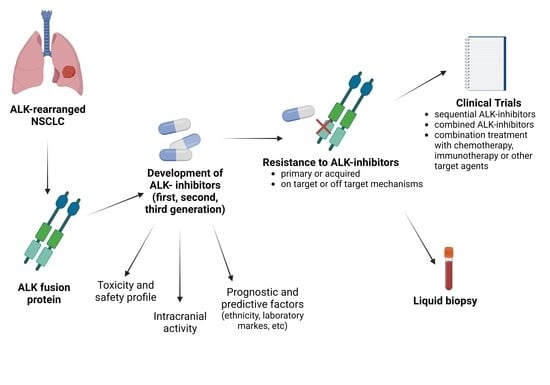
The Landscape of ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Clinicopathologic, Genomic Characteristics, and Therapeutic Perspectives
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Oncogenic ALK Mutations: Insight into Molecular Alterations
3. ALK-TKIs: Current Approvals and Daily Clinical Practice
3.1. Crizotinib
3.2. Ceritinib
3.3. Alectinib
3.4. Brigatinib
3.5. Ensartinib
3.6. Lorlatinib
3.7. ALK-i Safety and Toxicity
3.8. Treatment Sequence with ALK-i: A Challenge
4. Prognostic and Predictive Factors in Patients Treated with ALK-i
4.1. Role of Ethnicity
4.2. Inflammatory and Nutritional Laboratory Markers
5. Mechanisms of Resistance to ALK-i
5.1. On-Target Resistance Mechanisms
5.2. Off-Target Resistance Mechanisms
6. Current and Future Applications of Liquid Biopsy in ALK-Rearranged NSCLC
6.1. Cancer Detection and Characterization
6.2. Monitoring Response to Treatment
7. Combination Treatment Strategies and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeage, M.J.; Tin Tin, S.; Khwaounjoo, P.; Sheath, K.; Dixon-McIver, A.; Ng, D.; Sullivan, R.; Cameron, L.; Shepherd, P.; Laking, G.R.; et al. Screening for Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Gene Rearrangements in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in New Zealand. Intern. Med. J. 2020, 50, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.C.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, B.; Croix, D.; Abraham, A.; Redpath, S.; Engstrom-Melynk, J.; Shah, R.; Madala, J.; Bernicker, E.H. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Rearrangement Prevalence in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the United States: Retrospective Real World Data. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangachari, D.; Yamaguchi, N.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Folch, E.; Mahadevan, A.; Floyd, S.R.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Wong, E.T.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Huberman, M.S.; et al. Brain Metastases in Patients with EGFR-Mutated or ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancers. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesinger, F.; Roeper, J.; Pöttgen, C.; Willborn, K.C.; Eberhardt, W.E.E. Brain Metastases in ALK-Positive NSCLC—Time to Adjust Current Treatment Algorithms. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B. First-Line Treatment Options for ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, R. Drug Resistance in Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a Kinase Gene, ALK, to a Nucleolar Protein Gene, NPM, in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, B.; Luu, A.; Jones, R.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. The Function and Therapeutic Targeting of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer 2018, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, G.E.; Kuo, A.; Aigner, A.; Sunitha, I.; Souttou, B.; Malerczyk, C.; Caughey, D.J.; Wen, D.; Karavanov, A.; Riegel, A.T.; et al. Identification of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase as a Receptor for the Growth Factor Pleiotrophin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16772–16779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoica, G.E.; Kuo, A.; Powers, C.; Bowden, E.T.; Sale, E.B.; Riegel, A.T.; Wellstein, A. Midkine Binds to Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) and Acts as a Growth Factor for Different Cell Types. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35990–35998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnyak, A.V.; Murray, P.B.; Shi, X.; Mo, E.S.; Mohanty, J.; Tome, F.; Bai, H.; Gunel, M.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J. Augmentor α and β (FAM150) Are Ligands of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinases ALK and LTK: Hierarchy and Specificity of Ligand-Receptor Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15862–15867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.Y.; Ouyang, T.; Miething, C.; Morris, S.W.; Peschel, C.; Duyster, J. Nucleophosmin-Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Associated with Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma Activates the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Antiapoptotic Signaling Pathway. Blood 2000, 96, 4319–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagimura, N.; Takeuchi, S.; Fukuda, K.; Arai, S.; Tanimoto, A.; Nishiyama, A.; Ogo, N.; Takahashi, H.; Asai, A.; Watanabe, S.; et al. STAT3 Inhibition Suppresses Adaptive Survival of ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer Cells through Transcriptional Modulation of Apoptosis. Npj Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliss, R.; Choi, J.; Fennell, D.A.; Fry, A.M.; Richards, M.W. Molecular Mechanisms That Underpin EML4-ALK Driven Cancers and Their Response to Targeted Drugs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1209–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H. The Role of the ALK Receptor in Cancer Biology. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, iii4–iii15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollmann, M.; Parwaresch, R.; Adam-Klages, S.; Kruse, M.L.; Buck, F.; Heidebrecht, H.J. Human EML4, a Novel Member of the EMAP Family, Is Essential for Microtubule Formation. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 3241–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.I.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the Transforming EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Oya, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Shimizu, J.; Horio, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Sakao, Y.; Hida, T.; Yatabe, Y. Differential Crizotinib Response Duration among ALK Fusion Variants in ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3383–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Nagasaka, M.; Zhu, V.W.; Ou, S.H.I.; Soo, R.A. How to Select the Best Upfront Therapy for Metastatic Disease? Focus on ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2521–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbour, K.C.; Riely, G.J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2017, 31, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shao, Y.; Qin, H.F.; Tai, Y.H.; Gao, H.J. ALK-Rearrangement in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-Line Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in ALK -Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, I.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Palmer, J.D.; Mehra, R.; Lu, B. Targeting Brain Metastases in ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e510–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.J.; et al. First-Line Ceritinib versus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ASCEND-4): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takanashi, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Kondoh, O.; Sakamoto, H. Antitumor Activity of the Selective ALK Inhibitor Alectinib in Models of Intracranial Metastases. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK -Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.J.; Yang, J.C.H.; Han, J.Y.; Hochmair, M.J.; Lee, K.H.; Delmonte, A.; Garcia Campelo, M.R.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Brigatinib Versus Crizotinib in ALK Inhibitor–Naive Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC: Final Results of Phase 3 ALTA-1L Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 2091–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Akimoto, K.; Sato, H.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Homma, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; et al. Brigatinib and Alectinib for ALK Rearrangement-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with or without Central Nervous System Metastasis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.; Poddubskaya, E.; Mok, T.; Reck, M.; Wakelee, H.; Chiappori, A.A.; Lee, D.H.; Breder, V.; et al. Ensartinib vs. Crizotinib for Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Lorlatinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popat, S.; Brustugun, O.T.; Cadranel, J.; Felip, E.; Garassino, M.C.; Griesinger, F.; Helland, Å.; Hochmair, M.; Pérol, M.; Bent-Ennakhil, N.; et al. Real-World Treatment Outcomes with Brigatinib in Patients with Pretreated ALK+ Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2021, 157, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descourt, R.; Pérol, M.; Rousseau-Bussac, G.; Planchard, D.; Mennecier, B.; Wislez, M.; Cadranel, J.; Cortot, A.B.; Guisier, F.; Galland, L.; et al. Brigatinib for Pretreated, ALK-Positive, Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancers: Long-Term Follow-Up and Focus on Post-Brigatinib Lorlatinib Efficacy in the Multicenter, Real-World BrigALK2 Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.; Bauer, T.M.; De Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. LBA2 Lorlatinib vs. Crizotinib in the First-Line Treatment of Patients (Pts) with Advanced ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Results of the Phase III CROWN Study. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1180–S1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib or Crizotinib in Advanced ALK -Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Ding, K.-L.; Liu, Y.-F.; Zhao, W.-J.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Chang, X.-S.; Chen, Y.-D.; Xiao, Z.-Z.; Yu, Y.-Y.; et al. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of First-Line Treatments for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with ALK-Rearranged: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunta, E.F.; Signori, A.; West, H.J.; Metro, G.; Friedlaender, A.; Parikh, K.; Banna, G.L.; Addeo, A. Beyond Crizotinib: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors as First-Line Treatment for ALK-Translocated Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 921854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.J.; Yang, J.C.H.; Han, J.Y.; Hochmair, M.J.; Lee, K.H.; Delmonte, A.; García Campelo, M.R.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Brigatinib Versus Crizotinib in Advanced ALK Inhibitor–Naive ALK-Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Second Interim Analysis of the Phase III ALTA-1L Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3592–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Nokihara, H.; Kondo, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Azuma, K.; Seto, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Yoshioka, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Patients with ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (J-ALEX): An Open-Label, Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Kim, S.W.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, J.J.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Bu, L.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated Asian Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ALESIA): A Randomised Phase 3 Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Yoshida, T.; Kumagai, T.; Hida, T.; Toyozawa, R.; Shimokawaji, T.; Goto, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Ohe, Y.; Seto, T.; et al. Brigatinib in Japanese Patients With ALK-Positive NSCLC Previously Treated With Alectinib and Other Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Outcomes of the Phase 2 J-ALTA Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.L.; Chen, H.L.; Tsai, Y.M.; Lee, T.H.; Chang, H.M.; Tsai, Y.C.; Chuang, C.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Tu, Y.K.; Yang, C.J.; et al. First-Line Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (Alk) Inhibitors for Alk-Positive Lung Cancer in Asian Populations: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenci, E.; Cantini, L.; Pecci, F.; Cognigni, V.; Agostinelli, V.; Mentrasti, G.; Lupi, A.; Ranallo, N.; Paoloni, F.; Rinaldi, S.; et al. The Gustave Roussy Immune (GRIm)-Score Variation Is an Early-on-Treatment Biomarker of Outcome in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients Treated with First-Line Pembrolizumab. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banna, G.L.; Cortellini, A.; Cortinovis, D.L.; Tiseo, M.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Barbieri, F.; Giusti, R.; Bria, E.; Grossi, F.; Pizzutilo, P.; et al. The Lung Immuno-Oncology Prognostic Score (LIPS-3): A Prognostic Classification of Patients Receiving First-Line Pembrolizumab for PD-L1 ≥ 50% Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xing, P.; Hao, X.; Li, J. Clinical Value of Serum Albumin Level in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Rearrangement. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 12403–12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, G.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. The Value of Blood Biomarkers of Progression and Prognosis in ALK-Positive Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Crizotinib. Asia. Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Hong, L.; Sun, L.; Zhuang, H.; Sun, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X. Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio Is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients with ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Futur. Oncol. 2017, 13, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucà, G.; Beninato, T.; Bini, M.; Mazzeo, L.; Di Guardo, L.; Cimminiello, C.; Randon, G.; Apollonio, G.; Bisogno, I.; Del Vecchio, M.; et al. The Pan-Immune-Inflammation Value in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma Receiving First-Line Therapy. Target. Oncol. 2021, 16, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligorio, F.; Fucà, G.; Zattarin, E.; Lobefaro, R.; Zambelli, L.; Leporati, R.; Rea, C.; Mariani, G.; Bianchi, G.V.; Capri, G.; et al. The Pan-Immune-Inflammation-Value Predicts the Survival of Patients with Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (Her2)—Positive Advanced Breast Cancer Treated with First-Line Taxane-Trastuzumab-Pertuzumab. Cancers 2021, 13, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hong, X.; Chen, G.; Xue, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, F.; Ali, W.A.; Dullah, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. The Pan-Immune-Inflammation Value Predicts the Survival of Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with First-Line ALK Inhibitor. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 17, 101338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Yamada, T.; Tanimura, K.; Nakano, T.; Ishida, M.; Tachibana, Y.; Shiotsu, S.; Horiuchi, S.; Hibino, M.; Okada, A.; et al. Prognostic Markers of Survival among Japanese Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Receiving First-Line Alectinib. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Moran, J.P.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Folch, E.; Majid, A.; Kent, M.S.; Gangadharan, S.P.; Rangachari, D.; Huberman, M.S.; et al. De Novo ALK Kinase Domain Mutations Are Uncommon in Kinase Inhibitor-Naïve ALK Rearranged Lung Cancers. Lung Cancer 2016, 99, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Riely, G.J.; Shaw, A.T. Targeting ALK: Precision Medicine Takes on Drug Resistance. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolle, E.; Taucher, V.; Lindenmann, J.; Jost, P.J.; Pichler, M. Current Knowledge about Mechanisms of Drug Resistance against ALK Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Yu, R.; Bao, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Shao, Y.; et al. Real-World Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis Depicts Resistance Mechanism and Clonal Evolution in ALK Inhibitor-Treated Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, R.; Shaw, A.T.; Khan, T.M.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Solomon, B.J.; Halmos, B.; Jessop, N.A.; Wain, J.C.; Yeo, A.T.; Benes, C.; et al. Cancer: Mechanisms of Acquired Crizotinib Resistance in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 120ra17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagitani, N.; Uchibori, K.; Koike, S.; Tsukahara, M.; Kitazono, S.; Yoshizawa, T.; Horiike, A.; Ohyanagi, F.; Tambo, Y.; Nishikawa, S.; et al. Drug Resistance Mechanisms in Japanese Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer and the Clinical Responses Based on the Resistant Mechanisms. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK -Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, V.W.; Nagasaka, M.; Madison, R.; Schrock, A.B.; Cui, J.; Ou, S.H.I. A Novel Sequentially Evolved EML4-ALK Variant 3 G1202R/S1206Y Double Mutation In Cis Confers Resistance to Lorlatinib: A Brief Report and Literature Review. JTO Clin. Res. Reports 2021, 2, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.Y.; Friboulet, L.; Kodack, D.P.; Engstrom, L.D.; Li, Q.; West, M.; Tang, R.W.; Wang, H.; Tsaparikos, K.; Wang, J.; et al. PF-06463922, an ALK/ROS1 Inhibitor, Overcomes Resistance to First and Second Generation ALK Inhibitors in Preclinical Models. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Recondo, G.; Mezquita, L.; Facchinetti, F.; Planchard, D.; Gazzah, A.; Bigot, L.; Rizvi, A.Z.; Frias, R.L.; Thiery, J.P.; Scoazec, J.Y.; et al. Diverse Resistance Mechanisms to the Third-Generation ALK Inhibitor Lorlatinib in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Koivunen, J.; Ogino, A.; Yanagita, M.; Nikiforow, S.; Zheng, W.; Lathan, C.; Marcoux, J.P.; Du, J.; Okuda, K.; et al. A Novel ALK Secondary Mutation and EGFR Signaling Cause Resistance to ALK Kinase Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6051–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, T.; Ozasa, H.; Aoki, W.; Aburaya, S.; Funazo, T.; Furugaki, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Ajimizu, H.; Okutani, R.; Yasuda, Y.; et al. Alectinib Resistance in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer by Dual Salvage Signaling in a Clinically Paired Resistance Model. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Filho, S.N.M.; Li, M.; Fares, A.; Weiss, J.; Pham, N.A.; Ludkovski, O.; Raghavan, V.; Li, Q.; Ravi, D.; et al. BRAF V600E Mutation and MET Amplification as Resistance Pathways of the Second-Generation Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibitor Alectinib in Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 146, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Ou, Q.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Ding, Y.; Shao, Y.W.; Lu, S. Concomitant Resistance Mechanisms to Multiple Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiho, T.; Nakajima, T.; Iwasawa, S.; Yonemori, Y.; Yoshino, I. ALK Rearrangement Adenocarcinoma with Histological Transformation to Squamous Cell Carcinoma Resistant to Alectinib and Ceritinib. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2020, 13, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.H.I.; Lee, T.K.; Young, L.; Fernandez-Rocha, M.Y.; Pavlick, D.; Schrock, A.B.; Zhu, V.W.; Milliken, J.; Ali, S.M.; Gitlitz, B.J. Dual Occurrence of ALK G1202R Solvent Front Mutation and Small Cell Lung Cancer Transformation as Resistance Mechanisms to Second Generation ALK Inhibitors without Prior Exposure to Crizotinib. Pitfall of Solely Relying on Liquid Re-Biopsy? Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Van Derwekken, A.J.; Saber, A.; Terpstra, M.M.; Schuuring, E.; Timens, W.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Groen, H.J.M.; Van Den Berg, A.; Kok, K. Mutations in EMT-Related Genes in ALK Positive Crizotinib Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Cancers 2018, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating Liquid Biopsies into the Management of Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.C.M.; Massie, C.; Garcia-Corbacho, J.; Mouliere, F.; Brenton, J.D.; Caldas, C.; Pacey, S.; Baird, R.; Rosenfeld, N. Liquid Biopsies Come of Age: Towards Implementation of Circulating Tumour DNA. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, H.; Velculescu, V.E. Cancer DNA in the Circulation. JAMA 2017, 318, 1272–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Chabner, B.A. Application of Cell-Free DNA Analysis to Cancer Treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Ritterhouse, L.L. The Role of Plasma Genotyping in ALK- And ROS1-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2557–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volckmar, A.L.; Sültmann, H.; Riediger, A.; Fioretos, T.; Schirmacher, P.; Endris, V.; Stenzinger, A.; Dietz, S. A Field Guide for Cancer Diagnostics Using Cell-Free DNA: From Principles to Practice and Clinical Applications. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2018, 57, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzer, E.; Haque, I.S.; Roberts, C.E.S.; Speicher, M.R. Current and Future Perspectives of Liquid Biopsies in Genomics-Driven Oncology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Aisner, D.L.; Arcila, M.E.; Beasley, M.B.; Bernicker, E.H.; Colasacco, C.; Dacic, S.; Hirsch, F.R.; Kerr, K.; et al. Updated molecular testing guideline for the selection of lung cancer patients for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Guideline from the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 323–358. [Google Scholar]
- Rolfo, C.; Mack, P.C.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Baas, P.; Barlesi, F.; Bivona, T.G.; Herbst, R.S.; Mok, T.S.; Peled, N.; Pirker, R.; et al. Liquid Biopsy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Statement Paper from the IASLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1248–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, P.; Li, B.T.; Brown, D.N.; Jung, B.; Hubbell, E.; Shen, R.; Abida, W.; Juluru, K.; De Bruijn, I.; Hou, C.; et al. High-Intensity Sequencing Reveals the Sources of Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Variants. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, P. Detecting Resistance to Therapeutic Alk Inhibitors in Tumor Tissue and Liquid Biopsy Markers: An Update to a Clinical Routine Practice. Cells 2021, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezquita, L.; Hu, Y.; Howarth, K.; Jovelet, C.; Planchard, D.; Lacroix, L.; Swalduz, A.; Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Avrillon, V.; Plagnol, V.; et al. Abstract 4581: Feasibility of an Amplicon-Based Liquid Biopsy for ALK and ROS1 Fusions in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Whisenant, J.G.; Wakelee, H.; Reckamp, K.L.; Qiao, H.; Leal, T.A.; Du, L.; Hernandez, J.; Huang, V.; Blumenschein, G.R.; et al. Monitoring Therapeutic Response and Resistance: Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA in Patients With ALK+ Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoach, C.E.; Blakely, C.M.; Banks, K.C.; Levy, B.; Chue, B.M.; Raymond, V.M.; Le, A.T.; Lee, C.E.; Diaz, J.; Waqar, S.N.; et al. Clinical Utility of Cell-Free DNA for the Detection of ALK Fusions and Genomic Mechanisms of ALK Inhibitor Resistance in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2758–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Brannon, A.R.; Ferris, L.A.; Campbell, C.D.; Lin, J.J.; Schultz, K.R.; Ackil, J.; Stevens, S.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; et al. Tracking the Evolution of Resistance to ALK Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Through Longitudinal Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Noe, J.; Nowicka, M.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Cheema, P.; Pavlakis, N.; de Marinis, F.; et al. Updated Efficacy and Safety Data and Impact of the EML4-ALK Fusion Variant on the Efficacy of Alectinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Global Phase III ALEX Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Peters, S.; Alexander, J.A.A.; Leighl, N.B.; Sriuranpong, V.; Perol, M.; De Castro, G.; Nadal, E.; De Marinis, F.; et al. Phase II/III Blood First Assay Screening Trial (BFAST) in Patients (Pts) with Treatment-Naïve NSCLC: Initial Results from the ALK+ Cohort. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Martini, J.-F.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Soo, R.A.; Riely, G.J.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Abbattista, A.; Toffalorio, F.; et al. Early Circulating Tumor (Ct)DNA Dynamics and Efficacy of Lorlatinib in Patients (Pts) with Advanced ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Lin, C.C.; Soo, R.A.; Riely, G.J.; Ignatius Ou, S.H.; Clancy, J.S.; Li, S.; et al. ALK Resistance Mutations and Efficacy of Lorlatinib in Advanced Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles, A.K.; Christopoulos, P.; Yuan, Z.; Bauer, S.; Janke, F.; Ogrodnik, S.J.; Reck, M.; Schlesner, M.; Meister, M.; Schneider, M.A.; et al. Early Identification of Disease Progression in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer Using Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis. npj Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Rooney, M.; Lin, J.J.; Nagy, R.J.; Yeap, B.Y.; Hubbeling, H.; Chin, E.; Ackil, J.; Farago, A.F.; Hata, A.N.; et al. Treatment with Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors Fuels Plasma ALK Mutation Diversity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6662–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zugazagoitia, J.; Gómez-Rueda, A.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; Isla, D.; Camps, C.; Ramos, I.; Trigo, J.M.; Bernabé, R.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Sanchez-Torres, J.M.; et al. Clinical Utility of Plasma-Based Digital next-Generation Sequencing in Oncogene-Driven Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance. Lung Cancer 2019, 134, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Herrero, E.; Serna-Blasco, R.; Ivanchuk, V.; García-Campelo, R.; Dómine Gómez, M.; Sánchez, J.M.; Massutí, B.; Reguart, N.; Camps, C.; Sanz-Moreno, S.; et al. NGS-Based Liquid Biopsy Profiling Identifies Mechanisms of Resistance to ALK Inhibitors: A Step toward Personalized NSCLC Treatment. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 2363–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, J.; Feng, J.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, W.; et al. Decoding the Evolutionary Response to Ensartinib in Patients With ALK-Positive NSCLC by Dynamic Circulating Tumor DNA Sequencing. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, M.; Sharma, G.G.; Manfroni, C.; Cortinovis, D.; Mologni, L. New Advances in Liquid Biopsy Technologies for Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (Alk)—Positive Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondaca, S.; Lebow, E.S.; Namakydoust, A.; Razavi, P.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Shen, R.; Offin, M.; Tu, H.Y.; Murciano-Goroff, Y.; Xu, C.; et al. Clinical Utility of Next-Generation Sequencing-Based CtDNA Testing for Common and Novel ALK Fusions. Lung Cancer 2021, 159, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigatinib and Bevacizumab for the Treatment of ALK-Rearranged Locally Advanced, Metastatic, or Recurrent NSCLC—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04227028 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Phase I/II Trial of Alectinib and Bevacizumab in Patients With Advanced, Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)-Positive, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02521051 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Kim, D.W.; Gadgeel, S.; Gettinger, S.N.; Riely, G.J.; Oxnard, G.R.; Mekhail, T.; Schmid, P.; Dowlati, A.; Heist, R.S.; Wozniak, A.J.; et al. Brief Report: Safety and Antitumor Activity of Alectinib Plus Atezolizumab From a Phase 1b Study in Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC. JTO Clin. Res. Reports 2022, 3, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study of Safety and Efficacy of Ceritinib in Combination With Nivolumab in Patients With ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02393625 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Study to Evaluate Safety, Efficacy, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Avelumab in Combination with Either Crizotinib or PF-06463922 In Patients With NSCLC. (Javelin Lung 101)—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02584634 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Study of Safety and Efficacy of Brigatinib Plus Chemotherapy or Brigatinib Only in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer (MASTERPROTOCOL ALK)—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05200481 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Ensartinib, Carboplatin, Pemetrexed and Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Stage IIIC or IV or Recurrent ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04837716 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- A Phase IB/II Study of Alectinib Combined With Cobimetinib in Advanced ALK-Rearranged (ALK+) NSCLC—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03202940 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Brigatinib and Binimetinib in Treating Patients With Stage IIIB-IV ALK or ROS1-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04005144 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Lorlatinib Combinations in Lung Cancer—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04292119 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- A Study of TPX-0131, a Novel Oral ALK Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients With ALK+ Advanced or Metastatic NSCLC—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04849273 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- A Study of NVL-655 in Patients With Advanced NSCLC and Other Solid Tumors Harboring ALK Rearrangement or Activating ALK Mutation (ALKOVE-1)—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05384626 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Ji, J.; Mitra, A.; Camidge, D.R.; Riess, J.W. Early Alectinib Resistance From MET Amplification in ALK-Rearranged NSCLC: Response to Crizotinib with Re-Response to Alectinib and Crizotinib. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, e851–e855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Garon, E.B.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Ponce Aix, S.; Paz-Ares, L.; Chiu, C.H.; Park, K.; Novello, S.; Nadal, E.; et al. Ramucirumab plus Erlotinib in Patients with Untreated, EGFR-Mutated, Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (RELAY): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Cui, Z.; Tao, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Cui, P.; Chen, S.; Huang, D.; Yang, B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Crizotinib plus Bevacizumab in ALK/ROS-1/c-MET Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: An Open-Label, Single-Arm, Prospective Observational Study. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 1526. [Google Scholar]
- Mazieres, J.; Drilon, A.; Lusque, A.; Mhanna, L.; Cortot, A.B.; Mezquita, L.; Thai, A.A.; Mascaux, C.; Couraud, S.; Veillon, R.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer and Oncogenic Driver Alterations: Results from the IMMUNOTARGET Registry. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanzeb, M.; Lin, H.M.; Pan, X.; Yin, Y.; Baumann, P.; Langer, C.J. Immunotherapy Treatment Patterns and Outcomes Among ALK-Positive Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Reynolds, C.; Waterhouse, D.; Garon, E.B.; Chandler, J.; Babu, S.; Thurmes, P.; Spira, A.; Jotte, R.; Zhu, J.; et al. Phase 1/2 Study of the Safety and Tolerability of Nivolumab Plus Crizotinib for the First-Line Treatment of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Translocation—Positive Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer (CheckMate 370). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felip, E.; de Braud, F.G.; Maur, M.; Loong, H.H.; Shaw, A.T.; Vansteenkiste, J.F.; John, T.; Liu, G.; Lolkema, M.P.; Selvaggi, G.; et al. Ceritinib plus Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of an Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase 1B Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 15, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.P.; Pakkala, S.; Pennell, N.A.; Reckamp, K.L.; Lanzalone, S.; Polli, A.; Tarazi, J.; Robert-Vizcarrondo, F. Phase Ib Study of Crizotinib plus Pembrolizumab in Patients with Previously Untreated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with ALK Translocation. Oncologist 2020, 25, 562-e1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, A.W.; Patel, S.; Boucher, K.; Cannon, L.; Esplin, M.; Luckart, J.; Graves, N.; Van Duren, T.; Akerley, W. Phase I Trial of Targeted EGFR or ALK Therapy with Ipilimumab in Metastatic NSCLC with Long-Term Follow-Up. Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kono, S.A.; Lu, X.; Okuyama, S.; Barón, A.E.; Oton, A.B.; Davies, A.M.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Franklin, W.; Doebele, R.C. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Gene Rearrangements in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Are Associated with Prolonged Progression-Free Survival on Pemetrexed. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.O.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.; Jeon, Y.K.; Chung, D.H.; Kim, W.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Yang, S.C.; et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Translocation: A Predictive Biomarker of Pemetrexed in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WJOG 14720L|NIPH Clinical Trials Search. Available online: https://rctportal.niph.go.jp/en/detail?trial_id=jRCTs041210103 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- A Study Evaluating Platinum-Pemetrexed-Atezolizumab (+/-Bevacizumab) for Patients With Stage IIIB/IV Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer With EGFR Mutations, ALK Rearrangement or ROS1 Fusion Progressing After Targeted Therapies—Full Text View—Clin. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04042558 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Study of Atezolizumab Combination Carboplatin + Paclitaxel + Bevacizumab in EGRF Mutation or ALK Translocation NSCLC—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03991403 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Pembrolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Chemotherapy for ALK-Rearranged NSCLC With Persistent 5′ALK—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05266846 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Voena, C.; Menotti, M.; Mastini, C.; Di Giacomo, F.; Longo, D.L.; Castella, B.; Merlo, M.E.B.; Ambrogio, C.; Wang, Q.; Minero, V.G.; et al. Efficacy of a Cancer Vaccine against ALK-Rearranged Lung Tumors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Clinical Trials with Angiogenesis Inhibitors and ALK-i | |||||||
| Trial Name | Intervention | Phase | Design | Center | Planned Participant Enrollment | Status | Primary Objective |
| NCT04227028 [95] | Brigatinib + Bevacizumab | I | Single group assignment, open label | Multicenter, 4 sites | 31 | Recruiting | Recommended dose, safety |
| NCT02521051 [96] | Alectinib + Bevacizumab | I/II | Single group assignment, open label | Multicenter, 2 sites | 43 | Recruiting | Recommended dose, safety |
| Clinical Trials with ICIs and ALK-i | |||||||
| Trial Name | Intervention | Phase | Design | Center | Planned Participant Enrollment | Status | Primary Objective |
| NCT02013219 [97] | Atezolizumab + Erlotinib or Alectinib | I | Non-randomized, sequential assignment, open label | Multicenter, 17 sites | 52 | Completed | Safety, recommended dose, pharmacokinetics |
| NCT02393625 [98] | Nivolumab + Ceritinib | I | Non-randomized, parallel assignment, open label | Multicenter, 11 sites | 57 | Active, not recruiting | MTD and/or recommended dose for expansion, overall response rate |
| NCT02584634 [99] | Avelumab + Erlotinib or Lorlatinib | I/II | Non-randomized, open label | Multicenter, 21 sites | 43 | Active, not recruiting | DLTs, ORR, CR |
| Clinical Trials with Chemotherapy and ALK-i | |||||||
| Trial Name | Intervention | Phase | Design | Center | Planned Participant Enrollment | Status | Primary Objective |
| NCT05200481 [100] | Carboplatin + Pemetrexed + Brigatinib | II | Randomized, open label, non-comparative | Multicenter, 30 sites | 110 | Recruiting | PFS, OS, ORR |
| NCT04837716 [101] | Carboplatin + Pemetrexed + Bevacizumab + Ensartinib | I | Single group assignment, open label | Single center | 12 | Recruiting | Safety, recommended dose |
| Clinical Trials with MEK Inhibitors and ALK-i | |||||||
| Trial Name | Intervention | Phase | Design | Center | Planned Participant Enrollment | Status | Primary Objective |
| NCT03202940 [102] | Alectinib + Cobimetinib | I/II | Single group assignment, open label | Single center | 31 | Recruiting | MTD |
| NCT04005144 [103] | Brigatinib + Binimetinib | I | Single group assignment, open label | Single center | 18 | Recruiting | Safety, tolerability |
| Clinical Trials with ALK-i Combination | |||||||
| Trial Name | Intervention | Phase | Design | Center | Planned Participant Enrollment | Status | Primary Objective |
| NCT04292119 [104] | Lorlatinib + Crizotinib or Binimetinib, or TNO155 | Ib/II | Non-randomized, parallel assignment, open label | Multicenter, 2 sites | 96 | Recruiting | MTD, ORR |
| Clinical Trials with Novel Oral ALK-i | |||||||
| Trial Name | Intervention | Phase | Design | Center | Planned Participant Enrollment | Status | Primary Objective |
| NCT04849273 [105] | TPX-0131 | I/II | Single group assignment, open label | Multicenter, 15 sites | 210 | Recruiting | Safety, recommended dose, overall response rate |
| NCT05384626 [106] | NVL-655 | I/II | Non-randomized, open label, sequential assignment | Multicenter, 6 sites | 214 | Recruiting | DLTs, RP2D, ORR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cognigni, V.; Pecci, F.; Lupi, A.; Pinterpe, G.; De Filippis, C.; Felicetti, C.; Cantini, L.; Berardi, R. The Landscape of ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Clinicopathologic, Genomic Characteristics, and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 4765. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194765
Cognigni V, Pecci F, Lupi A, Pinterpe G, De Filippis C, Felicetti C, Cantini L, Berardi R. The Landscape of ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Clinicopathologic, Genomic Characteristics, and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4765. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194765
Chicago/Turabian StyleCognigni, Valeria, Federica Pecci, Alessio Lupi, Giada Pinterpe, Chiara De Filippis, Cristiano Felicetti, Luca Cantini, and Rossana Berardi. 2022. "The Landscape of ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Clinicopathologic, Genomic Characteristics, and Therapeutic Perspectives" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4765. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194765
APA StyleCognigni, V., Pecci, F., Lupi, A., Pinterpe, G., De Filippis, C., Felicetti, C., Cantini, L., & Berardi, R. (2022). The Landscape of ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Clinicopathologic, Genomic Characteristics, and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers, 14(19), 4765. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194765