Shape Effects of Ceria Nanoparticles on the Water‒Gas Shift Performance of CuOx/CeO2 Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphological Characterization (TEM)
2.2. Structural and Textural Characterization (XRD/BET)
2.3. Electronic Properties (UV-Vis)
2.4. Redox Properties (H2-TPR)
2.5. Surface Analysis (XPS)
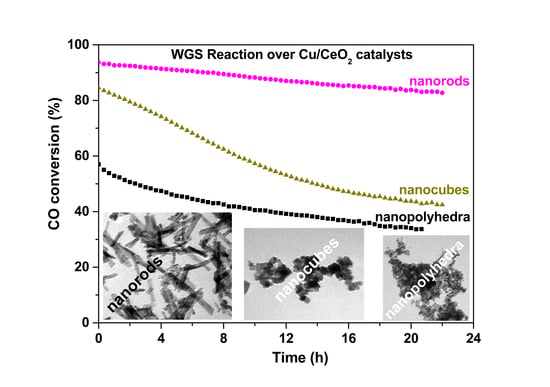
2.6. Water–Gas Shift Reaction
- CO adsorption on the Cu+ active sites;
- Oxidation of CO from surface oxygen towards the formation of CO2 and oxygen vacancy;
- Dissociation of H2O on the oxygen vacancy and production of H2;
- Re-oxidation of the support from H2O.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Materials Synthesis
3.3. Materials Characterization
3.4. Catalytic Evaluation Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebrahimi, P.; Kumar, A.; Khraisheh, M. A review of recent advances in water-gas shift catalysis for hydrogen production. Emergent Mater. 2020, 3, 881–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.M.; Peña, M.A.; Fierro, J.L.G. Hydrogen production reactions from carbon feedstocks: Fossil fuels and biomass. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3952–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.; Shabani, B. Re-envisioning the role of hydrogen in a sustainable energy economy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 1184–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.E.; Madeira, L.M.; Wu, Y.-J.; Faria, R. Sorption Enhanced Reaction Processes; World Scientific Publishing Europe Ltd.: 57 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London, UK, 2018; ISBN 9781786343567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.B.; Chand, R.; Upadhyay, S.N.; Mishra, P.K. Performance of water gas shift reaction catalysts: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Ma, Z. Water-gas shift on gold catalysts: Catalyst systems and fundamental studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 15260–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Xue, D. Size-dependent oxygen storage ability of nano-sized ceria. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 14414–14419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montini, T.; Melchionna, M.; Monai, M.; Fornasiero, P. Fundamentals and catalytic applications of CeO2-based materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5987–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monte, M.; Munuera, G.; Costa, D.; Conesa, J.C.; Martínez-Arias, A. Near-ambient XPS characterization of interfacial copper species in ceria-supported copper catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 29995–30004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayle, T.X.T.; Caddeo, F.; Zhang, X.; Sakthivel, T.; Das, S.; Seal, S.; Ptasinska, S.; Sayle, D.C. Structure-activity map of ceria nanoparticles, nanocubes, and mesoporous architectures. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 7287–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabilskiy, M.; Djinović, P.; Tchernychova, E.; Pintar, A. N2O decomposition over CuO/CeO2 catalyst: New insights into reaction mechanism and inhibiting action of H2O and NO by operando techniques. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 197, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabilskiy, M.; Djinović, P.; Tchernychova, E.; Tkachenko, O.P.; Kustov, L.M.; Pintar, A. Nanoshaped CuO/CeO2 materials: Effect of the exposed ceria surfaces on catalytic activity in N2O decomposition reaction. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5357–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, R.K.; Shukla, A.; Yadav, A.; Sivakumar Konathala, L.N.; Bal, R. Effect of metal-support interaction on activity and stability of Ni-CeO2 catalyst for partial oxidation of methane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 202, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Howe, J.; Meyer, H.M., III; Overbury, S.H. Probing defect sites on CeO2 nanocrystals with well-defined surface planes by Raman spectroscopy and O2 adsorption. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16595–16606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, A.; Ning, J.; Shen, W. Electronic and geometric structure of the copper-ceria interface on Cu/CeO2 catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnello, M.; Doan-Nguyen, V.V.T.; Gordon, T.R.; Diaz, R.E.; Stach, E.A.; Gorte, R.J.; Fornasiero, P.; Murray, C.B. Control of metal nanocrystal size reveals metal-support interface role for ceria catalysts. Science 2013, 341, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, N.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z. Peculiar surface-interface properties of nanocrystalline ceria-cobalt oxides with enhanced oxygen storage capacity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 22659–22664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Papista, E.; Marnellos, G.E.; Tavares, P.B.; Agostinho Moreira, J.; Romaguera-Barcelay, Y.; Figueiredo, J.L. Effect of preparation method on the solid state properties and the deN2O performance of CuO–CeO2 oxides. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 3714–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M. The role of Copper–Ceria interactions in catalysis science: Recent theoretical and experimental advances. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 198, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Lykaki, M. Recent advances on the rational design of non-precious metal oxide catalysts exemplified by CuOx/CeO2 binary system: Implications of size, shape and electronic effects on intrinsic reactivity and metal-support interactions. Catalysts 2020, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.-C.; Wang, J.-S.; Qiu, Y.-Q.; Liu, C.-G. Ensemble effect of heterogeneous Cu atoms promoting water-gas shift reaction. Mol. Catal. 2020, 493, 111046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, S.; Fazlollahi, F.; Najari, S.; Iranshahi, D.; Klemeš, J.J.; Baxter, L.L. Hydrogen production: Perspectives, separation with special emphasis on kinetics of WGS reaction: A state-of-the-art review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 49, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Miao, S.; Li, Y.; Kuld, S.; Sehested, J.; Liu, J.; Aoki, T.; Hong, S.; et al. Structure of the catalytically active copper–ceria interfacial perimeter. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudiyanselage, K.; Senanayake, S.D.; Feria, L.; Kundu, S.; Baber, A.E.; Graciani, J.; Vidal, A.B.; Agnoli, S.; Evans, J.; Chang, R.; et al. Importance of the metal-oxide interface in catalysis: In situ studies of the water-gas shift reaction by ambient-pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5101–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, R.; Raitano, J.; Yi, N.; Zhang, L.; Chan, S.-W.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Structure sensitivity of the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction on Cu-CeO2 catalysts. Catal. Today 2012, 180, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, W. Atomically dispersed copper species on ceria for the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykaki, M.; Pachatouridou, E.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Iliopoulou, E.; Andriopoulou, C.; Kallithrakas-Kontos, N.; Boghosian, S.; Konsolakis, M. Ceria nanoparticles shape effects on the structural defects and surface chemistry: Implications in CO oxidation by Cu/CeO2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 230, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Peng, F.; Li, J.; Liang, X.; Chen, B. Morphology-dependent properties of Cu/CeO2 catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Catalysts 2017, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, S.Y.; Xu, W.Q.; Johnston-Peck, A.C.; Zhao, F.Z.; Liu, Z.Y.; Luo, S.; Senanayake, S.D.; Martínez-Arias, A.; Liu, W.J.; Rodriguez, J.A. Morphological effects of the nanostructured ceria support on the activity and stability of CuO/CeO2 catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 17183–17195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Zhu, X.; Hensen, E.J.M.; Mojet, B.L.; Lefferts, L. Surface-dependence of defect chemistry of nanostructured ceria. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 12423–12433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.-S.; Song, R.; Cao, T.; Luo, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, W.-X.; Huang, W. The most active Cu facet for low-temperature water gas shift reaction. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Lykaki, M. Facet-dependent reactivity of ceria nanoparticles exemplified by CeO2-based transition metal catalysts: A critical review. Catalysts 2021, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwar, A.; Md Noor, A.; Nawi, M. Textural characteristics of activated carbons prepared from oil palm shells activated with ZnCl2 and pyrolysis under nitrogen and carbon dioxide. J. Phys. Sci. 2008, 19, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Tao, Q.; Gao, H.; Li, J.; Jia, D.; Yang, M. Preparation and catalytic performance of mesoporous ceria-base composites CuO/CeO2, Fe2O3/CeO2 and La2O3/CeO2. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 24, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anushree; Kumar, S.; Sharma, C. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic wet air oxidation property of mesoporous Ce1-xFexO2 mixed oxides. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 155, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmandjou, M.; Zarinkamar, M. Synthesis of nano-sized ceria (CeO2) particles via a cerium hydroxy carbonate precursor and the effect of reaction temperature on particle morphology. J. Ultrafine Grained Nanostruct. Mater. 2015, 48, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Peng, F.; Chen, B.; Mei, D.; Li, J. A combined experimental and computational study of water-gas shift reaction over rod-shaped Ce0.75M0.25O2 (M = Ti, Zr, and Mn) supported Cu catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 30086–30097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Pérez, L.; Ramos-Fernández, E.V.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A. Effect of the CeO2 synthesis method on the behaviour of Pt/CeO2 catalysis for the water-gas shift reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 21837–21846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykaki, M.; Pachatouridou, E.; Iliopoulou, E.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Konsolakis, M. Impact of the synthesis parameters on the solid state properties and the CO oxidation performance of ceria nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 6160–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Duan, A.; Jiang, G.; Yang, Q. The highly active catalysts of nanometric CeO2-supported cobalt oxides for soot combustion. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboukaïs, A.; Skaf, M.; Hany, S.; Cousin, R.; Aouad, S.; Labaki, M.; Abi-Aad, E. A comparative study of Cu, Ag and Au doped CeO2 in the total oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 177, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Yan, S.; Liu, M.; Zhou, R. High performance CuO-CeO2 catalysts for selective oxidation of CO in excess hydrogen: Effect of hydrothermal preparation conditions. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2009, 18, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, R. A new insight into the morphology effect of ceria on CuO/CeO2 catalysts for CO selective oxidation in hydrogen-rich gas. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3862–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, R.S.; Deevi, S. CO oxidation activity of Cu-CeO2 nano-composite catalysts prepared by laser vaporization and controlled condensation. J. Nanopart. Res. 2006, 8, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampa, S.; Wangkawee, K.; Tantisriyanurak, S.; Changpradit, J.; Jamieson, A.M.; Chaisuwan, T.; Luengnaruemitchai, A.; Wongkasemjit, S. High performance and stability of copper loading on mesoporous ceria catalyst for preferential oxidation of CO in presence of excess of hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 42, 5537–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Konsolakis, M.; Marnellos, G.E.N.; Asad, M.F.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Tavares, P.B.; Pereira, M.F.R.; De Melo Órfão, J.J.; Figueiredo, J.L. Ethyl acetate abatement on copper catalysts supported on ceria doped with rare earth oxides. Molecules 2016, 21, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Hart, B.R.; Polack, R.; Kobe, B.A.; Smart, R.S.C. Analysis of mineral surface chemistry in flotation separation using imaging XPS. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Dai, W.-L. Support morphology and crystal plane effect of Cu/CeO2 nanomaterial on the physicochemical and catalytic properties for carbonate hydrogenation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7752–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, X.; Lin, B.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, L. Sacrificial adsorbate strategy achieved strong metal-support interaction of stable Cu nanocatalysts. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.-W.; Na, H.-S.; Shim, J.-O.; Jang, W.-J.; Roh, H.-S.; Jung, U.H.; Yoon, W.L. Hydrogen production from low temperature WGS reaction on co-precipitated Cu-CeO2 catalysts: An optimization of Cu loading. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 9135–9142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, Z.; Xu, W.; Yao, S.; Si, R.; Johnston-Peck, A.C.; Martínez-Arias, A.; Hanson, J.C.; Senanayake, S.D.; Rodriguez, J.A. Pulse studies to decipher the role of surface morphology in CuO/CeO2 nanocatalysts for the water gas shift reaction. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Lykaki, M.; Stefa, S.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Varvoutis, G.; Papista, E.; Marnellos, G.E. CO2 hydrogenation over nanoceria-supported transition metal catalysts: Role of ceria morphology (nanorods versus nanocubes) and active phase nature (Co versus Cu). Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saitzek, S.; Blach, J.-F.; Villain, S.; Gavarri, J.-R. Nanostructured ceria: A comparative study from X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy and BET specific surface measurements. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2008, 205, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, M.A.; Rocha, C.; Tosti, S.; Mendes, A.; Madeira, L.M. COx free hydrogen production through water-gas shift reaction in different hybrid multifunctional reactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, M.; Soria, M.A.; Madeira, L.M. Hydrogen and/or syngas production through combined dry and steam reforming of biogas in a membrane reactor: A thermodynamic study. Renew. Energy 2020, 157, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample | N2 Adsorption-Desorption | XRD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) | Average Crystallite Diameter, DXRD (nm) 1 | ||
| CeO2 | CuO | ||||
| CeO2 (C) | 40 | 0.12 | 12.5 | 19.2 | - |
| CeO2 (R) | 92 | 0.71 | 30.9 | 13.2 | - |
| CeO2 (P) | 109 | 1.04 | 38.1 | 9.5 | - |
| Cu/CeO2 (C) | 34 | 0.29 | 33.4 | 19.2 | 52 |
| Cu/CeO2 (R) | 75 | 0.40 | 21.2 | 11.6 | 43 |
| Cu/CeO2 (P) | 91 | 0.29 | 12.7 | 9.6 | 31 |
| Sample | H2 Consumption (mmol H2/g) 1 | TPR Peak Temperature (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 (C) | 0.41 | 589 | 809 |
| CeO2 (R) | 0.59 | 545 | 788 |
| CeO2 (P) | 0.48 | 555 | 804 |
| Cu/CeO2 (C) | 1.50 | 194 | 228 |
| Cu/CeO2 (R) | 1.80 | 181 | 217 |
| Cu/CeO2 (P) | 1.65 | 176 | 201 |
| Sample | OI/OIΙ | Ce3+ (%) | Cu+ (%) | Cu/Ce Atomic Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 (C) | 1.99 | 23.3 | - | |
| CeO2 (P) | 2.04 | 25.3 | - | |
| CeO2 (R) | 2.13 | 24.3 | - | |
| Cu/CeO2 (C) | 1.89 | 21.9 | 11.8 | 0.16 |
| Cu/CeO2 (P) | 1.96 | 23.3 | 13.0 | 0.35 |
| Cu/CeO2 (R) | 2.02 | 23.9 | 16.1 | 0.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lykaki, M.; Stefa, S.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Soria, M.A.; Madeira, L.M.; Konsolakis, M. Shape Effects of Ceria Nanoparticles on the Water‒Gas Shift Performance of CuOx/CeO2 Catalysts. Catalysts 2021, 11, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11060753
Lykaki M, Stefa S, Carabineiro SAC, Soria MA, Madeira LM, Konsolakis M. Shape Effects of Ceria Nanoparticles on the Water‒Gas Shift Performance of CuOx/CeO2 Catalysts. Catalysts. 2021; 11(6):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11060753
Chicago/Turabian StyleLykaki, Maria, Sofia Stefa, Sónia A. C. Carabineiro, Miguel A. Soria, Luís M. Madeira, and Michalis Konsolakis. 2021. "Shape Effects of Ceria Nanoparticles on the Water‒Gas Shift Performance of CuOx/CeO2 Catalysts" Catalysts 11, no. 6: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11060753
APA StyleLykaki, M., Stefa, S., Carabineiro, S. A. C., Soria, M. A., Madeira, L. M., & Konsolakis, M. (2021). Shape Effects of Ceria Nanoparticles on the Water‒Gas Shift Performance of CuOx/CeO2 Catalysts. Catalysts, 11(6), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11060753