Pt/Re/CeO2 Based Catalysts for CO-Water–Gas Shift Reaction: from Powders to Structured Catalyst
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Powder Catalysts
2.1.1. Characterization Results
2.1.2. Activity Tests
2.1.3. Kinetic Measurements
2.2. Structured Catalyst
2.2.1. Characterization Results
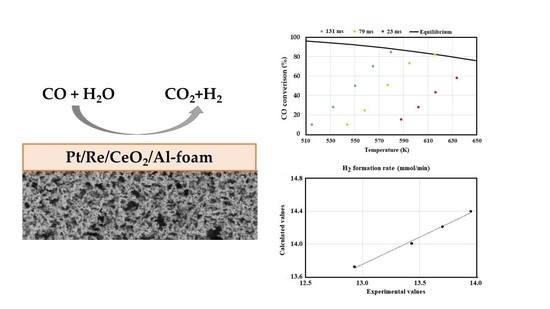
2.2.2. Kinetic Measurements
2.2.3. Activity Tests
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Powder Catalysts Preparation
3.2. Structured Catalyst Preparation
3.3. Catalysts Characterization
3.4. Catalytic Activity Tests
3.5. Kinetic Measurements
- The WGS reaction: CO + H2O = CO2 + H2
- The CO methanation: CO + 3H2 = CH4 + H2O
- The CO2 methanation: CO2 + 4H2 = CH4 + 2H2O
- with
- -
- Pi is the partial pressure of the component “i”.
- -
- ki (T) is the reaction rate constant according to the Arrhenius law: , with k0,i = pre-exponential factor and EA,i = the activation energy.
- -
- Kj (T) are the adsorption constants for the component “j”, expressed according to the Arrhenius law [41]: , with K0,j = pre-exponential factor and ΔHA,j = the adsorption heat.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palma, V.; Ruocco, C.; Cortese, M.; Martino, M. Recent Advances in Structured Catalysts Preparation and Use in Water-Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts 2019, 9, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.-W.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Eom, H.-J.; Moon, D.J.; Lee, K.-Y. The review of Cr-free Fe-based catalysts for high-temperature water-gas shift reactions. Catal. Today 2013, 210, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.; Isogai, N.; Oba, M.; Hasegawa, T. The zinc oxide copper catalyst for carbon monoxide-shift conversion. I. The dependency of the catalytic activity on the chemical composition of the catalyst. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1967, 40, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cifuentes, B.; Bustamante, F.; Cobo, M. Single and Dual Metal Oxides as Promising Supports for Carbon Monoxide Removal from an Actual Syngas: The Crucial Role of Support on the Selectivity of the Au–Cu System. Catalysts 2019, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palma, V.; Pisano, D.; Martino, M. CFD modeling of the influence of carrier thermal conductivity for structured catalysts in the WGS reaction. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 178, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, H.A.J.; Boon, J.; Nyqvist, R.N.; Van Den Brink, R.W. Development of a single stage heat integrated water-gas shift reactor for fuel processing. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 159, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Pisano, D.; Martino, M.; Ricca, A.; Ciambelli, P. High Thermal Conductivity Structured Carriers for Catalytic Processes Intensification. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 43, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Pisano, D.; Martino, M. Structured noble metal-based catalysts for the WGS process intensification. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 11745–11754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiegler, T.; Meltzer, K.; Tremel, A.; Baldauf, M.; Wasserscheid, P.; Albert, J. Development of a Structured Reactor System for CO2 Methanation under Dynamic Operating Conditions. Energy Technol. 2019, 7, 1900047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Pisano, D.; Martino, M. Comparative Study Between Aluminum Monolith and Foam as Carriers for The Intensification of The CO Water Gas Shift Process. Catalysts 2018, 8, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kam, R.; Scott, J.; Amal, R.; Selomulya, C. Pyrophoricity and stability of copper and platinum based water-gas shift catalysts during oxidative shut-down/start-up operation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 6461–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wachs, I.E. Iron-Based Catalysts for the High-Temperature Water-Gas Shift (HTWGS) Reaction: A Review. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruettinger, W.; Ilinich, O.; Farrauto, R.J. A new generation of water gas shift catalysts for fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2003, 118, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, P.; Kondarides, D.I. Effect of the nature of the support on the catalytic performance of noble metal catalysts for the water–gas shift reaction. Catal. Today 2008, 112, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de León, J.N.D.; Loera-Serna, S.; Zepeda, T.A.; Domínguez, D.; Pawelec, B.; Venezia, A.M.; Fuentes-Moyado, S. Noble metals supported on binary γ-Al2O3-α-Ga2O3 oxide as potential low temperature water-gas shift catalysts. Fuel 2020, 266, 117031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chein, R.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chyou, Y.P.; Chung, J.N. Study on water-gas shift reaction performance using Pt-based catalysts at high temperatures. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 18854–18862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño, M.G.; Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Pt vs. Au in water–gas shift reaction. J. Catal. 2014, 314, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Martino, M. Pt-Re Based Catalysts for the Realization of a Single Stage Water Gas Shift Process. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 57, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Terada, K.; Hasegawa, S.; Miyao, T.; Naito, S. Mechanistic study of water–gas-shift reaction over TiO2 supported Pt–Re and Pd–Re catalysts. Appl. Cat. A-Gen. 2005, 296, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasquillo-Flores, R.; Gallo, J.M.R.; Hahn, K.; Dumesic, J.A.; Mavrikakis, M. Density Functional Theory and Reaction Kinetics Studies of the Water–Gas Shift Reaction on Pt–Re Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 3690–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, H.; Igarashi, A. Structure characterization of Pt-Re/TiO2 (rutile) and Pt-Re/ZrO2 catalysts for water gas shift reaction at low-temperature. Appl. Cat. A-Gen. 2006, 303, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, S.Y.; Ferrandon, M.; Krause, T. Pt-Re bimetallic supported on CeO2-ZrO2 mixed oxides as water–gas shift catalysts. Catal. Today 2005, 99, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Terada, K.; Soma, Y.; Miyao, T.; Naito, S. Marked addition effect of Re upon the water gas shift reaction over TiO2 supported Pt, Pd and Ir catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2006, 7, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, K.G.; Babich, I.V.; Seshan, K.; Lefferts, L. Role of Re in Pt–Re/TiO2 catalyst for water gas shift reaction: A mechanistic and kinetic study. Appl. Cat. B-Environ. 2008, 80, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Villar, V.; Barrio, L.; Helmi, A.; Van Sint Annaland, M.; Gallucci, F.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Navarro, R.M. Effect of Re addition on the WGS activity and stability of Pt/CeO2–TiO2 catalyst for membrane reactor applications. Catal. Today 2016, 268, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Ruocco, C.; Meloni, E.; Ricca, A. Renewable Hydrogen from Ethanol Reforming over CeO2-SiO2 Based Catalysts. Catalysts 2017, 7, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.; Davies, T.E.; Morgan, D.J.; Golunski, S.; Taylor, S.H. Influence of the Preparation Method of Ag-K/CeO2-ZrO2-Al2O3 Catalysts on Their Structure and Activity for the Simultaneous Removal of Soot and NOx. Catalysts 2020, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, M.; Teng, B.; Fan, M.; Liu, X. Resolving a Decade-Long Question of Oxygen Defects in Raman Spectra of Ceria-Based Catalysts at Atomic Level. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 18889–18894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Howe, J.; Mayer III, H.M.; Overbury, S.H. Probing Defect Sites on CeO2 Nanocrystals with Well-Defined Surface Planes by Raman Spectroscopy and O2 Adsorption. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16595–16606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogan, M.S.; Dines, T.J.; Cairns, J.A. Raman spectroscopic study of the Pt-CeO2 interaction in the Pt/Al2O3-CeO2 catalyst. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1994, 90, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, F.D.; Wachs, I.E.; Horsley, J.A.; Via, G.H. The structure of surface rhenium oxide on alumina from laser raman spectroscopy and x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy. J. Mol. Catal. 1988, 46, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchini, E.; Trovarelli, A.; Llorca, J.; Graham, G.W.; Weber, W.H.; Maciejewski, M.; Baiker, A. Relationships between Structural/Morphological Modifications and Oxygen Storage–Redox Behavior of Silica-Doped Ceria. J. Catal. 2000, 194, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, R. Hydrogen spillover. Facts and fiction. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2714–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.-W.; Potdar, H.S.; Shim, J.-O.; Jang, W.-J.; Roh, H.-S. H2 production from a single stage water-gas shift reaction over Pt/CeO2, Pt/ZrO2, and Pt/Ce(1-x)Zr(x)O2 catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4502–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Willigan, R.R.; Dardas, Z.; Vanderspurt, T.H. Water gas shift activity and kinetics of Pt/Re catalysts supported on ceria-zirconia oxides. Appl. Cat. B-Environ. 2006, 66, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabalà, M.; Armelao, L.; Buchberger, A.; Calliari, I. Cerium-based conversion layers on aluminum alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 172, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Goodall, R.; Thompson, A.; Ruocco, C.; Renda, S.; Leach, R.; Martino, M. Ceria-coated Replicated Aluminium Sponges as Catalysts for the CO-Water Gas Shift Process. Int J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiani, C.; Visconti, C.G.; Finocchio, E.; Gallo Stampino, P.; Forzatti, P. Towards the rationalization of the washcoating process conditions. Catal. Today 2009, 147, S24–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia, P.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Schwank, J.W. A review on oxygen storage capacity of CeO2-based materials: Influence factors, measurement techniques, and applications in reactions related to catalytic automotive emissions control. Catal. Today 2019, 327, 90–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, L.; Medrano Jimenez, J.A.; Assefa Wassie, S.; Gallucci, F.; Palo, E.; Colozzi, M.; Taraschi, S.; Galdieri, G. Process design for green hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 7266–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Martino, M.; Truda, L. Nano-CeO2 Coating on Aluminum Foam Carriers for Structured Catalysts Preparation. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 73, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasamy, C.; Wagner, J. Water Gas Shift Catalysis. Catal. Rev.-Sci. Eng. 2009, 51, 325–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Chemical Composition (wt%) | SSAB.E.T. (m2/g) | H2 Uptake (mmol/g) | Crystallite Size (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 | Pt | Re | Exp. | Theor. | |||
| CeO2 | - | - | - | 175 | - | - | 6.10 |
| W1 (2Pt/1Re/CeO2) | 99.12 | 0.59 | 0.29 | 171 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 6.09 |
| W2 (1Pt/1Re/CeO2) | 99.10 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 169 | 0.84 | 0.15 | 6.05 |
| W3 (1Pt/2Re/CeO2) | 99.11 | 0.30 | 0.59 | 168 | 0.84 | 0.16 | 6.15 |
| W1 | W2 | W3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| k0, WGS (mol/(g·min·atm2)) | 1608326 | 1225116014 | 1225116014 |
| Ea, WGS (kJ/mol) | 78 | 114 | 118 |
| k0, CO (mol/(g·min·atm2)) | 2989 | 40000 | 40000 |
| Ea, CO (kJ/mol) | 94 | 85 | 85 |
| k0, CO2 (mol/(g·min·atm2)) | 0.00712 | 6.9 | 6.9 |
| Ea, CO2 (kJ/mol) | 16 | 50 | 48 |
| Catalytic Formulation | SSAB.E.T. (m2/g) | H2 Uptake (mmol/g) | Relative Density (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loading (wt%) | Pt/Re Ratio | Exp. | Theor. | |||
| Al-foam | - | - | 1 | - | - | 25 |
| S1 | 5.1 | 1.9 | 3.8 | 1.2 | 0.13 | - |
| k0 (mol/(g·min·atm2)) | Ea (kJ/mol) | |
|---|---|---|
| rWGS | 1608326 | 80 |
| rCO | 2500 | 85 |
| rCO2 | 1000 | 75 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palma, V.; Gallucci, F.; Pullumbi, P.; Ruocco, C.; Meloni, E.; Martino, M. Pt/Re/CeO2 Based Catalysts for CO-Water–Gas Shift Reaction: from Powders to Structured Catalyst. Catalysts 2020, 10, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050564
Palma V, Gallucci F, Pullumbi P, Ruocco C, Meloni E, Martino M. Pt/Re/CeO2 Based Catalysts for CO-Water–Gas Shift Reaction: from Powders to Structured Catalyst. Catalysts. 2020; 10(5):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050564
Chicago/Turabian StylePalma, Vincenzo, Fausto Gallucci, Pluton Pullumbi, Concetta Ruocco, Eugenio Meloni, and Marco Martino. 2020. "Pt/Re/CeO2 Based Catalysts for CO-Water–Gas Shift Reaction: from Powders to Structured Catalyst" Catalysts 10, no. 5: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050564
APA StylePalma, V., Gallucci, F., Pullumbi, P., Ruocco, C., Meloni, E., & Martino, M. (2020). Pt/Re/CeO2 Based Catalysts for CO-Water–Gas Shift Reaction: from Powders to Structured Catalyst. Catalysts, 10(5), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050564