Biopsy and Margins Optimize Outcomes after Thermal Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
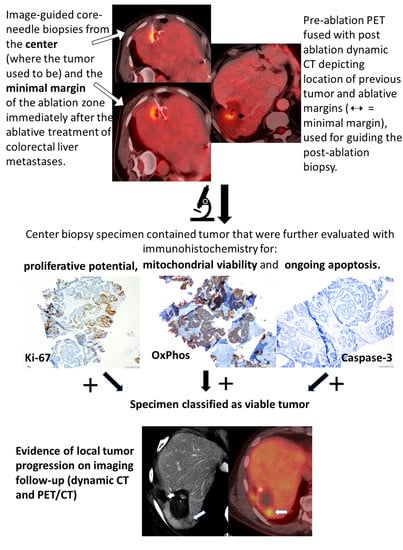
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria and Treatment
2.2. Margin Assessment
2.3. Histopathologic Analysis
2.4. Imaging Follow-Up
2.5. Definitions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Thermal Ablation Efficacy
3.2. Tissue Findings
3.3. LTP Findings
3.4. Patient Survival
3.5. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Chen, M.-H.; Choi, B.I.; De Baère, T.; Dodd, G.D.; et al. Image-guided Tumor Ablation: Standardization of Terminology and Reporting Criteria—A 10-Year Update. Radiology 2014, 273, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puijk, R.S.; Ahmed, M.; Adam, A.; Arai, Y.; Arellano, R.; de Baère, T.; Bale, R.; Bellera, C.; Binkert, C.A.; Brace, C.L.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for the Definition of Time-to-Event End Points in Image-guided Tumor Ablation: Results of the SIO and DATECAN Initiative. Radiology 2021, 301, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, A.B.; Venook, A.P.; Al-Hawary, M.M.; Arain, M.A.; Chen, Y.J.; Ciombor, K.K.; Cohen, S.; Cooper, H.S.; Deming, D.; Farkas, L.; et al. Colon Cancer, Version 2. 2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2021, 19, 329–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijerink, M.R.; Puijk, R.S.; Van Tilborg, A.A.J.M.; Henningsen, K.H.; Fernandez, L.G.; Neyt, M.; Heymans, J.; Frankema, J.S.; De Jong, K.P.; Richel, D.J.; et al. Radiofrequency and Microwave Ablation Compared to Systemic Chemotherapy and to Partial Hepatectomy in the Treatment of Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruers, T.; Van Coevorden, F.; Punt, C.J.A.; Pierie, J.-P.E.N.; Borel-Rinkes, I.; Ledermann, J.A.; Poston, G.; Bechstein, W.; Lentz, M.-A.; Mauer, M.; et al. Local Treatment of Unresectable Colorectal Liver Metastases: Results of a Randomized Phase II Trial. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djx015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shady, W.; Petre, E.N.; Gonen, M.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Brown, K.T.; Covey, A.M.; Alago, W.; Durack, J.; Maybody, M.; Brody, L.A.; et al. Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: Factors Affecting Outcomes—A 10-year Experience at a Single Center. Radiology 2016, 278, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calandri, M.; Yamashita, S.; Gazzera, C.; Fonio, P.; Veltri, A.; Bustreo, S.; Sheth, R.A.; Yevich, S.M.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Odisio, B.C. Ablation of colorectal liver metastasis: Interaction of ablation margins and RAS mutation profiling on local tumour progression-free survival. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Petre, E.N.; Gonen, M.; Do, K.G.; Brown, K.T.; Covey, A.M.; Brody, L.A.; Alago, W.; et al. Margin Size is an Independent Predictor of Local Tumor Progression After Ablation of Colon Cancer Liver Metastases. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odisio, B.C.; Yamashita, S.; Huang, S.Y.; Harmoush, S.; Kopetz, S.; Ahrar, K.; Chun, Y.S.; Conrad, C.; Aloia, T.A.; Gupta, S.; et al. Local tumour progression after percutaneous ablation of colorectal liver metastases according to RAS mutation status. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Paolucci, I.; Brock, K.; Odisio, B. Image-Guided Ablation for Colorectal Liver Metastasis: Principles, Current Evidence, and the Path Forward. Cancers 2021, 13, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, X.; Qu, J.; Lu, W.; Pang, Z.; Shao, T.; Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Periprocedural risk factors for incomplete radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases from colorectal cancer: A single-center retrospective analysis. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izaaryene, J.; Drai, M.; Deniel, C.; Bridge, P.; Rico, G.; Daidj, N.; Gilabert, M.; Ewald, J.; Turrini, O.; Piana, G. Computed tomography-guided microwave ablation of perivascular liver metastases from colorectal cancer: A study of the ablation zone, feasibility, and safety. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, E.A.; Cornelis, F.H.; Petre, E.N.; Tyagi, N.; Shady, W.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Solomon, S.B.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Durack, J.C. Volumetric 3D assessment of ablation zones after thermal ablation of colorectal liver metastases to improve prediction of local tumor progression. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 29, 2698–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotirchos, V.S.; Petrovic, L.M.; Gonen, M.; Klimstra, D.S.; Do, R.K.G.; Petre, E.N.; Garcia, A.R.; Barlas, A.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Brown, K.T.; et al. Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: Biopsy of the Ablation Zone and Margins Can Be Used to Predict Oncologic Outcome. Radiology 2016, 280, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simon, R.; E Wittes, R. Methodologic guidelines for reports of clinical trials. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1985, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.-C.; Nakano, H.; Bachellier, P.; Oussoultzoglou, E.; Inoue, K.; Shimura, H.; Wolf, P.; Chenard-Neu, M.-P.; Jaeck, D. Is a proliferation index of cancer cells a reliable prognostic factor after hepatectomy in patients with colorectal liver metastases? Am. J. Surg. 2001, 182, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofocleous, C.T.; Garg, S.; Petrovic, L.M.; Gonen, M.; Petre, E.N.; Klimstra, D.S.; Solomon, S.B.; Brown, K.T.; Brody, L.A.; Covey, A.M.; et al. Ki-67 is a Prognostic Biomarker of Survival after Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Malignancies. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 4262–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fine, J.P.; Gray, R.J. A Proportional Hazards Model for the Subdistribution of a Competing Risk. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solbiati, L.; Ahmed, M.; Cova, L.; Ierace, T.; Brioschi, M.; Goldberg, S.N. Small Liver Colorectal Metastases Treated with Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation: Local Response Rate and Long-term Survival with Up to 10-year Follow-up. Radiology 2012, 265, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, J.C.; Fong, Y.; Gonen, M.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Allen, P.J.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Kingham, T.P. A Retrospective Comparison of Microwave Ablation vs. Radiofrequency Ablation for Colorectal Cancer Hepatic Metastases. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 4278–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidensticker, M.; Wust, P.; Rühl, R.; Mohnike, K.; Pech, M.; Wieners, G.; Gademann, G.; Ricke, J. Safety margin in irradiation of colorectal liver metastases: Assessment of the control dose of micrometastases. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shady, W.; Petre, E.N.; Do, K.G.; Gonen, M.; Yarmohammadi, H.; Brown, K.T.; Kemeny, N.E.; D’Angelica, M.; Kingham, P.T.; Solomon, S.B.; et al. Percutaneous Microwave versus Radiofrequency Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases: Ablation with Clear Margins (A0) Provides the Best Local Tumor Control. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 268–275.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, Y.; Fortner, J.; Sun, R.L.; Brennan, M.F.; Blumgart, L.H. Clinical score for predicting recurrence after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: Analysis of 1001 consecutive cases. Ann. Surg. 1999, 230, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Are, C.; Gonen, M.; Zazzali, K.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Fong, Y.; Blumgart, L.H.; D’Angelica, M. The Impact of Margins on Outcome after Hepatic Resection for Colorectal Metastasis. Ann. Surg. 2007, 246, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanko, M.; Shimada, H.; Yamaoka, H.; Tanaka, K.; Masui, H.; Matsuo, K.; Ike, H.; Oki, S.; Hara, M. Micrometastatic colorectal cancer lesions in the liver. Surg. Today 1998, 28, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creasy, J.M.; Sadot, E.; Koerkamp, B.G.; Chou, J.F.; Gonen, M.; Kemeny, N.E.; Balachandran, V.P.; Kingham, T.P.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Allen, P.J.; et al. Actual 10-year survival after hepatic resection of colorectal liver metastases: What factors preclude cure? Surgery 2018, 163, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Yan, G.-X.; Xin, H.; Liu, Z.-Y. Oncological outcomes and predictors of radiofrequency ablation of colorectal cancer liver metastases. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, T.J.; Bs, M.A.C.; Khajanchee, Y.S.; Diwan, T.S.; Hammill, C.W.; Hansen, P.D. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for the management of colorectal liver metastases: 10-year experience. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 107, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shady, W.; Petre, E.N.; Vakiani, E.; Ziv, E.; Gonen, M.; Brown, K.T.; Kemeny, N.E.; Solomon, S.B.; Solit, D.B.; Sofocleous, C.T. Kras mutation is a marker of worse oncologic outcomes after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 66117–66127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snoeren, N.; Huiskens, J.; Rijken, A.M.; Van Hillegersberg, R.; Van Erkel, A.R.; Slooter, G.D.; Klaase, J.M.; Tol, P.M.V.D.; Kate, F.J.W.T.; Jansen, M.C.; et al. Viable Tumor Tissue Adherent to Needle Applicators after Local Ablation: A Risk Factor for Local Tumor Progression. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 3702–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snoeren, N.; Jansen, M.C.; Rijken, A.M.; Van Hillegersberg, R.; Slooter, G.; Klaase, J.; Tol, P.M.V.D.; Van Der Linden, E.; Kate, F.J.T.; Van Gulik, T.M. Assessment of Viable Tumour Tissue Attached to Needle Applicators after Local Ablation of Liver Tumours. Dig. Surg. 2009, 26, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, M.; Sugimori, K.; Shirato, K.; Kokawa, A.; Tomita, N.; Saito, T.; Tanaka, N.; Nozawa, A.; Hara, M.; Sekihara, H.; et al. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with radiofrequency ablation: Radiologic-histologic correlation during follow-up periods. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutiani, N.; Philips, P.; Martin, R.C., II; Scoggins, C.R. Impact of surgical margin clearance for resection of secondary hepatic malignancies. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 113, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandu, R.-M.; Paolucci, I.; Ruiter, S.J.S.; Sznitman, R.; de Jong, K.P.; Freedman, J.; Weber, S.; Tinguely, P. Volumetric Quantitative Ablation Margins for Assessment of Ablation Completeness in Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, F.; Taghavi, M.; van der Reijd, D.; Gomez, F.; Imani, F.; Klompenhouwer, E.; Meek, D.; Roberti, S.; de Boer, M.; Lambregts, D.; et al. Predicting local tumour progression after ablation for colorectal liver metastases: CT-based radiomics of the ablation zone. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 141, 109773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laimer, G.; Jaschke, N.; Schullian, P.; Putzer, D.; Eberle, G.; Solbiati, M.; Solbiati, L.; Goldberg, S.N.; Bale, R. Correction to: Volumetric assessment of the periablational safety margin after thermal ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6489–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solbiati, M.; Muglia, R.; Goldberg, S.N.; Ierace, T.; Rotilio, A.; Passera, K.M.; Marre, I.; Solbiati, L. A novel software platform for volumetric assessment of ablation completeness. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 36, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luu, H.M.; Moelker, A.; Klein, S.; Niessen, W.J.; Van Walsum, T. Quantification of nonrigid liver deformation in radiofrequency ablation interventions using image registration. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 175005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, G.; Gennaro, N.; De Beni, S.; Ierace, T.; Goldberg, S.N.; Rodari, M.; Solbiati, L.A. Real-Time US-18FDG-PET/CT Image Fusion for Guidance of Thermal Ablation of 18FDG-PET-Positive Liver Metastases: The Added Value of Contrast Enhancement. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 42, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadaban, L.C.; Catalano, P.J.; Lee, L.K.; Hyun, H.; Tuncali, K.; Gerbaudo, V.H.; Shyn, P.B. Assessing ablation margins of FDG-avid liver tumors during PET/CT-guided thermal ablation procedures: A retrospective study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 48, 2914–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyn, P.B.; Casadaban, L.C.; Sainani, N.I.; Sadow, C.A.; Bunch, P.M.; Levesque, V.M.; Kim, C.K.; Gerbaudo, V.H.; Silverman, S.G. Intraprocedural Ablation Margin Assessment by Using Ammonia Perfusion PET during FDG PET/CT–guided Liver Tumor Ablation: A Pilot Study. Radiology 2018, 288, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, S.; Bruners, P.; Schiffl, K.; Sedlmair, M.; Mühlenbruch, G.; Günther, R.W.; Das, M.; Mahnken, A.H. Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Metastases—Software-Assisted Evaluation of the Ablation Zone in MDCT: Tumor-Free Follow-Up Versus Local Recurrent Disease. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 33, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laimer, G.; Schullian, P.; Putzer, D.; Eberle, G.; Goldberg, S.N.; Bale, R. Can accurate evaluation of the treatment success after radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors be achieved by visual inspection alone? Results of a blinded assessment with 38 interventional oncologists. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, S.N.; Gazelle, G.S.; Compton, C.C.; Mueller, P.R.; Tanabe, K.K. Treatment of intrahepatic malignancy with radiofrequency ablation: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Cancer 2000, 88, 2452–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofocleous, C.T.; Garg, S.K.; Cohen, P.; Petre, E.N.; Gonen, M.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Downey, R.J.; Travis, W.D.; Solomon, S.B. Ki 67 is an Independent Predictive Biomarker of Cancer Specific and Local Recurrence-Free Survival After Lung Tumor Ablation. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofocleous, C.T.; Klein, K.M.; Hubbi, B.; Brown, K.T.; Weiss, S.; Kannarkat, G.; Hinrichs, C.R.; Contractor, D.; Bahramipour, P.; Barone, A.; et al. Histopathologic Evaluation of Tissue Extracted on the Radiofrequency Probe After Ablation of Liver Tumors:Preliminary Findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004, 183, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markezana, A.; Ahmed, M.; Kumar, G.; Zorde-Khvalevsky, E.; Rozenblum, N.; Galun, E.; Goldberg, S.N. Moderate hyperthermic heating encountered during thermal ablation increases tumor cell activity. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurilova, I.; Bendet, A.; Petre, E.N.; Boas, F.E.; Kaye, E.; Gonen, M.; Covey, A.; Brody, L.A.; Brown, K.T.; Kemeny, N.E.; et al. Factors Associated with Local Tumor Control and Complications After Thermal Ablation of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: A 15-year Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin. Color. Cancer 2021, 20, e82–e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Kim, J.H.; Yang, S.G.; Park, S.H.; Choi, H.-K.; Chun, S.-Y.; Kim, P.N.; Park, J.; Lee, M. A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis of Periprocedural Variables Affecting Local Tumor Progression after Radiofrequency Ablation of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. Radiology 2021, 298, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaible, J.; Pregler, B.; Bäumler, W.; Einspieler, I.; Jung, E.-M.; Stroszczynski, C.; Beyer, L.P. Safety margin assessment after microwave ablation of liver tumors: Inter- and intrareader variability. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 54, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, B.M.; Lin, Y.; Lin, E.Y.; Cazoulat, G.; Gupta, S.; Jones, A.K.; Odisio, B.C.; Brock, K.K. A novel use of biomechanical model-based deformable image registration (DIR) for assessing colorectal liver metastases ablation outcomes. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 6226–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tselikas, L.; de Baere, T.; Deschamps, F.; Hakimé, A.; Besse, B.; Teriitehau, C.; de Montpreville, V.; Adam, J. Diagnostic yield of a biopsy performed immediately after lung radiofrequency ablation. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofocleous, C.T.; Nascimento, R.G.; Petrovic, L.M.; Klimstra, D.S.; Gonen, M.; Brown, K.T.; Brody, L.A.; Covey, A.M.; Thornton, R.H.; Fong, Y.; et al. Histopathologic and immunohistochemical Features of Tissue Adherent to Multitined Electrodes after RF Ablation of Liver Malignancies Can Help Predict Local Tumor Progression: Initial Results. Radiology 2008, 249, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockey, D.C.; Caldwell, S.H.; Goodman, Z.D.; Nelson, R.C.; Smith, A.D. Liver biopsy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1017–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, A.Z.; Saad, W.A.; Ribeiro, M.A., Jr. Complications after Radiofrequency Ablation of 233 Hepatic Tumors. Oncology 2015, 89, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schullian, P.; Johnston, E.; Laimer, G.; Putzer, D.; Eberle, G.; Amann, A.; Effenberger, M.; Maglione, M.; Freund, M.C.; Loizides, A.; et al. Frequency and risk factors for major complications after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors in 1235 ablation sessions: A 15-year experience. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 31, 3042–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patient (n = 107) and Tumor (n = 182) Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Characteristic | Value |
| Age (y) * | 59 (32–82) |
| Sex | |
| Female | 42 (39) |
| Male | 65 (61) |
| Race | |
| Asian/Far East/Indian Subcontinent | 5 (5) |
| Black/African American | 7 (7) |
| Other | 1 (1) |
| Patient refused to answer | 2 (2) |
| White | 92 (92) |
| Tumor size (cm) ** | 2.0 (0.6–4.6) |
| LN status at staging of primary disease | |
| Positive | 70 (65) |
| Negative | 37 (35) |
| Synchronous CLM | 77 (72) |
| Time between diagnosis of colorectal cancer and ablation (mo) * | 31 (2–151) |
| No. of tumors treated per patient within protocol ** | 1.7 (1–9) |
| Tumor Characteristics as Predictors of LTP (n = 178) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Tumors | LTP Rate (%) | p Value | |
| Biopsy | <0.001 | ||
| Positive- Viable tumor | 64 | 52 (33/64) | |
| Negative- Coagulation Necrosis | 114 | 23 (25/114) | |
| Ablation Margin (mm) | <0.001 | ||
| <5 | 33 | 70 (23/33) | |
| ≥5 | 145 | 24 (35/145) | |
| Tumor size (cm) | 0.036 | ||
| ≥3 | 26 | 50 (13/26) | |
| <3 | 152 | 30 (45/152) | |
| Ablation Modality | 0.2 | ||
| MWA | 90 | 36 (32/90) | |
| RFA | 88 | 30 (26/88) | |
| PET Guidance | 0.3 | ||
| Yes | 131 | 31 (41/131) | |
| No | 47 | 36 (17/47) | |
| CEA level (ng/mL [μg/L]) | 0.4 | ||
| ≤30 | 156 | 31 (50/156) | |
| >30 | 22 | 36 (8/22) | |
| EHD | 0.4 | ||
| Yes | 86 | 31 (27/86) | |
| No | 92 | 34 (31/92) | |
| Prior Liver Resection | 0.034 | ||
| Yes | 147 | 29 (43/147) | |
| No | 31 | 48 (15/31) | |
| Prior Systemic Chemotherapy | 0.5 | ||
| Yes | 166 | 33 (54/166) | |
| No | 12 | 33 (4/12) | |
| Prior HAIC | 0.4 | ||
| Yes | 99 | 31 (31/99) | |
| No | 79 | 34 (27/79) | |
| Post-Ablation Systemic Chemotherapy | 0.1 | ||
| Yes | 140 | 35 (49/140) | |
| No | 38 | 24 (9/38) | |
| Post-Ablation HAIC | 0.3 | ||
| Yes | 60 | 35 (21/60) | |
| No | 118 | 31 (37/118) | |
| Univariate and Multivariate Analyses of Factors Associated with Local Tumor Progression by Using the Competing-Risks Regression Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
| Variable | p Value | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p Value |
| Biopsy result (V vs. N) | <0.001 | 2.4 | 1.4, 4.1 | 0.002 |
| Minimal margin size < 5 mm | <0.001 | 3.5 | 2.0, 6.2 | <0.001 |
| Tumor size ≥3 cm | 0.036 | 1.5 | 0.9, 2.7 | 0.133 |
| Patient Characteristics as Predictors of OS (n = 106) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Patients | Median OS (mo) | p Value | |
| LTP | 0.1 | ||
| Yes | 38 | 37 | |
| No | 68 | 49 | |
| CEA level (ng/mL [μg/L]) | <0.001 | ||
| ≤30 | 92 | 52 | |
| >30 | 14 | 22 | |
| EHD | 0.1 | ||
| Yes | 54 | 42 | |
| No | 52 | 49 | |
| Prior Liver Resection | 0.1 | ||
| Yes | 83 | 49 | |
| No | 23 | 34 | |
| Prior Systemic Chemotherapy | - | ||
| Yes | 105 | 46 | |
| No | 1 | - | |
| Prior HAIC | 0.3 | ||
| Yes | 67 | 49 | |
| No | 39 | 36 | |
| Post-ablation Systemic Chemotherapy | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 78 | 36 | |
| No | 28 | 76 | |
| Post-Ablation HAIC | 0.9 | ||
| Yes | 33 | 49 | |
| No | 73 | 44 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasiniotis Kamarinos, N.; Vakiani, E.; Gonen, M.; Kemeny, N.E.; Sigel, C.; Saltz, L.B.; Brown, K.T.; Covey, A.M.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Brody, L.A.; et al. Biopsy and Margins Optimize Outcomes after Thermal Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases. Cancers 2022, 14, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030693
Vasiniotis Kamarinos N, Vakiani E, Gonen M, Kemeny NE, Sigel C, Saltz LB, Brown KT, Covey AM, Erinjeri JP, Brody LA, et al. Biopsy and Margins Optimize Outcomes after Thermal Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030693
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasiniotis Kamarinos, Nikiforos, Efsevia Vakiani, Mithat Gonen, Nancy E. Kemeny, Carlie Sigel, Leonard B. Saltz, Karen T. Brown, Anne M. Covey, Joseph P. Erinjeri, Lynn A. Brody, and et al. 2022. "Biopsy and Margins Optimize Outcomes after Thermal Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases" Cancers 14, no. 3: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030693
APA StyleVasiniotis Kamarinos, N., Vakiani, E., Gonen, M., Kemeny, N. E., Sigel, C., Saltz, L. B., Brown, K. T., Covey, A. M., Erinjeri, J. P., Brody, L. A., Ziv, E., Yarmohammadi, H., Kunin, H., Barlas, A., Petre, E. N., Kingham, P. T., D’Angelica, M. I., Manova-Todorova, K., Solomon, S. B., & Sofocleous, C. T. (2022). Biopsy and Margins Optimize Outcomes after Thermal Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases. Cancers, 14(3), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030693