Modulation of the Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy by Nitric Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nitric Oxide and Nitric Oxide Synthases
3. Nitric Oxide: Positive and Negative Biological Effects
4. Nitric Oxide Signaling in Cancer
5. Nitric Oxide and PDT: Early Studies
6. Nitric Oxide and PDT: Relatively Recent Studies
6.1. Breast Cancer Cells
6.2. Prostate Cancer Cells
6.3. Glioblastoma Cells
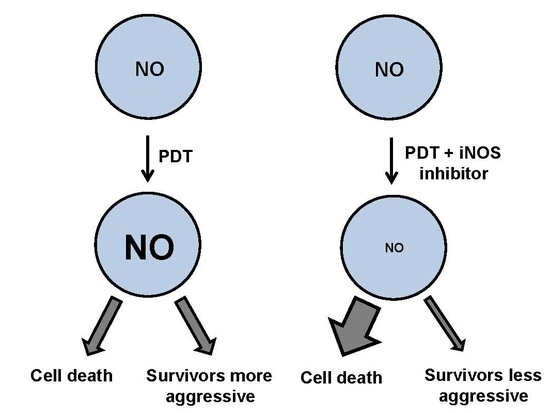
7. Duality of iNOS/NO-Mediated Signaling in PDT
8. Role of iNOS-Derived NO in PDT Bystander Effects
9. iNOS Inhibitors as Potential PDT Adjuvants
10. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wink, D.A.; Mitchell, J.B. Chemical biology of nitric oxide: Insights into the regulatory, cytotoxic, and cytoprotective mechanisms of nitric oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 25, 434–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridnour, L.A.; Thomas, D.D.; Donzelli, S.; Espey, M.G.; Roberts, D.D.; Wink, D.A.; Isenberg, J.S. The biphasic nature of nitric oxide responses in tumor biology. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.D.; Ridnour, L.A.; Isenberg, J.S.; Flores-Santana, W.; Switzer, C.H.; Donzelli, S.; Hussain, P.; Vecoli, C.; Paolocci, N.; Ambs, S.; et al. The chemical biology of nitric oxide: Implications in cellular signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, T.A.; da Silva, R.S.; Miranda, K.M.; Switzer, C.H.; Wink, D.A.; Fukuto, J.M. Biological nitric oxide signaling; chemistry and terminology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, R.G.; Moncada, S. Nitric oxide synthases in mammals. Biochem. J. 1994, 298, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderton, W.K.; Cooper, C.E.; Knowles, R.G. Nitric oxide synthases: Structure, function and inhibition. Biochem. J. 2001, 357, 593–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.D.; Heinecke, J.L.; Ridnour, L.A.; Cheng, R.Y.; Kesarwala, A.H.; Switzer, C.H.; McVicar, D.W.; Roberts, D.D.; Glynn, S.; Fukuto, J.M.; et al. Signaling and stress: The redox landscape in NOS2 biology. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 87, 204–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, E.E.; Wagner, B.A.; Buettner, G.R.; Burns, C.P. Nitric oxide inhibits iron-induced lipid peroxidation in HL-60 cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 370, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korytowski, W.; Zareba, M.; Girotti, A.W. Nitric oxide inhibition of free radical-mediated cholesterol peroxidation in liposomal membranes. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 6918–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korytowski, W.; Zareba, M.; Girotti, A.W. Inhibition of free radical-mediated cholesterol peroxidation by diazeniumdiolate-derived nitric oxide; effect of release rate on mechanism of action in a membrane system. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2000, 13, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotti, A.W. Lipid hydroperoxide generation, turnover, and effector action in biological systems. J. Lipid Res. 1998, 39, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wink, D.A.; Hines, H.B.; Cheng, R.Y.; Switzer, C.H.; Flores-Santana, W.; Vitek, M.P.; Ridnour, L.A.; Colton, C.A. Nitric oxide and redox mechanisms in the immune response. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 873–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowell, J.A.; Steele, V.E.; Sigman, C.C.; Fay, J.R. Is inducible nitric oxide synthase a target for chemoprevention? Mol. Cancer Ther. 2003, 1, 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Sikora, A.G.; Gelbard, A.; Davies, M.A.; Sano, D.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Kwon, J.; Hailemichael, Y.; Jayaraman, P.; Myers, J.N.; Grimm, E.A.; et al. Targeted inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibits growth of human melanoma in vivo and synergizes with chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyler, C.E.; Wu, Q.; Yan, K.; MacSwords, J.M.; Chandler-Militello, D.; Misuraca, K.L.; Lathia, J.D.; Forrester, M.T.; Lee, J.; Stamler, J.S.; et al. Glioma stem cell proliferation and tumor growth are promoted by nitric oxide synthase-2. Cell 2011, 146, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, T.; Chelluboina, B.; Ponnala, S.; Velpula, K.K.; Rehman, A.A.; Chetty, C.; Zakharian, E.; Rao, J.S.; Veeravalli, K.K. Involvement of nitric oxide synthase in matrix metalloproteinase-9- and/or urokinase plasminogen activator receptor-mediated glioma cell migration. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinecke, J.L.; Ridnour, L.A.; Cheng, R.Y.; Switzer, C.H.; Lizardo, M.M.; Khanna, C.; Glynn, S.A.; Hussain, S.P.; Young, H.A.; Ambs, S.; et al. Tumor microenvironment-based feed-forward regulation of NOS2 in breast cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6323–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T.; Yamaji, Y.; Tomokuni, T.; Morita, H.; Morikawa, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Yonezawa, A.; Endo, S.; Ikari, A.; Iguchi, K.; et al. Nitric oxide confers cisplatin resistance in human lung cancer cells through upregulation of aldo-keto reductase 1B10 and proteasome. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switzer, C.H.; Glynn, S.A.; Ridnour, L.A.; Cheng, R.Y.; Vitek, M.P.; Ambs, S.; Wink, D.A. Nitric oxide and protein phosphatase 2A provide novel therapeutic opportunities in ER-negative breast cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, K.; Ambs, S.; Lupold, S.E.; Kapust, R.B.; Spillare, E.A.; Weinberg, W.C.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Wang, X.W.; Geller, D.A.; Tzeng, E.; et al. Nitric oxide-induced p53 accumulation and regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by wild-type p53. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2442–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambs, S.; Ogunfusika, M.O.; Merriam, W.G.; Bennett, W.P.; Billiar, T.R.; Harris, C.C. Up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in cancer-prone p53 knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8823–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calmels, S.; Hainaut, P.; Ohshima, H. Nitric oxide induces conformational and functional modifications of wild-type p53 tumor suppressor protein. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 3365–3369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ambs, S.; Merriam, W.G.; Ogunfusika, M.O.; Bennett, W.P.; Ishibe, N.; Hussain, S.P.; Tzeng, E.E.; Geller, D.A.; Billiar, T.R.; Harris, C.C. p53 and vascular endothelial growth factor regulate tumor growth of NOS2-expressing human carcinoma cells. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broniowska, K.A.; Hogg, N. The chemical biology of S-nitrosothiols. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.D.; Jord’heuil, D. S-nitrosation: Current concepts and new developments. Antiox. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Huh, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, E.J. Nitric oxide negatively regulates C-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase by means of S-nitrosylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14382–14387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Wu, J.-W.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, M.-S.; Huh, S.-H.; Ryoo, K.; Choi, E.J. Inhibition of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 by nitric oxide through a thiol redox mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 7584–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Tannenbaum, S.R. S-Nitrosation regulates the activation of endogenous procaspase-9 in HT-29 human colon carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 9758–9764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, N.; Vallyathan, V.; Wang, L.; Tantishaiyakul, V.; Stehlik, C.; Leonardm, S.S.; Rojanasakul, Y. S-nitrosylation of Bcl-2 inhibits its ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34124–34134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switzer, C.H.; Glynn, S.A.; Cheng, R.Y.; Ridnour, L.A.; Green, J.E.; Ambs, S.; Wink, D.A. S-nitrosylation of EGFR and Src activates an oncogenic signaling network in human basal-like breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, Y.D.; Ma, T.; Diao, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Hsu, J.; Lipton, S.A.; Masliah, E.; Xu, H.; Liao, F.F. NO signaling and S-nitrosylation regulate PTEN inhibition in neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 2010, 5, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.; Sha, J.; Chen, X.; Xing, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, Z. S-Nitrosylation of mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 suppresses radiation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2012, 314, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, W.; Suzuki, Y.; Mobaraki, A.; Yoshida, Y.; Noda, S.; Saitoh, J.I.; Nakano, T. Reduction of nitric oxide level enhances the radiosensitivity of hypoxic non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T.; Yamaji, Y.; Tomokuni, T.; Morita, H.; Morikawa, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Yonezawa, A.; Endo, S.; Ikari, A.; Iguchi, K.; et al. Nitric oxide confers cisplatin resistance in human lung cancer cells through upregulation of aldo-keto reductase 1B10 and proteasome. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Ahmad, N.; Mukhtar, H. Involvement of nitric oxide during phthalocyanine (Pc4) photodynamic therapy-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 2548–2552. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, E.R.; Almeida, R.D.; Carvalho, A.P.; Duarte, C.B. Nitric oxide modulates tumor cell death induced by photodynamic therapy through a cGMP-dependent mechanism. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 76, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.W.; Sitnik-Busch, T.M.; Vaughan, L.A. Potentiation of photodynamic therapy antitumor activity in mice by nitric oxide synthase inhibition is fluence rate dependent. Photochem. Photobiol. 1999, 70, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbelik, M.; Shibuya, H.; Cecic, I. Relevance of nitric oxide to the response of tumors to photodynamic therapy. SPIE Proc. 1998, 3247, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Korbelik, M.; Parkins, C.S.; Shibuya, H.; Cecic, I.; Stratford, R.M.L.; Chaplin, D.J. Nitric oxide production by tumor tissue: Impact on the response to photodynamic therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, K.L.; Reed, M.W.R.; Brown, N.J. The role of nitric oxide in the treatment of tumours with aminolaevulinic acid-induced photodynamic therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2010, 101, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Berg, K.; Moan, J.; Kongshaug, M.; Nesland, J.M. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy: Principles and experimental research. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 65, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriska, T.; Korytowski, W.; Girotti, A.W. Hyperresistance to photosensitized lipid peroxidation and apoptotic killing in 5-aminolevulinate-treated tumor cells overexpressing mitochondrial GPX4. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 1389–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis, P.; Berg, K.; Cengel, K.A.; Foster, T.H.; Girotti, A.W.; Gollnick, S.O.; Hahn, S.M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Juzeniene, A.; Kessel, D.; et al. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 250–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benov, L. Photodynamic therapy: Current status and future directions. Med. Princ. Pract. 2015, 24, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotti, A.W. Photosensitized oxidation of membrane lipids: Reaction pathways, cytotoxic effects, and cytoprotective mechanisms. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2001, 63, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niziolek, M.; Korytowski, W.; Girotti, A.W. Nitric oxide inhibition of free radical-mediated lipid peroxidation in photodynamically treated membranes and cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niziolek, M.; Korytowski, W.; Girotti, A.W. Chain-breaking antioxidant and cytoprotective action of nitric oxide on photodynamically stressed tumor cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2003, 78, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niziolek, M.; Korytowski, W.; Girotti, A.W. Nitric oxide-induced resistance to lethal photooxidative damage in a breast tumor cell line. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 40, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niziolek-Kierecka, M.; Korytowski, W.; Girotti, A.W. Tumor cell hyperresistance to photodynamic killing arising from nitric oxide preconditioning. SPIE Proc. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, R.; Girotti, A.W. Cytoprotective induction of nitric oxide synthase in a cellular model of 5-aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, R.; Girotti, A.W. Rapid upregulation of cytoprotective nitric oxide in breast tumor cells subjected to a photodynamic therapy-like oxidative challenge. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 87, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, R.; Girotti, A.W. Cytoprotective signaling associated with nitric oxide upregulation in tumor cells subjected to photodynamic therapy-like oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 57, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahey, J.M.; Girotti, A.W.; Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA. Unpublished data 1. 2015.
- Bhowmick, R.; Girotti, A.W. Signaling events in apoptotic photokilling of 5-aminolevulinic acid-treated tumor cells: Inhibitory effects of nitric oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahey, J.M.; Girotti, A.W. Nitric oxide-mediated resistance to photodynamic therapy in a human breast tumor xenograft model: improved outcome with NOS2 inhibitors. Nitric Oxide 2016. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmick, R.; Girotti, A.W. Pro-survival and pro-growth effects of stress-induced nitric oxide in a prostate cancer photodynamic therapy model. Cancer Lett. 2014, 343, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahey, J.M.; Girotti, A.W. Accelerated migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells after a photodynamic therapy-like challenge: Role of nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide 2015, 49, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahey, J.M.; Girotti, A.W.; Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA. Unpublished data 2. 2015.
- Stamenkovic, I. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2000, 10, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, S.; Medina, C.; Ledwidge, M.; Radomski, M.W.; Gilmer, J.F. Nitric oxide-matrix metalloproteinase-9 interactions: Biology and pharmacological significance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahey, J.M.; Emmer, J.V.; Korytowski, W.; Hogg, N.; Girotti, A.W. Antagonistic effects of endogenous nitric oxide in a glioblastoma photodynamic therapy model. Photochem. Photobiol. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behin, A.; Hoang-Suan, K.; Carpentier, A.F.; Delattre, J.Y. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 2003, 361, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylli, S.S.; Kaye, A.H.; MacGregor, L.; Howes, M.; Rajendra, P. Photodynamic therapy of high grade glioma: Long-term survival. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2005, 12, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechet, D.; Mordon, S.R.; Guillemin, F.; Barberi-Heyob, M.A. Photodynamic therapy of malignant brain tumours: A complementary approach to conventional therapies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, H.T. High-grade glioma/glioblastoma multiforme: Is there a role for photodynamic therapy? J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2012, 10, S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quirk, B.J.; Brandal, G.; Donlon, S.; Vera, J.C.; Mang, T.S.; Foy, A.B.; Lew, S.M.; Girotti, A.W.; Jogal, S.; LaViolette, P.S.; et al. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) for malignant brain tumors—Where do we stand? Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2015, 12, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam-Himlin, D.; Espey, M.G.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Castellani, R.J. Malignant glioma progression and nitric oxide. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 49, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahani-Asi, A.; Bonni, A. iNOS: A potential therapeutic target for malignant glioma. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriover, N.; Ulu, M.O.; Isler, C.; Durak, H.; Oz, B.; Uzan, M.; Akar, Z. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression in glial tumors: Correlation with malignancy and tumor proliferation. Neurol Res. 2008, 30, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapozzi, V.; Umezawa, K.; Xodo, L.E. Role of NF-κB/Snail/RKIP loop in the response of tumor cells to photodynamic therapy. Lasers Surg. Med. 2011, 43, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapozzi, V.; Della, P.E.; Zorzet, S.; Zacchigna, M.; Bonavida, B.; Xodo, L.E. Nitric oxide-mediated activity in anti-cancer photodynamic therapy. Nitric Oxide 2013, 30, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapozzi, V.; Della Pietra, E.; Bonavida, B. Dual roles of nitric oxide in the regulation of tumor cell response and resistance to photodynamic therapy. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Pietra, E.; Simonella, F.; Bonavida, B.; Xodo, L.E.; Rapozzi, V. Repeated sub-optimal photodynamic treatments with pheophorbide-a induce an epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells via nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide 2015, 45, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, S.; Baay-Guzman, G.; Gonzalez-Bonilla, C.R.; Livingston, E.H.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Bonavida, B. In vitro and in vivo sensitization of SW620 metastatic colon cancer cells to CDDP-induced apoptosis by the nitric oxide donor DETANONOate: Involvement of AIF. Nitric Oxide 2009, 20, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, E.I.; de Toledo, S.M.; Little, J.B. Stress signaling from irradiated to non-irradiated cells. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2006, 4, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, R. Emerging role of radiation-induced bystander effects: Cell communications and carcinogenesis. Genome Integr. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hei, T.K.; Zhou, H.; Chai, Y.; Ponnaiya, B.; Ivanov, V.N. Radiation-induced non-targeted response: Mechanism and potential clinical implications. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 4, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakovlev, V.A. Role of nitric oxide in the radiation-induced bystander effect. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Held, K.D.; Prise, K.M.; Liber, H.L.; Redmond, R.W. Bystander effects induced by diffusing mediators after phododynamic stress. Radiat. Res. 2009, 172, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, N.; Rajadurai, A.; Held, K.D.; Prise, K.M.; Liber, H.L.; Redmond, R.W. Real-time imaging of novel spatial and temporal responses to photodynamic stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazak, J.; Fahey, J.M.; Kowytowski, W.; Girotti, A.W. Enhanced aggressiveness of bystander cells in an anti-tumor photodynamic therapy model: Role of nitric oxide produced by targeted cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Richards, D.; Knowles, R.G.; Schwartz, S.; Woodcock, A.; Langley, S.; O’Connor, B.J. Selective inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition has no effect on allergen challenge in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel, T.T.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Donnelly, L.E.; Erin, E.M.; Currie, M.G.; Moore, W.M.; Manning, P.T.; Recker, D.P.; Barnes, P.J. A selective inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibits exhaled breath nitric oxide in healthy volunteers and asthmatics. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1298–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Girotti, A.W. Modulation of the Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy by Nitric Oxide. Cancers 2016, 8, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers8100096
Girotti AW. Modulation of the Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy by Nitric Oxide. Cancers. 2016; 8(10):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers8100096
Chicago/Turabian StyleGirotti, Albert W. 2016. "Modulation of the Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy by Nitric Oxide" Cancers 8, no. 10: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers8100096
APA StyleGirotti, A. W. (2016). Modulation of the Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy by Nitric Oxide. Cancers, 8(10), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers8100096