Dual LSD1 and HDAC6 Inhibition Induces Doxorubicin Sensitivity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inhibitor Synthesis
2.2. LSD1 MALDI-TOF Enzyme Assay
2.3. HDAC Enzyme Assay
2.4. Cell Lines
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. Protein Extraction
2.9. SDS-PAGE Gel Electrophoresis and Western Blotting
2.10. Combination Treatments with Antileukemic Drugs
2.11. DNA Damage Repair/ABC/Sensitizer Gene Expression
2.12. Mechanistic Studies with Doxorubicin Combinations
2.13. Annexin V Staining
2.14. Caspase 3/7 Staining
2.15. γH2Ax Activation Determination
2.16. Reactive Oxygen Species Activation
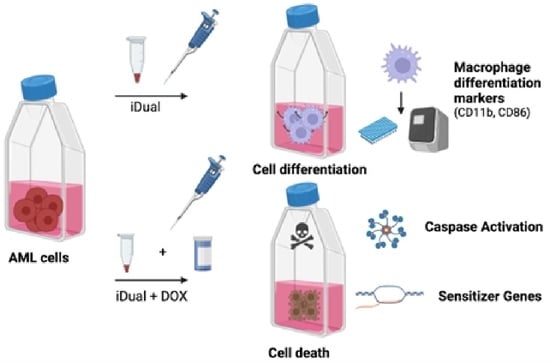
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. IDual inhibits LSD1 and HDAC6
3.2. LSD1 Is Overexpressed in Leukemic Cell Lines
3.3. IDual Reduces Leukemic Cell Viability
3.4. IDual Increases Cellular Protein Methylation/Acetylation and Induces Cell Differentiation of THP-1 Cells
3.5. iDual Sensitizes AML Cells to Doxorubicin
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganesan, A.; Arimondo, P.B.; Rots, M.G.; Jeronimo, C.; Berdasco, M. The timeline of epigenetic drug discovery: From reality to dreams. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bates, S.E. Epigenetic Therapies for Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A. Epigenetic drug discovery: A success story for cofactor interference. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepali, K.; Liou, J.P. Recent developments in epigenetic cancer therapeutics: Clinical advancement and emerging trends. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shvedunova, M.; Akhtar, A. Modulation of cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; Burchell, J.M. Histone Methylases and Demethylases Regulating Antagonistic Methyl Marks: Changes Occurring in Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, T.; Yin, W.; Yan, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, D. Therapeutic potential of targeting LSD1/ KDM1A in cancers. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.S.; Chan, A.H.Y.; Ganesan, A. Thirty Years of HDAC Inhibitors: 2020 Insight and Hindsight. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12460–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalawansha, D.A.; Pflum, M.K. LSD1 Substrate Binding and Gene Expression Are Affected by HDAC1-Mediated Deacetylation. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayakawa, T.; Nakayama, J. Physiological roles of class I HDAC complex and histone demethylase. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 129383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, D.; Kahen, E.; Fridley, B.; Brohl, A.S.; Cubitt, C.L.; Reed, D.R. Small molecule inhibition of lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) alone and in combination in Ewing sarcoma cell lines. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A. Multitarget Drugs: An Epigenetic Epiphany. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Lera, A.R.; Ganesan, A. Two-hit wonders: The expanding universe of multitargeting epigenetic agents. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 57, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelkebir, H.; Hodgkinson, C.; Duriez, P.J.; Hayden, A.L.; Bulleid, R.A.; Crabb, S.J.; Packham, G.; Ganesan, A. Enantioselective synthesis of tranylcypromine analogues as lysine demethylase (LSD1) inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 3709–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halley, F.; Reinshagen, J.; Ellinger, B.; Wolf, M.; Niles, A.L.; Evans, N.J.; Kirkland, T.A.; Wagner, J.M.; Jung, M.; Gribbon, P.; et al. A bioluminogenic HDAC activity assay: Validation and screening. J. Biomol. Screen 2011, 16, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cevatemre, B.; Ulukaya, E.; Dere, E.; Dilege, S.; Acilan, C. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Contributes to Drug Resistance of Lung Cancer Cells Through Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 738916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, Y.; Adiguzel, Z.; Polat, H.U.; Akkoc, T.; Tas, A.; Cevatemre, B.; Celik, G.; Carikci, B.; Yilmaz, V.T.; Ulukaya, E.; et al. A palladium(II)-saccharinate complex of terpyridine exerts higher anticancer potency and less toxicity than cisplatin in a mouse allograft model. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2017, 28, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, B.; Bulut, I.; Xia, Y.; Waller, Z.A.E.; Yildizhan, Y.; Acilan, C.; Lord, R.M. Understanding the Potential In Vitro Modes of Action of Bis(beta-diketonato) Oxovanadium(IV) Complexes. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.P.; Smitheman, K.N.; Kamat, C.D.; Soong, D.; Federowicz, K.E.; van Aller, G.S.; Schneck, J.L.; Carson, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Butticello, M.; et al. A DNA Hypomethylation Signature Predicts Antitumor Activity of LSD1 Inhibitors in SCLC. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, T.M.; Besse, B.; Martinez-Marti, A.; Trigo, J.M.; Moreno, V.; Garrido, P.; Ferron-Brady, G.; Wu, Y.; Park, J.; Collingwood, T.; et al. Phase I, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Study of the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Efficacy of GSK2879552 in Relapsed/Refractory SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.C.; Ma, Y.C.; Qin, W.P.; Ding, L.N.; Zheng, Y.C.; Zhu, Y.L.; Zhai, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.Y.; Guan, Y.Y. Design and synthesis of tranylcypromine derivatives as novel LSD1/HDACs dual inhibitors for cancer treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 140, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalin, J.H.; Wu, M.; Gomez, A.V.; Song, Y.; Das, J.; Hayward, D.; Adejola, N.; Wu, M.; Panova, I.; Chung, H.J.; et al. Targeting the CoREST complex with dual histone deacetylase and demethylase inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milelli, A.; Marchetti, C.; Turrini, E.; Catanzaro, E.; Mazzone, R.; Tomaselli, D.; Fimognari, C.; Tumiatti, V.; Minarini, A. Novel polyamine-based Histone deacetylases-Lysine demethylase 1 dual binding inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santo, L.; Hideshima, T.; Kung, A.L.; Tseng, J.C.; Tamang, D.; Yang, M.; Jarpe, M.; van Duzer, J.H.; Mazitschek, R.; Ogier, W.C.; et al. Preclinical activity, pharmacodynamic, and pharmacokinetic properties of a selective HDAC6 inhibitor, ACY-1215, in combination with bortezomib in multiple myeloma. Blood 2012, 119, 2579–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakaidos, P.; Verigos, J.; Magklara, A. LSD1/KDM1A, a Gate-Keeper of Cancer Stemness and a Promising Therapeutic Target. Cancers 2019, 11, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, J.T.; Harris, W.J.; Somervaille, T.C. LSD1 inhibition: A therapeutic strategy in cancer? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartha, A.; Gyorffy, B. TNMplot.com: A Web Tool for the Comparison of Gene Expression in Normal, Tumor and Metastatic Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, S.L.; Hassan, C.; Khunte, M.; Soldatenko, A.; Jong, Y.; Afshinnekoo, E.; Mason, C.E. Epigenetic Modifications in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Prognosis, Treatment, and Heterogeneity. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gambacorta, V.; Gnani, D.; Vago, L.; Di Micco, R. Epigenetic Therapies for Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Their Immune-Related Effects. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Lee, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G. The potential underlying mechanism of the leukemia caused by MLL-fusion and potential treatments. Mol. Carcinog. 2020, 59, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillico, R.; Lawrence, C.K.; Lakowski, T.M. Selective DOT1L, LSD1, and HDAC Class I Inhibitors Reduce HOXA9 Expression in MLL-AF9 Rearranged Leukemia Cells, But Dysregulate the Expression of Many Histone-Modifying Enzymes. J. Proteome. Res. 2018, 17, 2657–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.M.; So, C.W.E. Novel therapeutic strategies for MLL-rearranged leukemias. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveen Sadhu, M.; Sivanandhan, D.; Gajendran, C.; Tantry, S.; Dewang, P.; Murugan, K.; Chickamunivenkatappa, S.; Zainuddin, M.; Nair, S.; Vaithilingam, K.; et al. Novel dual LSD1/HDAC6 inhibitors for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 34, 127763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yong, S.; Salas-Burgos, A.; Koomen, J.; Olashaw, N.; Parsons, J.T.; Yang, X.J.; Dent, S.R.; et al. HDAC6 modulates cell motility by altering the acetylation level of cortactin. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, Z.K.; Huang, Y.Q.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, X.K.; Ma, X.D. Silencing of LSD1 gene modulates histone methylation and acetylation and induces the apoptosis of JeKo-1 and MOLT-4 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugino, N.; Kawahara, M.; Tatsumi, G.; Kanai, A.; Matsui, H.; Yamamoto, R.; Nagai, Y.; Fujii, S.; Shimazu, Y.; Hishizawa, M.; et al. A novel LSD1 inhibitor NCD38 ameliorates MDS-related leukemia with complex karyotype by attenuating leukemia programs via activating super-enhancers. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, L.; Dalvai, M.; Kocanova, S.; Moutahir, F.; Bystricky, K. Activation of p21 by HDAC inhibitors requires acetylation of H2A.Z. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, C.Y.; Ngo, L.; Xu, W.S.; Richon, V.M.; Marks, P.A. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor activation of p21WAF1 involves changes in promoter-associated proteins, including HDAC1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, J.H.; Chou, C.W.; Chang, Y.F.; Yeh, S.H.; Chen, C.C. Statins increase p21 through inhibition of histone deacetylase activity and release of promoter-associated HDAC1/2. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, P.; Tu, B.; He, Q.; Zhu, W.G. The HDAC inhibitor depsipeptide transactivates the p53/p21 pathway by inducing DNA damage. DNA Repair 2012, 11, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xie, Y.; Sun, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Yao, R.; Xu, K. The selective HDAC6 inhibitor Nexturastat A induces apoptosis, overcomes drug resistance and inhibits tumor growth in multiple myeloma. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auzmendi-Iriarte, J.; Saenz-Antonanzas, A.; Mikelez-Alonso, I.; Carrasco-Garcia, E.; Tellaetxe-Abete, M.; Lawrie, C.H.; Sampron, N.; Cortajarena, A.L.; Matheu, A. Characterization of a new small-molecule inhibitor of HDAC6 in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Ying, H.; Mao, T.; Fang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zang, I.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, M.; et al. Upregulation of CD11b and CD86 through LSD1 inhibition promotes myeloid differentiation and suppresses cell proliferation in human monocytic leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 85085–85101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morel, D.; Jeffery, D.; Aspeslagh, S.; Almouzni, G.; Postel-Vinay, S. Combining epigenetic drugs with other therapies for solid tumours-past lessons and future promise. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad, Y.; Gellerman, G.; Lonard, D.M.; O’Malley, B.W. Drug Combination in Cancer Treatment-From Cocktails to Conjugated Combinations. Cancers 2021, 13, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Mahendran, A.; Yao, Y.; Ngo, L.; Venta-Perez, G.; Choy, M.L.; Kim, N.; Ham, W.S.; Breslow, R.; Marks, P.A. Development of a histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor and its biological effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15704–15709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, H.J.; Lin, Y.J.; Chao, M.W.; Sung, T.Y.; Wu, Y.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Liou, J.P.; Pan, S.L.; Yang, C.R. The anticancer effects of MPT0G211, a novel HDAC6 inhibitor, combined with chemotherapeutic agents in human acute leukemia cells. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verigos, J.; Karakaidos, P.; Kordias, D.; Papoudou-Bai, A.; Evangelou, Z.; Harissis, H.V.; Klinakis, A.; Magklara, A. The Histone Demethylase LSD1/KappaDM1A Mediates Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer via Regulation of a Stem Cell Program. Cancers 2019, 11, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorn, C.F.; Oshiro, C.; Marsh, S.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; McLeod, H.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Doxorubicin pathways: Pharmacodynamics and adverse effects. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 2011, 21, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Teves, S.S.; Kemp, C.J.; Henikoff, S. Doxorubicin, DNA torsion, and chromatin dynamics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1845, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, K.; Almasan, A. Histone H2AX phosphorylation: A marker for DNA damage. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 920, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robey, R.W.; Pluchino, K.M.; Hall, M.D.; Fojo, A.T.; Bates, S.E.; Gottesman, M.M. Revisiting the role of ABC transporters in multidrug-resistant cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; Lu, J.; Li, M.Q.; Shan, Q.; Wu, D.M.; Sun, C.H.; Hu, B.; et al. AGPAT9 suppresses cell growth, invasion and metastasis by counteracting acidic tumor microenvironment through KLF4/LASS2/V-ATPase signaling pathway in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18406–18417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Skibbe, J.R.; Hu, C.; Dong, L.; Ferchen, K.; Su, R.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Weng, H.; Huang, H.; et al. ALOX5 exhibits anti-tumor and drug-sensitizing effects in MLL-rearranged leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, Y.B.; Park, T.J.; Lim, I.K. B cell translocation gene 2 enhances susceptibility of HeLa cells to doxorubicin-induced oxidative damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33110–33118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Wen, P.; Li, F.; Yao, C.; Wang, T.; Liang, B.; Yang, Q.; Ma, L.; He, L. HIPK2 inhibits cell metastasis and improves chemosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.C.; Tung, S.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, P.M.; Chu, P.Y. IFI44L is a novel tumor suppressor in human hepatocellular carcinoma affecting cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance via regulating met/Src signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyer, V.V.; Priya, P.Y.; Kangeyavelu, J. Effects of increased accumulation of doxorubicin due to emodin on efflux transporter and LRP1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma and colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2018, 449, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Tang, M.; Tan, W.; Sun, T.; Deng, Y. miR-342-5p inhibits osteosarcoma cell growth, migration, invasion, and sensitivity to Doxorubicin through targeting Wnt7b. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 3325–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; van der Zanden, S.Y.; Wander, D.P.A.; Borras, D.M.; Song, J.Y.; Li, X.; van Duikeren, S.; van Gils, N.; Rutten, A.; van Herwaarden, T.; et al. Uncoupling DNA damage from chromatin damage to detoxify doxorubicin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15182–15192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| IC50 (μM) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | LSD1 | HDAC1 | HDAC3 | HDAC6 | HDAC8 |
| GSK2879552 | 1.54 ± 0.41 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| iDual | 0.54 ± 0.03 | 5.31 ± 0.25 | 2.29 ± 0.14 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.04 |
| iHDAC6 | >100 | 7.57 ± 0.29 | 4.09 ± 0.26 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.45 ± 0.07 |
| iNC | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| IC50 (μM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | THP-1 | MOLM-13 | K-562 | Jurkat |
| GSK2879552 | >20 | 15.0 ± 3.5 | >20 | >20 |
| ricolinostat | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.03 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.003 |
| iDual | 16.3 ± 5.4 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 16.6 ± 2.7 | 15.5 ± 1.4 |
| iHDAC6 | 9.7 ± 2.4 | 6.7 ± 1.6 | 17.6 ± 1.6 | 10.7 ± 0.8 |
| iNC | >20 | >20 | >20 | >20 |
| Name | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| AGPAT9 | Increased AGPAT9 expression in MCF-7 cells increases chemosensitivity to doxorubicin | [53] |
| ALOX5 | ALOX5 exhibits antitumor and doxorubicin-sensitizing effects in MLL-rearranged leukemia | [54] |
| BTG1 | Doxorubicin-induced cell death is mediated by BTG family | [55] |
| HIPK2 | HIPK2 regulates chemosensitivity including doxorubicin | [56] |
| IFI44L | Overexpression of IFI44L decreased chemoresistance towards doxorubicin | [57] |
| LRP1 | Increased LRP1 may be associated with higher endocytosis of upregulated transporter proteins at the cell surface, thus increased doxorubicin accumulation | [58] |
| WNT7B | Wnt7B inhibits osteosarcoma cell growth, migration, invasion, and sensitivity to doxorubicin | [59] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bulut, I.; Lee, A.; Cevatemre, B.; Ruzic, D.; Belle, R.; Kawamura, A.; Gul, S.; Nikolic, K.; Ganesan, A.; Acilan, C. Dual LSD1 and HDAC6 Inhibition Induces Doxorubicin Sensitivity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 6014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14236014
Bulut I, Lee A, Cevatemre B, Ruzic D, Belle R, Kawamura A, Gul S, Nikolic K, Ganesan A, Acilan C. Dual LSD1 and HDAC6 Inhibition Induces Doxorubicin Sensitivity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):6014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14236014
Chicago/Turabian StyleBulut, Ipek, Adam Lee, Buse Cevatemre, Dusan Ruzic, Roman Belle, Akane Kawamura, Sheraz Gul, Katarina Nikolic, A. Ganesan, and Ceyda Acilan. 2022. "Dual LSD1 and HDAC6 Inhibition Induces Doxorubicin Sensitivity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells" Cancers 14, no. 23: 6014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14236014
APA StyleBulut, I., Lee, A., Cevatemre, B., Ruzic, D., Belle, R., Kawamura, A., Gul, S., Nikolic, K., Ganesan, A., & Acilan, C. (2022). Dual LSD1 and HDAC6 Inhibition Induces Doxorubicin Sensitivity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Cancers, 14(23), 6014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14236014