An Aging Model of NH3 Storage Sites for Predicting Kinetics of NH3 Adsorption, Desorption and Oxidation over Hydrothermally Aged Cu-Chabazite
Abstract
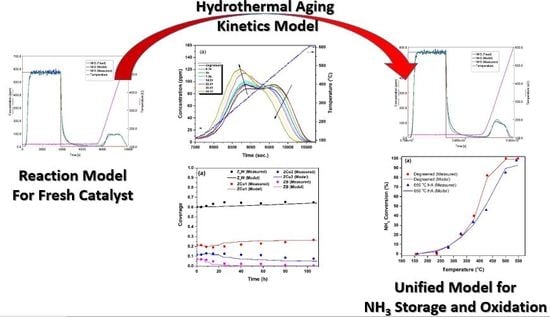
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hydrothermal Aging Kinetics of NH3 Storage Sites
2.2. 4-Site Kinetic Model for Degreened Cu-CHA
2.3. Modeling the Effects of HA on NH3 Adsorption, Desorption and Oxidation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Laboratory Tests
3.2. HA Methodology
3.3. Modelling
3.3.1. The Reactor Model
3.3.2. Kinetic Model
4. Conclusions
- HA kinetics model successfully captured the changes in the fractional coverages of the NH3 storage sites, which could be identified with their NH3-TPD peak centres observed at 317, 456 and 526 °C, namely ZCu1, ZCu2 and ZB, respectively, for the degreened catalyst. The fractional coverages of ZCu2 and ZCu1 initially increased and decreased, respectively, with HA time after isothermal HA at 650 °C, which was well represented by the HA kinetics model. The major effects of HA were the decrease in the fractional coverages of ZCu2 and ZB and the increase in the fractional coverage of ZCu1 with further increases in both HA time and temperature. These effects were also well captured by the model;
- HA kinetics model was then linked with a 4-site transient kinetic model of adsorption, desorption and oxidation of NH3 developed for degreened Cu-CHA. This linkage was possible via incorporating the changes in the fractional coverages of the NH3 storage sites to the coverages of the active sites within the reactor model through the utilization of HA kinetics, while keeping the turnover rate constants and the activation energies associated with reactions occurring on the degreened catalysts unchanged;
- The kinetic model is able to describe the kinetics of NH3 adsorption and isothermal desorption of NH3, TPD of NH3 and NH3 oxidation of the degreened and hydrothermally aged Cu-CHA up to 46, 24 and 21 h at 650, 700 and 800 °C, respectively. The decreases in high temperature NH3 oxidation performance upon HA, at 650 °C for 46 h and at 700 °C for 24 h were very well predicted by the model;
- Both the HA methodology and the method used to create a link between the HA kinetics and the reaction models developed in this study could be extended to a variety of other catalytic systems for the prediction catalytic activity after HA. Along this line, the development of an HA model capable of describing the NH3-SCR performance after mild HA is on-going in our laboratory.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Active site concentration for reaction j, (molsite∙m−3∙catalyst) | |
| Ak | Active site concentration for coverage k, (mol∙m−3∙catalyst) |
| Turnover rate constant for reaction j | |
| Ci | Intraporous concentration of species i (mol·m−3) |
| Binary diffusion coefficient of species i in the mixture (m2·s−1) | |
| Effective diffusivity for species i (m2·s−1) | |
| Knudsen diffusion coefficient for species i (m2·s−1) | |
| Hydraulic diameter (m) | |
| dp | Washcoat pore size available for gas diffusion (m) |
| EA,j | Activation energy for reaction j (kJ·mol−1) |
| EA,j,0 | Activation energy for reaction j at zero coverage (kJ·mol−1) |
| Fi,z0 | Molar flow rate of species i at z = 0 |
| Fi,zL | Molar flow rate of species i at z = L |
| Solid fraction of washcoat | |
| G | Surface area per reactor volume (m−1) |
| Turnover rate constant for the reaction j | |
| External mass transfer coefficient for species i (kg·m−2 s−1) | |
| L | Reactor length |
| Molecular weight of species i (kg·mol−1) | |
| Reaction rate for reaction j (mol·s−1·molsite−1) | |
| R | Gas constant (J·mol−1·K−1) |
| Species mass rate for generation or consumption (kg·m−3·s−1) | |
| Stoichiometric coefficient of species i for reaction j | |
| Sherwood number | |
| Vi | Diffusion volume for species i (cm3·mol−1) |
| v | Interstitial velocity (m·s−1) |
| Greek letters | |
| Coverage dependence | |
| Washcoat thickness (m) | |
| Void fraction of reactor | |
| Void fraction of washcoat | |
| Density of bulk gas in reactor channels (kg·m−3) | |
| Density of gas at catalyst surface (kg·m−3) | |
| Intraporous mass fraction of species i | |
| Mass fraction of species i in the bulk gas | |
| Mass fraction of species i in the gas-solid interface | |
| Fractional coverage of species k | |
| Stoichiometric coefficient of species j in reaction k | |
References
- Kwak, J.H.; Tonkyn, R.G.; Kim, D.H.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Excellent activity and selectivity of Cu-SSZ-13 in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Catal. 2010, 275, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depcik, C.; Assanis, D. One-dimensional automotive catalyst modeling. Progr. Energy Combust. Sci. 2005, 31, 308–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Burkhardt, T.; Bandl-Konrad, B.; Braun, T.; Tronconi, E.; Nova, I.; Ciardelli, C. Numerical Simulation of Ammonia SCR-Catalytic Converters: Model Development and Application. SAE Tech. Paper Ser. 2005, 114, 437–448. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, D.; Burkhardt, T.; Weibel, M.; Nova, I.; Grossale, A.; Tronconi, E. Numerical Simulation of Zeolite- and V-Based SCR Catalytic Converters 2007-01-1136. SAE Tech. Paper Ser. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieg, S.J.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, C.H.; Brown, D.B.; Lee, J.H.; Peden, C.H.F.; Kim, D.H. Thermal durability of Cu-CHA NH3-SCR catalysts for diesel NOx reduction. Catal. Today 2012, 184, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Cheng, Y.; Cavataio, G.; McCabe, R.W.; Fu, L.; Li, J. Characterization of commercial Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts with hydrothermal treatment for NH3-SCR of NOx in diesel exhaust. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, D.; Kumar, A.; Li, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.; Yezerets, A. Identification of two types of Cu sites in Cu/SSZ-13 and their unique responses to hydrothermal aging and sulfur poisoning. Catal. Today 2016, 267, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; An, H.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.W.; Yezerets, A.; Watkins, T.; Allard, L. Impact of Accelerated Hydrothermal Aging on Structure and Performance of Cu-SSZ-13 SCR Catalysts. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Ye, Q.; Cheng, S.; Kang, T.; Dai, H. Effect of the hydrothermal aging temperature and Cu/Al ratio on the hydrothermal stability of CuSSZ-13 catalysts for NH3-SCR. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Walter, E.D.; Karp, E.M.; Luo, J.Y.; Tonkyn, R.G.; Kwak, J.H.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Structure-activity relationships in NH3-SCR over Cu-SSZ-13 as probed by reaction kinetics and EPR studies. J. Catal. 2013, 300, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Tran, D.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F.; Lee, J.H. The Effect of Copper Loading on the Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitric Oxide by Ammonia Over Cu-SSZ-13. Catal. Lett. 2012, 142, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Washton, N.M.; Wang, Y.; Kollár, M.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Effects of Si/Al ratio on Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR catalysts: Implications for the active Cu species and the roles of Brønsted acidity. J. Catal. 2015, 331, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Walter, E.D.; Kollar, M.; Wang, Y.L.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Understanding ammonia selective catalytic reduction kinetics over Cu/SSZ-13 from motion of the Cu ions. J. Catal. 2014, 319, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Qi, G.S.; Weng, D. Location and nature of Cu species in Cu/SAPO-34 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Catal. 2012, 289, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.H.; Kamasamudram, K.; Epling, W.S. NH3-SCR over Cu/SAPO-34—Zeolite acidity and Cu structure changes as a function of Cu loading. Catal. Today 2014, 231, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.A.; Verma, A.A.; Paolucci, C.; Parekh, A.A.; Anggara, T.; Yezerets, A.; Schneider, W.F.; Miller, J.T.; Delgass, W.N.; Ribeiro, F.H. Identification of the active Cu site in standard selective catalytic reduction with ammonia on Cu-SSZ-13. J. Catal. 2014, 312, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groothaert, M.H.; Van Bokhoven, J.A.; Battiston, A.A.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Schoonheydt, R.A. Bis(mu-oxo)dicopper in Cu-ZSM-5 and its role in the decomposition of NO: A combined in situ XAFS, UV-Vis-Near-IR, and kinetic study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7629–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolucci, C.; Khurana, I.; Parekh, A.A.; Li, S.; Shih, A.J.; Li, H.; Di Iorio, J.R.; Albarracin-Caballero, J.D.; Yezerets, A.; Miller, J.T.; et al. Dynamic multinuclear sites formed by mobilized copper ions in NOx selective catalytic reduction. Science 2017, 357, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Kamasamudram, K.; Epling, W.S. In Situ-DRIFTS Study of Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3 over Cu-Exchanged SAPO-34. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordanino, F.; Vennestrom, P.N.R.; Lundegaard, L.F.; Stappen, F.N.; Mossin, S.; Beato, P.; Bordiga, S.; Lamberti, C. Characterization of Cu-exchanged SSZ-13: A comparative FTIR, UV-Vis, and EPR study with Cu-ZSM-5 and Cu-beta with similar Si/Al and Cu/Al ratios. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 12741–12761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borfecchia, E.; Lomachenko, K.A.; Giordanino, F.; Falsig, H.; Beato, P.; Soldatov, A.V.; Bordiga, S.; Lamberti, C. Revisiting the nature of Cu sites in the activated Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for SCR reaction. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janssens, T.V.W.; Falsig, H.; Lundegaard, L.F.; Vennestrom, P.N.R.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Moses, P.G.; Giordanino, F.; Borfecchia, E.; Lomachenko, K.A.; Lamberti, C.; et al. A Consistent Reaction Scheme for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides with Ammonia. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2832–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paolucci, C.; Parekh, A.A.; Khurana, I.; Di Iorio, J.R.; Li, H.; Albarracin Caballero, J.D.; Shih, A.J.; Anggara, T.; Delgass, W.N.; Miller, J.T.; et al. Catalysis in a Cage: Condition-Dependent Speciation and Dynamics of Exchanged Cu Cations in SSZ-13 Zeolites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6028–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipek, B.; Wulfers, M.J.; Kim, H.; Göltl, F.; Hermans, I.; Smith, J.P.; Booksh, K.S.; Brown, C.M.; Lobo, R.F. Formation of [Cu2O2]2+ and [Cu2O]2+ toward C–H Bond Activation in Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-SSZ-39. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 4291–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzotto, V.; Chen, P.; Simon, U. Mobility of NH3-Solvated CuII Ions in Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-ZSM-5 NH3-SCR Catalysts: A Comparative Impedance Spectroscopy Study. Catalysts 2018, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marberger, A.; Petrov, A.W.; Steiger, P.; Elsener, M.; Kröcher, O.; Nachtegaal, M.; Ferri, D. Time-resolved copper speciation during selective catalytic reduction of NO on Cu-SSZ-13. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahami, A.R.; Günter, T.; Doronkin, D.E.; Casapu, M.; Zengel, D.; Vuong, T.H.; Simon, M.; Breher, F.; Kucherov, A.V.; Brückner, A.; et al. The dynamic nature of Cu sites in Cu-SSZ-13 and the origin of the seagull NOx conversion profile during NH3-SCR. React. Chem. Eng. 2019, 4, 1000–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leistner, K.; Kumar, A.; Kamasamudram, K.; Olsson, L. Mechanistic study of hydrothermally aged Cu/SSZ-13 catalysts for ammonia-SCR. Catal. Today 2018, 307, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistner, K.; Xie, K.; Kumar, A.; Kamasamudram, K.; Olsson, L. Ammonia Desorption Peaks Can Be Assigned to Different Copper Sites in Cu/SSZ-13. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, L.; Wijayanti, K.; Leistner, K.; Kumar, A.; Joshi, S.Y.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.W.; Yezerets, A. A multi-site kinetic model for NH3-SCR over Cu/SSZ-13. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 174, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, L.; Sjovall, H.; Blint, R.J. A kinetic model for ammonia selective catalytic reduction over Cu-ZSM-5. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 81, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, P.S.; Balakotaiah, V.; Harold, M.P. Experimental and kinetic modeling study of NO oxidation: Comparison of Fe and Cu-zeolite catalysts. Catal. Today 2012, 184, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, P.S.; Harold, M.P.; Balakotaiah, V. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx on combined Fe- and Cu-zeolite monolithic catalysts: Sequential and dual layer configurations. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 111, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.Y.; Kumar, A.; Luo, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.W.; Yezerets, A. Combined experimental and kinetic modeling study of the bi-modal NOx conversion profile on commercial Cu-SAPO-34 catalyst under standard SCR conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roduit, B.; Wokaun, A.; Baiker, A. Global Kinetic Modeling of Reactions occurring during Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by NH3 over Vanadia/Titania-Based Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1998, 37, 4577–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozbağ, S.E.; Şimşek, M.; Demir, O.; Şanlı, D.; Ozener, B.; Hisar, G.; Erkey, C. Assessment of the Single-Site Kinetic Model for NH3-SCR on Cu-Chabazite for the Prediction of NOx Emissions in Dynamometer Tests. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Nova, I.; Tronconi, E. Detailed kinetic modeling of the NH3-NO/NO2 SCR reactions over a commercial Cu-zeolite catalyst for Diesel exhausts after treatment. Catal. Today 2012, 197, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendrich, M.; Scheuer, A.; Hayes, R.E.; Votsmeier, M. Unified mechanistic model for Standard SCR, Fast SCR, and NO2 SCR over a copper chabazite catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 222, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Gong, J.; Tan, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z. Modeling intraphase and interphase mass transfer limitations for NH3–SCR over Cu–ZSM–5. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 207, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvray, X.; Partridge, W.; Choi, J.-S.; Pihl, J.; Coehlo, F.; Yezerets, A.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.; Olsson, L. Kinetic modeling of NH3-SCR over a supported Cu zeolite catalyst using axial species distribution measurements. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 163, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhillon, P.S.; Harold, M.P.; Wang, D.; Kumar, A.; Joshi, S.Y. Modeling and analysis of transport and reaction in washcoated monoliths: Cu-SSZ-13 SCR and dual-layer Cu-SSZ-13 + Pt/Al2O3 ASC. React. Chem. Eng. 2019, 4, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.Y.; Kumar, A.; Luo, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.W.; Yezerets, A. New insights into the mechanism of NH3-SCR over Cu- and Fe-zeolite catalyst: Apparent negative activation energy at high temperature and catalyst unit design consequences. App. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 226, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-La-Torre, U.; Pereda-Ayo, B.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, M.A.; González-Marcos, J.A.; González-Velasco, J.R. Steady-state NH3-SCR global model and kinetic parameter estimation for NOx removal in diesel engine exhaust aftertreatment with Cu/chabazite. Catal. Today 2017, 296, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya, R.; Desai, C.; Vernham, B. Development and Validation of a Two-Site Kinetic Model for NH3-SCR over Cu-SSZ-13. Part 1. Detailed Global Kinetics Development Based on Mechanistic Considerations. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2018, 4, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjovall, H.; Blint, R.J.; Olsson, L. Detailed kinetic modeling of NH3 SCR over Cu-ZSM-5. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 92, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangjou, Y.; Sampara, C.S.; Gu, Y.; Wang, D.; Kumar, A.; Li, J.; Epling, W.S. Mechanism-based kinetic modeling of Cu-SSZ-13 sulfation and desulfation for NH3-SCR applications. React. Chem. Eng. 2019, 4, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamaina, R.; Liu, S.; Nova, I.; Tronconi, E.; Ruggeri, M.P.; Collier, J.; York, A.; Thompsett, D. Speciation of Cu Cations in Cu-CHA Catalysts for NH3-SCR: Effects of SiO2/AlO3 Ratio and Cu-Loading Investigated by Transient Response Methods. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 8916–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriyanto; Wijayanti, K.; Kumar, A.; Joshi, S.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.W.; Yezerets, A.; Olsson, L. Global kinetic modeling of hydrothermal aging of NH3-SCR over Cu-zeolites. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 163, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, M.P.; Nova, I.; Tronconi, E.; Schmeißer, V.; Weibel, M. Modelling the Hydrothermal Ageing of a Fe-Zeolite Catalyst for Automotive NH3-SCR Applications. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2018, 90, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Walter, E.D.; Washton, N.M.; Mei, D.; Kovarik, L.; Engelhard, M.H.; Prodinger, S.; Wang, Y.; Peden, C.H.F.; et al. Toward Rational Design of Cu/SSZ-13 Selective Catalytic Reduction Catalysts: Implications from Atomic-Level Understanding of Hydrothermal Stability. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8214–8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarracin-Caballero, J.D.; Khurana, I.; Di Iorio, J.R.; Shih, A.J.; Schmidt, J.E.; Dusselier, M.; Davis, M.E.; Yezerets, A.; Miller, J.T.; Ribeiro, F.H.; et al. Structural and kinetic changes to small-pore Cu-zeolites after hydrothermal aging treatments and selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia. React. Chem. Eng. 2017, 2, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Chen, Z.; Pang, L.; Ming, S.; Zhang, X.; Albert, K.B.; Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Li, T. The influence of Si/Al ratio on the catalytic property and hydrothermal stability of Cu-SSZ-13 catalysts for NH3-SCR. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 550, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.E.; Oord, R.; Guo, W.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Nanoscale tomography reveals the deactivation of automotive copper-exchanged zeolite catalysts. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Peng, Z.; Qiao, H.; Han, L.; Bao, W.; Chang, L.; Feng, G.; Liu, W. Influence of aging on in situ hydrothermally synthesized Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for NH3-SCR reaction. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 42403–42411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.K.; Min, K.M.; Hong, S.B.; Nam, I.-S.; Cho, B.K. Hydrothermal stability of CuSSZ13 for reducing NOx by NH3. J. Catal. 2014, 311, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Gao, F.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.; Peden, C.H.F.; Yezerets, A. New insights into Cu/SSZ-13 SCR catalyst acidity. Part I: Nature of acidic sites probed by NH3 titration. J. Catal. 2017, 348, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.; Yezerets, A. NH3-TPD methodology for quantifying hydrothermal aging of Cu/SSZ-13 SCR catalysts. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 190, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya, R.; Joshi, S.Y.; Luo, J.; Dadi, R.K.; Currier, N.W.; Yezerets, A. On kinetic modeling of change in active sites upon hydrothermal aging of Cu-SSZ-13. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 263, 118368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, G.H. Three-site Kinetic Model for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOX with Ammonia over a Commercial Catalyst for Calibration of Aftertreatment Systems in Diesel Powered Heavy Duty Vehicles. Ph.D. Thesis, Koç University, Istanbul, Turkey, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karadag, H.G.; Bozbag, S.E.; Şanli, D.; Demir, O.; Ozener, B.; Hisar, G.; Erkey, C. Mass Transfer Effects in SCR Reactor for NOx Abatement in Diesel Engines. In Exergetic, Energetic and Environmental Dimensions; Dincer, I., Colpan, C.O., Kizilkan, O., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 961–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GT-SUITE Exhaust Aftertreatment Application Manual; Gamma Technologies LLC.: Westmont, IL, USA, 2018.
- Bissett, E.J. An Asymptotic Solution for Washcoat Pore Diffusion in Catalytic Monoliths. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, E.N.; Schettler, P.D.; Giddings, J.C. A New Method for Prediciton of Binary Gas-Phase Diffusion Coefficients. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1966, 58, 19–27. [Google Scholar]







| Reaction Number | Reaction | Rate Expression |
|---|---|---|
| Reactions related to HA | ||
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| Reactions related to NH3 adsorption and desorption | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 | ||
| Reactions related to NH3 oxidation | ||
| 12 | ||
| 13 | ||
| Reaction Number | Turnover Rate Constant, Aj | Units of Aj | Activation Energy, EA,j,0 (kJ∙mol−1) | Kj | α/nj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.11 × 10 −7 | mol·s−1·mol−1site | 7.0 | - | - |
| 2 | 2.00 × 10 5 | mol·s−1·mol−1site | 129.7 | 0.48 | 1.7 |
| 3 | 3.16 × 10 14 | mol·s−1·mol−1site | 280.3 | - | 4.3 |
| 4 | 1.30 × 10 1 | m3·s−1·mol−1site | 0.0 | - | - |
| 5 | 8.43 × 10 0 | mol·s−1·mol−1site | 16.6 | - | - |
| 6 | 7.04 × 10−1 | m3·s−1·mol−1site | 0.0 | - | - |
| 7 | 8.01 × 105 | mol·s−1·mol−1site | 104.8 | - | 0.99 |
| 8 | 1.75 × 10 2 | m3·s−1·mol−1site | 0.0 | - | - |
| 9 | 1.14 × 10 8 | mol·s−1·mol−1site | 122.3 | - | - |
| 10 | 2.50 × 10 2 | m3·s−1·mol−1site | 0.0 | - | - |
| 11 | 6.41 × 10 7 | mol·s−1·mol−1site | 131.2 | - | - |
| 12 | 3.87 × 101 | mol0.75·m0.75·s−1·mol−1site | 61.6 | - | 0.25 |
| 13 | 2.87 × 105 | mol0.59·m1.77·s−1·mol−1site | 120.2 | - | 0.59 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bozbag, S.E.; Şanlı, D.; Özener, B.; Hisar, G.; Erkey, C. An Aging Model of NH3 Storage Sites for Predicting Kinetics of NH3 Adsorption, Desorption and Oxidation over Hydrothermally Aged Cu-Chabazite. Catalysts 2020, 10, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040411
Bozbag SE, Şanlı D, Özener B, Hisar G, Erkey C. An Aging Model of NH3 Storage Sites for Predicting Kinetics of NH3 Adsorption, Desorption and Oxidation over Hydrothermally Aged Cu-Chabazite. Catalysts. 2020; 10(4):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040411
Chicago/Turabian StyleBozbag, Selmi Erim, Deniz Şanlı, Barkın Özener, Gökhan Hisar, and Can Erkey. 2020. "An Aging Model of NH3 Storage Sites for Predicting Kinetics of NH3 Adsorption, Desorption and Oxidation over Hydrothermally Aged Cu-Chabazite" Catalysts 10, no. 4: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040411
APA StyleBozbag, S. E., Şanlı, D., Özener, B., Hisar, G., & Erkey, C. (2020). An Aging Model of NH3 Storage Sites for Predicting Kinetics of NH3 Adsorption, Desorption and Oxidation over Hydrothermally Aged Cu-Chabazite. Catalysts, 10(4), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040411