Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate Metabolism as a Surrogate for Tumor Grade and Poor Outcome in Renal Cell Carcinoma—A Proof of Principle Study
Abstract
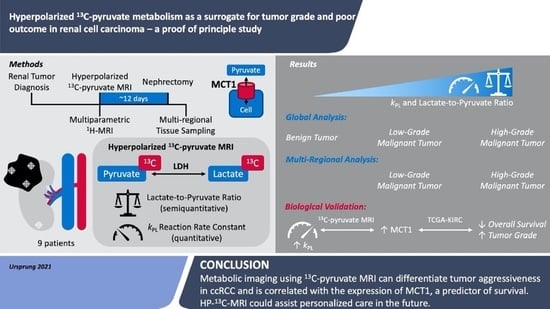
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment and Ethics
2.2. Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate MRI Acquisition
2.3. 13C-MRI Data Analysis
2.4. Proton (1H) MRI
2.5. D-Printed Patient Specific Tumor Molds
2.6. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.7. TCGA-KIRC Data
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Hyperpolarized 13C-MRI
3.3. Immunohistochemistry
3.4. TCGA-KIRC RNA Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Cheville, J.C.; Lohse, C.M.; Zincke, H.; Weaver, A.L.; Blute, M.L. Comparisons of Outcome and Prognostic Features Among Histologic Subtypes of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungberg, B.; Albiges, L.; Abu-Ghanem, Y.; Bensalah, K.; Dabestani, S.; Montes, S.F.P.; Giles, R.H.; Hofmann, F.; Hora, M.; Kuczyk, M.A.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2019 Update. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumundsson, E.; Hellborg, H.; Lundstam, S.; Erikson, S.; Ljungberg, B. Metastatic potential in renal cell carcinomas <7 cm: Swedish kidney cancer quality register data. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, L.; Dabestani, S.; Lam, T.B.; Hofmann, F.; Stewart, F.; Norrie, J.; Bex, A.; Bensalah, K.; Canfield, S.E.; Hora, M.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumour biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahunt, B.; Cheville, J.C.; Martignoni, G.; Humphrey, P.A.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; McKenney, J.; Egevad, L.; Algaba, F.; Moch, H.; Grignon, D.J.; et al. The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading system for renal cell carcinoma and other prognostic parameters. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 1490–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dagher, J.; Delahunt, B.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Egevad, L.; Srigley, J.R.; Coughlin, G.; Dunglinson, N.; Gianduzzo, T.; Kua, B.; Malone, G.; et al. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Validation of World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology grading. Histopathology 2017, 71, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, A.; Ricciardi, C.; Cuocolo, R.; Romeo, V.; Petrone, J.; Sarnataro, M.; Mainenti, P.P.; Improta, G.; De Rosa, F.; Insabato, L.; et al. MRI Radiomics for the Prediction of Fuhrman Grade in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Machine Learning Exploratory Study. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursprung, S.; Beer, L.; Bruining, A.; Woitek, R.; Stewart, G.D.; Gallagher, F.A.; Sala, E. Radiomics of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in renal cell carcinoma—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linehan, W.M.; Srinivasan, R.; Schmidt, L.S. The genetic basis of kidney cancer: A metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, M.L.; Jaeger, E.; Shi, Y.; Durocher, J.A.; Mahurkar, S.; Zaridze, D.; Matveev, V.; Janout, V.; Kollarova, H.; Bencko, V.; et al. Improved Identification of von Hippel-Lindau Gene Alterations in Clear Cell Renal Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4726–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wettersten, H.I.; Hakimi, A.A.; Morin, D.; Bianchi, C.; Johnstone, M.E.; Donohoe, D.R.; Trott, J.F.; Abu Aboud, O.; Stirdivant, S.; Neri, B.; et al. Grade-dependent metabolic reprogramming in kidney cancer revealed by combined proteomics and metabolomics analysis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2541–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, L.; Guigonis, J.M.; Borchiellini, D.; Durand, M.; Pourcher, T.; Ambrosetti, D. LC-MS based metabolomic profiling for renal cell carcinoma histologic subtypes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witney, T.H.; Kettunen, M.I.; Day, S.E.; Hu, D.; Neves, A.A.; Gallagher, F.A.; Fulton, S.M.; Brindle, K.M. A comparison between radiolabeled fluorodeoxyglucose uptake and hyperpolarized 13C-labeled pyruvate utilization as methods for detecting tumor response to treatment. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaccagna, F.; Grist, J.T.; Deen, S.S.; Woitek, R.; Lechermann, L.M.; McLean, M.A.; Basu, B.; Gallagher, F.A. Hyperpolarized carbon-13 magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging: A clinical tool for studying tumour metabolism. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woitek, R.; McLean, M.A.; Gill, A.B.; Grist, J.T.; Provenzano, E.; Patterson, A.J.; Ursprung, S.; Torheim, T.; Zaccagna, F.; Locke, M.; et al. Hyperpolarized 13C MRI of Tumor Metabolism Demonstrates Early Metabolic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2020, 2, e200017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, M.J.; Bok, R.; Chen, A.P.; Cunningham, C.H.; Zierhut, M.L.; Zhang, V.Y.; Kohler, S.J.; Tropp, J.; Hurd, R.E.; Yen, Y.F.; et al. Hyperpolarized 13C lactate, pyruvate, and alanine: Noninvasive biomarkers for prostate cancer detection and grading. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8607–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grist, J.T.; McLean, M.A.; Riemer, F.; Schulte, R.F.; Deen, S.S.; Zaccagna, F.; Woitek, R.; Daniels, C.J.; Kaggie, J.D.; Matyz, T.; et al. Quantifying normal human brain metabolism using hyperpolarized [1–13C]pyruvate and magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 2019, 189, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C.H.; Lau, J.Y.C.; Chen, A.P.; Geraghty, B.J.; Perks, W.J.; Roifman, I.; Wright, G.A.; Connelly, K.A. Hyperpolarized 13 C Metabolic MRI of the Human Heart. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, F.A.; Woitek, R.; McLean, M.A.; Gill, A.B.; Garcia, R.M.; Provenzano, E.; Riemer, F.; Kaggie, J.; Chhabra, A.; Ursprung, S.; et al. Imaging breast cancer using hyperpolarized carbon-13 MRI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2092–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, S.; Meng, M.V.; Slater, J.B.; Gordon, J.W.; Vigneron, D.B.; Stohr, B.A.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Wang, Z.J. Metabolic imaging with hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate magnetic resonance imaging in patients with renal tumors—Initial experience. Cancer 2021, 127, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felmlee, M.A.; Jones, R.S.; Rodriguez-Cruz, V.; Follman, K.E.; Morris, M.E. Monocarboxylate transporters (SLC16): Function, regulation, and role in health and disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 466–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granlund, K.L.; Tee, S.S.; Vargas, H.A.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Reznik, E.; Fine, S.; Laudone, V.; Eastham, J.A.; Touijer, K.A.; Reuter, V.E.; et al. Hyperpolarized MRI of Human Prostate Cancer Reveals Increased Lactate with Tumor Grade Driven by Monocarboxylate Transporter 1. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creighton, C.J.; Morgan, M.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Wheeler, D.A.; Gibbs, R.A.; Robertson, G.; Chu, A.; Beroukhim, R.; Cibulskis, K.; Signoretti, S.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature 2013, 499, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiesinger, F.; Weidl, E.; Menzel, M.I.; Janich, M.A.; Khegai, O.; Glaser, S.J.; Haase, A.; Schwaiger, M.; Schulte, R.F. IDEAL spiral CSI for dynamic metabolic MR imaging of hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Autry, A.W.; Brender, J.R.; Kishimoto, S.; Krishna, M.C.; Vareth, M.; Bok, R.A.; Reed, G.D.; Carvajal, L.; Gordon, J.W.; et al. Tensor image enhancement and optimal multichannel receiver combination analyses for human hyperpolarized 13C MRSI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 3351–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khegai, O.; Schulte, R.F.; Janich, M.A.; Menzel, M.I.; Farrell, E.; Otto, A.M.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Glaser, S.J.; Haase, A.; Schwaiger, M.; et al. Apparent rate constant mapping using hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate. NMR Biomed. 2014, 27, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Gehrung, M.; Ursprung, S.; Gill, A.B.; Warren, A.Y.; Beer, L.; Gallagher, F.A.; Mitchell, T.J.; Mendichovszky, I.A.; Priest, A.N.; et al. Three-Dimensional Printed Molds for Image-Guided Surgical Biopsies: An Open Source Computational Platform. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2020, 4, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshari, K.R.; Sriram, R.; Koelsch, B.L.; Van Criekinge, M.; Wilson, D.M.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Wang, Z.J. Hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate magnetic resonance reveals rapid lactate export in metastatic renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sriram, R.; Van Criekinge, M.; Santos, J.D.; Keshari, K.R.; Wilson, D.M.; Peehl, D.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Wang, Z.J. Non-Invasive Differentiation of Benign Renal Tumors from Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinomas Using Clinically Translatable Hyperpolarized C Pyruvate Magnetic Resonance. Tomography 2016, 2, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, R.; Gordon, J.; Baligand, C.; Ahamed, F.; Santos, J.D.; Qin, H.; Bok, R.A.; Vigneron, D.B.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Larson, P.E.Z.; et al. Non-Invasive Assessment of Lactate Production and Compartmentalization in Renal Cell Carcinomas Using Hyperpolarized 13 C Pyruvate MRI. Cancers 2018, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parks, S.K.; Chiche, J.; Pouysségur, J. Disrupting proton dynamics and energy metabolism for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S. Expression of lactate/H+ symporters MCT1 and MCT4 and their chaperone CD147 predicts tumor progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Immunohistochemical and the Cancer Genome Atlas data analyses. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosetti, D.; Dufies, M.; Dadone, B.; Durand, M.; Borchiellini, D.; Amiel, J.; Pouyssegur, J.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Pages, G.; Burel-Vandenbos, F.; et al. The two glycolytic markers GLUT1 and MCT1 correlate with tumor grade and survival in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woitek, R.; McLean, M.A.; Ursprung, S.; Rueda, O.M.; Manzano Garcia, R.; Locke, M.J.; Beer, L.; Baxter, G.; Rundo, L.; Provenzano, E.; et al. Hyperpolarized Carbon-13 MRI for Early Response Assessment of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 6004–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y. Value of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in differentiating the pathological grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 11, 10923–10928. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, S.A.; Zheng, J.; Dou, W.Q. Quantitative Evaluation of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion and Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in Assessment of Pathological Grade of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, e176–e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Gammon, S.; Zacharias, N.M.; Liu, T.; Salzillo, T.; Xi, Y.; Wang, J.; Bhattacharya, P.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate-to-[1-13C]lactate conversion is rate-limited by monocarboxylate transporter-1 in the plasma membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22378–22389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisel, P.; Kruck, S.; Winter, S.; Bedke, J.; Hennenlotter, J.; Nies, A.T.; Scharpf, M.; Fend, F.; Stenzl, A.; Schwab, M.; et al. DNA methylation of the SLC16A3 promoter regulates expression of the human lactate transporter MCT4 in renal Cancer with consequences for clinical outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5170–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dimmer, K.S.; Friedrich, B.; Lang, F.; Deitmer, J.W.; Broer, S. The low-affinity monocarboxylate transporter MCT4 is adapted to the export of lactate in highly glycolytic cells. Biochem. J. 2000, 350, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlinger, M.; Santos, C.R.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Martinez, P.; Endesfelder, D.; Burrell, R.A.; Vetter, M.; Jiang, M.; Saunders, R.E.; Kelly, G.; et al. Genome-wide RNA interference analysis of renal carcinoma survival regulators identifies MCT4 as a Warburg effect metabolic target. J. Pathol. 2012, 227, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, S.; Kumar, A.; Matasar, M.; Schöder, H.; Rademaker, J. Imaging for Staging and Response Assessment in Lymphoma. Radiology 2015, 276, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Eskandari, R.; Ray, C.; Granlund, K.L.; Dos Santos-Cunha, L.; Miloushev, V.Z.; Tee, S.S.; Jeong, S.; Aras, O.; Chen, Y.B.; et al. Hyperpolarized MRI visualizes Warburg effects and predicts treatment response to mTOR inhibitors in patient-derived CCRCC xenograft models. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerlinger, M.; Rowan, A.J.; Horswell, S.; Larkin, J.; Endesfelder, D.; Gronroos, E.; Martinez, P.; Matthews, N.; Stewart, A.; Tarpey, P.; et al. Intratumor Heterogeneity and Branched Evolution Revealed by Multiregion Sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Patient Characteristics | Distribution |
|---|---|
| Patients (male/female) | 9 (8/1) |
| Patient Age (median ± IQR) (years) | 59.5 ± 8.7 |
| Histology | 6 clear cell renal cell carcinoma 1 Pheochromocytoma 1 Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma 1 Renal Oncocytoma |
| Tumor Stage at Surgery (RCC only) | 2 pT1b pNx cM0 3 pT3a pN0 cM0 1 pT3b pNx cM1 |
| WHO/ISUP Tumor Grade at Surgery (RCC only) | 1 Grade 2 2 Grade 3 3 Grade 4 |
| Location of Metastasis | 1 Lung |
| Patient Weight (median ± IQR) (kg) | 90.1 ± 13.5 |
| Time between imaging and surgery (median ± IQR) (days) | 12 ± 11 |
| Laterality | 5 left/4 right |
| Plasma glucose (median ± IQR) (mmol/l) | 5.0 ± 0.3 |
| Patients (male/female) | 9 (8/1) |
| Covariates | p Value | HR | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| Age | 0.002 | 1.034 | 1.012 | 1.058 |
| Female Sex | 0.17 | 0.696 | 0.416 | 1.162 |
| LN | 0.30 | 1.579 | 0.665 | 3.748 |
| Metastasis | <0.001 | 3.179 | 1.834 | 5.510 |
| Size | 0.36 | 1.191 | 0.818 | 1.734 |
| Grade | ||||
| Grade 1 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0 | ∞ |
| Grade 2 | 0.15 | 0.591 | 0.287 | 1.218 |
| Grade 3 | 0.50 | 0.799 | 0.414 | 1.540 |
| MCT1 | 0.010 | 1.309 | 1.065 | 1.609 |
| MCT4 | 0.55 | 1.073 | 0.850 | 1.355 |
| LDHA | 0.082 | 0.797 | 0.617 | 1.029 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ursprung, S.; Woitek, R.; McLean, M.A.; Priest, A.N.; Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Brodie, C.R.; Gill, A.B.; Gehrung, M.; Beer, L.; Riddick, A.C.P.; et al. Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate Metabolism as a Surrogate for Tumor Grade and Poor Outcome in Renal Cell Carcinoma—A Proof of Principle Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020335
Ursprung S, Woitek R, McLean MA, Priest AN, Crispin-Ortuzar M, Brodie CR, Gill AB, Gehrung M, Beer L, Riddick ACP, et al. Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate Metabolism as a Surrogate for Tumor Grade and Poor Outcome in Renal Cell Carcinoma—A Proof of Principle Study. Cancers. 2022; 14(2):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020335
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrsprung, Stephan, Ramona Woitek, Mary A. McLean, Andrew N. Priest, Mireia Crispin-Ortuzar, Cara R. Brodie, Andrew B. Gill, Marcel Gehrung, Lucian Beer, Antony C. P. Riddick, and et al. 2022. "Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate Metabolism as a Surrogate for Tumor Grade and Poor Outcome in Renal Cell Carcinoma—A Proof of Principle Study" Cancers 14, no. 2: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020335
APA StyleUrsprung, S., Woitek, R., McLean, M. A., Priest, A. N., Crispin-Ortuzar, M., Brodie, C. R., Gill, A. B., Gehrung, M., Beer, L., Riddick, A. C. P., Field-Rayner, J., Grist, J. T., Deen, S. S., Riemer, F., Kaggie, J. D., Zaccagna, F., Duarte, J. A. G., Locke, M. J., Frary, A., ... Gallagher, F. A. (2022). Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate Metabolism as a Surrogate for Tumor Grade and Poor Outcome in Renal Cell Carcinoma—A Proof of Principle Study. Cancers, 14(2), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020335