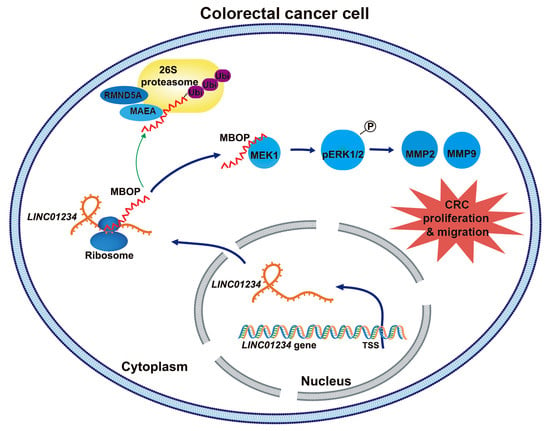
Oncopeptide MBOP Encoded by LINC01234 Promotes Colorectal Cancer through MAPK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. Human Tissue Samples
2.3. Plasmid Construction
2.4. Antibody Generation
2.5. Animal Assay
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.8. Cytoplasmic and Nucleic RNA/Protein Extraction
2.9. Cell Migration Assay with Transwell Chambers
2.10. Wound-Healing Assay
2.11. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.12. Immunoprecipitation and Mass Spectrometry Assay
2.13. Colony-Formation Assay
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LINC01234 Has Ribosome Binding Sites across Several Perspectives
3.2. LINC01234 Encodes an Endogenous Peptide Highly Expressed in CRC
3.3. MBOP Promotes CRC Progression through Cell Migration and Proliferation
3.4. MBOP Interacts with MEK1 in CRC
3.5. The MBOP/MEK1/pERK/MMP2/MMP9 Axis in CRC
3.6. MBOP Is Degraded by the Ubiquitin–Proteasome System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sveen, A.; Kopetz, S.; Lothe, R.A. Biomarker-guided therapy for colorectal cancer: Strength in complexity. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatos, G.; Köhne, C.H.; Bodoky, G. Current therapy of advanced colorectal cancer according to RAS/RAF mutational status. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, J.S.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, S.; Matrone, N.; Muddassir, A.L.; Martini, G.; Sorokin, A.; De Falco, V.; Giunta, E.F.; Ciardiello, D.; Martinelli, E.; Belli, V.; et al. Triple blockade of EGFR, MEK and PD-L1 has antitumor activity in colorectal cancer models with constitutive activation of MAPK signaling and PD-L1 overexpression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Deng, J.; Li, F.; Guo, B.; Zhang, S.; Wu, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. LncRNA-encoded polypeptide ASRPS inhibits triple-negative breast cancer angiogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, jem.20190950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, H.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Mao, C.; Liu, S. Peptide SMIM30 promotes HCC development by inducing SRC/YES1 membrane anchoring and MAPK pathway activation. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, J.Z.; Chen, D.; He, Y.T.; Meng, N.; Chen, M.; Lu, R.X.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Yan, G.R. An oncopeptide regulates m(6)A recognition by the m(6)A reader IGF2BP1 and tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, B.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, W.; Wu, C.; et al. A novel protein encoded by a circular RNA circPPP1R12A promotes tumor pathogenesis and metastasis of colon cancer via Hippo-YAP signaling. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, Y.J.; Yang, D.C.; Kong, L.; Hou, M.; Meng, Y.Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC2: A fast and accurate coding potential calculator based on sequence intrinsic features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W12–W16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Park, H.J.; Dasari, S.; Wang, S.; Kocher, J.P.; Li, W. CPAT: Coding-Potential Assessment Tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.H.; Huang, H.Y.; Hsu, J.B.; Weng, S.L.; Horng, J.T.; Huang, H.D. An enhanced computational platform for investigating the roles of regulatory RNA and for identifying functional RNA motifs. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14 (Suppl. S2), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michel, A.M.; Kiniry, S.J.; O’Connor, P.B.F.; Mullan, J.P.; Baranov, P.V. GWIPS-viz: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D823–D830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xi, X.; Bao, P.; Ma, Z.; Kapral, T.H.; Chen, S.; Zagrovic, B.; Yang, Y.T.; et al. POSTAR3: An updated platform for exploring post-transcriptional regulation coordinated by RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D287–D294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, N.; Chen, M.; Chen, D.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, J.Z.; Zhu, S.; He, Y.T.; Zhang, X.L.; Lu, R.X.; Yan, G.R. Small Protein Hidden in lncRNA LOC90024 Promotes "Cancerous" RNA Splicing and Tumorigenesis. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2020, 7, 1903233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.A.; Huong, S.M.; Huang, E.S. Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 by human cytomegalovirus infection through two distinct pathways: A novel mechanism for activation of p38. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, P.J.; Shahrier, A.Z.; Whitman, A.G.; Dyson, O.F.; Reber, A.J.; McCubrey, J.A.; Akula, S.M. Targeting the PI3K and MAPK pathways to treat Kaposi’s-sarcoma-associated herpes virus infection and pathogenesis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sadat, S.H.; Ebisumoto, K.; Sakai, A.; Panuganti, B.A.; Ren, S.; Goto, Y.; Haft, S.; Fukusumi, T.; Ando, M.; et al. Cannabinoids promote progression of HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via p38 MAPK activation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, P.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, H.; Pan, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. PEBP1 suppresses HIV transcription and induces latency by inactivating MAPK/NF-κB signaling. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.Y.; Richardson, B.C. The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; Li, Y.; Lee, J.; Schwartz, A.L.; Bu, G. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 promotes cancer cell migration and invasion by inducing the expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Q.; Lan, F.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Zheng, F.; Han, J.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xie, F.; et al. IL-1β-induced activation of p38 promotes metastasis in gastric adenocarcinoma via upregulation of AP-1/c-fos, MMP2 and MMP9. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Xia, H.; Hu, M.; Chen, C.; Fu, J.; Shi, G.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Shi, J.; et al. Isotalatizidine, a C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloid, attenuates chronic neuropathic pain through stimulating ERK/CREB signaling pathway-mediated microglial dynorphin A expression. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, N.; Palmieri, D.; Coppola, V. The CTLH Complex in Cancer Cell Plasticity. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 4216750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Yu, S.; Nie, F.; Yan, S.; Ma, P.; Chen, Q.; Wei, C.; Fu, H.; Xu, T.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC01234 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate CBFB expression by sponging miR-204-5p in gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2002–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Feng, X.; Tang, H.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, J.; Fu, B. LINC01234/microRNA-31-5p/MAGEA3 axis mediates the proliferation and chemoresistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cao, J.; Peng, X. LINC01234 facilitates growth and invasiveness of oral squamous cell carcinoma through regulating the miR-637/NUPR1 axis. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 120, 109507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y. Long noncoding RNA LINC01234 promotes serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 expression and proliferation by competitively binding miR-642a-5p in colon cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Han, L.N.; Song, J.R.; Bai, X.M.; Wang, J.Z.; Meng, L.F.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Feng, Y.; Feng, W.R.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC01234 silencing exerts an anti-oncogenic effect in esophageal cancer cells through microRNA-193a-5p-mediated CCNE1 downregulation. Cell Oncol. (Dordr.) 2020, 43, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Lei, T.; Gu, Y.; Gu, J.; Huang, J.; Lu, B.; Yuan, L.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z. Integrative analysis of NSCLC identifies LINC01234 as an oncogenic lncRNA that interacts with HNRNPA2B1 and regulates miR-106b biogenesis. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, B.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Lei, T.; Nie, F.; Gu, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, C.; et al. Up-regulated LINC01234 promotes non-small-cell lung cancer cell metastasis by activating VAV3 and repressing BTG2 expression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahronian, L.G.; Sennott, E.M.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wagle, N.; Kwak, E.L.; Faris, J.E.; Godfrey, J.T.; Nishimura, K.; Lynch, K.D.; Mermel, C.H.; et al. Clinical acquired resistance to RAF inhibitor combinations in BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer through MAPK pathway alterations. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corcoran, R.B.; André, T.; Atreya, C.E.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Yoshino, T.; Bendell, J.C.; Hollebecque, A.; McRee, A.J.; Siena, S.; Middleton, G.; et al. Combined BRAF, EGFR, and MEK inhibition in patients with BRAF(V600E)-mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ros, J.; Baraibar, I.; Sardo, E.; Mulet, N.; Salvà, F.; Argilés, G.; Martini, G.; Ciardiello, D.; Cuadra, J.L.; Tabernero, J.; et al. BRAF, MEK and EGFR inhibition as treatment strategies in BRAF V600E metastatic colorectal cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1758835921992974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Zheng, G.; Ning, Q.; Zheng, J.; Dong, D. Translation and functional roles of circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, J.; Lin, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Ramirez-Moya, J.; Du, P.; Kim, W.; Tang, S.; Sliz, P.; et al. mRNA circularization by METTL3-eIF3h enhances translation and promotes oncogenesis. Nature 2018, 561, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.W.; Yakymovych, I.; Jia, M.; Yakymovych, M.; Souchelnytskyi, S. Phosphorylation of eEF1A1 at ser300 by TβR-I results in inhibition of mRNA translation. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, W.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Ou, F.; Zeng, S.; Lin, N.; Yu, L. Oncopeptide MBOP Encoded by LINC01234 Promotes Colorectal Cancer through MAPK Signaling Pathway. Cancers 2022, 14, 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092338
Tang C, Zhou Y, Sun W, Hu H, Liu Y, Chen L, Ou F, Zeng S, Lin N, Yu L. Oncopeptide MBOP Encoded by LINC01234 Promotes Colorectal Cancer through MAPK Signaling Pathway. Cancers. 2022; 14(9):2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092338
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Chunyuan, Ying Zhou, Wen Sun, Haihong Hu, Yuxi Liu, Lu Chen, Fengting Ou, Su Zeng, Nengming Lin, and Lushan Yu. 2022. "Oncopeptide MBOP Encoded by LINC01234 Promotes Colorectal Cancer through MAPK Signaling Pathway" Cancers 14, no. 9: 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092338
APA StyleTang, C., Zhou, Y., Sun, W., Hu, H., Liu, Y., Chen, L., Ou, F., Zeng, S., Lin, N., & Yu, L. (2022). Oncopeptide MBOP Encoded by LINC01234 Promotes Colorectal Cancer through MAPK Signaling Pathway. Cancers, 14(9), 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14092338