Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
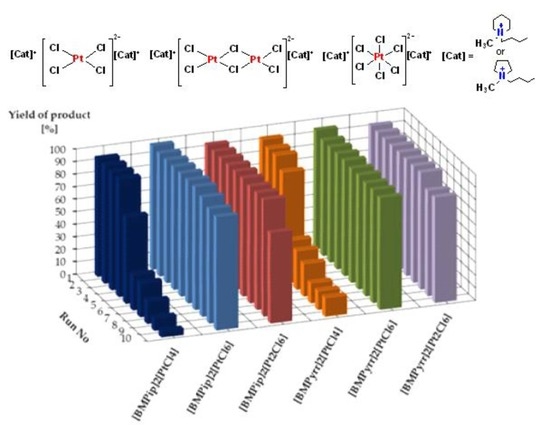
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Analytical Techniques
3.3. Synthesis of Transition-Metal-Based Complexes
3.4. General Procedure for Catalytic Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniec, B.; Maciejewski, H.; Pietraszuk, C.; Pawluć, P. Hydrosilylation: A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances; Marciniec, B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Trogel, D.; Strohrer, J. Recent advances and actual challenges in late transition metal catalyzed hydrosilylation of olefins from an industrial point of view. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1440–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniec, B.; Maciejewski, H.; Pawluć, P. Organosilicon Compounds; Lee, V.Y., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Chapter 5; pp. 169–218. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniec, B.; Maciejewski, H.; Pietraszuk, C.; Pawluć, P. Applied Homogeneous Catalysis with Organometallic Compounds; Cornils, B., Hermann, W.A., Belier, M., Pawelo, R., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Chapter 8; pp. 569–620. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, Y.; Shimada, S. Hydrosilylation reaction of olefins: Recent advances and perspectives. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 20603–20616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. (Eds.) Ionic Liquids–Industrial Applications to Green Chemistry; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dyson, P.J.; Geldbach, T.J. Metal Catalysed Reactions in Ionic Liquids; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hardacre, C.; Parvulescu, V. Catalysis in Ionic Liquids. From Catalyst Synthesis to Application; RS Chemistry: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vekariya, R.L. A review of ionic liquids: Applications towards catalytic organic transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozokwelu, D.; Zhang, S.; Okafor, O.C.; Cheng, W.; Litombe, N. Novel Catalytic and Separation Processes Based on Ionic Liquids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, P. (Ed.) Sustainable Catalysis in Ionic Liquids; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Behr, A.; Toslu, N. Hydrosilylation reactions in single and two phases. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2000, 23, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, N.; Bauer, A.; Auer, T.; Stanjek, V.; Schulz, P.; Taccardi, N.; Wasserscheid, P. Liquid-liquid biphasic, platinum-catalyzed hydrosilylation of allyl chloride with trichlorosilane using an ionic liquid catalyst phase in a continuous loop reactor. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 2599–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccardi, N.; Fekete, M.; Berger, M.E.; Stanjek, V.; Schulz, P.; Wasserscheid, P. Catalyst recycling in monophasic Pt-catalyzed hydrosilylation reactions using ionic liquids. Appl. Catal. A 2011, 399, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyershausen, B.; Hell, K.; Hesse, U. Industrial application of ionic liquids as process aid. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, T.; Strassner, T. Biphasic platinum catalyzed hydrosilylation of terminal alkenes in TAAILs. J. Organometal. Chem. 2013, 744, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, H.; Szubert, K.; Marciniec, B.; Pernak, J. Hydrosilylation of functionalised olefins catalysed by rhodium siloxide complexes in ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, W.; Kukawka, R.; Maciejewski, H.; Smiglak, M. Ionic liquids as solvents for rhodium and platinum catalysts used in hydrosilylation reaction. Molecules 2016, 21, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maciejewski, H.; Szubert, K.; Fiedorow, R.; Giszter, R.; Niemczak, M.; Pernak, J. Diallyldimethylammonium and trimethylvinylammonium ionic liquids—Synthesis and application to catalysis. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 451, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, H.; Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Dabek, I.; Fiedorow, R. The effect of the morpholinium ionic liquid anion on the catalytic activity of Rh (or Pt) complex–ionic liquid systems in hydrosilylation processes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 26922–26927. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Kukawaka, R.; Smiglak, M.; Maciejewski, H. The effect of the catalyst and the type of ionic liquid on the hydrosilylation process under batch and continuous reaction conditions. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 5229–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luska, K.L.; Demmans, K.Z.; Stratton, S.A.; Moores, A. Rhodium complexes stabilized by phosphine-functionalized phosphonium ionic liquids used as higher alkene hydroformylation catalysts: Influence of the phosphonium headgroup on catalytic activity. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13533–13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xu, X.-F.; Zhao, K. Amino acid- and imidazolium-tagged chiral pyrrolidinodiphosphine ligands and their applications in catalytic asymmetric hydrogenations in ionic liquid systems. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2012, 23, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yao, W.M.; Zhao, X.L.; Vo-Thanh, G.; Liu, Y. An ionic phosphine-ligated rhodium (III) complex as the efficient and recyclable catalyst for biphasic hydroformylation of 1-octene. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 378, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Bartlewicz, O.; Szpecht, A.; Zając, A.; Smiglak, M.; Maciejewski, H. Platinum and rhodium complexes ligated by imidazolium-substituted phosphine as efficient and recyclable catalysts for hydrosilylation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29396–29404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartlewicz, O.; Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Maciejwski, H. Highly efficient and reusable alkyne hydrosilylation catalysts based on rhodium complexes ligated by imidazolium- substituted phosphine. Catalysts 2020, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvulescu, V.I.; Hardacre, C.h. Catalysis in ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2615–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Chan, Y.S.; Jang, H.B.; Song, C.E.; Lee, S.-G. Toward understanding the origin of positive effects of ionic liquids on catalysis: Formation of more reactive catalysts and stabilization of reactive intermediates and transition states in ionic liquids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hui, S.; Shengjie, C.h.; Honqxing, Y.H.; Ye, L. Applications of transition metallates in catalysis. Prog. Chem. 2012, 24, 2287–2298. [Google Scholar]
- Estager, J.; Holbrey, J.D.; Swadzba-Kwasny, M. Halometallate ionic liquids–revisited. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiappe, C.; Ghilardi, T.; Pomelli, C.S. Structural features and properties of metal complexes in ionic liquids: Application in alkylation reactions. Top. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 51, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.C.; Hogg, J.M.; Swadzba-Kwasny, M. Lewis Acidic Ionic Liquids. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 5, 78–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkes, J.S. A short history of ionic liquids—From molten salts to neoteric solvents. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Kozhevnikov, I.V.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Femoni, C.; Steiner, A.; Winterton, N. N,N‘-dialkylimidazolium chloroplatinate(II), chloroplatinate(IV), and chloroiridate(IV) salts and an N-heterocyclic carbene complex of platinum(II): Synthesis in ionic liquids and crystal structures. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Sasaki, T.; Jimbo-Kobayashi, A.; Fujiwara, E.; Kobayashi, A.; Tada, M.; Iwasawa, Y. Syntheses, structures, and properties of a series of metal ion-containing dialkylimidazolium ionic liquids. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 12, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Bartlewicz, O.; Walczak, A.; Stefankiewicz, A.R.; Maciejewski, H. Highly efficient hydrosilylation catalysts based on chloroplatinate ionic liquids. J. Catal. 2019, 374, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, H.; Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Bartlewicz, O. New Anionic Platinum Complexes, Method for Obtaining Them and Application, Preferably for Hydrosilylation Processes. Polish Patent PL 233547, 11 March 2019. [Google Scholar]







| Catalyst | Melting Point [°C] |
|---|---|
| [BMPip]2 [PtCl4] | 151 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [PtCl4] | 134 |
| [BMPip]2 [PtCl6] | 178 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [PtCl6] | 169 |
| [BMPip]2 [Pt2Cl6] | 189 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [Pt2Cl6] | 165 |
| Catalyst | Decomposition Temperature [°C] |
|---|---|
| [BMPip]2 [PtCl4] | 219.84 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [PtCl4] | 212.95 |
| [BMPip]2 [PtCl6] | 225.88 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [PtCl6] | 233.07 |
| [BMPip]2 [Pt2Cl6] | 220.69 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [Pt2Cl6] | 237.40 |
| Catalyst | Product Yield in the Reaction with | |
|---|---|---|
| 1-octene 1 [%] | Allyl Glycidyl Ether 2 [%] | |
| [BMPip]2[PtCl4] | 94 | 96 |
| [BMPip]2[PtCl6] | 99 | 94 |
| [BMPip]2[Pt2Cl6] | 94 | 99 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl4] | 93 | 85 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl6] | 95 | 89 |
| [BMPyrr]2[Pt2Cl6] | 93 | 98 |
| Catalyst | Yield of Product in Subsequent Cycle [%] | Total TON |
|---|---|---|
| [BMPip]2[PtCl4] | 94 (94, 94, 94, 69, 28, 27, 18, 10, 5) | 53,300 |
| [BMPip]2[PtCl6] | 99 (98, 98, 98, 98, 98, 98, 95, 91, 90) | 96,300 |
| [BMPip]2[Pt2Cl6] | 94 (94, 94, 94, 94, 94, 93, 93, 93, 72) | 91,500 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl4] | 93 (91, 91, 83, 34, 31, 26, 16, 15, 15) | 49,500 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl6] | 95 (92, 92, 92, 92, 91, 91, 90, 90, 89) | 91,400 |
| [BMPyrr]2[Pt2Cl6] | 93 (93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 84, 84) | 91,200 |
| Catalyst | Yield of Product in Subsequent Cycle [%] | Total TON |
|---|---|---|
| [BMPip]2[PtCl4] | 94 (94, 94, 94, 69, 28, 27, 18, 10, 5) | 53,300 |
| [BMPip]2[PtCl6] | 99 (98, 98, 98, 98, 98, 98, 95, 91, 90) | 96,300 |
| [BMPip]2[Pt2Cl6] | 94 (94, 94, 94, 94, 94, 93, 93, 93, 72) | 91,500 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl4] | 93 (91, 91, 83, 34, 31, 26, 16, 15, 15) | 49,500 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl6] | 95 (92, 92, 92, 92, 91, 91, 90, 90, 89) | 91,400 |
| [BMPyrr]2[Pt2Cl6] | 93 (93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 84, 84) | 91,200 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Bartlewicz, O.; Pietras, P.; Maciejewski, H. Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation. Catalysts 2020, 10, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080919
Jankowska-Wajda M, Bartlewicz O, Pietras P, Maciejewski H. Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation. Catalysts. 2020; 10(8):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080919
Chicago/Turabian StyleJankowska-Wajda, Magdalena, Olga Bartlewicz, Przemysław Pietras, and Hieronim Maciejewski. 2020. "Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation" Catalysts 10, no. 8: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080919
APA StyleJankowska-Wajda, M., Bartlewicz, O., Pietras, P., & Maciejewski, H. (2020). Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation. Catalysts, 10(8), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080919