Defining Optimal Conditions for Tumor Extracellular Vesicle DNA Extraction for Mutation Profiling
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
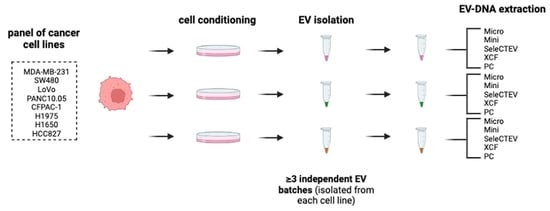
2.1. Preparation of Conditioned Cell Culture Media—Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.2. Plasma Samples and Ethics Statement
2.3. Extracellular Vesicle Isolation and Characterization
2.3.1. EV Isolation by Ultracentrifugation
2.3.2. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.3.3. Protein Quantification
2.3.4. Western Blotting
2.3.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.4. Mass Spectrometry
2.5. DNA Extraction
2.6. DNA Quantification and Quality Analysis
2.6.1. Qubit Fluorometer 3.0
2.6.2. Fragment Analyzer
2.7. DNA Mutational Analysis
2.7.1. PNA-Q-PCR (TaqMan) for Mutation Testing
2.7.2. NGS for Mutation Testing
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of EVs Isolated from Conditioned Media
3.2. Preparation of EV-DNA for Mutational Analyses
3.2.1. Comparison of EV-DNA Extraction Methods
3.2.2. Assessment of KRAS and EGFR Mutations in EV-DNA and gDNA by TaqMan
3.2.3. Mutation Detection in EV-DNA by NGS
3.3. Plasma EV-DNA Mutation Detection by TaqMan
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doyle, L.; Wang, M. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Cornils, K.; Speiseder, T.; Badbaran, A.; Reimer, R.; Indenbirken, D.; Grundhoff, A.; Brunswig-Spickenheier, B.; Alawi, M.; Lange, C. Indication of Horizontal DNA Gene Transfer by Extracellular Vesicles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Shao, Y.; Gao, L.; Yin, H.; Cui, C.; et al. DNA in serum extracellular vesicles is stable under different storage conditions. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Visakorpi, T.; Escobedo-Lucea, C.; Siljander, P.; Ayuso-Sacido, Á.; Yliperttula, M. Different gDNA content in the subpopulations of prostate cancer extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes. Prostate 2014, 74, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Okada, R.; Nagao, K.; Kawamata, Y.; Hanyu, A.; Yoshimoto, S.; Takasugi, M.; Watanabe, S.; Kanemaki, M.T.; Obuse, C.; et al. Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torralba, D.; Baixauli, F.; Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Fernández-Delgado, I.; Latorre-Pellicer, A.; Acín-Pérez, R.; Martín-Cófreces, N.B.; Jaso-Tamame, Á.L.; Iborra, S.; Jorge, I.; et al. Priming of dendritic cells by DNA-containing extracellular vesicles from activated T cells through antigen-driven contacts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vagner, T.; Spinelli, C.; Minciacchi, V.R.; Balaj, L.; Zandian, M.; Conley, A.; Zijlstra, A.; Freeman, M.R.; Demichelis, F.; De, S.; et al. Large extracellular vesicles carry most of the tumour DNA circulating in prostate cancer patient plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1505403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahlert, C.; Melo, S.; Protopopov, A.; Tang, J.; Seth, S.; Koch, M.; Zhang, J.; Weitz, J.; Chin, L.; Futreal, A.; et al. Identification of Double-stranded Genomic DNA Spanning All Chromosomes with Mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the Serum Exosomes of Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3869–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thakur, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Becker, A.; Matei, I.; Huang, Y.; Costa-Silva, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Brazier, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: A novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allenson, K.; Castillo, J.; Lucas, F.A.S.; Scelo, G.; Kim, D.U.; Bernard, V.; Davis, G.; Kumar, T.; Katz, M.; Overman, M.J.; et al. High prevalence of mutantKRAS in circulating exosome-derived DNA from early-stage pancreatic cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Che, S.P.Y.; Kurywchak, P.; Tavormina, J.L.; Gansmo, L.B.; de Sampaio, P.C.; Tachezy, M.; Bockhorn, M.; Gebauer, F.; Haltom, A.R.; et al. Detection of mutant KRAS and TP53 DNA in circulating exosomes from healthy individuals and patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, G.G.; García, G.G.; Soto, J.Z.; Medina, A.I.; Rotzinger-Rodríguez, M.; Aguilar, G.A.C.; Pacheco, C.P.L.; Aguayo, Á.; Aguilar-Hernandez, M.M. Analysis of RNA yield in extracellular vesicles isolated by membrane affinity column and differential ultracentrifugation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, E.N.; de Souza Fonseca, M.A.; Dezem, F.S.; Lester, J.; Karlan, B.Y.; Noushmehr, H.; Lin, X.; Lawrenson, K. Optimizing exosomal RNA isolation for RNA-Seq analyses of archival sera specimens. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klump, J.; Phillipp, U.; Follo, M.; Eremin, A.; Lehmann, H.; Nestel, S.; von Bubnoff, N.; Nazarenko, I. Extracellular vesicles or free circulating DNA: Where to search for BRAF and cKIT mutations? Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, M.R.; Jiang, C.; Krzyzanowski, G.D.; Ryan, W.L. New evidence that a large proportion of human blood plasma cell-free DNA is localized in exosomes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svennerholm, K.; Rodsand, P.; Hellman, U.; Waldenström, A.; Lundholm, M.; Ahrén, D.; Biber, B.; Ronquist, G.; Haney, M. DNA Content in Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Porcine Coronary Venous Blood Directly after Myocardial Ischemic Preconditioning. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocco, D.; Bernardi, S.; Novelli, M.; Astrua, C.; Fava, P.; Zarovni, N.; Carpi, F.M.; Bianciardi, L.; Malavenda, O.; Quaglino, P.; et al. Isolation of extracellular vesicles improves the detection of mutant DNA from plasma of metastatic melanoma patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Han, Y.; Ren, H.; Chen, C.; He, D.; Zhou, L.; Eisner, G.M.; Asico, L.D.; Jose, P.A.; Zeng, C. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of donor genomic DNA to recipient cells is a novel mechanism for genetic influence between cells. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 5, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, M.; Johansson, C.; Xiao, F.; Stone, P.R.; James, J.L.; Chen, Q.; Cree, L.M.; Chamley, L.W. Antiphospholipid antibodies increase the levels of mitochondrial DNA in placental extracellular vesicles: Alarmin-g for preeclampsia. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 16556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Németh, A.; Orgovan, N.; Sódar, B.W.; Osteikoetxea, X.; Pálóczi, K.; Szabó-Taylor, K.; Vukman, K.V.; Kittel, Á.; Turiák, L.; Wiener, Z.; et al. Antibiotic-induced release of small extracellular vesicles (exosomes) with surface-associated DNA. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, A.; Villar-Prados, A.; Oliphint, P.A.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; De Hoff, P.; Morey, R.; Liu, J.; Roszik, J.; Clise-Dwyer, K.; et al. Mechanisms of nuclear content loading to exosomes. Sci Adv. 2019, 5, eaax8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montermini, L.; Meehan, B.; Garnier, D.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, T.H.; Guha, A.; Al-Nedawi, K.; Rak, J. Inhibition of oncogenic epidermal growth factor receptor kinase triggers release of exosome-like extracellular vesicles and impacts their phosphoprotein and DNA content. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24534–24546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maia, J.; Otake, A.H.; Poças, J.; Carvalho, A.S.; Beck, H.C.; Magalhães, A.; Matthiesen, R.; Moraes, M.C.S.; Costa-Silva, B. Transcriptome Reprogramming of CD11b+ Bone Marrow Cells by Pancreatic Cancer Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 592518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, N.; Marques, A.; Águas, H.; Bandarenka, H.; Martins, R.; Bodo, C.; Costa-Silva, B.; Fortunato, E. Label-Free Nanosensing Platform for Breast Cancer Exosome Profiling. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2073–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talman, V.; Teppo, J.; Pöhö, P.; Movahedi, P.; Vaikkinen, A.; Karhu, S.T.; Trošt, K.; Suvitaival, T.; Heikkonen, J.; Pahikkala, T.; et al. Molecular Atlas of Postnatal Mouse Heart Development. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e010378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Cao, M.; Casas, C.M.D.L.; Ariza, N.J.; Manzano, J.L.; Molina-Vila, M.; Soriano, V.; Puertolas, T.; Balada, A.; Soria, A.; Majem, M.; et al. Early evolution of BRAFV600 status in the blood of melanoma patients correlates with clinical outcome and identifies patients refractory to therapy. Melanoma Res. 2018, 28, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo-De-Las-Casas, C.; Jordana-Ariza, N.; Garzón-Ibañez, M.; Balada-Bel, A.; Bertrán-Alamillo, J.; Viteri-Ramírez, S.; Reguart, N.; Muñoz-Quintana, M.A.; Lianes-Barragan, P.; Camps, C.; et al. Large scale, prospective screening of EGFR mutations in the blood of advanced NSCLC patients to guide treatment decisions. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villatoro, S.; Mayo-De-Las-Casas, C.; Jordana-Ariza, N.; Viteri-Ramírez, S.; Garzón-Ibañez, M.; Moya-Horno, I.; García-Peláez, B.; González-Cao, M.; Malapelle, U.; Balada-Bel, A.; et al. Prospective detection of mutations in cerebrospinal fluid, pleural effusion, and ascites of advanced cancer patients to guide treatment decisions. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 2633–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoshino, A.; Kim, H.S.; Bojmar, L.; Gyan, K.E.; Cioffi, M.; Hernandez, J.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Rodrigues, G.; Molina, H.; Heissel, S.; et al. Extracellular vesicle and particle biomarkers define multiple human cancers. Cell 2020, 182, 1044–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horlitz, M.; Lucas, A.; Sprenger-Haussels, M. Optimized Quantification of Fragmented, Free Circulating DNA in Human Blood Plasma Using a Calibrated Duplex Real-Time PCR. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallagher, S.R. Quantitation of DNA and RNA with Absorption and Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2011, 56, A.1K.1–A.1K.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Chennakrishnaiah, S.; Audemard, E.; Montermini, L.; Meehan, B.; Rak, J. Oncogenic ras-driven cancer cell vesiculation leads to emission of double-stranded DNA capable of interacting with target cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 451, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehrich, B.M.; Liang, Y.; Fiandaca, M.S. Foetal bovine serum influence on in vitro extracellular vesicle analyses. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, F.A.S.; Allenson, K.; Bernard, V.; Castillo, J.; Kim, D.U.; Ellis, K.; Ehli, E.A.; Davies, G.E.; Petersen, J.L.; Li, D.; et al. Minimally invasive genomic and transcriptomic profiling of visceral cancers by next-generation sequencing of circulating exosomes. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 27, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.J.; Gray, W.D.; Hayek, S.S.; Ko, Y.-A.; Thomas, S.; Rooney, K.; Awad, M.; Roback, J.D.; Quyyumi, A.; Searles, C.D. Platelets confound the measurement of extracellular miRNA in archived plasma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, L.; Hong, C.-S.; Stolz, D.B.; Watkins, S.C.; Whiteside, T.L. Isolation of biologically-active exosomes from human plasma. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 411, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.H.; Yi, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Kroh, E.M.; Chien, J.W.; Eaton, K.D.; Goodman, M.T.; Tait, J.F.; Tewari, M.; Pritchard, C.C. Plasma Processing Conditions Substantially Influence Circulating microRNA Biomarker Levels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legras, A.; Barritault, M.; Tallet, A.; Fabre, E.; Guyard, A.; Rance, B.; Digan, W.; Pecuchet, N.; Giroux-Leprieur, E.; Julie, C.; et al. Validity of Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing in Routine Care for Identifying Clinically Relevant Molecular Profiles in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 20, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Extraction Method | Manufacturer | Number of Times Used in the Literature | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit | Qiagen | 3 | [7,10,11] |
| QIAamp DNA Micro Kit | Qiagen | 2 | [14,17] |
| Phenol–Chloroform | N/A | 2 | [5,6] |
| QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit | Qiagen | 1 | [18] |
| Qiagen Allprep DNA/RNA Mini Kit | Qiagen | 1 | [19] |
| QIAamp DNA Mini Kit | Qiagen | 1 | [12] |
| SeleCTEV Low Input DNA Enrichement Kit | Exosomics | 1 | [20] |
| TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit | Tiangen Biotech Co. Ltd. | 1 | [21] |
| Quick-gDNA Miniprep Kit | Zymo Research | 1 | [22] |
| Genomic DNA Mini Kit | Geneaid | 1 | [23] |
| XCF Exosomal DNA Isolation Kit | System Biosciences | 1 | [24] |
| Isopropyl alcohol precipitation | N/A | 1 | [25] |
| Proteinase K | Wako | 1 | [8] |
| EV-DNA Purification Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Cell-Line-Derived EVs | Micro | Mini | SeleCTEV | XCF | PC |
| KRAS | MDA-MB-231 | 2/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 |
| SW480 | 3/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | |
| LoVo | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | |
| PANC10.05 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 2/3 | |
| CFPAC-1 | 3/3 | 2/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 2/3 | |
| EGFR | H1975 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 |
| H1650 | 2/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 | |
| HCC827 | 2/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 | |
| Samples with detected mutations | 21/24 (87.5%) | 22/24 (91.7%) | 23/24 (95.8%) | 22/24 (91.7%) | 14/24 (58.3%) | |
| Method | Mini | Micro | SeleCTEV | XCF | PC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Exon | Mutation | Allelic fraction | ||||
| EGFR | 21 | c.2573T > G | 66% | 65% | 67% | 62% | N/A |
| 20 | c.2369C > T | 64% | 64% | 65% | 69% | N/A | |
| TP53 | 8 | c.818G > A | 98% | 97% | 97% | 96% | N/A |
| Method | Reads | Nucleotides | Average Read Length | Reads with Average Quality > 25 | Reads Mapped | Reads in Target Regions | Base Positions in Regions of Interest with UMI Coverage > 100× | Base Positions in Regions of Interest with UMI Coverage > 60× |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mini | 4023974 | 505992583 | 125.74 | 95.15% | 3980643 (98.2%) | 3557632 (89.37%) | 97.68% | 98.54% |
| Micro | 4034733 | 512374900 | 126.99 | 94.89% | 4023363 (99.72%) | 3332780 (82.84%) | 97.04% | 97.55% |
| SeleCTEV | 4194485 | 523511719 | 124.81 | 94.59% | 4183430 (99.74%) | 2398744 (57.34%) | 96.75% | 97.31% |
| XCF | 4875693 | 127.70 | 94.93 | 94.93% | 4868494 (99.85%) | 4568724 (93.84%) | 97.60% | 98.28% |
| PC | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Patient | Tumor Type | Gene | Position | Mutant Allelic Fraction % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Melanoma | BRAF | p.V600E | 0.74 ± 0.04 |
| #2 | Colorectal | KRAS | p.G12V | 20.33 ± 1.81 |
| #3 | Lung | KRAS | p.G12C | 4.65 ± 0.83 |
| #4 | Lung | KRAS | p.G12D | 4.84 ± 1.25 |
| #5 | Lung | KRAS | p.G12V | 0.39 ± 0.55 |
| #6 | Lung | BRAF | p.V600E | 0.84 |
| Extraction Method | DNA Yield | DNA Quality (Integrity) | Suitability for TaqMan | Suitability for NGS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QIAamp DNA Mini Kit | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ |
| QIAamp DNA Micro Kit | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ |
| SeleCTEV Exosomal DNA Kit | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| XCF Exosomal DNA Isolation Kit | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ |
| Phenol–Chloroform | + | +++ | + | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elzanowska, J.; Berrocal, L.; García-Peláez, B.; Vives-Usano, M.; Sebo, B.P.; Maia, J.; Batista, S.; Teppo, J.; Varjosalo, M.; Moraes, M.C.S.; et al. Defining Optimal Conditions for Tumor Extracellular Vesicle DNA Extraction for Mutation Profiling. Cancers 2022, 14, 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133258
Elzanowska J, Berrocal L, García-Peláez B, Vives-Usano M, Sebo BP, Maia J, Batista S, Teppo J, Varjosalo M, Moraes MCS, et al. Defining Optimal Conditions for Tumor Extracellular Vesicle DNA Extraction for Mutation Profiling. Cancers. 2022; 14(13):3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133258
Chicago/Turabian StyleElzanowska, Julia, Laura Berrocal, Beatriz García-Peláez, Marta Vives-Usano, Beatriz Passos Sebo, Joana Maia, Silvia Batista, Jaakko Teppo, Markku Varjosalo, Maria Carolina Strano Moraes, and et al. 2022. "Defining Optimal Conditions for Tumor Extracellular Vesicle DNA Extraction for Mutation Profiling" Cancers 14, no. 13: 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133258
APA StyleElzanowska, J., Berrocal, L., García-Peláez, B., Vives-Usano, M., Sebo, B. P., Maia, J., Batista, S., Teppo, J., Varjosalo, M., Moraes, M. C. S., Molina-Vila, M. Á., & Costa-Silva, B. (2022). Defining Optimal Conditions for Tumor Extracellular Vesicle DNA Extraction for Mutation Profiling. Cancers, 14(13), 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133258