The Effect of Electrolytes on the Photodegradation Kinetics of Caffeine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
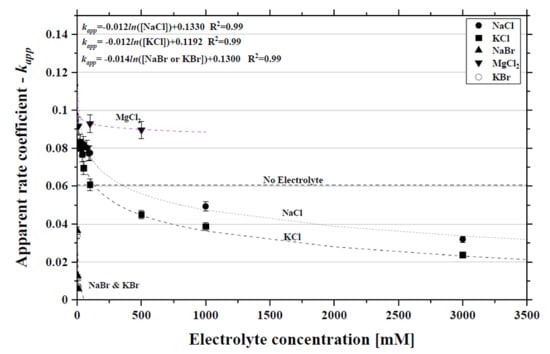
2.1. Caffeine Photodegradation in the Presence of NaCl, KCl and MgCl2 Electrolytes
2.2. Caffeine Photodegradation in the Presence of KBr and NaBr Electrolytes
3. Materials and Methods
Experimental Setup
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Apparent Rate Coefficient Calculations
Appendix B
| Exp. # | Apparent Rate Coefficient kapp [min−1] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-Zero-Order | R2 | Pseudo-First-Order | R2 | Pseudo-Second-Order | R2 | |
| 32 | 0.0090 | 0.9374 | 0.0150 | 0.9987 | 0.0288 | 0.9485 |
| 33 | 0.0049 | 0.9347 | 0.0063 | 0.9831 | 0.0084 | 0.9974 |
| 34 | 0.0029 | 0.8980 | 0.0035 | 0.9423 | 0.0050 | 0.9916 |
| 35 | 0.0286 | 0.9914 | 0.0451 | 0.9771 | 0.0799 | 0.8629 |
| 36 | 0.0230 | 0.9902 | 0.0368 | 0.9755 | 0.0669 | 0.8508 |
| 37 | 0.0111 | 0.9626 | 0.0168 | 0.9985 | 0.0283 | 0.9564 |
| 38 | 0.0054 | 0.9307 | 0.0072 | 0.9859 | 0.0098 | 0.9980 |
| 39 | 0.0365 | 0.9936 | 0.0614 | 0.9788 | 0.1320 | 0.8342 |
| 40 | 0.0126 | 0.9318 | 0.0208 | 0.9988 | 0.0392 | 0.9389 |
| 41 | 0.0058 | 0.7668 | 0.0091 | 0.9398 | 0.0157 | 0.9930 |
| 42 | 0.0598 | 0.9919 | 0.0934 | 0.9842 | 0.1625 | 0.8967 |
| 43 | 0.0208 | 0.9630 | 0.0348 | 0.9921 | 0.0784 | 0.8814 |
| 44 | 0.0108 | 0.9194 | 0.0176 | 0.9972 | 0.0340 | 0.9691 |
| 45 | 0.0341 | 0.9906 | 0.0504 | 0.9901 | 0.1009 | 0.8736 |
| 46 | 0.0111 | 0.8709 | 0.0205 | 0.9958 | 0.0467 | 0.9304 |
| 47 | 0.0069 | 0.8704 | 0.0101 | 0.9659 | 0.0159 | 0.9934 |
| Empirical Curves | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaBr [mM] | Pseudo-zero-order | R2 | Pseudo-first-order | R2 | Pseudo-second-order | R2 |
| 1 | kapp = 0.0216ln([H2O2]) − 0.0542 | 0.96 | kapp = 0.0338ln([H2O2]) − 0.0836 | 0.98 | kapp = 0.0609ln([H2O2]) − 0.1461 | 0.97 |
| 5 | kapp = 0.0064ln([H2O2]) − 0.0134 | 0.94 | kapp = 0.0117ln([H2O2]) − 0.0271 | 0.95 | kapp = 0.0287ln([H2O2]) − 0.0761 | 0.92 |
| 10 | kapp = 0.0031ln([H2O2]) − 0.0063 | 0.87 | kapp = 0.0057ln([H2O2]) − 0.0135 | 0.89 | kapp = 0.0119ln([H2O2]) − 0.0316 | 0.86 |
| H2O2 [µM] | Pseudo-zero-order | R2 | Pseudo-first-order | R2 | Pseudo-second-order | R2 |
| 163.0 | kapp = −0.022ln([NaBr]) + 0.2095 | 0.99 | kapp = −0.034ln([NaBr]) + 0.3240 | 0.99 | kapp = −0.055ln([NaBr]) + 0.5448 | 0.99 |
| 81.50 | kapp = −0.014ln([NaBr]) + 0.1300 | 0.99 | kapp = −0.023ln([NaBr]) + 0.2206 | 0.99 | kapp = −0.052ln([NaBr]) + 0.4874 | 0.99 |
| 40.75 | kapp = −0.008ln([NaBr]) + 0.0761 | 0.99 | kapp = −0.013ln([NaBr]) + 0.1237 | 0.99 | kapp = −0.024ln([NaBr]) + 0.2277 | 0.99 |
| 16.30 | kapp = −0.003ln([NaBr]) + 0.0272 | 0.99 | kapp = −0.005ln([NaBr]) + 0.0499 | 0.99 | kapp = −0.011ln([NaBr]) + 0.1023 | 0.97 |
References
- Gracia-Lor, E.; Rousis, N.I.; Zuccato, E.; Bade, R.; Baz-Lomba, J.A.; Castrignanò, E.; Causanilles, A.; Hernández, F.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Kinyua, J.; et al. Estimation of caffeine intake from analysis of caffeine metabolites in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dafouz, R.; Cáceres, N.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.L.; Mastroianni, N.; López de Alda, M.; Barceló, D.; de Miguel, Á.G.; Valcárcel, Y. Does the presence of caffeine in the marine environment represent an environmental risk? A regional and global study. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nödler, K.; Voutsa, D.; Licha, T. Polar organic micropollutants in the coastal environment of different marine systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buerge, I.J.; Poiger, T.; Müller, M.D.; Buser, H.R. Caffeine, an anthropogenic marker for wastewater contamination of surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, H. Caffeine tracks contamination. Nature 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ernst, F.; Conkle, J.L.; Gan, J. Comparative uptake and translocation of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) by common vegetables. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, B.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: Current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Res. 2015, 72, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebele, A.J.; Abou-Elwafa Abdallah, M.; Harrad, S. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the freshwater aquatic environment. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.; Carvalho, R.; Comero, S.; António, D.; Ghiani, M.; Lettieri, T.; Locoro, G.; Paracchini, B.; Tavazzi, S.; Gawlik, B. EU Wide Monitoring Survey on Waste Water Treatment Plant Effluents. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6475–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Fan, Q. Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals, caffeine and DEET in wastewater treatment plants of Beijing, China. Water Res. 2010, 44, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehner, S.; Piccioni, W.; Machado, K.S.; Aisse, M.M. Removal capacity of caffeine, hormones, and bisphenol by aerobic and anaerobic sewage treatment. Water. Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 216, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovó, A.G.; Silva, T.F.S.; Gomes, O.; Machado, A.E.H.; Neto, W.B.; Muller, P.S.; Daniel, D. Degradation of caffeine by photo-Fenton process: Optimization of treatment conditions using experimental design. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glaze, W.H.; Kang, J.-W.; Chapin, D.H. The Chemistry of Water Treatment Processes Involving Ozone, Hydrogen Peroxide and Ultraviolet Radiation. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1987, 9, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Cardenas, J.A.; Esteban-García, B.; Agüera, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Wastewater treatment by advanced oxidation process and their worldwide research trends. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuerda-correa, E.M.; Alexandre-franco, M.F.; Fern, C. Antibiotics from Water. An Overview. Water 2020, 12, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rytwo, G.; Klein, T.; Margalit, S.; Mor, O.; Naftaly, A.; Daskal, G. A continuous-flow device for photocatalytic degradation and full mineralization of priority pollutants in water. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 57, 16424–16434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwo, G.; Daskal, G. A System for Treatment of Polluted Effluents 2016. U.S. Patent 15/512,516, 19 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Oturan, M.A.; Aaron, J.-J. Advanced Oxidation Processes in Water/Wastewater Treatment: Principles and Applications. A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2577–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendel, P.M.; Rytwo, G. Degradation kinetics of caffeine in water by UV/H2O2 and UV/TiO2. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 173, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autin, O.; Hart, J.; Jarvis, P.; MacAdam, J.; Parsons, S.A.; Jefferson, B. The impact of background organic matter and alkalinity on the degradation of the pesticide metaldehyde by two advanced oxidation processes: UV/H2O2 and UV/TiO2. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2041–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Muñoz, P.; Dachtler, W.; Altmayer, B.; Schulz, R.; Robert, D.; Seitz, F.; Rosenfeldt, R.; Keller, N. Reaction pathways, kinetics and toxicity assessment during the photocatalytic degradation of glyphosate and myclobutanil pesticides: Influence of the aqueous matrix. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzafame, G.M.; Sarakha, M.; Fabbri, D.; Vione, D. Degradation of methyl 2-aminobenzoate (methyl anthranilate) by H2O2/UV: Effect of inorganic anions and derived radicals. Molecules 2017, 22, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.H.; Kang, S.F.; Wu, F.A. Hydroxyl radical scavenging role of chloride and bicarbonate ions in the H2O2/UV process. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riga, A.; Soutsas, K.; Ntampegliotis, K.; Karayannis, V.; Papapolymerou, G. Effect of system parameters and of inorganic salts on the decolorization and degradation of Procion H-exl dyes. Comparison of H2O2/UV, Fenton, UV/Fenton, TiO2/UV and TiO2/UV/H2O2 processes. Desalination 2007, 211, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioja, N.; Zorita, S.; Peñas, F.J. Effect of water matrix on photocatalytic degradation and general kinetic modeling. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 180, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laat, J.; Truong Le, G.; Legube, B. A comparative study of the effects of chloride, sulfate and nitrate ions on the rates of decomposition of H2O2 and organic compounds by Fe(II)/H2O2 and Fe(III)/H2O2. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Ahmad, J.; Flora, S.J.S. Application of advanced oxidation processes and toxicity assessment of transformation products. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. PHREEQC 2.14. 3 A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimentional transport and inverse geochemical calculation. Water-Resour. Investig. Rep. 2007, 99, 4259. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, W.C.; Livingston, R.S. The catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in a bromine-bromide solution, and a study of the steady state. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1923, 45, 1251–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology: Gold Book. IUPAC Compend. Chem. Terminol. 2014, 1670. [Google Scholar]





| Exp. # | Electrolyte Type | Electrolyte Concentration [mmol L−1] | H2O2 Concentration [µmol L−1] | Apparent Rate Coefficient kapp [min−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Non,Baseline | 0 | 81.5 | 0.0607 |
| 2 | NaCl | 1 | 81.5 | 0.0760 |
| 3 | NaCl | 3 | 81.5 | 0.0816 |
| 4 | NaCl | 5 | 81.5 | 0.0805 |
| 5 | NaCl | 10 | 81.5 | 0.0796 |
| 6 | NaCl | 25 | 81.5 | 0.0794 |
| 7 | NaCl | 50 | 81.5 | 0.0821 |
| 8 | NaCl | 75 | 81.5 | 0.0802 |
| 9 | NaCl | 90 | 81.5 | 0.0772 |
| 10 | NaCl | 100 | 81.5 | 0.0786 |
| 11 | NaCl | 1000 | 81.5 | 0.0493 |
| 12 | NaCl | 3000 | 81.5 | 0.0320 |
| 13 | KCl | 1 | 81.5 | 0.0725 |
| 14 | KCl | 1.5 | 81.5 | 0.0804 |
| 15 | KCl | 3 | 81.5 | 0.0851 |
| 16 | KCl | 5 | 81.5 | 0.0762 |
| 17 | KCl | 10 | 81.5 | 0.0742 |
| 18 | KCl | 15 | 81.5 | 0.0744 |
| 19 | KCl | 20 | 81.5 | 0.0768 |
| 20 | KCl | 25 | 81.5 | 0.0831 |
| 21 | KCl | 30 | 81.5 | 0.0800 |
| 22 | KCl | 40 | 81.5 | 0.0766 |
| 23 | KCl | 50 | 81.5 | 0.0695 |
| 24 | KCl | 100 | 81.5 | 0.0607 |
| 25 | KCl | 500 | 81.5 | 0.0450 |
| 26 | KCl | 1000 | 81.5 | 0.0387 |
| 27 | KCl | 3000 | 81.5 | 0.0237 |
| 28 | MgCl2 | 1 | 81.5 | 0.0771 |
| 29 | MgCl2 | 10 | 81.5 | 0.0917 |
| 30 | MgCl2 | 100 | 81.5 | 0.0929 |
| 31 | MgCl2 | 500 | 81.5 | 0.0896 |
| 32 | NaBr | 1 | 16.3 | 0.0090 |
| 33 | NaBr | 5 | 16.3 | 0.0049 |
| 34 | NaBr | 10 | 16.3 | 0.0029 |
| 35 | NaBr | 0.5 | 40.75 | 0.0286 |
| 36 | NaBr | 1 | 40.75 | 0.0230 |
| 37 | NaBr | 5 | 40.75 | 0.0111 |
| 38 | NaBr | 10 | 40.75 | 0.0054 |
| 39 | NaBr | 1 | 81.5 | 0.0365 |
| 40 | NaBr | 5 | 81.5 | 0.0126 |
| 41 | NaBr | 10 | 81.5 | 0.0058 |
| 42 | NaBr | 1 | 163 | 0.0598 |
| 43 | NaBr | 5 | 163 | 0.0208 |
| 44 | NaBr | 10 | 163 | 0.0108 |
| 45 | KBr | 1 | 81.5 | 0.0341 |
| 46 | KBr | 5 | 81.5 | 0.0111 |
| 47 | KBr | 10 | 81.5 | 0.0069 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rendel, P.M.; Rytwo, G. The Effect of Electrolytes on the Photodegradation Kinetics of Caffeine. Catalysts 2020, 10, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060644
Rendel PM, Rytwo G. The Effect of Electrolytes on the Photodegradation Kinetics of Caffeine. Catalysts. 2020; 10(6):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060644
Chicago/Turabian StyleRendel, Pedro M., and Giora Rytwo. 2020. "The Effect of Electrolytes on the Photodegradation Kinetics of Caffeine" Catalysts 10, no. 6: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060644
APA StyleRendel, P. M., & Rytwo, G. (2020). The Effect of Electrolytes on the Photodegradation Kinetics of Caffeine. Catalysts, 10(6), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060644