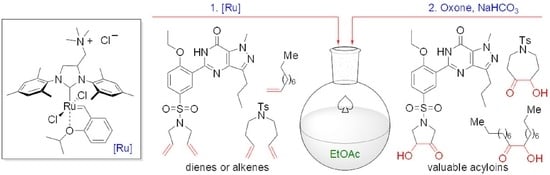
Tandem Olefin Metathesis/α-Ketohydroxylation Revisited
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiaden, A.; Spirig, T.; Hilbi, H. Bacterial gene regulation by alpha-hydroxyketone signaling. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, A.A.; Stierle, D.B.; Decato, D.; Priestley, N.D.; Alverson, J.B.; Hoody, J.; McGrath, K.; Klepacki, D. The Berkeleylactones, Antibiotic Macrolides from Fungal Coculture. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gala, D.; DiBenedetto, D.J.; Clark, J.E.; Murphy, B.L.; Schumacher, D.P.; Steinman, M. Preparations of antifungal Sch 42427/SM 9164: Preparative chromatographic resolution, and total asymmetric synthesis via enzymatic preparation of chiral α-hydroxy arylketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Marett, L.; Hughen, R.W.; Flores, M.; Forteza, I.; Ammon, M.A.; Concepcion, G.P.; Espino, S.; Olivera, B.M.; Rosenberg, G.; et al. Neuroactive diol and acyloin metabolites from cone snail-associated bacteria. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4867–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, O.B.; Smith, D.W.; Deshpande, M.S.; Polson, C.; Felsenstein, K.M. Inhibitors of Aβ production: Solid-phase synthesis and SAR of α-hydroxycarbonyl derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Kawase, M.; Tani, S. α-Hydroxyketones as inhibitors of urease. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, K.T. The Acyloin Condensation as a Cyclization Method. Chem. Rev. 1964, 64, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, J.J.; Owsley, D.C.; Nelke, J.M. The Acyloin Condensation. Org. React. 2004, 23, 259–404. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.S. The Synthesis of Macrocyclic Musks. Synthesis 1999, 1999, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytniczuk, A.; Milewski, M.; Kajetanowicz, A.; Grela, K. Preparation of macrocyclic musks via olefin metathesis: Comparison with classical syntheses and recent advances. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2020, 89, 469–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prelog, V.; Frenkiel, L.; Kobelt, M.; Barman, P. Zur Kenntnis des Kohlenstoffringes. Ein Herstellungsverfahren für vielgliedrige Cyclanone. Helv. Chim. Acta 1947, 30, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühlmann, K. Die Umsetzung von Carbonsäureestern mit Natrium in Gegenwart von Trimethylchlorsilan. Synthesis 1971, 1971, 236–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.S.; Biju, A.T.; Nair, V. Recent advances in N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)-catalysed benzoin reactions. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaggero, N.; Pandini, S. Advances in chemoselective intermolecular cross-benzoin-type condensation reactions. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 6867–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamao, K.; Maeda, K. Silafunctional compounds in organic synthesis. 29.1 Oxidation of (alkenyl)alkoxysilanes to α-hydroxy ketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Feng, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, G. An Efficient Method for the Synthesis of α-Hydroxyalkyl Aryl Ketones. Synthesis 2008, 2008, 3205–3208. [Google Scholar]
- Gala, D.; DiBenedetto, D.J. A rational approach to chiral α-hydroxy aryl ketones from chiral aryl epoxides via regioselective, stereo retentive oxidative epoxide opening: Its application to the synthesis of antifungal Sch 42427/SM 9164. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 8299–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, J.; Li, Z. Enantioselective Cascade Biocatalysis via Epoxide Hydrolysis and Alcohol Oxidation: One-Pot Synthesis of (R)-α-Hydroxy Ketones from Meso- or Racemic Epoxides. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Ros, S.; Jayan, C.N. Gallium Mediated Barbier Reactions of 1,2-diones: A Facile Synthesis of α-hydroxy ketones. J. Chem. Res. 2001, 2001, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, R.; Sahara, T.; Shimizu, M. Reduction of 1,2-diketones with titanium tetraiodide: A simple approach to α-hydroxy ketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 7939–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Dash, J.; Sudheer, C. Indium-Mediated Regio- and Diastereoselective Reduction of Norbornyl α-Diketones. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2004, 10, 2507–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.M.; Huang, W.-S.; Jamison, T.F. Catalytic Asymmetric Reductive Coupling of Alkynes and Aldehydes: Enantioselective Synthesis of Allylic Alcohols and α-Hydroxy Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3442–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Qi, C.; Hu, X.; Guan, Y.; Jiang, H. Efficient synthesis of tertiary α-hydroxy ketones through CO2-promoted regioselective hydration of propargylic alcohols. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3729–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, K. (Ed.) Olefin Metathesis: Theory and Practice; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Grubbs, R.H.; Wenzel, A.G.; O’Leary, D.J.; Khosravi, E. (Eds.) Handbook of Metathesis; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alcaide, B.; Almendros, P. Non-Metathetic Behavior Patterns of Grubbs’ Carbene. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2003, 9, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaide, B.; Almendros, P.; Luna, A. Grubbs’ Ruthenium-Carbenes Beyond the Metathesis Reaction: Less Conventional Non-Metathetic Utility. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3817–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, G.K.; Grela, K. Tandem Catalysis Utilizing Olefin Metathesis Reactions. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 9440–9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, G.K.; Samojłowicz, C.; Wdowik, T.; Grela, K. In tandem or alone: A remarkably selective transfer hydrogenation of alkenes catalyzed by ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 2684–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zieliński, G.K.; Majtczak, J.; Gutowski, M.; Grela, K. A Selective and Functional Group-Tolerant Ruthenium-Catalyzed Olefin Metathesis/Transfer Hydrogenation Tandem Sequence Using Formic Acid as Hydrogen Source. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 2542–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogg, D.E.; dos Santos, E.N. Tandem catalysis: A taxonomy and illustrative review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 2365–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beligny, S.; Eibauer, S.; Maechling, S.; Blechert, S. Sequential Catalysis: A Metathesis/Dihydroxylation Sequence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1900–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornan, P.K.; Wickens, Z.K.; Grubbs, R.H. Tandem Z-Selective Cross-Metathesis/Dihydroxylation: Synthesis of anti-1,2-Diols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7134–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, M.; Ceborska, M.; Witkowski, G.; Jarosz, S. Ruthenium-catalyzed one-pot ring-closing metathesis/syn-dihydroxylation in the synthesis of bicyclic iminosugars. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2015, 26, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plietker, B.; Niggemann, M. An Improved Protocol for the RuO4-Catalyzed Dihydroxylation of Olefins. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 3353–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plietker, B. RuO4-Catalyzed Ketohydroxylation of Olefins. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 7123–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plietker, B. The RuO4-Catalyzed Ketohydroxylation. Part 1. Development, Scope, and Limitation. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 8287–8296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plietker, B. The RuO4-Catalyzed Ketohydroxylation, Part II: A Regio-, Chemo- and Stereoselectivity Study. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2005, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholte, A.A.; An, M.H.; Snapper, M.L. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Tandem Olefin Metathesis−Oxidations. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 4759–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajetanowicz, A.; Grela, K. Nitro and Other Electron Withdrawing Group Activated Ruthenium Catalysts for Olefin Metathesis Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13738–13756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewski, T.K.; Bieniek, M.; Skowerski, K.; Grela, K. A New Tool in the Toolbox: Electron-Withdrawing Group Activated Ruthenium Catalysts for Olefin Metathesis. Synlett 2013, 24, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Grela, K. Forged and fashioned for faithfulness—ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts bearing ammonium tags. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chołuj, A.; Nogaś, W.; Patrzałek, M.; Krzesiński, P.; Chmielewski, M.J.; Kajetanowicz, A.; Grela, K. Preparation of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts Immobilized on MOF, SBA-15, and 13X for Probing Heterogeneous Boomerang Effect. Catalysts 2020, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, G.; Kosinski, K.; Grela, K. Towards “cleaner” olefin metathesis: Tailoring the NHC ligand of second generation ruthenium catalysts to afford auxiliary traits. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4474–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowerski, K.; Wierzbicka, C.; Szczepaniak, G.; Gulajski, L.; Bieniek, M.; Grela, K. Easily removable olefin metathesis catalysts. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 3264–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, G.; Piątkowski, J.; Nogaś, W.; Lorandi, F.; Yerneni, S.S.; Fantin, M.; Ruszczyńska, A.; Enciso, A.E.; Bulska, E.; Grela, K.; et al. An isocyanide ligand for the rapid quenching and efficient removal of copper residues after Cu/TEMPO-catalyzed aerobic alcohol oxidation and atom transfer radical polymerization. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4251–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szczepaniak, G.; Nogaś, W.; Piątkowski, J.; Ruszczyńska, A.; Bulska, E.; Grela, K. Semiheterogeneous Purification Protocol for the Removal of Ruthenium Impurities from Olefin Metathesis Reaction Products Using an Isocyanide Scavenger. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, G.; Ruszczyńska, A.; Kosiński, K.; Bulska, E.; Grela, K. Highly efficient and time economical purification of olefin metathesis products from metal residues using an isocyanide scavenger. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytniczuk, A.; Leszczyńska, A.; Kajetanowicz, A.; Grela, K. Preparation of Musk-Smelling Macrocyclic Lactones from Biomass: Looking for the Optimal Substrate Combination. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 3157–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, D.J.; Muirhead, G.J.; Harness, J.A. Pharmacokinetics of sildenafil after single oral doses in healthy male subjects: Absolute bioavailability, food effects and dose proportionality. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 53, 5S–12S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patrzałek, M.; Zasada, A.; Kajetanowicz, A.; Grela, K. Tandem Olefin Metathesis/α-Ketohydroxylation Revisited. Catalysts 2021, 11, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11060719
Patrzałek M, Zasada A, Kajetanowicz A, Grela K. Tandem Olefin Metathesis/α-Ketohydroxylation Revisited. Catalysts. 2021; 11(6):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11060719
Chicago/Turabian StylePatrzałek, Michał, Aleksandra Zasada, Anna Kajetanowicz, and Karol Grela. 2021. "Tandem Olefin Metathesis/α-Ketohydroxylation Revisited" Catalysts 11, no. 6: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11060719
APA StylePatrzałek, M., Zasada, A., Kajetanowicz, A., & Grela, K. (2021). Tandem Olefin Metathesis/α-Ketohydroxylation Revisited. Catalysts, 11(6), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11060719