bipolar Versus Monopolar Resection for Treatment of Bladder Tumors. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2016, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Xing, J.; Yu, W.; Jin, J. Impact of Preoperative Diagnostic TURBT on Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Pathological High-Grade, Stage T3/T4 Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89228–89235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zehnder, P.; Studer, U.E.; Skinner, E.C.; Thalmann, G.N.; Miranda, G.; Roth, B.; Cai, J.; Birkhäuser, F.D.; Mitra, A.P.; Burkhard, F.C.; et al. Unaltered Oncological Outcomes of Radical Cystectomy with Extended Lymphadenectomy over Three Decades. BJU Int. 2013, 112, E51–E58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Kessel, K.E.M.; van der Keur, K.A.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Algaba, F.; Welvaart, N.Y.C.; Beukers, W.; Segersten, U.; Keck, B.; Maurer, T.; Simic, T.; et al. Molecular Markers Increase Precision of the European Association of Urology Non–Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Progression Risk Groups. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soria, F.; Krabbe, L.-M.; Todenhöfer, T.; Dobruch, J.; Mitra, A.P.; Inman, B.A.; Gust, K.M.; Lotan, Y.; Shariat, S.F. Molecular Markers in Bladder Cancer. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flaig, T.W.; Wilson, S.; van Bokhoven, A.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Wolfe, P.; Maroni, P.; Genova, E.E.; Morales, D.; Lucia, M.S. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Metastatic and Clinically Localized Urothelial Carcinoma. Urology 2011, 78, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riethdorf, S.; O’Flaherty, L.; Hille, C.; Pantel, K. Clinical Applications of the CellSearch Platform in Cancer Patients. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 125, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, M.; Chun, F.K.; Dahlem, R.; Soave, A.; Minner, S.; Hansen, J.; Stoupiec, M.; Coith, C.; Kluth, L.A.; Ahyai, S.A.; et al. Prognostic Role and HER2 Expression of Circulating Tumor Cells in Peripheral Blood of Patients Prior to Radical Cystectomy: A Prospective Study. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poste, G.; Fidler, I.J. The Pathogenesis of Cancer Metastasis. Nature 1980, 283, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sikic, D.; Eckstein, M.; Weyerer, V.; Kubon, J.; Breyer, J.; Roghmann, F.; Kunath, F.; Keck, B.; Erben, P.; Hartmann, A.; et al. High Expression of ERBB2 Is an Independent Risk Factor for Reduced Recurrence-Free Survival in Patients with Stage T1 Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2022, 40, 63.e9–63.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyelu, T.T.; Moya-Garcia, A.A.; Orengo, C. Exploiting Protein Family and Protein Network Data to Identify Novel Drug Targets for Bladder Cancer. Oncotarget 2022, 13, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masilamani, A.P.; Fischer, A.; Schultze-Seemann, S.; Kuckuck, I.; Wolf, I.; Dressler, F.F.; Gratzke, C.; Wolf, P. Epidermal Growth Factor Based Targeted Toxin for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 3741–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, G.G.; Önalan, E.E.; Kuloğlu, T.; Aydoğ, G.; Keleş, İ.; Tonyali, Ş.; Ceylan, C. Potential Role of Melastatin-Related Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Subfamily M Gene Expression in the Pathogenesis of Urinary Bladder Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 5235–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Miao, B.; Dymerska, D.; Kuswik, M.; Bueno-Martínez, E.; Sanoguera-Miralles, L.; Velasco, E.A.; Paramasivam, N.; Schlesner, M.; Kumar, A.; et al. Germline Variants of CYBA and TRPM4 Predispose to Familial Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verigos, J.; Kordias, D.; Papadaki, S.; Magklara, A. Transcriptional Profiling of Tumorspheres Reveals TRPM4 as a Novel Stemness Regulator in Breast Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgström, A.; Peinelt, C.; Stokłosa, P. TRPM4 in Cancer—A New Potential Drug Target. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Rahman, M.A.; Chen, Z.G.; Shin, D.M. Multiple Biological Functions of Twist1 in Various Cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20380–20393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, D.; Li, X.; Wong, Y.-C.; Xin, D.; Guan, X.-Y.; Chua, C.W.; Leung, S.C.L.; Na, Y.; Wang, X. Significance of TWIST Expression and Its Association with E-Cadherin in Bladder Cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fondrevelle, M.E.; Kantelip, B.; Reiter, R.E.; Chopin, D.K.; Thiery, J.P.; Monnien, F.; Bittard, H.; Wallerand, H. The Expression of Twist Has an Impact on Survival in Human Bladder Cancer and Is Influenced by the Smoking Status. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2009, 27, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Mao, X.; Wang, H.; Su, G.; Mo, C.; Cao, K.; Qiu, S. Vasculogenic Mimicry in Bladder Cancer and Its Association with the Aberrant Expression of ZEB1. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5193–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Y.; Zu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; He, W.; Qi, L. The VIM-AS1/MiR-655/ZEB1 Axis Modulates Bladder Cancer Cell Metastasis by Regulating Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinkova, L.; Nikolaieva, N.; Smolkova, B.; Ciernikova, S.; Kajo, K.; Bella, V.; Kajabova, V.H.; Kosnacova, H.; Minarik, G.; Fridrichova, I. MiR-205-5p Downregulation and ZEB1 Upregulation Characterize the Disseminated Tumor Cells in Patients with Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-M.; Yoo, J.; Moon, H.W.; Hur, K.J.; Choi, J.B.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, J.Y.; Ha, U.-S. Distinct Mutation Profiles between Primary Bladder Cancer and Circulating Tumor Cells Warrant the Use of Circulating Tumors Cells as Cellular Resource for Mutation Follow-Up. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Variable | Patients |
|---|---|
| All, n (%) | 60 (100.0%) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 52 (86.7%) |
| Female | 8 (13.3%) |
| Age, years | |
| Range | 47–93 |
| Median | 74 |
| Tumor grade, n (%) | |
| Low | 45 (75.0%) |
| High | 15 (25.0%) |
| Tumor stage, n (%) | |
| Tx | 3 (5.0%) |
| Tis | 4 (6.7%) |
| Ta | 37 (61.75) |
| T1 | 8 (13.3%) |
| T2 | 4 (6.7%) |
| T3 | 3 (5.05) |
| T4 | 1 (1.65) |
| Histology | |
| Papillary | 34 (56.6%) |
| No papillary | 26 (43.4%) |
| CTC status | |
| Negative | 3 (5.6%) |
| Positive | 50 (94.4%) |
| Local Recurrence | |
| No | 35 (58.3%) |
| Yes | 25 (41.7%) |
| Infiltrated nodes | |
| No | 60 (100%) |
| Yes | 0 (0%) |
| Metastasis | |
| No | 60 (100%) |
| Yes | 0 (0%) |
| Diabetes type II | |
| Yes | 18 (30%) |
| No | 42 (70%) |
| Hypertension | |
| Yes | 29 (48.3%) |
| No | 31 (51.7%) |
| Markers | Biopsy n (%) | CTC n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIRC5 | 0 (0.0) | 32 (64.0) | * p = 0.0008 |
| CDH11 | 2 (25.0) | 38 (76.0) | * p = 0.0082 |
| EGFR | 3 (37.5) | 38 (76.0) | * p = 0.0082 |
| EPCAM | 8 (100.0) | 46 (92.0) | NS, p > 0.9999 |
| KRT18 | 7 (87.5) | 40 (80.0) | NS, p > 0.9999 |
| SPP1 | 2(25.0) | 40 (80.0) | * p = 0.0001 |
| TNC | 2 (25.0) | 39 (78.0) | * p = 0.0057 |
| TRPC1 | 4 (50.0) | 41 (82.0) | NS, p = 0.0660 |
| TRPC6 | 4 (50.0) | 42 (84.0) | * p = 0.0489 |
| TRPV6 | 0 (0.0) | 45 (90.0) | * p < 0.0001 |
| TRPM4 | 3 (37.5) | 42 (84.0) | * p = 0.0105 |
| TWIST1 | 1 (12.5) | 32 (64.0) | * p = 0.0161 |
| VEGFA | 4 (50.0) | 42 (84.0) | *p = 0.0489 |
| VIM | 7 (87.5) | 36 (72.0) | NS, p = 0.6660 |
| ZEB1 | 2 (25.0) | 42 (84.0) | * p = 0.0016 |
| Markers | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| BIRC5 | 2.60 (3.36 × 10−3–2010) | NS, 0.778 |
| EGFR | 20.120 (1.01–419.4) | 0.050 * |
| KRT18 | 0.049 (5.28 × 10−04–4.58) | NS, 0.193 |
| SPP1 | 8.46 (0.60–118.2) | NS, 0.113 |
| TNC | 24.49 (0.13–4681) | NS, 0.233 |
| TRPM4 | 91.33 (1.02–8944) | 0.050 * |
| TRPV6 | 0.28 (7.35 × 10−04–105.3) | NS, 0.673 |
| TWIST1 | 212.89 (5.43–8348) | 0.005 * |
| VEGFA | 17.83 (0.78–406.4) | NS, 0.071 |
| VIM | 5.17 × 10−3 (1.42 × 10−05–1.88) | NS, 0.080 |
| ZEB1 | 33.42 (1.25–891.3) | 0.036 * |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
| Grade | HG/LG | 1.46 (0.40–5.32) | 0.566 | 2.03 (0.42–9.77) | 0.375 |
| Stage | Ta-Tis-T1/T2–4 | 2.56 (0.33–20.1) | 0.371 | 2.08 (0.16–27.64) | 0.579 |
| Diabetes type II | Yes/No | 1.29 (0.45–3.74) | 0.824 | 0.75 (0.23–2.42) | 0.630 |
| Hypertension | Yes/No | 1.97 (0.54–7.18) | 0.301 | 3.13 (0.72–13.53) | 0.127 |
| Risk score | High/Low | 1.35 (1.03–1.76) | 0.027 * | 1.35 (1.03–1.77) | 0.030 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amantini, C.; Maggi, F.; Rossi de Vermandois, J.A.; Gubbiotti, M.; Giannantoni, A.; Mearini, E.; Nabissi, M.; Tomassoni, D.; Santoni, G.; Morelli, M.B. The Prognostic Value of the Circulating Tumor Cell-Based Four mRNA Scoring System: A New Non-Invasive Setting for the Management of Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133118
Amantini C, Maggi F, Rossi de Vermandois JA, Gubbiotti M, Giannantoni A, Mearini E, Nabissi M, Tomassoni D, Santoni G, Morelli MB. The Prognostic Value of the Circulating Tumor Cell-Based Four mRNA Scoring System: A New Non-Invasive Setting for the Management of Bladder Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(13):3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133118
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmantini, Consuelo, Federica Maggi, Jacopo Adolfo Rossi de Vermandois, Marilena Gubbiotti, Antonella Giannantoni, Ettore Mearini, Massimo Nabissi, Daniele Tomassoni, Giorgio Santoni, and Maria Beatrice Morelli. 2022. "The Prognostic Value of the Circulating Tumor Cell-Based Four mRNA Scoring System: A New Non-Invasive Setting for the Management of Bladder Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 13: 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133118
APA StyleAmantini, C., Maggi, F., Rossi de Vermandois, J. A., Gubbiotti, M., Giannantoni, A., Mearini, E., Nabissi, M., Tomassoni, D., Santoni, G., & Morelli, M. B. (2022). The Prognostic Value of the Circulating Tumor Cell-Based Four mRNA Scoring System: A New Non-Invasive Setting for the Management of Bladder Cancer. Cancers, 14(13), 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133118