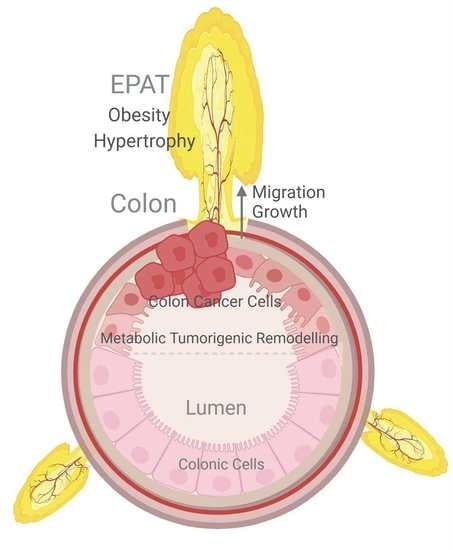
Epiploic Adipose Tissue (EPAT) in Obese Individuals Promotes Colonic Tumorigenesis: A Novel Model for EPAT-Dependent Colorectal Cancer Progression
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Samples
2.2. Mouse Model for High-Fat Diet Obesity and Colonic Tumorigenesis (Transcriptomic Data)
2.3. Cells
2.4. Epiploic Colonic Microphysiological System (CRC-MPS) and Conditioned Media
2.5. BrdU and EdU Staining and Migration Assays
2.6. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.7. Quantitative PCR
2.8. RNA Sequencing and Differential Expression
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bluher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2019, 14, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraiyarasan, S.; Adefuye, M.; Manjunatha, N.; Ganduri, V.; Rajasekaran, K. Colon Cancer and Obesity: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e27589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.C.; Itzkowitz, S.H. Colorectal Cancer in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Mechanisms and Management. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 715–730 e713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenkov, M.; Ma, Y.; Gassler, N.; Chen, Y. Metabolic Reprogramming of Colorectal Cancer Cells and the Microenvironment: Implication for Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Fitchev, P.S.; Cornwell, M.L.; Greenberg, J.; Cabe, M.; Weber, C.R.; Roy, H.K.; Crawford, S.E.; Savkovic, S.D. FOXO3 growth inhibition of colonic cells is dependent on intraepithelial lipid droplet density. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 16274–16281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, R.; Penrose, H.M.; King, A.N.; Samudre, J.S.; Collins, M.E.; Hartono, A.B.; Lee, S.B.; Lau, F.; Baddoo, M.; Flemington, E.F.; et al. Elevated ATGL in colon cancer cells and cancer stem cells promotes metabolic and tumorigenic reprogramming reinforced by obesity. Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, H.M.; Heller, S.; Cable, C.; Nakhoul, H.; Baddoo, M.; Flemington, E.; Crawford, S.E.; Savkovic, S.D. High-fat diet induced leptin and Wnt expression: RNA-sequencing and pathway analysis of mouse colonic tissue and tumors. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, L.; Didt, K.; Karkossa, I.; Bernhart, S.H.; Kehr, S.; Subramanian, N.; Lindhorst, A.; Schaudinn, A.; Tabei, S.; Keller, M.; et al. Multiomics reveal unique signatures of human epiploic adipose tissue related to systemic insulin resistance. Gut 2021, 71, 2179–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannis, D.; Matenoglou, E.; Sidiropoulou, M.S.; Papalampros, A.; Schmitz, R.; Felekouras, E.; Moris, D. Epiploic appendagitis: Pathogenesis, clinical findings and imaging clues of a misdiagnosed mimicker. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, H.; Goethals, L.; Belsack, D.; Brucker, Y.; Allemeersch, G.J.; Ilsen, B.; Vandenbroucke, F.; de Mey, J. Fat misbehaving in the abdominal cavity: A pictorial essay. Pol. J. Radiol. 2020, 85, e32–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, M.; Gelos, M.; Bechara, F.G.; Sand, D.; Wiese, T.H.; Steinstraesser, L.; Mann, B. Epiploic appendagitis-clinical characteristics of an uncommon surgical diagnosis. BMC Surg. 2007, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onogi, Y.; Ussar, S. Is epiploic fat the dermal fat of the intestine? Gut 2021, 71, 2147–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.I.; Woo, H.S.; Chung, J.W.; Shim, Y.S.; Kwon, K.A.; Kim, K.O.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, D.K. Primary epiploic appendagitis: Compared with diverticulitis and focused on obesity and recurrence. Intest. Res. 2019, 17, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugent, J.P.; Ouellette, H.A.; O’Leary, D.P.; Khosa, F.; Nicolaou, S.; McLaughlin, P.D. Epiploic appendagitis: 7-year experience and relationship with visceral obesity. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, F.H.; Vogel, K.; Luckett, J.P.; Hunt, M.; Meyer, A.; Rogers, C.L.; Tessler, O.; Dupin, C.L.; St Hilaire, H.; Islam, K.N.; et al. Sandwiched White Adipose Tissue: A Microphysiological System of Primary Human Adipose Tissue. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2018, 24, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrala, R.; Byrne, C.E.; Brown, L.M.; Tiongco, R.F.P.; Matossian, M.D.; Savoie, J.J.; Collins-Burow, B.M.; Burow, M.E.; Martin, E.C.; Lau, F.H. Quantifying Breast Cancer-Driven Fiber Alignment and Collagen Deposition in Primary Human Breast Tissue. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 618448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scahill, S.D.; Hunt, M.; Rogers, C.L.; Lau, F.H. A Microphysiologic Platform for Human Fat: Sandwiched White Adipose Tissue. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 138, e57909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.L.; Strong, T.A.; Rhodes, L.V.; Semon, J.A.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.; Gimble, J.M.; Burow, M.E.; Bunnell, B.A. Obesity associated alterations in the biology of adipose stem cells mediate enhanced tumorigenesis by estrogen dependent pathways. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourin, P.; Bunnell, B.A.; Casteilla, L.; Dominici, M.; Katz, A.J.; March, K.L.; Redl, H.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoshimura, K.; Gimble, J.M. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: A joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penrose, H.M.; Heller, S.; Cable, C.; Nakhoul, H.; Ungerleider, N.; Baddoo, M.; Pursell, Z.F.; Flemington, E.K.; Crawford, S.E.; Savkovic, S.D. In colonic rho(0) (rho0) cells reduced mitochondrial function mediates transcriptomic alterations associated with cancer. Oncoscience 2017, 4, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, C.; Garcia, J.M.; Larriba, M.J.; Barderas, R.; Gomez, I.; Herrera, M.; Garcia, V.; Silva, J.; Dominguez, G.; Rodriguez, R.; et al. SNAI1 expression in colon cancer related with CDH1 and VDR downregulation in normal adjacent tissue. Oncogene 2009, 28, 4375–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Guo, K.; Sun, X.; Hu, F.; Chen, Q.; Luo, X.; Wang, G.; Hu, J.; Sun, L. TRIB2 functions as novel oncogene in colorectal cancer by blocking cellular senescence through AP4/p21 signaling. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaa, G.M.; Vitre, B.; Carpenter, G.; Abramowicz, I.; Gleeson, J.G.; Paciorkowski, A.R.; Cleveland, D.W.; Dobyns, W.B.; O’Driscoll, M. Mutations in CENPE define a novel kinetochore-centromeric mechanism for microcephalic primordial dwarfism. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 1023–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhn, S.C.; Liu, J.; Ye, C.; Lu, H.; Jiang, X.; Feng, X.; Ganesan, S.; White, E.; Shen, Z. Regulation of spindle integrity and mitotic fidelity by BCCIP. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4750–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Wang, H.; Fang, J.; Zheng, J.; Liu, B.; Xia, L.; Li, D. Overexpression of OAS1 Is Correlated With Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 944194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. Prognostic characterization of OAS1/OAS2/OAS3/OASL in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, M.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, H.; Chang, W.; Yu, G.; Niu, Y. Accumulation of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase (NNMT) in Cancer-associated Fibroblasts: A Potential Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker for Gastric Carcinoma. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2021, 69, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, C.W.Y.; Martin, A.; Sepich-Poore, G.D.; Shi, B.; Wang, Y.; Gouin, K.; Humphrey, G.; Sanders, K.; Ratnayake, Y.; Chan, K.S.L.; et al. Translocation of Viable Gut Microbiota to Mesenteric Adipose Drives Formation of Creeping Fat in Humans. Cell 2020, 183, 666–683 e617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernstedt Asterholm, I.; Tao, C.; Morley, T.S.; Wang, Q.A.; Delgado-Lopez, F.; Wang, Z.V.; Scherer, P.E. Adipocyte inflammation is essential for healthy adipose tissue expansion and remodeling. Cell Metabolism 2014, 20, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Brooks, R.S.; Ciappio, E.D.; Kim, S.J.; Crott, J.W.; Bennett, G.; Greenberg, A.S.; Mason, J.B. Diet-induced obesity elevates colonic TNF-alpha in mice and is accompanied by an activation of Wnt signaling: A mechanism for obesity-associated colorectal cancer. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, J.E. Molecular mechanisms linking adipokines to obesity-related colon cancer: Focus on leptin. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2012, 71, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftikhar, R.; Penrose, H.M.; King, A.N.; Kim, Y.; Ruiz, E.; Kandil, E.; Machado, H.L.; Savkovic, S.D. FOXO3 Expression in Macrophages Is Lowered by a High-Fat Diet and Regulates Colonic Inflammation and Tumorigenesis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penrose, H.M.; Cable, C.; Heller, S.; Ungerleider, N.; Nakhoul, H.; Baddoo, M.; Hartono, A.B.; Lee, S.B.; Burow, M.E.; Flemington, E.F.; et al. Loss of Forkhead Box O3 Facilitates Inflammatory Colon Cancer: Transcriptome Profiling of the Immune Landscape and Novel Targets. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, D.; Ma, X.; Li, H.Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, Q.; Zhang, P.; Song, E.L.; Huang, Q.B.; et al. Downregulation of FOXO3a promotes tumor metastasis and is associated with metastasis-free survival of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborative, R.; Zaborowski, A.M.; Abdile, A.; Adamina, M.; Aigner, F.; d’Allens, L.; Allmer, C.; Alvarez, A.; Anula, R.; Andric, M.; et al. Characteristics of Early-Onset vs Late-Onset Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuik, F.E.; Nieuwenburg, S.A.; Bardou, M.; Lansdorp-Vogelaar, I.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Bento, M.J.; Zadnik, V.; Pellise, M.; Esteban, L.; Kaminski, M.F.; et al. Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer in young adults in Europe over the last 25 years. Gut 2019, 68, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iftikhar, R.; Snarski, P.; King, A.N.; Ghimire, J.; Ruiz, E.; Lau, F.; Savkovic, S.D. Epiploic Adipose Tissue (EPAT) in Obese Individuals Promotes Colonic Tumorigenesis: A Novel Model for EPAT-Dependent Colorectal Cancer Progression. Cancers 2023, 15, 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030977
Iftikhar R, Snarski P, King AN, Ghimire J, Ruiz E, Lau F, Savkovic SD. Epiploic Adipose Tissue (EPAT) in Obese Individuals Promotes Colonic Tumorigenesis: A Novel Model for EPAT-Dependent Colorectal Cancer Progression. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030977
Chicago/Turabian StyleIftikhar, Rida, Patricia Snarski, Angelle N. King, Jenisha Ghimire, Emmanuelle Ruiz, Frank Lau, and Suzana D. Savkovic. 2023. "Epiploic Adipose Tissue (EPAT) in Obese Individuals Promotes Colonic Tumorigenesis: A Novel Model for EPAT-Dependent Colorectal Cancer Progression" Cancers 15, no. 3: 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030977
APA StyleIftikhar, R., Snarski, P., King, A. N., Ghimire, J., Ruiz, E., Lau, F., & Savkovic, S. D. (2023). Epiploic Adipose Tissue (EPAT) in Obese Individuals Promotes Colonic Tumorigenesis: A Novel Model for EPAT-Dependent Colorectal Cancer Progression. Cancers, 15(3), 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030977