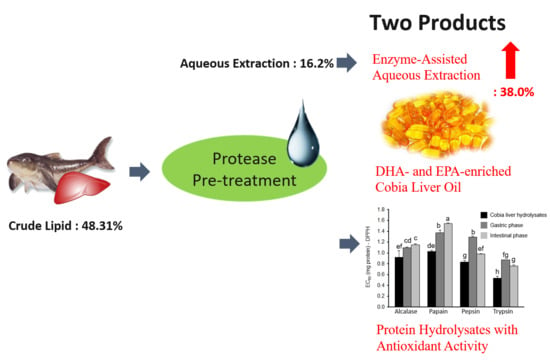
Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction of Cobia Liver Oil and Protein Hydrolysates with Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Optimal Conditions of Aqueous Extraction
2.2. Effects of Different Proteases Pretreatment on Oil Extractability
2.3. Optimal Conditions of Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction
2.4. Fatty Acid Composition
2.5. Antioxidant Activities of Protein Hydrolysates After In Vitro Simulated Gastro-Intestinal Digestion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Aqueous Extraction
3.3. Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction
3.4. In Vitro Simulated Gastro-Intestinal Digestion
3.5. Antioxidant Activity Analysis
3.6. Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.-T.; Miao, S.; Nan, F.-H.; Jung, S.-M. Study on regional production and economy of cobia Rachycentron canadum commercial cage culture. Aquac. Int. 2011, 19, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Ueng, P.-S.; Nan, F.-H. Effects of medicinal herbs “Plantago asiatica”, “Houttuynia cordata” and “Mentha haplocalyx” on non-specific immune responses of cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 58, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Cultured Aquatic Species Information Programme Rachycentron canadum (Linnaeus, 1766). Available online: http://www.fao.org/fishery/culturedspecies/Rachycentron_canadum/en (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- Kuo, C.H.; Liao, H.Z.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, H.M.D.; Shieh, C.J.; Tseng, C.Y. Highly efficient extraction of EPA/DHA-enriched oil from cobia liver using homogenization plus sonication. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimat, V.; Vlahović, J.; Soldo, B.; Skroza, D.; Ljubenkov, I.; Generalić Mekinić, I. Production and refinement of omega-3 rich oils from processing by-products of farmed fish species. Foods 2019, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manuelli, M.; Della Guardia, L.; Cena, H. Enriching diet with n-3 PUFAs to help prevent cardiovascular diseases in healthy adults: Results from clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Méndez, L.; Dasilva, G.; Taltavull, N.; Romeu, M.; Medina, I. Marine lipids on cardiovascular diseases and other chronic diseases induced by diet: An insight provided by proteomics and lipidomics. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Castro, G.S.; Deminice, R.; Simões-Ambrosio, L.M.C.; Calder, P.C.; Júnior, A.A.J.; Vannucchi, H. Dietary docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid influence liver triacylglycerol and insulin resistance in rats fed a high-fructose diet. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1864–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Gong, S.; Ye, S.Q.; Lyman, B.; Geng, L.; Chen, P.; Li, D.-Y. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children: Focus on nutritional interventions. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4691–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duttaroy, A.K. Docosahexaenoic acid supports feto-placental growth and protects cardiovascular and cognitive function: A mini review. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawczynski, C.; Dittrich, M.; Neumann, T.; Goetze, K.; Welzel, A.; Oelzner, P.; Völker, S.; Schaible, A.; Troisi, F.; Thomas, L. Docosahexaenoic acid in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized cross-over study with microalgae vs. sunflower oil. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthymiopoulos, I.; Hellier, P.; Ladommatos, N.; Kay, A.; Mills-Lamptey, B. Effect of solvent extraction parameters on the recovery of oil from spent coffee grounds for biofuel production. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soto, C.; Chamy, R.; Zuniga, M. Enzymatic hydrolysis and pressing conditions effect on borage oil extraction by cold pressing. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaram, S.; Mirhosseini, H.; Tan, C.P.; Ghazali, H.M. Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and solvent extraction of papaya seed oil: Yield, fatty acid composition and triacylglycerol profile. Molecules 2013, 18, 12474–12487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khoei, M.; Chekin, F. The ultrasound-assisted aqueous extraction of rice bran oil. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Chu, K.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. Extraction of Lepidium apetalum seed oil using supercritical carbon dioxide and anti-oxidant activity of the extracted oil. Molecules 2011, 16, 10029–10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Su, Z.; Chen, Y. Microwave-assisted extraction of silkworm pupal oil and evaluation of its fatty acid composition, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein-Knudsen, N.; Ale, M.T.; Meyer, A.S. Seaweed hydrocolloid production: An update on enzyme assisted extraction and modification technologies. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3340–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, B.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Shieh, C.-J. Production of resveratrol by piceid deglycosylation using cellulase. Catalysts 2016, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-A.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, B.-Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Shieh, C.-J. A novel enzyme-assisted ultrasonic approach for highly efficient extraction of resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 32, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Wang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zou, B.; Zhao, P.; Yuan, Z. Enzyme-assisted extraction of oil from wet microalgae Scenedesmus sp. G4. Energies 2015, 8, 8165–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Encalada, A.M.I.; Pérez, C.D.; Flores, S.K.; Rossetti, L.; Fissore, E.N.; Rojas, A.M. Antioxidant pectin enriched fractions obtained from discarded carrots (Daucus carota L.) by ultrasound-enzyme assisted extraction. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihua, M.W.; Guihéneuf, F.; Mohammed, H.; Margassery, L.M.; Jackson, S.A.; Stengel, D.B.; Clarke, D.J.; Dobson, A.D. Microbial population changes in decaying Ascophyllum nodosum result in macroalgal-polysaccharide-degrading bacteria with potential applicability in enzyme-assisted extraction technologies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Latif, S.; Anwar, F. Aqueous enzymatic sesame oil and protein extraction. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.S.P.; Dias, F.F.; Koblitz, M.G.B.; Bell, J.M.L.N.D.M. Aqueous and enzymatic extraction of oil and protein from almond cake: A comparative study. Processes 2019, 7, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Zhang, S.; Qi, B.-K.; Li, H.; Xie, F.-Y.; Li, Y. Molecular distillation-induced deacidification of soybean oil isolated by enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction: Effect of distillation parameters. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, B.X.; Li, B.; Li, X.D.; Zaaboul, F.; Jiang, J.; Li, J.W.; Li, Q.; Cao, P.R.; Liu, Y.F. Using short-wave infrared radiation to improve aqueous enzymatic extraction of peanut oil: Evaluation of peanut cotyledon microstructure and oil quality. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1700285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamać, M.; Kosińska-Cagnazzo, A.; Kulczyk, A. Use of different proteases to obtain flaxseed protein hydrolysates with antioxidant activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, C.J.; Yang, J.I. The effect of process variables for production of cobia (Rachycentron canadum) skin gelatin hydrolysates with antioxidant properties. J. Food Biochem. 2011, 35, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, A.; Li, Y.; Zheng, G. Enzymatic hydrolysis of Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) skin and antioxidant activity of the resulting hydrolysate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Regenstein, J.; Su, X. In vitro and in vivo anti-oxidation and anti-fatigue effect of monkfish liver hydrolysate. Food Biosci. 2017, 18, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.B.; Lee, K.H.; Je, J.Y. Enzymatic production of bioactive protein hydrolysates from tuna liver: Effects of enzymes and molecular weight on bioactivity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.-Y.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, M.H.; Ahn, C.-B. Antioxidant and antihypertensive protein hydrolysates produced from tuna liver by enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; He, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Sun, L. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) frame protein. Molecules 2012, 17, 12836–12850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Li, T.; Yu, R.; Yan, C.; Ren, S.; Zhao, Y. Antioxidant activities of hydrolysates of Arca subcrenata prepared with three proteases. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y. Antioxidant activities of sorghum kafirin alcalase hydrolysates and membrane/gel filtrated fractions. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.-I.; Ho, H.-Y.; Chu, Y.-J.; Chow, C.-J. Characteristic and antioxidant activity of retorted gelatin hydrolysates from cobia (Rachycentron canadum) skin. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaurah, P.W.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, N.; Attkan, A.K.; Panghal, A.; Singh, V.K.; Garg, M.K. Novel oil extraction technologies: Process conditions, quality parameters, and optimization. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, B.W.; Qin, L.; Zhou, D.Y.; Wu, H.T.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.F.; Li, D.M.; Dong, X.P.; Murata, Y. Extraction of lipid from sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus nudus) gonad by enzyme-assisted aqueous and supercritical carbon dioxide methods. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jia, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Ran, J. Optimization of enzyme-assisted extraction of the Lycium barbarum polysaccharides using response surface methodology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gong, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Jia, S.; Qin, F.; Ren, H.; Liu, Y. Response surface optimization of enzyme-assisted extraction polysaccharides from Dictyophora indusiata. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalakshmi, N.; Sundaram, P.V. Stability of native and covalently modified papain. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2015, 8, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, L.; Wen, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, J. Enzyme-assisted extraction optimization, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from sea cucumber Phyllophorus proteus. Molecules 2018, 23, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Li, T.; Liu, D.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y. Enzyme assisted extraction, purification and structure analysis of the polysaccharides from naked pumpkin seeds. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Khare, S.K.; Gupta, M.N. Enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction of rice bran oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Guo, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Oil extraction and evaluation from yellow horn using a microwave-assisted aqueous saline process. Molecules 2019, 24, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarker, M.Z.I.; Selamat, J.; Habib, A.S.M.; Ferdosh, S.; Akanda, M.J.H.; Jaffri, J.M. Optimization of supercritical CO2 extraction of fish oil from viscera of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11312–11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-W.; Wang, H.-M.D.; Shieh, C.-J. Concentration of docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acid from cobia liver oil by acetone fractionation of fatty acid salts. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 192, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-L.; Kuo, W.-C.; Hsieh, S.-L.; Shieh, C.-J. Synthesis of DHA/EPA ethyl esters via lipase-catalyzed acidolysis using Novozym® 435: A kinetic study. Catalysts 2020, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Qu, Y.; Ye, F. Antioxidant activity and anti-exercise-fatigue effect of highly denatured soybean meal hydrolysate prepared using neutrase. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1982–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajapakse, N.; Mendis, E.; Jung, W.-K.; Je, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K. Purification of a radical scavenging peptide from fermented mussel sauce and its antioxidant properties. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Kouzuma, Y.; Yonekura, M. Structures and properties of antioxidative peptides derived from royal jelly protein. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanasiritham, L.; Theerakulkait, C.; Wickramasekara, S.; Maier, C.S.; Stevens, J.F. Isolation and identification of antioxidant peptides from enzymatically hydrolyzed rice bran protein. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, M.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, C.; Kakuda, Y.; Xue, S.J. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from grass carp muscle hydrolysates by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaranayaka, A.G.; Li-Chan, E.C. Food-derived peptidic antioxidants: A review of their production, assessment, and potential applications. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhao, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ren, J. Changes in the antioxidant activity of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) protein hydrolysates during a simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, S.; Han, F. Aqueous enzymatic extraction of oil and protein hydrolysates from peanut. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2008, 14, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hathwar, S.C.; Bijinu, B.; Rai, A.K.; Narayan, B. Simultaneous recovery of lipids and proteins by enzymatic hydrolysis of fish industry waste using different commercial proteases. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.-F.; Hu, F.-Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.-R.; Luo, H.-Y. Influence of amino acid compositions and peptide profiles on antioxidant capacities of two protein hydrolysates from skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) dark muscle. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2580–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farvin, K.S.; Andersen, L.L.; Nielsen, H.H.; Jacobsen, C.; Jakobsen, G.; Johansson, I.; Jessen, F. Antioxidant activity of Cod (Gadus morhua) protein hydrolysates: In vitro assays and evaluation in 5% fish oil-in-water emulsion. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-C.; Chen, H.-M.; Shiau, C.-Y. Free amino acids and peptides as related to antioxidant properties in protein hydrolysates of mackerel (Scomber austriasicus). Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; He, J.; Cheng, W.; Ren, G. In vitro antioxidant activity of peptides from simulated gastro-intestinal digestion products of Cyprinus carpio haematopterus scale gelatin. Foods 2019, 8, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carriere, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food–an international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Lee, C.-H. Antibacterial and antioxidant capacities and attenuation of lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by low-molecular-weight fucoidans prepared from compressional-puffing-pretreated sargassum crassifolium. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.-R.; Yu, H.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, J.-M.; Chang, C.; Shieh, C.-J.; Kuo, C.-H. Bioprocessed Production of Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Wine: Simultaneous Rice Wine Fermentation, Extraction, and Transformation of Piceid to Resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum Roots. Foods 2019, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gnanou, J.; Srinivas, S.; Kurpad, A. Automated derivatization with o-phthalaldehyde for the estimation of amino acids in plasma using reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 41, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sultana, H.; Onodera, R.; Or-Rashid, M.M.; Wadud, S. Convenient method for the determination of arginine and its related compounds in rumen fluid by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 755, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Fatty Acid (%) | Alcalase | Papain | Pepsin | Trypsin | Aqueous | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14:0 | 1.11 | ± | 0.13 | 1.03 | ± | 0.04 | 1.07 | ± | 0.08 | 1.00 | ± | 0.05 | 1.57 | ± | 0.22 |
| C16:0 | 29.12 | ± | 0.30 | 28.34 | ± | 0.18 | 29.00 | ± | 0.13 | 28.63 | ± | 0.26 | 27.96 | ± | 1.36 |
| C16:1 | 4.46 | ± | 0.09 | 4.35 | ± | 0.04 | 4.49 | ± | 0.20 | 4.31 | ± | 0.00 | 6.69 | ± | 0.19 |
| C18:0 | 11.38 | ± | 0.12 | 11.17 | ± | 0.01 | 11.25 | ± | 0.43 | 11.43 | ± | 0.15 | 8.05 | ± | 0.27 |
| C18:1n9 | 33.51 | ± | 0.49 | 33.93 | ± | 0.01 | 33.46 | ± | 0.42 | 33.76 | ± | 0.08 | 32.92 | ± | 1.04 |
| C18:2n6 | 0.56 | ± | 0.02 | 0.56 | ± | 0.02 | 0.54 | ± | 0.01 | 0.55 | ± | 0.03 | 0.84 | ± | 0.15 |
| C18:3n3 | 0.57 | ± | 0.04 | 0.58 | ± | 0.00 | 0.57 | ± | 0.02 | 0.57 | ± | 0.02 | 0.68 | ± | 0.12 |
| C20:0 | 0.33 | ± | 0.02 | 0.33 | ± | 0.01 | 0.34 | ± | 0.00 | 0.34 | ± | 0.01 | 0.24 | ± | 0.02 |
| C20:1 | 1.23 | ± | 0.06 | 1.25 | ± | 0.01 | 1.26 | ± | 0.01 | 1.25 | ± | 0.04 | 1.22 | ± | 0.06 |
| C22:0 | 0.18 | ± | 0.01 | 0.15 | ± | 0.03 | 0.16 | ± | 0.00 | 0.18 | ± | 0.04 | 0.11 | ± | 0.03 |
| C20:5n3 (EPA) | 3.80 | ± | 0.08 | 3.93 | ± | 0.03 | 3.81 | ± | 0.07 | 3.86 | ± | 0.15 | 4.15 | ± | 0.65 |
| C22:6n3 (DHA) | 13.75 | ± | 0.20 | 14.37 | ± | 0.21 | 14.05 | ± | 0.18 | 14.13 | ± | 0.29 | 15.59 | ± | 1.52 |
| SFA 2 | 42.12 | ± | 0.43 1a | 41.01 | ± | 0.21 a | 41.82 | ± | 0.33 a | 41.58 | ± | 0.38 a | 37.92 | ± | 1.44 b |
| MUFA | 39.20 | ± | 0.47 b | 39.54 | ± | 0.02 b | 39.21 | ± | 0.50 b | 39.32 | ± | 0.07 b | 40.82 | ± | 1.17 a |
| PUFA | 18.68 | ± | 0.29 a,b | 19.45 | ± | 0.23 a,b | 18.97 | ± | 0.28 a,b | 19.10 | ± | 0.45 a,b | 21.26 | ± | 2.42 a |
| EPA + DHA | 17.55 | ± | 0.24 a,b | 18.30 | ± | 0.24 a,b | 17.86 | ± | 0.25 a,b | 17.99 | ± | 0.41 a,b | 19.73 | ± | 2.16 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-H.; Kuo, C.-H.; Lee, C.-L.; Kuo, W.-C.; Tsai, M.-L.; Sun, P.-P. Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction of Cobia Liver Oil and Protein Hydrolysates with Antioxidant Activity. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10111323
Wang Y-H, Kuo C-H, Lee C-L, Kuo W-C, Tsai M-L, Sun P-P. Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction of Cobia Liver Oil and Protein Hydrolysates with Antioxidant Activity. Catalysts. 2020; 10(11):1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10111323
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu-Hsiang, Chia-Hung Kuo, Chien-Liang Lee, Wen-Cheng Kuo, Mei-Ling Tsai, and Pei-Pei Sun. 2020. "Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction of Cobia Liver Oil and Protein Hydrolysates with Antioxidant Activity" Catalysts 10, no. 11: 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10111323
APA StyleWang, Y. -H., Kuo, C. -H., Lee, C. -L., Kuo, W. -C., Tsai, M. -L., & Sun, P. -P. (2020). Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction of Cobia Liver Oil and Protein Hydrolysates with Antioxidant Activity. Catalysts, 10(11), 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10111323