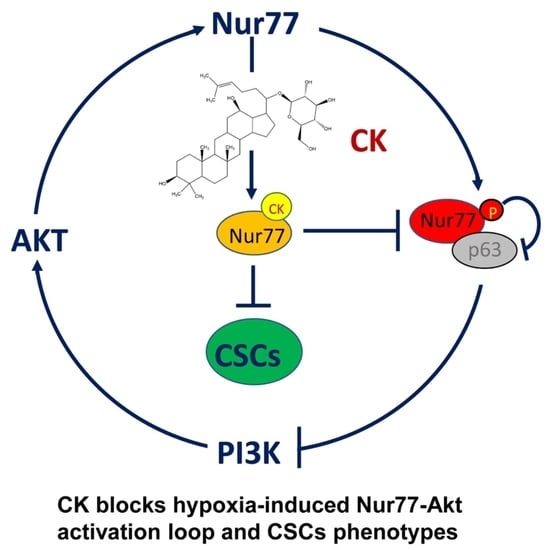
The Ginsenoside Compound K Suppresses Stem-Cell-like Properties and Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Hypoxia-Driven Nur77-Akt Feed-Forward Signaling
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies and Reagents
2.2. Molecular Docking
2.3. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC)
2.4. Fluorescence Titration
2.5. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.6. Co-Immunoprecipitation
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Real-Time PCR and qPCR
2.9. Tumor Sphere Formation Assay
2.10. CRISPR/Cas9
2.11. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assays
2.12. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.13. Animal Experiments
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CK as a New Ligand for Nur77
3.2. CK Inhibits CSC Phenotypes Dependent on Nur77
3.3. Nur77 Is Hyper-Phosphorylated under a Hypoxic Microenvironment
3.4. Akt-Mediated Phosphorylation Regulates Nur77 Interaction with p63
3.5. CK Disrupts Hypoxia-Induced Nur77 Complex with p63 on Dicer Promoter by Modulating Nur77 Phosphorylation
3.6. Depletion of CSC Markers by CK Is Associated with the Disruption of the Nur77-Akt Feed-Forward Loop
3.7. The Anti-Metastasis Effect of CK In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.C.S.; Huang, J.; Lok, V.; Wang, J.; Fung, F.; Ding, H.; Zheng, Z.J. Differences in Incidence and Mortality Trends of Colorectal Cancer Worldwide Based on Sex, Age, and Anatomic Location. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2021, 19, 955–966.e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biller, L.H.; Schrag, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopetz, S.; Grothey, A.; Yaeger, R.; Van Cutsem, E.; Desai, J.; Yoshino, T.; Wasan, H.; Ciardiello, F.; Loupakis, F.; Hong, Y.S.; et al. Encorafenib, Binimetinib, and Cetuximab in BRAF V600E-Mutated Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.P.; Ke, T.W.; Cheng, R.; Wang, J.Y. Ramucirumab in the second-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: A narrative review of literature from clinical trials. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 5645–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Qi, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Z.; Wang, X.; Lu, M.; Shen, L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety Comparison of Regorafenib and Fruquintinib in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer-An Observational Cohort Study in the Real World. Clin. Color. Cancer 2022, 21, e152–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.L.; Cole, S.W. Ziv-aflibercept (Zaltrap) for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Shiu, K.K.; Kim, T.W.; Jensen, B.V.; Jensen, L.H.; Punt, C.; Smith, D.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Benavides, M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for microsatellite instability-high or mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer (KEYNOTE-177): Final analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Yang, M.; Wang, M.X.; Jiang, J.H.; Jiang, D.Y.; Chen, Z.L.; Yang, L. Refractory hypokalemia caused by cetuximab with advanced colorectal cancer patients: The case series and literature review. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2022, 33, e789–e794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Albéniz, X.; Alonso, V.; Escudero, P.; Méndez, M.; Gallego, J.; Rodríguez, J.R.; Salud, A.; Fernández-Plana, J.; Manzano, H.; Zanui, M.; et al. Prospective Biomarker Study in Advanced RAS Wild-Type Colorectal Cancer: POSIBA Trial (GEMCAD 10-02). Oncologist 2019, 24, e1115–e1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A.; Christou, N.; Akil, H.; Melin, C.; Battu, S.; Jauberteau, M.O.; Denizot, Y. Hallmarks in colorectal cancer: Angiogenesis and cancer stem-like cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 4189–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.P.; Lee, Y.T.; Yang, S.H.; Miller, S.A.; Chiou, S.H.; Hung, M.C.; Hung, S.C. Colon cancer stem cells resist antiangiogenesis therapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2013, 328, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, G.; Aziz, S.G.; Jaghi, N.Z.Z. EMT, cancer stem cells and autophagy; The three main axes of metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsalias, A.; Kozovska, Z. Personalized medicine: Stem cells in colorectal cancer treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeuner, A.; Todaro, M.; Stassi, G.; De Maria, R. Colorectal cancer stem cells: From the crypt to the clinic. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaupel, P.; Mayer, A. Hypoxia in cancer: Significance and impact on clinical outcome. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007, 26, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia—A key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schito, L.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors: Master Regulators of Cancer Progression. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ding, Z.; Peng, Y.; Pan, F.; Li, J.; Zou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H. HIF-1α inhibition reverses multidrug resistance in colon cancer cells via downregulation of MDR1/P-glycoprotein. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Hou, M.; Guan, Y.S.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Y.; Gou, H.F. Expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in colorectal cancer: Association with clinical outcomes and prognostic implications. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiory, F.; Mirra, P.; Nigro, C.; Pignalosa, F.C.; Zatterale, F.; Ulianich, L.; Prevete, N.; Formisano, P.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Role of the HIF-1α/Nur77 axis in the regulation of the tyrosine hydroxylase expression by insulin in PC12 cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 11861–11870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Park, S.C.; Kang, G.H.; Liu, J.O.; Youn, H.D. Nur77 activated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha overproduces proopiomelanocortin in von Hippel-Lindau-mutated renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; To, S.K.Y.; Zhang, S.; Deng, S.; Artemenko, M.; Zhang, M.; Tang, J.; Zeng, J.Z.; Wong, A.S.T. Hypoxia-induced Nur77 activates PI3K/Akt signaling via suppression of Dicer/let-7i-5p to induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3376–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.R.; Gan, W.J.; Li, X.M.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.X.; Li, J.M.; Wu, H. Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by regulating MMP-9 and E-cadherin. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2474–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, W.; Sun, Z.; Gao, W.; Zhang, H.; Xie, L.; Jiang, F.; Qin, B.; Yan, T.; et al. Regulation of Nur77 expression by β-catenin and its mitogenic effect in colon cancer cells. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2011, 25, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, T.K. Panax ginseng—A non-organ-specific cancer preventive? Lancet Oncol. 2001, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Wang, R.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z. Ginsenosides in Panax genus and their biosynthesis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1813–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhao, Y. Current evaluation of the millennium phytomedicine—Ginseng (I): Etymology, pharmacognosy, phytochemistry, market and regulations. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.K.; Jin, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kang, W.Y.; Seong, S.J.; Yoon, Y.R.; Han, Y.H.; Song, I.S. Tolerability and pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, and compound K after single or multiple administration of red ginseng extract in human beings. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Choi, M.S.; Jeung, W.; Ra, J.; Yoo, H.H.; Kim, D.H. Effects of gut microbiota on the pharmacokinetics of protopanaxadiol ginsenosides Rd, Rg3, F2, and compound K in healthy volunteers treated orally with red ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Luo, Q.; Alitongbieke, G.; Chong, S.; Xu, C.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Celastrol-Induced Nur77 Interaction with TRAF2 Alleviates Inflammation by Promoting Mitochondrial Ubiquitination and Autophagy. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 141–153.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.; Kim, J.S. Compound K derived from ginseng: Neuroprotection and cognitive improvement. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 4506–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekarsky, Y.; Hallas, C.; Palamarchuk, A.; Koval, A.; Bullrich, F.; Hirata, Y.; Bichi, R.; Letofsky, J.; Croce, C.M. Akt phosphorylates and regulates the orphan nuclear receptor Nur77. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3690–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.H.; Cao, X.; Lin, B.; Lin, F.; Kolluri, S.K.; Stebbins, J.; Reed, J.C.; Dawson, M.I.; Zhang, X.K. Regulation of Nur77 nuclear export by c-Jun N-terminal kinase and Akt. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2974–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.Z.; Zhao, B.X.; Zhao, W.X.; Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Q. Akt phosphorylates the TR3 orphan receptor and blocks its targeting to the mitochondri. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2078–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.M.; Kim, E.; Chun, S. Ginsenoside Compound K Induces Ros-Mediated Apoptosis and Autophagic Inhibition in Human Neuroblastoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saus, E.; Iraola-Guzmán, S.; Willis, J.R.; Brunet-Vega, A.; Gabaldón, T. Microbiome and colorectal cancer: Roles in carcinogenesis and clinical potential. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 69, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnière, J.; Raisch, J.; Veziant, J.; Barnich, N.; Bonnet, R.; Buc, E.; Bringer, M.A.; Pezet, D.; Bonnet, M. Gut microbiota imbalance and colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.M.; Liu, H.L. Fusobacterium nucleatum and colorectal cancer: A review. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2018, 10, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ding, S.; Sun, L.; Feng, Y.; Guo, K.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, D.; Ruan, S. Characteristics and differences of gut microbiota in patients with different Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndromes of Colorectal Cancer and normal population. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 7357–7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Guo, F.; Yu, Y.; Sun, T.; Ma, D.; Han, J.; Qian, Y.; Kryczek, I.; Sun, D.; Nagarsheth, N.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Promotes Chemoresistance to Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Autophagy. Cell 2017, 170, 548–563.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Gan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhi, F. Streptococcus gallolyticus conspires myeloid cells to promote tumorigenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 506, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, P.Y.; Bae, K.H.; Cho, S.; Park, B.C.; Shin, H.; Park, S.G. Ginsenoside Rb1 is transformed into Rd and Rh2 by Microbacterium trichothecenolyticum. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 1802–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giannoni, E.; Parri, M.; Chiarugi, P. EMT and oxidative stress: A bidirectional interplay affecting tumor malignancy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, V.T.; Bindra, R.S.; Yuan, J.; Campisi, D.; Narayanan, L.; Jensen, R.; Giordano, F.; Johnson, R.S.; Rockwell, S.; Glazer, P.M. Decreased expression of the DNA mismatch repair gene Mlh1 under hypoxic stress in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 3265–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.Z.; Li, L.; Wang, W.J.; Du, X.D.; Wen, Q.; He, J.P.; Zhao, B.X.; Li, G.D.; Zhou, W.; Xia, Y.; et al. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 stabilizes and activates orphan nuclear receptor TR3 to promote mitogenesis. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2876–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slagsvold, H.H.; Østvold, A.C.; Fallgren, A.B.; Paulsen, R.E. Nuclear receptor and apoptosis initiator NGFI-B is a substrate for kinase ERK2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 291, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Liu, Q.F.; Li, L.; Wang, W.J.; Yao, L.M.; Yang, M.; Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Zhan, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.Q.; et al. The orphan receptor TR3 suppresses intestinal tumorigenesis in mice by downregulating Wnt signalling. Gut 2012, 61, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, S.K.; Zeng, J.Z.; Wong, A.S. Nur77: A potential therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowsky, K.; Nitsche, U.; Janssen, K.P.; Bader, F.G.; Späth, C.; Drecoll, E.; Keller, G.; Höfler, H.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Becker, K.F. Activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway correlates with prognosis in stage II colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spangle, J.M.; Roberts, T.M.; Zhao, J.J. The emerging role of PI3K/AKT-mediated epigenetic regulation in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2017, 1868, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; To, S.K.Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, H.; Wong, A.S.T.; et al. The Ginsenoside Compound K Suppresses Stem-Cell-like Properties and Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Hypoxia-Driven Nur77-Akt Feed-Forward Signaling. Cancers 2023, 15, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010024
Zhang M, Shi Z, Zhang S, Li X, To SKY, Peng Y, Liu J, Chen S, Hu H, Wong AST, et al. The Ginsenoside Compound K Suppresses Stem-Cell-like Properties and Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Hypoxia-Driven Nur77-Akt Feed-Forward Signaling. Cancers. 2023; 15(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Minda, Zeyu Shi, Shuaishuai Zhang, Xudan Li, Sally Kit Yan To, Yijia Peng, Jie Liu, Siming Chen, Hongyu Hu, Alice Sze Tsai Wong, and et al. 2023. "The Ginsenoside Compound K Suppresses Stem-Cell-like Properties and Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Hypoxia-Driven Nur77-Akt Feed-Forward Signaling" Cancers 15, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010024
APA StyleZhang, M., Shi, Z., Zhang, S., Li, X., To, S. K. Y., Peng, Y., Liu, J., Chen, S., Hu, H., Wong, A. S. T., & Zeng, J. -Z. (2023). The Ginsenoside Compound K Suppresses Stem-Cell-like Properties and Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Hypoxia-Driven Nur77-Akt Feed-Forward Signaling. Cancers, 15(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010024