The Composition and Structure of Ultra-Dispersed Mixed Oxide (II, III) Particles and Their Influence on In-Situ Conversion of Heavy Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
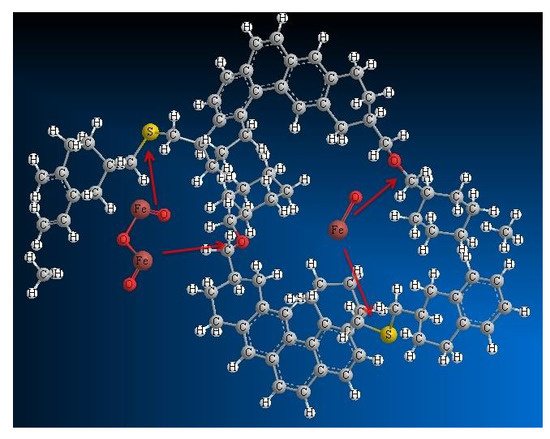
2. Results and Discussion
3. Objects and Research Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, B. Heavy hydrocarbons playing key role in peak-oil debate. Future energy supply. Oil Gas J. 2003, 101, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, R.F.; Attanasi, E.D.; Freeman, P.A. Heavy Oil and Natural Bitumen Resources in Geological Basins of the World. In US Geological Survey Open-File Report 2007-1084; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2007; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, M.S.; Sámano, V.; Ancheyta, J.; Diaz, J.A.I. A review of recent advances on process technologies for upgrading of heavy oils and residua. Fuel 2007, 86, 1216–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, A.; Sattarin, M.; Bridjanian, H. Investigation on effectiveness parameters in residue upgrading methods. Pet. Coal 2009, 51, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Lipaev, A.A. Development of Heavy Oil and Natural Bitumen Deposits; Institute of Computer Research: Moscow, Russia, 2013; p. 483. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sitnov, S.A.; Vakhin, A.V.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Onishchenko, Y.V.; Feoktistov, D.A. Effects of calcite and dolomite on conversion of heavy oil under subcritical condition. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokosova, N.N.; Rokosov, Y.V.; Uskov, S.I.; Bodoev, N.V. Simulation of transformations of organic matter into hydrothermal petroleum (A review). Pet. Chem. 2001, 41, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ramey, H., Jr. A Current Look at Thermal Recovery. In Proceedings of the SPE California Regional Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–7 November 1969; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Houston, TX, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Siskin, M.; Brons, G.; Katritzky, A.R.; Murugan, R. Aqueous Organic Chemistry. Part 2. Cross‐Linked Cyclohexyl Phenyl Compounds. Energy Fuels 1991, 4, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskin, M.; Brons, G.; Vaughn, S.N.; Katritzky, A.R.; Balasubramanian, M. Aqueous organic chemistry. 3. Aquathermolysis: Reactivity of ethers and esters. Energy Fuels 1990, 4, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitnov, S.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Shmeleva, E.I.; Aliev, F.A.; Vakhin, A.V. Influence of nanosized iron oxides (II, III) on conversion of biodegradated oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Sitnov, S.A.; Slavkina, O.V.; Bugaev, K.A.; Laikov, A.V.; Vakhin, A.V. The aquathermolysis of heavy oil from Riphean-Vendian complex with iron-based catalyst: FT-IR spectroscopy data. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Salih, I.S.; Vakhin, A.V. Changes in the subfractional composition of heavy oil asphaltenes under aquathermolysis with oil-soluble Co-based catalyst. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhin, A.V.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Aliev, F.A.; Kudryashov, S.I.; Afanasiev, I.S.; Petrashov, O.V.; Sitnov, S.A.; Chemodanov, A.E.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Nurgaliev, D.K. Aquathermolysis of heavy oil in reservoir conditions with the use of oil-soluble catalysts: Part II–changes in composition of aromatic hydrocarbons. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayukova, G.P.; Mikhailova, A.N.; Kosachev, I.P.; Feoktistov, D.A.; Vakhin, A.V. Conversion of Heavy Oil with Different Chemical Compositions under Catalytic Aquathermolysis with an Amphiphilic Fe-Co-Cu Catalyst and Kaolin. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 6488–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.K.; Ancheyta, J.; Marroquín, G. Catalytic aquathermolysis used for viscosity reduction of heavy crude oils: A review. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2809–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharypov, V.I.; Beregovtsova, N.G.; Kuznetsov, B.N. Conversion of coal into liquid products by hydrogenation and hydropyrolysis processes. Solid Fuel Chem. 2014, 48, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N.; Hassan, A.; Pereira-Almao, P. Comparative oxidation of adsorbed asphaltenes onto transition metal oxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 384, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayukova, G.P.; Feoktistov, D.A.; Mikhailova, A.N.; Kosachev, I.P.; Musin, R.Z.; Vakhin, A.V. Influence of the Nature of Metals and Modifying Additives on Changes in the Structure of Heavy Oil in a Catalytic Aquathermolysis System. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lee, C.W.; Keogh, R.A.; Demirel, B.; Davis, B.H. Thermal and catalytic conversion of asphaltenes. Fuel 2001, 80, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaytseva, O.V.; Magomadov, E.E.; Kadiev, K.M.; Chernysheva, E.A.; Kapustin, V.M.; Khadzhiev, S.N. A study of structural transformations of asphaltene molecules during hydroconversion of vacuum residue at various temperatures in the presence of nanosized molybdenum disulfide particles. Pet. Chem. 2013, 53, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitnov, S.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Vakhin, A.V.; Ivanova, A.G.; Voronina, E.V. Composition of aquathermolysis catalysts forming in situ from oil-soluble catalyst precursor mixtures. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 169, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Lee, R.L.; Liu, N. Hematite nanoparticles in aquathermolysis: A desulfurization study of thiophene. Fuel 2015, 145, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fumoto, E.; Tago, T.; Tsuji, T.; Masuda, T. Recovery of useful hydrocarbons from petroleum residual oil by catalytic cracking with steam over zirconia-supporting iron oxide catalyst. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Y.; Lu, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Peng, C.; Yang, C.; Feng, X. Morphological insights into the catalytic aquathermolysis of crude oil with an easily prepared high-efficiency Fe3O4-containing catalyst. Fuel 2019, 245, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Feng, X.; Wu, Y.; Ding, B.; Lu, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Yang, C. Insights into the synergy between recyclable magnetic Fe3O4 and zeolite for catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy crude oil. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 456, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, M.I.; Noorlaily, P.; Abdullah, M.; Iskandar, F. Synthesis of NixFe3-xO4 nanoparticles by microwave-assisted coprecipitation and their application in viscosity reduction of heavy oil. Mater. Sci. Forum Trans. Tech. Publ. 2013, 737, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xia, F. Laboratory experiments and field tests of an amphiphilic metallic chelate for catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurhayati, T.; Iskandar, F.; Mikrajuddin, A. Syntheses of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles using microwave-assisted calcination method. Mater. Sci. Forum Trans. Tech. Publ. 2013, 737, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhova, A.; Petrov, S.; Ibragimova, D.; Kayukova, G.; Safiulina, A.; Shinkarev, A.; Okekwe, R. Aquathermolysis of heavy oil using nano oxides of metals. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 153, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidullin, I.M.; Lakhova, A.I.; Ivanova, I.A.; Petrov, S.M.; Ibragimova, D.A.; Bashkirtseva, N.Y. Geothermal Transformatiom of Organic Matter in Supercritical Water with Magnetite and Coal Particles. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2017, 52, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogachev, M.K.; Kondrasheva, N.K. The Rheology of Oil and Oil Products; Publ. House Ugnuta: Ufa, Russia, 2000; p. 89. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Garipov, I.I.; Mukhamadiev, D.T.; Verkhovykh, A.A.; Elpidinskii, A.A. Pilot-Scale Testing of a Polymerization Inhibitor in a Unit for Separating Heavy Fractions from Pyrogas. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2017, 52, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, H. The effect of hydrogen donor additive on the viscosity of heavy oil during steam stimulation. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregermain, S. Hydroliquefaction of coal in presence of iron catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 1986, 12, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amestica, L.A.; Wolf, E.E. Catalytic liquefaction of coal with supercritical water/CO/solvent media. Fuel 1986, 65, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, B.N. Deep Processing of Brown Coal to Produce Liquid Fuels and Carbon Materials; Publ. House SB RAS: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2012; p. 212. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Vakhin, A.V.; Sitnov, S.A.; Khaidarova, A.R.; Zaripova, R.D.; Garifullina, E.I.; Katnov, V.E.; Stepin, S.N. Intraformation Transformation of Heavy Oil by Mixed Fe(II, III) Oxides. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2018, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitnov, S.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Vakhin, A.V.; Katnov, V.E.; Nurgaliev, D.K.; Lyabipov, M.R.; Amerkhanov, M.I. A Method of Producing a Nanosized Catalyst Based on Mixed Iron Oxide for Intensification of the Production of Heavy Hydrocarbon Feedstocks and a Catalyst Obtained by This Method. Patent No. 2655391 RU, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rudyk, S. Relationships between SARA fractions of conventional oil, heavy oil, natural bitumen and residues. Fuel 2018, 216, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Catalyst | Composition | Content, wt.% |
|---|---|---|
| Initial | γ-Fe2O3 (maghemite) | 57, 0 |
| Fe3O4 (magnetite) | 43, 0 | |
| The products of catalytic aquathermolysis (6 h) | Fe3O4 | 84, 0 |
| α-Fe2O3 (hematite) | 16, 0 | |
| The products of catalytic aquathermolysis (12 h) | Fe3O4 | 87, 0 |
| α-Fe2O3 | 13, 0 | |
| The products of catalytic aquathermolysis (24 h) | Fe3O4 | 97, 0 |
| α-Fe2O3 | 3, 0 |
| Catalyst | Composition | Content, wt.% |
|---|---|---|
| Initial | Fe3O4 | 43 |
| γ-Fe2O3 | 57 | |
| The products of catalytic aquathermolysis (6 h) | Fe3O4 | 71 |
| γ-Fe2O3 | 23 | |
| FeS2 | 6 | |
| The products of catalytic aquathermolysis (12 h) | Fe3O4 | 63 |
| FeS2 (pyrite) | 4 | |
| Fe1−xS (pyrrhotine) | 33 | |
| The products of catalytic aquathermolysis (24 h) | Fe3O4 | 100 |
| Properties | Values |
|---|---|
| Density at 20 °C, kg/m3 | 959.7 |
| Dynamic viscosity, mPa·s | |
| -at 20 °C | 2676 |
| Elemental composition, wt.% | |
| -carbon | 83.9 |
| -hydrogen | 11.3 |
| -oxygen | 1.2 |
| -sulfur | 3.2 |
| -nitrogen | 0.4 |
| -H/C | 1.62 |
| Group composition, wt.% | |
| -saturates | 26.33 |
| -aromatics | 39.55 |
| -resins | 27.37 |
| -asphaltenes | 6.75 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Khaidarova, A.R.; Zaripova, R.D.; Mukhamatdinova, R.E.; Sitnov, S.A.; Vakhin, A.V. The Composition and Structure of Ultra-Dispersed Mixed Oxide (II, III) Particles and Their Influence on In-Situ Conversion of Heavy Oil. Catalysts 2020, 10, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010114
Mukhamatdinov II, Khaidarova AR, Zaripova RD, Mukhamatdinova RE, Sitnov SA, Vakhin AV. The Composition and Structure of Ultra-Dispersed Mixed Oxide (II, III) Particles and Their Influence on In-Situ Conversion of Heavy Oil. Catalysts. 2020; 10(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukhamatdinov, Irek I., Aliya R. Khaidarova, Rumia D. Zaripova, Rezeda E. Mukhamatdinova, Sergey A. Sitnov, and Alexey V. Vakhin. 2020. "The Composition and Structure of Ultra-Dispersed Mixed Oxide (II, III) Particles and Their Influence on In-Situ Conversion of Heavy Oil" Catalysts 10, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010114
APA StyleMukhamatdinov, I. I., Khaidarova, A. R., Zaripova, R. D., Mukhamatdinova, R. E., Sitnov, S. A., & Vakhin, A. V. (2020). The Composition and Structure of Ultra-Dispersed Mixed Oxide (II, III) Particles and Their Influence on In-Situ Conversion of Heavy Oil. Catalysts, 10(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010114