Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
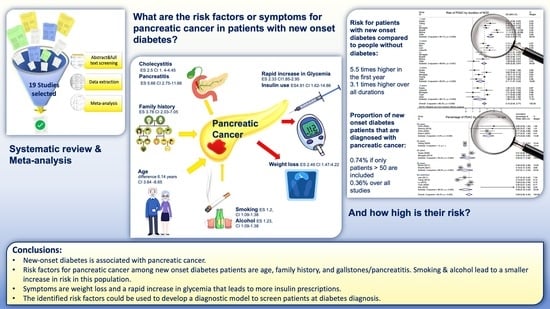
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Studies
3.2. Risk Factors for PDAC in NOD Patients
3.3. Association between NOD and PDAC
3.4. Proportion of NOD Caused by PDAC
4. Discussion
Limitations and Strengths of the Study
5. Conclusions
5.1. Interpretation of Findings
5.2. Importance of the Presented Work and Future Directions for Early Diagnosis Programs
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Search Terms
Appendix A.2. Effect Size of PDAC in NOD Patients versus No Diabetes Patients
Appendix A.3. Parameters for Meta-Analysis, Remarks about the Reported Risk Factors/Symptoms
Appendix A.4. Bias Assessment

Appendix A.5. Publication Bias

| First Author, Year | Journal | Title | Reason for Exclusion | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ballotari, 2017 | BMC Cancer | Diabetes and risk of cancer incidence: Results from a population-based cohort study in northern Italy. | Wrong population | |
| 2 | Zhang, 2018 | Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews | Clinical features and risk factors for cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes in Qingdao, China. | Conference abstract/letter/review | |
| 3 | Arthur, 2019 | Annals of Epidemiology | Adiposity, history of diabetes, and risk of pancreatic cancer in postmenopausal women. | Wrong population | |
| 4 | Gullo, 1999 | Annals of Oncology | Diabetes and the risk of pancreatic cancer. | Wrong outcomes | No other risk factors are looked at. |
| 5 | Jamal, 2009 | World J of Gastroenterology | Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for gastrointestinal cancer among American veterans. | Wrong population | |
| 6 | Gul, 2010 | The American J of the Medical Sciences | Ca 19-9 levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. | Wrong outcomes | Not about pancreatic cancer. Conference abstract, uploaded the corresponding article. |
| 7 | Brodovicz, 2011 | Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety | Synergistic effect of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and history of pancreatitis on pancreatic cancer risk: A retrospective cohort study from the general practice research database (GPRD). | Conference abstract | Abstract, unable to find paper |
| 8 | Hense, 2011 | Diabetology and Metabolic Syndrome | Cancer incidence in type 2 diabetes patients—First results from a feasibility study of the D2C cohort. | Wrong population | Could not find a sub-analysis on PDAC, only overall risk for cancer according to diabetes duration |
| 9 | Gong, 2012 | World J of Gastroenterology | ABO blood type, diabetes, and risk of gastrointestinal cancer in Northern China. | Wrong patient population | |
| 10 | Henry, 2012 | Cancer Research | History of diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer: The Iowa Women's Health study. | Conference abstract | Paper that followed had wrong patient population |
| 11 | Andersen, 2012 | Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews | The practical importance of recognizing pancreatogenic or type 3c diabetes. | letter | Letter about an article, imported it into full-text review. |
| 12 | Honjo, 2012 | Epidemiology/Genetics | An observational prospective study of cancer in Japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes with special reference to pancreatic cancer. | Conference abstract | Abstract, unable to find paper |
| 13 | Elena, 2013 | Cancer Causes and Control | Diabetes and risk of pancreatic cancer: A pooled analysis from the pancreatic cancer cohort consortium. | Wrong population | |
| 14 | Suceveanu, 2015 | Pancreatology | Diabetes mellitus, obesity, and chronic pancreatitis? Independent risk factors for pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAC) in the Romanian Black Sea coast area. | Conference abstract | Abstract, unable to find paper |
| 15 | Mansoor, 2016 | Gastroenterology | Risk factors for pancreatic cancer in new-onset diabetes mellitus: A population-based study. | Conference abstract | Abstract, unable to find paper |
| 16 | DeJong, 2016 | Gastroenterology | Gastrointestinal cancer incidence in type 2 diabetes mellitus; results from a large retrospective population-based cohort study. | Wrong population | |
| 17 | Lu, 2016 | British J of Cancer | Reply to Comment on "New-onset type 2 diabetes, elevated HbA1c, antidiabetic medications, and risk of pancreatic cancer". | letter | Answer to a comment over the paper |
| 18 | Dugnani, 2016 | Pancreatology | Diabetes associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is just diabetes: Results of a prospective observational study in surgical patients. | Wrong population | |
| 19 | Attner, 2012 | Cancer Causes & Control | Cancer among patients with diabetes, obesity and abnormal blood lipids: a population-based register study in Sweden. | Wrong population | The population are cancer cases, not NOD, and diabetes is the outcome. |
| 20 | Mizuno, 2013 | J of Gastroenterology | Risk factors and early signs of pancreatic cancer in diabetes: screening strategy based on diabetes onset age. | Wrong patient population | |
| 21 | Zhang, 2012 | BMC Public health | Increased risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective cohort study in China. | Wrong population | |
| 22 | Magliano, 2012 | European J of Endocrinology | Incidence and predictors of all-cause and site-specific cancer in type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. | Wrong population | |
| 23 | Lai, 2013 | The J of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism | The association between self-reported diabetes and cancer incidence in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. | Wrong population | |
| 24 | Tseng, 2013 | Acta Diabetologica | Diabetes, insulin use, smoking, and pancreatic cancer mortality in Taiwan. | Wrong population | |
| 25 | Ahn, 2013 | The Korean J of Gastroenterology | [New-onset diabetes as an early sign of pancreatic cancer]. | review | Article in Korean google translate shows that it is a review. |
| 26 | Valent, 2015 | J of Diabetes and Its Complications | Diabetes mellitus and cancer of the digestive organs: an Italian population-based cohort study. | Wrong population | |
| 27 | Kolb, 2009 | Cancer Biology & Therapy | Glucagon/insulin ratio as a potential biomarker for pancreatic cancer in patients with new-onset diabetes mellitus. | Wrong population | |
| 28 | Ogunleye, 2009 | British J of Cancer | A cohort study of the risk of cancer associated with type 2 diabetes. | Wrong population | |
| 29 | Hemminki, 2010 | The Oncologist | Risk of cancer following hospitalization for type 2 diabetes. | Wrong population | no NOD |
| 30 | Ben, 2012 | Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews | Clinical profiles and long-term outcomes of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and diabetes mellitus. | Conference abstract | Abstract, unable to find paper |
| 31 | LaVeccia, 1994 | British J of Cancer | A case-control study of diabetes mellitus and cancer risk. | Wrong population | No real NOD, only < 5 y. |
| 32 | Hjalgrim, 1997 | J of Internal Medicine | Cancer and diabetes—A follow-up study of two population-based cohorts of diabetic patients. | Wrong population | nothing about NOD; nothing about PC |
| 33 | He, 2017 | Oncotarget | Serum metabolomics differentiating pancreatic cancer from new-onset diabetes. | Wrong outcomes | Biomarker study |
| 34 | Pan, 2018 | American J of Epidemiology | Type 2 Diabetes and Risk of Incident Cancer in China: A Prospective Study among 0.5 Million Chinese Adults. | Wrong population | No PDAC group |
| 35 | Dakner, 2018 | Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews | Newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes may serve as a potential marker for pancreatic cancer. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 36 | deJong, 2018 | Cancer Epidemiology | Gastrointestinal cancer incidence in type 2 diabetes mellitus; results from a large population-based cohort study in the UK. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 37 | Dong, 2018 | Digestion | Predictive Factors for Differentiating Pancreatic Cancer-Associated Diabetes Mellitus from Common Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus for the Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. | Wrong population | Controls have long-standing diabetes. |
| 38 | Maitra, 2018 | Pancreas | A Prospective Study to Establish a New-Onset Diabetes Cohort: From the Consortium for the Study of Chronic Pancreatitis, Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer. | Conference abstract/letter/review | This is a study protocol, not a study. The study is ongoing. |
| 39 | Ewald, 2012 | Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews | Prevalence of diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (type 3c). | Wrong population | |
| 40 | Fest, 2019 | J of Internal Medicine | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate as an independent prognostic marker for mortality: a prospective population-based cohort study. | Wrong population | |
| 41 | Müller, 2018 | Pancreas | The Potential of Glycemic Control and Body Weight Change as Early Markers for Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with Long-standing Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. | Wrong population | |
| 42 | Eijgenraam, 2013 | British J of Cancer | Diabetes type II, other medical conditions and pancreatic cancer risk: A prospective study in the Netherlands. | Wrong population | NOD is excluded. |
| 43 | LaTorre, 2014 | BioMed Research International | Investigating the synergistic interaction of diabetes, tobacco smoking, alcohol consumption, and hypercholesterolemia on the risk of pancreatic cancer: A case-control study in Italy. | Wrong population | |
| 44 | Masclee, 2014 | Gastroenterology | Comparison of incidence rates of acute pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer among the general population and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients between different databases in the safeguard project. | Conference abstract | Conference abstract Neither the first nor last author published anything about diabetes and cancer later. |
| 45 | Illés, 2014 | Pancreatology | Benefits of screening for pancreatic cancer in new-onset diabetes mellitus. | Conference abstract | Conference abstract, follow-up publication is included |
| 46 | Freitas, 2014 | Endocrine Reviews | Hospitalization and mortality for pancreatic cancer and diabetes: A cohort from a tertiary hospital. | Conference abstract | Conference abstract, publication was not found. |
| 47 | DeBruijn, 2014 | Diabetologia | Diabetes and cancer risk in a population-based study with 20 years of follow-up: The Rotterdam Study. | Conference abstract/letter/review | Publication was by Fest, 2019 |
| 48 | Ritchey, 2014 | Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety | Electronic health data capture of clinical evaluation and pancreatic cancer (PC) diagnosis (DX) in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM). | Conference abstract | Publication is under Brodovicz |
| 49 | Czakó, 2014 | Pancreas | Screening for pancreatic cancer in new-onset diabetes mellitus is beneficial? | Conference abstract | Publication by Illes, 2016 |
| 50 | Koo, 2019 | Acta Diabetologica | Middle-aged men with type 2 diabetes as potential candidates for pancreatic cancer screening: A 10-year nationwide population-based cohort study. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 51 | Larsson, 2005 | Nature Publishing Group | Overall obesity, abdominal adiposity, diabetes, and cigarette smoking in relation to the risk of pancreatic cancer in two Swedish population-based cohorts. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 52 | Fisher, 2001 | World J of surgery | Diabetes: risk factor for developing pancreatic cancer or manifestation of the disease? | Review | Review of long-standing diabetes studies. |
| 53 | Chari, 2008 | Gastroenterology | Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus: prevalence and temporal association with diagnosis of cancer. | Wrong population | Their population is PDAC, not NOD |
| 54 | Makhoul, 2016 | SAGE Open Medicine | Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with increased risk of pancreatic cancer: A veteran administration registry study. | Wrong population | NOD is excluded |
| 55 | Li, 2018 | Medical Science Monitor: International Medical J of Experimental and Clinical Research | ABO Blood Group and Diabetes Mellitus Influence the Risk for Pancreatic Cancer in a Population from China. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 56 | Müller, 2017 | Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety | HbA1c Levels, Body Weight Change, and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer Among Patients With Long-Standing Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. | Conference abstract/letter/review | Conference abstract, study published by Müller, 2018 |
| 57 | Khurana, 2004 | American J of Gastroenterology | Diabetes Mellitus Is a Risk Factor for Pancreatic Cancer: A Case Control Study in Half a Million Veterans: 168. | Conference abstract/letter/review | Study published by Khurana, 2007. It is about medication. |
| 58 | Prizment, 2011 | AACR | History of diabetes mellitus, cholecystectomy, and gallstone disease and risk of pancreatic cancer | Conference abstract/letter/review | Conference abstract, Study: Henry, 2012 |
| 59 | Munigala, 2014 | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | 1045 Higher Pancreatic Cancer Risk Following New Onset of Diabetes Mellitus in Non-Obese Patients with Chronic Pancreatitis. | Conference abstract | Conference abstract, paper is Munigala, 2015 |
| 60 | Luo, 2007 | Cancer Causes and Control | Body mass index, physical activity and the risk of pancreatic cancer in relation to smoking status and history of diabetes: A large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan—The JPHC study. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 61 | Lo, 2013 | International J of Cancer | Modest increase in risk of specific types of cancer types in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 62 | Luo, 2013 | Cancer Causes and Control | Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for gastrointestinal cancers among postmenopausal women. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 63 | Lin, 2014 | British J of Cancer | Independent and joint effect of type 2 diabetes and gastric and hepatobiliary diseases on the risk of pancreatic cancer risk: 10-year follow-up of population-based cohort. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 64 | Liu, 2015 | International J of Cancer | Cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and their relatives. | Wrong outcomes | No other risk factors are studied |
| 65 | Christensen, 2016 | Journal of Diabetes and its Complications | Venous thromboembolism and risk of cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 66 | Koo, 2019 | J Clin Endocrinol Metab | The Incremental Risk of Pancreatic Cancer According to Fasting Glucose Levels: Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 67 | Fritz, 2020 | Int J Epidemiol | The triglyceride-glucose index as a measure of insulin resistance and risk of obesity-related cancers. | Wrong population | |
| 68 | Wlodarczyk, 2018 | J Clin Gastroenterol | The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) Axis in Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma (PDAC). | Conference abstract/letter/review | Review on IGF |
| 69 | Carey, 2013 | Gastroenterology | The differential effects of statins on the risk of developing pancreatic cancer. A case-control study in two centers in the UK. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 70 | Grote, 2011 | Diabetologia | Diabetes mellitus, glycated hemoglobin and C-peptide levels in relation to pancreatic cancer risk: A study within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort | Wrong population | |
| 71 | Silverman, 1999 | Nature Publishing Group | Diabetes mellitus, other medical conditions, and familial history of cancer as risk factors for pancreatic cancer | Wrong outcomes | |
| 72 | He, 2018 | Current Medical Research and Opinion | Retrospective database analysis of cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in China. | Wrong population | |
| 73 | Brodovicz, 2012 | Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism | Impact of diabetes duration and chronic pancreatitis on the association between type 2 diabetes and pancreatic cancer risk. | Wrong study design | |
| 74 | Johnson, 2011 | Diabetologia | Time-varying incidence of cancer after the onset of type 2 diabetes: evidence of potential detection bias. | Wrong outcomes | No additional risk factors |
| 75 | Lee, 2019 | Diabetes Care | Nationwide Trends in Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer Risk Among Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors. | Wrong population | Population was patients taking DPP4 inhibitors |
| 76 | Fang, 2018 | Endocrine Connections | Cancer risk in Chinese diabetes patients: A retrospective cohort study based on management data. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 77 | Oberaigner, 2014 | BMC Public Health | Increased cancer incidence risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Results from a cohort study in Tyrol/Austria. | Wrong outcomes | No additional risk factors |
| 78 | Antolino, 2022 | European J of Surgical Oncology | Is TP53 Arg72Pro a risk factor for pancreatic cancer in diabetic patients? | Conference abstract | |
| 79 | Yuan, 2020 | Diabetes | Is Type 2 Diabetes Causally Associated with Cancer Risk? Evidence From a Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 80 | Ma, 2022 | J of Diabetes | Diabetes duration and weight loss are associated with onset age and remote metastasis of pancreatic cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus. | Wrong population | |
| 81 | Roxana, 2019 | J of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases | Modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors for pancreatic cancer. | Conference abstract | |
| 82 | Shinyoji, 2020 | Japanese J of Clinical Oncology | Diverse transitions in diabetes status during the clinical course of patients with resectable pancreatic cancer. | Wrong study design | |
| 83 | Van de Pall-Franse, 2007 | International J of Cancer | Less aggressive treatment and worse overall survival in cancer patients with diabetes: a large population-based analysis. | Wrong population | |
| 84 | Everhart, 1995 | JAMA | Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer. A meta-analysis. | No original study | |
| 85 | Huxley, 2005 | British J of Cancer | Type-II diabetes and pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis of 36 studies. | No original study | |
| 86 | Pannala, 2008 | Gastroenterology | Prevalence and clinical profile of pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus. | Wrong population | |
| 87 | Wang, 2006 | Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention | Diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer in a population-based case-control study in the San Francisco Bay Area, California. | Wrong outcome | no risk factors on top of NOD |
| 88 | Hassan, 2007 | American J of Gastroenterology | Risk factors for pancreatic cancer: Case-control study. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 89 | Kalapothaki, 1993 | Cancer Causes Control | Tobacco, ethanol, coffee, pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, and cholelithiasis as risk factors for pancreatic carcinoma. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 90 | Canto, 2002 | Gastroenterology | Screening for pancreatic neoplasia in high-risk individuals: The Johns Hopkins Experience. | No full text | |
| 91 | Chow, 1995 | J of National Cancer Institute | Risk of pancreatic cancer following diabetes mellitus: a nationwide cohort study in Sweden. | Wrong population | NOD excluded |
| 92 | Gullo, 1994 | NEJM | Diabetes and the risk of pancreatic cancer. Italian Pancreatic Cancer Study Group. | Wrong outcome | No risk factors on top of NOD |
| 93 | Bonelli, 2003 | Pancreas | Exocrine pancreatic cancer, cigarette smoking, and diabetes mellitus: A case-control study in northern Italy. | Wrong outcome | No risk factors on top of NOD |
| 94 | Kim, 2014 | Pancreatology | Serum CA 19-9 as a screening test for pancreatic cancer in new-onset diabetic patients. | No full text | Probably conference abstract |
| 95 | Cui, 2012 | Endocrine-Related Cancer | Diabetes and pancreatic cancer. | Wrong population | |
| 96 | Atchinson, 2011 | International J of Cancer | Risk of cancer in a large cohort of U.S. veterans with diabetes. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 97 | Norell, 1986 | British J of Cancer | Diabetes, gallstone disease, and pancreatic cancer. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 98 | Olson, 2016 | Pancreas | Weight loss, diabetes, fatigue, and depression preceding pancreatic cancer. | Wrong outcomes | No risk factors on top of NOD |
| 99 | Stapley, 2012 | British J of Cancer | The risk of pancreatic cancer in symptomatic patients in primary care: a large case-control study using electronic records. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 100 | Mueller, 2018 | Pancreas | The potential of glycemic control and body weight change as early markers for pancreatic cancer in patients with long-standing diabetes mellitus: A case-control study. | Wrong population | |
| 101 | Aggarwal, 2012 | Pancreatology | New-onset diabetes in pancreatic cancer: a study in the primary care setting. | Wrong population | Seemed to be the same study as Chari 2013 |
| 102 | Chen, 2011 | Diabetes Care | Risk of malignant neoplasm of the pancreas in relation to diabetes: A population-based study in Taiwan. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 103 | Rousseau, 2006 | International J of Cancer | Diabetes mellitus and cancer risk in a population-based case-control study among men from Montreal, Canada. | Wrong population | No NOD |
| 104 | Bao, 2011 | Biochim Biophys Acta | The complexities of obesity, diabetes, and the development and progression of pancreatic cancer. | Basic research | |
| 105 | Wu, 2020 | JAMA | Association of Glycated Hemoglobin Levels with Risk of Pancreatic Cancer. | Wrong outcome | No risk factors on top of NOD |
| 106 | Setiawan, 2019 | National Cancer Institute | Pancreatic Cancer Following Incident Diabetes in African Americans and Latinos: The Multiethnic Cohort. | Wrong outcome | We tried to include it twice but found no data we could analyze, and authors did not respond |
| 107 | Keum, 2018 | Cancer Causes Control | Long-term patterns of fasting blood glucose levels and pancreatic cancer incidence | Wrong outcomes | No risk factors on top of NOD |
References
- Hu, J.-X.; Zhao, C.-F.; Chen, W.-B.; Liu, Q.-C.; Li, Q.-W.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Gao, F. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review of Epidemiology, Trend, and Risk Factors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4298–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyba, T.; Randi, G.; Bray, F.; Martos, C.; Giusti, F.; Nicholson, N.; Gavin, A.; Flego, M.; Neamtiu, L.; Dimitrova, N.; et al. The European Cancer Burden in 2020: Incidence and Mortality Estimates for 40 Countries and 25 Major Cancers. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 308–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation Cancer Fact Sheet Switzerland. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/756-switzerland-fact-sheets.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Jeong, H.R.; An, S.S.A. Causative Factors for Formation of Toxic Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Oligomer in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 1873–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Herrington, M.; Larsson, J.; Permert, J. The Relationship between Diabetes and Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2003, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permert, J.; Larsson, J.; Westermark, G.T.; Herrington, M.K.; Christmanson, L.; Pour, P.M.; Westermark, P.; Adrian, T.E. Islet Amyloid Polypeptide in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer and Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Flatt, P.R.; Permert, J.; Adrian, T.E. Pancreatic Cancer Cells Selectively Stimulate Islet β Cells to Secrete Amylin. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, N.; Sagar, G.; Dutta, S.K.; Smyrk, T.C.; Lau, J.S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Truty, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Kaufman, R.J.; Chari, S.T.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer–Derived Exosomes Cause Paraneoplastic β-Cell Dysfunction. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, G.; Ramachandran, V.; Javeed, N.; Arumugam, T.; Dutta, S.; Klee, G.G.; Klee, E.W.; Smyrk, T.C.; Bamlet, W.; Han, J.J.; et al. Adrenomedullin Is Up-Regulated in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer and Causes Insulin Resistance in β Cells and Mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1510–1517.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syrigos, K.N.; Konstantoulakis, M.M.; Fyssas, I.; Katsilambros, N.; Golematis, B.C. Autoantibodies against Insulin and β-Islet Cells in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Possible Explanation for Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 66, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, S.T.; Leibson, C.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Timmons, L.J.; Ransom, J.; de Andrade, M.; Petersen, G.M. Pancreatic Cancer–Associated Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence and Temporal Association with Diagnosis of Cancer. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannala, R.; Leibson, C.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Timmons, L.J.; Ransom, J.; de Andrade, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Temporal Association of Changes in Fasting Blood Glucose and Body Mass Index with Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 2318–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannala, R.; Basu, A.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. New-Onset Diabetes: A Potential Clue to the Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwahlen Nicola and Egger Matthias, M.L. Population-Based Screening—The Difficulty of How to Do More Good than Harm and How to Achieve It. Swiss. Med. Wkly. 2010, 140, w13061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, D.; Brooks, P.; Woolf, A.; Blyth, F.; March, L.; Bain, C.; Baker, P.; Smith, E.; Buchbinder, R. Assessing Risk of Bias in Prevalence Studies: Modification of an Existing Tool and Evidence of Interrater Agreement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2012, 65, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, D.; Terzin, V.; Holzinger, G.; Kosár, K.; Róka, R.; Zsóri, G.; Ábrahám, G.; Czakó, L. New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus–A High-Risk Group Suitable for the Screening of Pancreatic Cancer? Pancreatology 2016, 16, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Bertenthal, D.; Corley, D.; Shen, H.; Walter, L.C.; McQuaid, K. New-Onset Diabetes and Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursi, B.; Finkelman, B.; Giantonio, B.J.; Haynes, K.; Rustgi, A.K.; Rhim, A.D.; Mamtani, R.; Yang, Y.X. A Clinical Prediction Model to Assess Risk for Pancreatic Cancer among Patients with New-Onset Diabetes. Gastroenterology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.-A.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, J.K.; Bae, J.C.; Kim, K.W. New-Onset Diabetes Patients Need Pancreatic Cancer Screening? J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, e58–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, Q.; Cai, Q.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Ning, X.; Deng, S.; Wang, K. The Relationship between New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus and Pancreatic Cancer Risk: A Case–Control Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.; Lai, S.; Li, C.; Chen, W. Diabetes Mellitus Correlates with Increased Risk of Pancreatic Cancer: A Population-based Cohort Study in Taiwan. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.-H. New-Onset Diabetes with a History of Dyslipidemia Predicts Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2013, 42, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipworth, L.; Zucchetto, A.; Bosetti, C.; Franceschi, S.; Talamini, R.; Serraino, D.; McLaughlin, J.K.; la Vecchia, C.; Negri, E. Diabetes Mellitus, Other Medical Conditions and Pancreatic Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; García Rodríguez, L.A.; Malgerud, L.; González-Pérez, A.; Martín-Pérez, M.; Lagergren, J.; Bexelius, T.S. New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes, Elevated HbA1c, Anti-Diabetic Medications, and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.M.; Meier, C.R.; Jick, S.S.; Schneider, C. Weight Change and Blood Glucose Concentration as Markers for Pancreatic Cancer in Subjects with New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus: A Matched Case-Control Study. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munigala, S.; Singh, A.; Gelrud, A.; Agarwal, B. Predictors for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis Following New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Babic, A.; Khalaf, N.; Nowak, J.A.; Brais, L.K.; Rubinson, D.A.; Ng, K.; Aguirre, A.J.; Pandharipande, P.V.; Fuchs, C.S.; et al. Diabetes, Weight Change, and Pancreatic Cancer Risk. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e202948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosetti, C.; Rosato, V.; Li, D.; Silverman, D.; Petersen, G.M.; Bracci, P.M.; Neale, R.E.; Muscat, J.; Anderson, K.; Gallinger, S.; et al. Diabetes, Antidiabetic Medications, and Pancreatic Cancer Risk: An Analysis from the International Pancreatic Cancer Case-Control Consortium. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, S.T.; Leibson, C.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Ransom, J.; de Andrade, M.; Petersen, G.M. Probability of Pancreatic Cancer Following Diabetes: A Population-Based Study. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.A.; Kamada, P.; Rabe, K.G.; Srinivasan, S.; Basu, A.; Aggarwal, G.; Chari, S.T. Weight Loss Precedes Cancer-Specific Symptoms in Pancreatic Cancer-Associated Diabetes Mellitus. Pancreas 2011, 40, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.Z.; Pandol, S.J.; Jeon, C.Y.; Chari, S.T.; Sugar, C.A.; Chao, C.R.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Wu, B.U.; Setiawan, V.W. New-Onset Diabetes, Longitudinal Trends in Metabolic Markers, and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in a Heterogeneous Population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1812–1821.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kandlakunta, H.; Nagpal, S.J.S.; Feng, Z.; Hoos, W.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Model to Determine Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Patients With New-Onset Diabetes. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 730–739.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Butler, R.K.; Lustigova, E.; Chari, S.T.; Wu, B.U. Validation of the Enriching New-Onset Diabetes for Pancreatic Cancer Model in a Diverse and Integrated Healthcare Setting. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Montes, E.; Coscia, C.; Gómez-Rubio, P.; Fernández, A.; Boenink, R.; Rava, M.; Márquez, M.; Molero, X.; Löhr, M.; Sharp, L.; et al. Deciphering the Complex Interplay between Pancreatic Cancer, Diabetes Mellitus Subtypes and Obesity/BMI through Causal Inference and Mediation Analyses. Gut 2021, 70, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Safarudin, R.F.; Kupec, J.T. Validation of the ENDPAC Model: Identifying New-Onset Diabetics at Risk of Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; al Heraki, S.; Kupec, J.T. Noninvasive Models Screen New-Onset Diabetics at Low Risk of Early-Onset Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2021, 50, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayem Ullah, A.Z.M.; Stasinos, K.; Chelala, C.; Kocher, H.M. Temporality of Clinical Factors Associated with Pancreatic Cancer: A Case-Control Study Using Linked Electronic Health Records. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everhart, J.; Wright, D. Diabetes Mellitus as a Risk Factor for Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. JAMA 1995, 273, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.P.; Oldfield, L.; Ney, A.; Hart, P.A.; Keane, M.G.; Pandol, S.J.; Li, D.; Greenhalf, W.; Jeon, C.Y.; Koay, E.J.; et al. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, D.; Ivány, E.; Holzinger, G.; Kosár, K.; Adam, M.G.; Kamlage, B.; Zsóri, G.; Tajti, M.; Svébis, M.M.; Horváth, V.; et al. New Onset of DiabetEs in ASsociation with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (NODES Trial): Protocol of a Prospective, Multicentre Observational Trial. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, S.T.; Maitra, A.; Matrisian, L.M.; Shrader, E.E.; Wu, B.U.; Kambadakone, A.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Kenner, B.; Rinaudo, J.A.S.; Srivastava, S.; et al. Early Detection Initiative: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Algorithm-Based Screening in Patients with New Onset Hyperglycemia and Diabetes for Early Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2022, 113, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitra, A.; Sharma, A.; Brand, R.E.; van den Eeden, S.K.; Fisher, W.E.; Hart, P.A.; Hughes, S.J.; Mather, K.J.; Pandol, S.J.; Park, W.G.; et al. A Prospective Study to Establish a New-Onset Diabetes Cohort: From the Consortium for the Study of Chronic Pancreatitis, Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2018, 47, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.C.W.; Chan, J.C.N. Type 2 Diabetes in East Asians: Similarities and Differences with Populations in Europe and the United States. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1281, 64–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Author, Journal, Year | City or Region, Country, Database Name (When Available), Period (Years) | Study Design, Study Population, Sampling Method | Patient Characteristics in NOD (Mean Age, Obesity, Smoking) | NOD Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gupta et al., Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2006 [20] | USA, VA National Patient Care database 1998–2004 | Retrospective cohort, veterans, all without previous diagnosis of PDAC or DM were included, 36,631 developed NOD, of which 149 had PDAC | US veterans > 40 years, in NOD cohort 97% male, average age 64 years | 1 year |
| Boursi et al., Gastroenterology, 2017 [21] | UK, THIN database 1995–2013 | Retrospective cohort, all patients with incident DM were included: 109,385 patients with NOD, of which 390 had PDAC | All < 35 years were excluded | <3 years |
| Lee et al., Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2012 [22] | Seoul, Korea, 2003–2009 | Retrospective case-control Cases: 151 NOD with PDAC, Controls: 302 NOD, no cancer 1:2 matched, randomly selected | Mean age 61 years (cases) and 56 years (controls) 58% male in cases, 66% in controls | <2 years |
| Ben et al., European Journal of Cancer 2011 [23] | Shanghai, China, Hospital Data 2000–2009 | prospective case-control Cases: 1458 PDAC, of which 307 NOD Controls: 1:1 matched for time of admission, age, sex, sociodemographic variables, 1528 of which 88 NOD | Mean age 62 years 67% male | <2 years |
| Liao et al., Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012 [24] | Taiwan, National Health Insurance 1998–2007 | Retrospective cohort, entire population, nested case-control: Cases: all DM, of which 6911 had NOD, and 19 PDAC Controls: No DM, 1:4 matched for age and sex, randomly selected | Mean age of 55.9 years 54% male, Obesity 2.43% | <2 years |
| Tseng et al., Pancreas 2013 [25] | Taiwan, National Health Insurance 2005–2006 | Retrospective cohort, general population, random sample including 29,236 NOD and of those 32 PDAC | 48.5% male | Groups 1, 3 or >3 years |
| Lipworth et al., Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews 2011 [26] | Milan, Italy 1983–1992; 1991–2008 | Combined data from two prospective case-control studies, hospital population, convenience sample, including 51 PDAC/NOD cases and 39 NOD controls | Median age 55 years (controls), 63 years (cases) 63% resp. 53% male | Subgroup < 2 years |
| Lu et al., British Journal of Cancer 2015 [27] | UK, THIN Database 1996–2010 | Two retrospective cohorts from the general population NOD cohort 44,373, of which 175 had PDAC Control-cohort: 188,734 had no diabetes, of which 354 had PDAC | Mean age ~70 years (age groups) 58% male, 35% obesity, 23% current smokers | Groups 1, 2, 5, and >5 years |
| Müller et al., Pancreatology 2019 [28] | Great Britain, Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) 2004–2013 | retrospective case-control Cases: 588 PDAC and NOD Controls: 5486 NOD, 1:10, matched for age, sex, time DM diagnosis, follow up | Mean age ~70 years (age groups), 49.5% male, 28.7% BMI > 30, 18% current smokers | <2 years |
| Munigala et al., Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology 2015 [29] | St Louis, USA, Veterans’ Health Administration national medical care data sets 1998–2007 | Retrospective cohort, veterans, all without previous diagnosis of PDAC or DM, were included. 73,811 developed NOD, of which 183 had PDAC | Mean age 60.2 years, all < 40 years excluded by design 94% male, 74% white 46.8% obesity, 57% smoking | Groups 1, 2, 3, 4 years |
| Yuan et al., JAMA Oncology, 2020 [30] | USA Nurses’ Health Study (NHS), baseline 1978, Health Professionals Follow-Up Study (HPFS), baseline 1988 | Two retrospective cohorts, female nurses and male physicians, without previous diagnosis of PDAC or DM. Within the patients with NOD, 67 PDAC cases were observed. | Mean age 69 years White 93.3%, Black 3.5% Obesity 43% Ever-smokers 56% | <4 years |
| Bosetti et al., Annals of Oncology 2014 [31] | International, USA, Canada, Greece, Central Europe, Italy, Australia, 1983–2012 | Combined data from 15 case-control studies Cases: PDAC Controls: hospital/hospital visitors/populationNOD subgroup; including 525 NOD/PDAC cases | Not published for NOD subgroup | Groups < 1 years, 1–2, 2–5, >5 |
| Illés et al., Pancreatology, 2016 [19] | Szeged, Hungary 2012–2014 | Prospectively recruited, 108 patients with NOD, of which 3 had PDAC | Mean age 58 years 42.6% male, mean BMI 30.5, 29% ever smoker | <3 years |
| Chari et al., Gastroenterology 2005 [32] | Rochester, USA 1950–1994 | Cohort of 2122 NOD including 18 PDAC with nested case-control: Cases: NOD with PDAC, 18 cases Controls: NOD, 1:4 matched for age, sex, time of diabetes diagnosis, 72 controls | All < 50 years excluded by design No demographic data on cohort | <3 years |
| Hart et al., Pancreas 2011 [33] | Rochester, USA 1981–2007 | Retrospective case-control, 29 Cases: all NOD and PDAC in a 120-mile radius of Rochester 43 Controls: NOD matched for sex and age | Mean age 76 years cases, 72 years controls, 37% male cases, 56% controls | <3 years |
| Huang et al., Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2020 [34] | Kaiser Permanente Southern California, USA (KPSC, Insurance) 2006–2016 | Retrospective cohorts, all with sufficient data and without previous diagnosis of PDAC, were included. 110,699 NOD, of which 306 with PDAC | All < 45 years were excludedMean age 59 years, Male 52% Whites (44%), Hispanics (37%), Asians (15%) Blacks (15%). | <3 years |
| Sharma et al., Gastroenterology 2018 [35] | Rochester, USA, Rochester Epidemiology Project (REP) 2000–2015 | Retrospectively collected data from 4 independent cohorts, with 64 PDAC/NOD and 192 NOD-Controls in the discovery set, and a cohort of 1096 NOD, including 9 PDAC in the validation set | All < 50 years were excluded Mean age 65.6 years, 50% male | <3 years |
| Chen et al., Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2021 [36] | Kaiser Permanente Southern California, USA (KPSC, Insurance) 2010–2014 | Retrospective cohort of all patients without previous diagnosis of PDAC, meeting NOD criteria during the enrolment period, 13,947 NOD including 99 PDAC | All < 50 years were excluded No PDAC: 64.1 years, 48% male, 91 kg, PDAC: 69.2 years, 57% male, 84.4 kg | <3 years |
| Molina-Montes et al., Gut, 2021 [37] | PanGenEU, Europe, 28 centers from Spain, Italy, UK, Ireland, Germany, Sweden 2007–2014 | Retrospective case-control, we used only data from the subgroup with NOD, with general population as control. Data on long-standing diabetes was ignored. It included 200 cases of PDAC/NOD | 63.4% male, mean age ~65 years (age groups), 30.5% obese | <2 years |
| Khan, Pancreatology, 2021 [38] | TrinetX—Validation of ENDPAC | Retrospective cohort of 15,539 NOD patients, of which 48 had PDAC | <50 years excluded by design PDAC 68 years, 54% male, 81% white, 39% smokers No PDAC, 67 years, 50% male, 76% white, 21% smokers | <3 years |
| Khan, Pancreas, 2021 [39] | TrinetX—validation of Boursi | Retrospective cohort of 27,893 NOD patients, of which 52 had PDAC | <35 years excluded by design PDAC 74 years, No PDAC 64 years | <3 years |
| Ullah, BMC Cancer, 2021 [40] | EL-PaC-Epidem London, UK 2008–2020 | Case-Control study, 965 PDAC, 3963 Non-malignant pancreatic disease, 4355 Controls | Mean age 55.1, 51% male, 54.4% white | Groups 1,2,3 years |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mellenthin, C.; Balaban, V.D.; Dugic, A.; Cullati, S. Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4684. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194684
Mellenthin C, Balaban VD, Dugic A, Cullati S. Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4684. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194684
Chicago/Turabian StyleMellenthin, Claudia, Vasile Daniel Balaban, Ana Dugic, and Stephane Cullati. 2022. "Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4684. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194684
APA StyleMellenthin, C., Balaban, V. D., Dugic, A., & Cullati, S. (2022). Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 14(19), 4684. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194684