Continuous Process for Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Lysine and Tetrabutyl Phosphonium Lysinate Aqueous Mixtures in a Packed Tower
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. IL Chemical Characterization by NMR and FTIR
2.2. Packed-Column Performance as a Function of Operation Parameters
2.2.1. Effect of the CO2 Inlet Concentration
2.2.2. Effect of the Total Gas Flow Rate
2.2.3. Effect of the Liquid Flow Rate
2.2.4. Effect of the Absorbent Concentration
2.2.5. Temperature Effect
2.3. Performance of Absorption/Regeneration Cycles
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Ionic Liquid Synthesis
3.3. Analysis Method
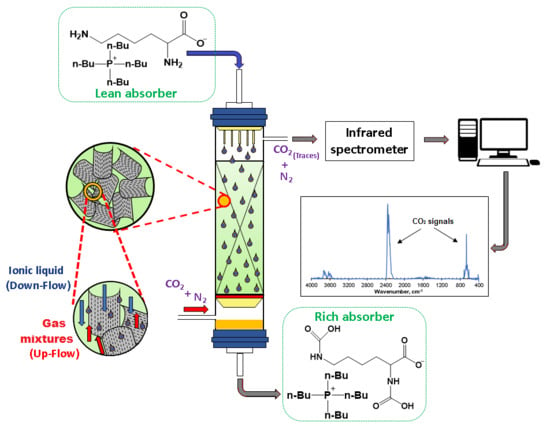
3.4. Experimental Apparatus and Procedures
3.4.1. Packed-Column Absorption Process
3.4.2. Batch-Cell-Absorbent-Regeneration Experiments
4. Determination of the Overall Mass Transfer Coefficient in Packed Column
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zareiekordshouli, F.; Lashanizadehgan, A.; Darvishi, P. Study on the use of an imidazolium-based acetate ionic liquid for CO2 capture from flue gas in absorber/stripper packed columns: Experimental and modeling. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2018, 70, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.S.; Shariff, A.M.; Lau, K.K.; Bustam, M.A. Factors affecting CO2 absorption efficiency in packed column: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrelli, E.A.; Armstrong, K.; Styring, P. Chapter 16: Potential CO2 utilisation contributions to a more carbon-sober future: A 2050 vision. In Carbon Dioxide Utilisation; Elsevier B.V.: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuéllar-Franca, R.M.; Azapagic, A. Carbon capture, storage and utilisation technologies: A critical analysis and comparison of their life cycle environmental impacts. J. CO2 Utiliz. 2015, 9, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catizzone, E.; Bonura, G.; Migliori, M.; Frusteri, F.; Giordano, G. CO2 recycling to dimethyl ether: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Molecules 2018, 23, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perathoner, S.; Centi, G. CO2 recycling: A key strategy to introduce green energy in the chemical production chain. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, E.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D. Current situation of carbon dioxide capture, storage, and enhanced oil recovery in the oil and gas industry. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 9999, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, A.; Poletto, M.; Barletta, D. Pure hydrogen co-production by membrane technology in an IGCC power plant with carbon capture. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 19279–19292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Guo, Y.; Niu, Z.; Lin, W. The absorption rate of CO2 by aqueous ammonia in a packed column. Fuel Proc. Technol. 2013, 108, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiflett, M.B.; Drew, D.W.; Cantini, R.A.; Yokozeki, A. Carbon dioxide capture using ionic liquid 1-butyl-3methylimidazolium acetate. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziobrowski, Z.; Krupiczka, R.; Rotkegel, A. Carbon dioxide absorption in a packed column using imidazolium based ionic liquids and MEA solution. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 47, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupiczka, R.; Rotkegel, A.; Ziobrowski, Z. Comparative study of CO2 absorption in packed column using imidazolium based ionic liquids and MEA solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, W.; Zhang, X. Dual amino-functionalized phosphonium ionic liquids for CO2 capture. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sistla, Y.S.; Khanna, A. Carbon dioxide absorption studies using amine-functionalized ionic liquids. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2497–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, K.; Ma, J.-W.; Wu, Y.-T.; Zhang, Z.-B. Absorption of CO2 in amino acid ionic liquid (AAIL) activated MDEA solutions. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 19, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagimoto, J.; Fukumoto, K.; Ohno, H. Effect of tetrabutylphosphonium cation on the physico-chemical properties of amino-acid ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2006, 21, 2254–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Łęgosz, B.; Walkiewicz, F.; Klejdysz, T.; Borkowskic, A.; Chrzanowskia, Ł. Ammonium ionic liquids with anions of natural origin. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65471–65480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, J.; Ortega-Guevara, C.; García de León, R.; Martínez-Palou, R. Absorption of CO2 with amino acid-based ionic liquids and corresponding amino acid precursors. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2017, 40, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pro-Pak® is a Registered Trademark of Cannon Instruments Co., and Their Product Characteristics is Reported in. Available online: https://www.cannoninstrument.com/en/product/distillation-packing2/pro-pak-distillation-packing--CANNON%20Pro-Pak (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- Field, L.D.; Sternhell, S.; Kalman, J.R. Organic Structures from Spectra, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-1-119-96461-2. [Google Scholar]
- Weigert, F.J.; Roberts, J.D. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Spin-spin coupling of carbon to phosphorus, mercury, nitrogen, and other elements. Inorg. Chem. 1973, 12, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Dong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Lv, X. Supported absorption of CO2 by tetrabutylphosphonium amino acid ionic liquids. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeria, A.; Einbub, A.; Wiigb, P.O.; Øi, L.E.; Svendsen, H.F. Experimental investigation of pressure drop, liquid hold-up and mass transfer parameters in a 0.5 m diameter absorber column. Energy Proc. 2011, 4, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zivdar, M.; Fard, M.H.; Prince, R.G. Evaluation of pressure drop and mass-transfer characteristics of a structured packing for production and separation of food flavors. Part 1: Pressure drop characteristics. Food Bioprod. Process. 2006, 84, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhamipour, M.; Mofarahi, M. Review on the mass transfer performance of CO2 absorption by amine-based solvents in low- and high-pressure absorption packed columns. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17857–17872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, A.; Aroonwilas, A. CO2 absorption into MEA-AMP blend: Mass transfer and absorber height index. Energy Proc. 2009, 1, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, S.; Fang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. Comparative analysis of CO2 separation from flue gas by membrane gas absorption technology and chemical absorption technology in China. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Zhang, P. Investigation of the absorption performance and viscosity for CO2 capture process using [Bmim][Gly] promoted MDEA (N-methyldiethanolamine) aqueous solution. Energy 2015, 87, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Sema, T.; Liang, Z.; Liu, H.; Na, Y.; Shi, H.; Idem, R.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P. Investigation of mass-transfer permeance for CO2 absorption into diethylenetriamine (DETA) in a randomly packed column. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 12058–12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Gao, H.; Luo, X.; Liao, H.; Liang, Z. Mass transfer performance of CO2 absorption into aqueous DEEA in packed columns. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Lv, J.; Zhong, H.; Sheng, C. Influence of particles on mass transfer performance for CO2 absorption using K2CO3 solution in a random θ-ring packed column. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2017, 58, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, K.H.; Mahmud, T.; Purba, E. Enhancement of mass transfer in a spray tower using swirling gas flow. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2006, 84, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; He, M.; Yu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, Z. Overall mass transfer of CO2 absorption in a diameter-varying spray tower. Energy Proc. 2017, 114, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tian, X.; Fu, D. CO2 removal in tray tower by using AAILs activated MDEA aqueous solution. Energy 2018, 161, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privalova, E.; Rasi, S.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Eränen, K.; Rintala, J.; Murzin, D.Y.; Mikkola, J.-P. CO2 capture from biogas: Absorbent selection. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 2979–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Size, mm | Material | Free Space,% | Surface Area, m2/m3 | Packing Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.41 | Stainless steel | 94 | 1890 | 693 |
| Parameter | Operation Conditions |
|---|---|
| Absorbent | [TBP][Lys], L-lysine, mixtures |
| Gas flow rate | 100, 150, 200 mL/min |
| Liquid flow rate | 3, 4, 5 mL/min |
| CO2 concentration | 10, 15, 20, 40 vol.% |
| Absorbent concentration | 5, 10, 15 wt.% |
| Liquid temperature | 15, 30, 40 °C |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zúñiga-Mendiola, A.d.J.; Gómora-Herrera, D.R.; García-González, J.M.; Guzmán-Pantoja, J. Continuous Process for Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Lysine and Tetrabutyl Phosphonium Lysinate Aqueous Mixtures in a Packed Tower. Catalysts 2020, 10, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040426
Zúñiga-Mendiola AdJ, Gómora-Herrera DR, García-González JM, Guzmán-Pantoja J. Continuous Process for Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Lysine and Tetrabutyl Phosphonium Lysinate Aqueous Mixtures in a Packed Tower. Catalysts. 2020; 10(4):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040426
Chicago/Turabian StyleZúñiga-Mendiola, Antonio de Jesús, Diana Rosa Gómora-Herrera, Juan Manuel García-González, and Javier Guzmán-Pantoja. 2020. "Continuous Process for Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Lysine and Tetrabutyl Phosphonium Lysinate Aqueous Mixtures in a Packed Tower" Catalysts 10, no. 4: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040426
APA StyleZúñiga-Mendiola, A. d. J., Gómora-Herrera, D. R., García-González, J. M., & Guzmán-Pantoja, J. (2020). Continuous Process for Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Lysine and Tetrabutyl Phosphonium Lysinate Aqueous Mixtures in a Packed Tower. Catalysts, 10(4), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040426