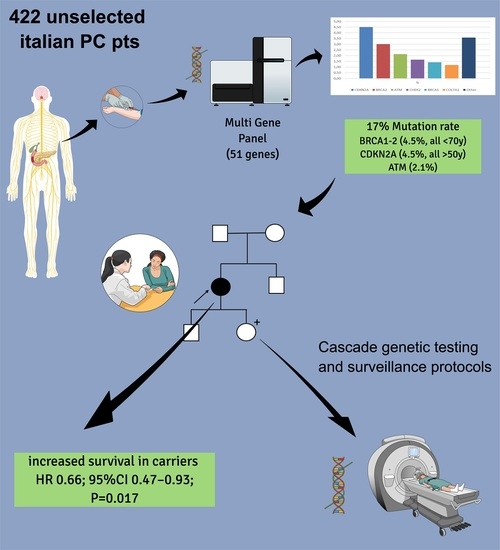
Clinical Significance of Germline Pathogenic Variants among 51 Cancer Predisposition Genes in an Unselected Cohort of Italian Pancreatic Cancer Patients
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients Selection and Characteristic
2.2. Gene Panel
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Pathogenic Variants in Pancreatic Cancer Susceptibility Genes: Correlation with Family History and Age at Diagnosis
3.2. Impact of Germline Pathogenic Variants on Patients’ Survival
3.3. Impact of Germline Pathogenic Variants on Response to Oxaliplatin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer: Global Trends, Etiology and Risk Factors. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting Cancer Incidence and Deaths to 2030: The Unexpected Burden of Thyroid, Liver, and Pancreas Cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.P.; Hong, T.S.; Bardeesy, N. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, Q.P.; O’Reilly, E.M.; van Eijck, C.H.J.; Groot Koerkamp, B. Neoadjuvant Treatment in Patients with Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welinsky, S.; Lucas, A.L. Familial Pancreatic Cancer and the Future of Directed Screening. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syngal, S.; Brand, R.E.; Church, J.M.; Giardiello, F.M.; Hampel, H.L.; Burt, R.W. American College of Gastroenterology ACG Clinical Guideline: Genetic Testing and Management of Hereditary Gastrointestinal Cancer Syndromes. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 223–262, quiz 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruban, R.H.; Canto, M.I.; Goggins, M.; Schulick, R.; Klein, A.P. Update on Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Adv. Surg. 2010, 44, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoffel, E.M.; McKernin, S.E.; Khorana, A.A. Evaluating Susceptibility to Pancreatic Cancer: ASCO Clinical Practice Provisional Clinical Opinion Summary. J. Oncol. Pract. 2019, 15, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, A.; Yachida, S.; Morizane, C. Genomic Features and Clinical Management of Patients with Hereditary Pancreatic Cancer Syndromes and Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempero, M.A.; Malafa, M.P.; Al-Hawary, M.; Behrman, S.W.; Benson, A.B.; Cardin, D.B.; Chiorean, E.G.; Chung, V.; Czito, B.; Del Chiaro, M.; et al. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.J.; Ward, K.C.; Hamilton, A.S.; Abrahamse, P.; Hawley, S.T.; Kurian, A.W. Association of Germline Genetic Test Type and Results with Patient Cancer Worry After Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.S. Genetic Testing: What Problem Are We Trying to Solve? J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3789–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, N.; Huang, G.; Scambia, G.; Chalas, E.; Pignata, S.; Fiorica, J.; Van Le, L.; Ghamande, S.; González-Santiago, S.; Bover, I.; et al. Evaluation of a Streamlined Oncologist-Led BRCA Mutation Testing and Counseling Model for Patients with Ovarian Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athens, A.; Amacker-North, L.; Warsinske, K.; Kadakia, K.C.; Kim, E.S.; Salem, M.E.; Elrefai, S. Changing the Landscape of Germline Testing in Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. JCO 2020, 38, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, M.A.; Wong, W.; Jordan, E.J.; Lee, J.W.; Kemel, Y.; Vijai, J.; Mandelker, D.; Zehir, A.; Capanu, M.; Salo-Mullen, E.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of Germline Alterations in Patients with Exocrine Pancreatic Neoplasms. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.-O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.-Y.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.-O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.-Y.; et al. Overall Survival from the Phase 3 POLO Trial: Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. JCO 2021, 39, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Moore, K.N.; Colombo, N.; Scambia, G.; Kim, B.-G.; Oaknin, A.; Friedlander, M.; Lisyanskaya, A.; Floquet, A.; Leary, A.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer and a BRCA Mutation (SOLO1/GOG 3004): 5-Year Follow-up of a Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutt, A.N.J.; Garber, J.E.; Kaufman, B.; Viale, G.; Fumagalli, D.; Rastogi, P.; Gelber, R.D.; de Azambuja, E.; Fielding, A.; Balmaña, J.; et al. Adjuvant Olaparib for Patients with BRCA1- or BRCA2-Mutated Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2394–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bono, J.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Durham, J.N.; Smith, K.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Aulakh, L.K.; Lu, S.; Kemberling, H.; Wilt, C.; Luber, B.S.; et al. Mismatch Repair Deficiency Predicts Response of Solid Tumors to PD-1 Blockade. Science 2017, 357, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves Olaparib for GBRCAm Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. 27 December 2019. Available online: Https://www.Fda.Gov/Drugs/Resources-Information-Approved-Drugs/Fda-Approves-Olaparib-Gbrcam-Metastatic-Pancreatic-Adenocarcinoma#:~:Text=On%20December%2027%2C%202019%2C%20the,An%20FDA%2Dapproved%20test%2C%20whose (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- EMA Approval Olaparib in Pancreatic Cancer. 8 July 2020. Available online: Https://www.Ema.Europa.Eu/En/Medicines/Human/EPAR/Lynparza (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Fogelman, D.; Sugar, E.A.; Oliver, G.; Shah, N.; Klein, A.; Alewine, C.; Wang, H.; Javle, M.; Shroff, R.; Wolff, R.A.; et al. Family History as a Marker of Platinum Sensitivity in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 76, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiorzo, P.; Fornarini, G.; Sciallero, S.; Battistuzzi, L.; Belli, F.; Bernard, L.; Bonelli, L.; Borgonovo, G.; Bruno, W.; De Cian, F.; et al. CDKN2A Is the Main Susceptibility Gene in Italian Pancreatic Cancer Families. J. Med. Genet. 2012, 49, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretti, U.; Cavaliere, A.; Niger, M.; Tortora, G.; Di Marco, M.C.; Rodriquenz, M.G.; Centonze, F.; Rapposelli, I.G.; Giordano, G.; De Vita, F.; et al. Germinal BRCA1-2 Pathogenic Variants (GBRCA1-2pv) and Pancreatic Cancer: Epidemiology of an Italian Patient Cohort. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiorzo, P.; Pensotti, V.; Fornarini, G.; Sciallero, S.; Battistuzzi, L.; Belli, F.; Bonelli, L.; Borgonovo, G.; Bruno, W.; Gozza, A.; et al. Contribution of Germline Mutations in the BRCA and PALB2 Genes to Pancreatic Cancer in Italy. Fam. Cancer 2012, 11, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, S.; Torrini, M.; Ollila, S.; Nasti, S.; Pastorino, L.; Cusano, R.; Bonelli, L.; Battistuzzi, L.; Mastracci, L.; Bruno, W.; et al. Germline MLH1 and MSH2 Mutations in Italian Pancreatic Cancer Patients with Suspected Lynch Syndrome. Fam. Cancer 2009, 8, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.R.; Rotunno, M.; Xiao, Y.; Ingvar, C.; Helgadottir, H.; Pastorino, L.; van Doorn, R.; Bennett, H.; Graham, C.; Sampson, J.N.; et al. Multiple Rare Variants in High-Risk Pancreatic Cancer-Related Genes May Increase Risk for Pancreatic Cancer in a Subset of Patients with and without Germline CDKN2A Mutations. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rainone, M.; Singh, I.; Salo-Mullen, E.E.; Stadler, Z.K.; O’Reilly, E.M. An Emerging Paradigm for Germline Testing in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Immediate Implications for Clinical Practice: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-L.; Mashl, R.J.; Wu, Y.; Ritter, D.I.; Wang, J.; Oh, C.; Paczkowska, M.; Reynolds, S.; Wyczalkowski, M.A.; Oak, N.; et al. Pathogenic Germline Variants in 10,389 Adult Cancers. Cell 2018, 173, 355–370.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantelli, M.; Pastorino, L.; Ghiorzo, P.; Barile, M.; Bruno, W.; Gargiulo, S.; Sormani, M.P.; Gliori, S.; Vecchio, S.; Ciotti, P.; et al. Early Onset May Predict G101W CDKN2A Founder Mutation Carrier Status in Ligurian Melanoma Patients. Melanoma Res. 2004, 14, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astiazaran-Symonds, E.; Goldstein, A.M. A Systematic Review of the Prevalence of Germline Pathogenic Variants in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieme, G.; Kral, J.; Rosseel, T.; Zemankova, P.; Parton, B.; Vocka, M.; Van Heetvelde, M.; Kleiblova, P.; Blaumeiser, B.; Soukupova, J.; et al. Prevalence of Germline Pathogenic Variants in Cancer Predisposing Genes in Czech and Belgian Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountzilas, E.; Eliades, A.; Koliou, G.-A.; Achilleos, A.; Loizides, C.; Tsangaras, K.; Pectasides, D.; Sgouros, J.; Papakostas, P.; Rallis, G.; et al. Clinical Significance of Germline Cancer Predisposing Variants in Unselected Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, E198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Hart, S.N.; Polley, E.C.; Gnanaolivu, R.; Shimelis, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Lilyquist, J.; Na, J.; Moore, R.; Antwi, S.O.; et al. Association between Inherited Germline Mutations in Cancer Predisposition Genes and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA 2018, 319, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremin, C.; Lee, M.K.-C.; Hong, Q.; Hoeschen, C.; Mackenzie, A.; Dixon, K.; McCullum, M.; Nuk, J.; Kalloger, S.; Karasinska, J.; et al. Burden of Hereditary Cancer Susceptibility in Unselected Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Referred for Germline Screening. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4004–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casolino, R.; Corbo, V.; Beer, P.; Hwang, C.-I.; Paiella, S.; Silvestri, V.; Ottini, L.; Biankin, A.V. Germline Aberrations in Pancreatic Cancer: Implications for Clinical Care. Cancers 2022, 14, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiorzo, P.; Pastorino, L.; Bonelli, L.; Cusano, R.; Nicora, A.; Zupo, S.; Queirolo, P.; Sertoli, M.; Pugliese, V.; Bianchi-Scarrà, G. INK4/ARF Germline Alterations in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Klein, A.P.; Hruban, R.H.; Roberts, N.J. The Role of Inherited Pathogenic CDKN2A Variants in Susceptibility to Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2021, 50, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, K.; Yu, J.; Suenaga, M.; Fesharakizadeh, S.; Cho, C.; Macgregor-Das, A.; Siddiqui, A.; Witmer, P.D.; Tamura, K.; Song, T.J.; et al. Deleterious Germline Mutations in Patients with Apparently Sporadic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWilliams, R.R.; Wieben, E.D.; Chaffee, K.G.; Antwi, S.O.; Raskin, L.; Olopade, O.I.; Li, D.; Highsmith, W.E.; Colon-Otero, G.; Khanna, L.G.; et al. CDKN2A Germline Rare Coding Variants and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Minority Populations. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, W.; Dalmasso, B.; Barile, M.; Andreotti, V.; Elefanti, L.; Colombino, M.; Vanni, I.; Allavena, E.; Barbero, F.; Passoni, E.; et al. Predictors of Germline Status for Hereditary Melanoma: 5 Years of Multi-Gene Panel Testing within the Italian Melanoma Intergroup. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, L.; Andreotti, V.; Dalmasso, B.; Vanni, I.; Ciccarese, G.; Mandalà, M.; Spadola, G.; Pizzichetta, M.A.; Ponti, G.; Tibiletti, M.G.; et al. Insights into Genetic Susceptibility to Melanoma by Gene Panel Testing: Potential Pathogenic Variants in ACD, ATM, BAP1, and POT1. Cancers 2020, 12, E1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmasso, B.; Puccini, A.; Catalano, F.; Borea, R.; Iaia, M.L.; Bruno, W.; Fornarini, G.; Sciallero, S.; Rebuzzi, S.E.; Ghiorzo, P. Beyond BRCA: The Emerging Significance of DNA Damage Response and Personalized Treatment in Pancreatic and Prostate Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astiazaran-Symonds, E.; Kim, J.; Haley, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Rao, H.S.; Genetics Center, R.; Carey, D.J.; Stewart, D.R.; Goldstein, A.M. A Genome-First Approach to Estimate Prevalence of Germline Pathogenic Variants and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Select Cancer Susceptibility Genes. Cancers 2022, 14, 3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, Z.; Yu, S.; Domchek, S.; Mamtani, R.; Reiss, K.A. Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Pancreatic Cancer and Pathogenic ATM Alterations. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2021, 5, pkaa121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosein, A.N.; Dougan, S.K.; Aguirre, A.J.; Maitra, A. Translational Advances in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Therapy. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javle, M.; Shacham-Shmueli, E.; Xiao, L.; Varadhachary, G.; Halpern, N.; Fogelman, D.; Boursi, B.; Uruba, S.; Margalit, O.; Wolff, R.A.; et al. Olaparib Monotherapy for Previously Treated Pancreatic Cancer with DNA Damage Repair Genetic Alterations Other Than Germline BRCA Variants: Findings From 2 Phase 2 Nonrandomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, M.; Ascierto, P.A.; Manzyuk, L.; Motola-Kuba, D.; Penel, N.; Cassier, P.A.; Bariani, G.M.; De Jesus Acosta, A.; Doi, T.; Longo, F.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Microsatellite Instability High or Mismatch Repair Deficient Cancers: Updated Analysis from the Phase 2 KEYNOTE-158 Study. Ann. Oncol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslanian, H.R.; Lee, J.H.; Canto, M.I. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Pancreas Cancer Screening in High-Risk Individuals: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, M.I.; Almario, J.A.; Schulick, R.D.; Yeo, C.J.; Klein, A.; Blackford, A.; Shin, E.J.; Sanyal, A.; Yenokyan, G.; Lennon, A.M.; et al. Risk of Neoplastic Progression in Individuals at High Risk for Pancreatic Cancer Undergoing Long-Term Surveillance. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 740–751.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiella, S.; Salvia, R.; De Pastena, M.; Pollini, T.; Casetti, L.; Landoni, L.; Esposito, A.; Marchegiani, G.; Malleo, G.; De Marchi, G.; et al. Screening/Surveillance Programs for Pancreatic Cancer in Familial High-Risk Individuals: A Systematic Review and Proportion Meta-Analysis of Screening Results. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signoretti, M.; Bruno, M.J.; Zerboni, G.; Poley, J.-W.; Delle Fave, G.; Capurso, G. Results of Surveillance in Individuals at High-Risk of Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiella, S.; Capurso, G.; Cavestro, G.M.; Butturini, G.; Pezzilli, R.; Salvia, R.; Signoretti, M.; Crippa, S.; Carrara, S.; Frigerio, I.; et al. Results of First-Round of Surveillance in Individuals at High-Risk of Pancreatic Cancer from the AISP (Italian Association for the Study of the Pancreas) Registry. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, G.; Paiella, S.; Carrara, S.; Butturini, G.; Secchettin, E.; Frulloni, L.; Zerbi, A.; Falconi, M. Italian Registry of Families at Risk of Pancreatic Cancer: AISP Familial Pancreatic Cancer Study Group. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Overall (N = 422) | Non-Carriers (N = 352) | PV Carriers (N = 70) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (range) | 67 (30–92) | 67.4 (30–92) | 64.3 (44–82) | 0.0254 |
| Female, N (%) | 221 (52) | 189 (54) | 32 (46) | 0.222 |
| Initial stage, N (%) | ||||
| Resectable | 92 (22) | 76 (22) | 16 (23) | 0.323 |
| Borderline | 25 (6) | 21 (6) | 4 (6) | |
| Unresectable | 51 (12) | 38 (11) | 13 (19) | |
| Metastatic | 188 (45) | 158 (45) | 30 (43) | |
| Missing | 66 (16) | 59 (17) | 7 (10) | |
| FH for PC, N (%) | 55 (13) | 37 (11) | 18 (26) | 0.001 |
| Personal/FH for BC/Ovarian, N (%) | 76 (18) | 51 (14) | 25 (36) | <0.001 |
| Personal/FH for melanoma, N (%) | 30 (7) | 17 (5) | 13 (19) | <0.001 |
| Other primary cancers, N (%) | 64 (16) | 43 (13) | 21 (32) | <0.001 |
| Genes | Cumulative Frequency | FH of PC | Personal and/or FH of BC and Ovary | Personal and/or FH of Melanoma | Frequency in Sporadic PC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 422 | n = 55 | n = 76 | n = 30 | n = 283 | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| ATM | 9 | (2.1) | 3 | (5.4) | 1 | (1.3) | 1 | (3.3) | 5 | (1.7) | * |
| BRCA1 | 6 | (1.4) | 1 | (1.8) | 5 | (6.6) | 1 | (3.3) | - | - | ** |
| BRCA2 | 13 | (3) | 1 | (1.8) | 7 | (9.2) | 2 | (6.7) | 5 | (1.7) | */** |
| BRCA1/2 | 19 | (4.5) | 2 | (3.6) | 12 | (15.8) | 3 | (10) | 5 | (1.7) | */** |
| CDKN2A | 19 | (4.5) | 8 | (14.5) | 5 | (6.6) | 6 | (20) | 8 | (2.8) | */** |
| CHEK2 | 7 | (1.6) | 1 | (1.8) | - | - | 1 | (3.3) | 5 | (1.7) | |
| COL7A1 | 5 | (1.2) | 1 | (1.8) | 1 | (1.3) | - | - | 3 | (1) | |
| ERCC4 | 1 | (0.2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | (0.3) | |
| FANCA/C/G | 3 | (0.7) | 2 | (3.6) | 2 | (2.6) | 1 | (3.3) | - | - | ** |
| MLH1 | 1 | (0.2) | - | - | 1 | (1,3) | - | - | - | - | |
| MSH2 | 2 | (0.4) | - | - | 1 | (1.3) | - | - | 1 | (0.3) | |
| NBN | 3 | (0.7) | - | - | 1 | (1.3) | 1 | (3.3) | 2 | (0.7) | * |
| RAD50/51 | 2 | (0.4) | 1 | (1.8) | 1 | (1.3) | 1 | (3.3) | - | - | ** |
| RET1 | 1 | (0.2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | (0.3) | |
| SDHA | 1 | (0.2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | (0.3) | |
| TP53 | 1 | (0.2) | - | - | 1 | (1.3) | - | - | |||
| All genes | 74 | (17.5) | 18 | (32.7) | 26 | (34.2) | 14 | (46.7) | 32 | (11.3) | |
| Univariable Cox Models | Multivariable Cox Model N = 340 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (10-years) *** | 1.18 (1.03–1.32) | 0.004 | 1.18 (1.06; 1.33) | 0.004 |
| Male vs. Female * | 1.06 (0.85–1.31) | 0.612 | 1.13 (0.91; 1.40) | 0.270 |
| Initial stage (N = 353) ** | ||||
| Resectable | 1.00 | Ref | 1.00 | Ref |
| Borderline | 1.24 (0.66–2.30) | 0.504 | 1.25 (0.66; 2.39) | 0.491 |
| Unresectable | 1.39 (0.93–2.08) | 0.113 | 1.39 (0.92; 2.09) | 0.116 |
| Metastatic | 3.20 (2.38–4.29) | <0.001 | 3.39 (2.51; 4.57) | <0.001 |
| FH for PC * | 0.85 (0.62–1.17) | 0.315 | 0.90 (0.65; 1.24) | 0.526 |
| Personal/FH for BC/Ovarian * | 0.91 (0.69–1.21) | 0.519 | 0.92 (0.69; 1.22) | 0.552 |
| Personal/FH for melanoma * | 0.99 (0.66–1.49) | 0.969 | 1.08 (0.71; 1.63) | 0.723 |
| Other primary cancers, (N = 395) * | 0.76 (0.56–1.04) | 0.089 | 0.74 (0.54; 1.01) | 0.061 |
| Presence of any PV vs. WT * | 0.78 (0.59–1.04) | 0.090 | 0.81 (0.61; 1.09) | 0.160 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puccini, A.; Ponzano, M.; Dalmasso, B.; Vanni, I.; Gandini, A.; Puglisi, S.; Borea, R.; Cremante, M.; Bruno, W.; Andreotti, V.; et al. Clinical Significance of Germline Pathogenic Variants among 51 Cancer Predisposition Genes in an Unselected Cohort of Italian Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184447
Puccini A, Ponzano M, Dalmasso B, Vanni I, Gandini A, Puglisi S, Borea R, Cremante M, Bruno W, Andreotti V, et al. Clinical Significance of Germline Pathogenic Variants among 51 Cancer Predisposition Genes in an Unselected Cohort of Italian Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2022; 14(18):4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184447
Chicago/Turabian StylePuccini, Alberto, Marta Ponzano, Bruna Dalmasso, Irene Vanni, Annalice Gandini, Silvia Puglisi, Roberto Borea, Malvina Cremante, William Bruno, Virginia Andreotti, and et al. 2022. "Clinical Significance of Germline Pathogenic Variants among 51 Cancer Predisposition Genes in an Unselected Cohort of Italian Pancreatic Cancer Patients" Cancers 14, no. 18: 4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184447
APA StylePuccini, A., Ponzano, M., Dalmasso, B., Vanni, I., Gandini, A., Puglisi, S., Borea, R., Cremante, M., Bruno, W., Andreotti, V., Allavena, E., Martelli, V., Catalano, F., Grassi, M., Iaia, M. L., Pirrone, C., Pastorino, A., Fornarini, G., Sciallero, S., ... Pastorino, L. (2022). Clinical Significance of Germline Pathogenic Variants among 51 Cancer Predisposition Genes in an Unselected Cohort of Italian Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Cancers, 14(18), 4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14184447