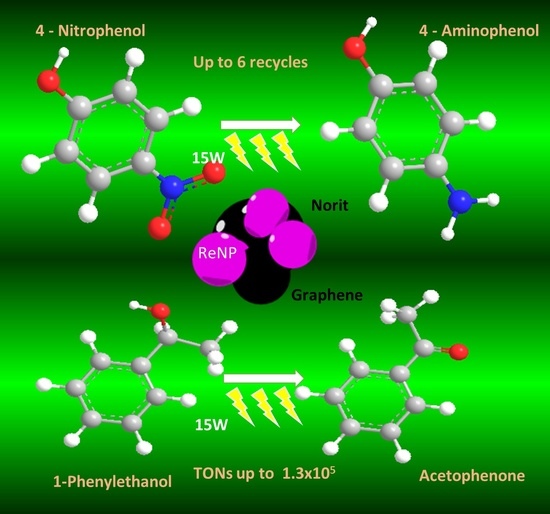
C-Heterogenized Re Nanoparticles as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Re/C and Re/G Catalysts
2.2. Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol Using Re/C and Re/G Catalysts
2.3. Mechanistic Considerations
2.4. Phenylethanol Oxidation Using Re/C and Re/G Catalysts
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol
3.3. Microwave-Assisted Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- De la Hoz, A.; Diaz-Ortiz, A.; Moreno, A. Microwaves in organic synthesis. Thermal and non-thermal microwave effects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, H.J.; Vallance, S.R.; Kennedy, J.L.; Tapia-Ruiz, N.; Carassiti, L.; Harrison, A.; Whittaker, A.G.; Drysdale, T.D.; Kingman, S.W.; Gregory, D.H. Modern microwave methods in solid-state inorganic materials chemistry: From fundamentals to manufacturing. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1170–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawande, M.B.; Shelke, S.N.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Microwave-Assisted Chemistry: Synthetic Applications for Rapid Assembly of Nanomaterials and Organics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrétien, S.; Buratto, S.K.; Metiu, H. Catalysis by very small Au clusters. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2007, 11, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Wang, A.; Qiao, B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T. Single-Atom Catalysts: A New Frontier in Heterogeneous Catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1740–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkov, G.Y.; Kozinkin, A.V.; Koksharov, Y.A.; Fionov, A.S.; Taratanov, N.A.; Vlasenko, V.G.; Pirog, I.V.; Shishilov, O.N.; Popkov, O.V. Synthesis and properties of rhenium–polyethylene nanocomposite. Compos. Part B 2012, 43, 3192–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaj, S.; Sakthikumar, K.; Elangovan, A.; Ravi, G.; Karthik, T.; Kundu, S. Ultra-small rhenium nanoparticles immobilized on DNA scaffolds: An excellent material for surface enhanced Raman scattering and catalysis studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 483, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzanska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Wolany, W.; Benke, G.; Rdzawsk, Z. The new MWCNTs–rhenium nanocomposite. Phys. Status Solidi B 2014, 251, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul-Gheit, A.K.; Abdel-Hamid, S.M.; Aboul-Fotouh, S.M.; Aboul-Gheit, N.A.K. Cyclohexene hydroconversion using monometallic and bimetallic catalysts supported on γ-Alumina. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2006, 53, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Pang, M.; Su, D.; Williams, C.T.; Liang, C. Hydrogenation of succinic acid over supported rhenium catalysts prepared by the microwave-assisted thermolytic method. Catal. Commun. 2012, 24, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Shao, Z.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Liang, C. Hydrogenation of succinic acid over supported rhenium catalysts prepared by the microwave-assisted thermolytic method. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, M.S.A.; Uddin, M.N.; Islam, M.M. Synthesis of graphene. Int. Nano Lett. 2016, 6, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkateshaiah, A.; Silvestri, D.; Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Wacławek, S.; Padil, V.V.T.; Černík, M.; Varma, R.S. Gum Kondagoagu/Reduced Graphene Oxide Framed Platinum Nanoparticles and Their Catalytic Role. Molecules 2019, 24, 3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rónavári, A.; Igaz, N.; Adamecz, D.I.; Szerencsés, B.; Molnar, C.; Kónya, Z.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kiricsi, M. Green Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: Biological Synthesis Approaches and Potentials for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Hou, C. Preparation of Magnetic CuFe2O4@Ag@ZIF-8 Nanocomposites with Highly Catalytic Activity Based on Cellulose Nanocrystals. Molecules 2020, 25, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shultz, L.R.; McCullough, B.; Newsome, W.J.; Ali, H.; Shaw, T.E.; Davis, K.O.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Baudelet, M.; Jurca, T. A Combined Mechanochemical and Calcination Route to Mixed Cobalt Oxides for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrophenols. Molecules 2020, 25, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hervés, P.; Pérez-Lorenzo, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Dzubiella, J.; Lu, Y.; Ballauff, M. Catalysis by metallic nanoparticles in aqueous solution: Model reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5577–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Dhenadhayalan, N.; Lin, K.C.; Liu, S.B. Highly stable ruthenium nanoparticles on 3D mesoporous carbon: An excellent opportunity for reduction reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23448–23457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, L.C.; Sun, H.; Ni, J.; Cao, Y.; He, H.Y.; Fan, K.N. Efficient and selective room-temperature gold-catalyzed reduction of nitro compounds with CO and H2O as the hydrogen source. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9538–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.M.; Sasaki, T.; Bhanage, B.M. Immobilized iron metal-containing ionic liquid-catalyzed chemoselective transfer hydrogenation of nitroarenes into anilines. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksu, H.; Ho, S.F.; Metin, C.; Korkmaz, K.; Garcia, A.M.; ltekin, M.S.; Sun, S. Tandem dehydrogenation of ammonia borane and hydrogenation of nitro/nitrile compounds catalyzed by graphene supported NiPd alloy nanoparticles. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Fujii, K.; Nabeshima, S.; Ikeda, M.S.; Konakahara, T. Highly selective conversion of nitrobenzenes using a simple reducing system combined with a trivalent indium salt and a hydrosilane. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3173–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Garlyyev, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Determining the mechanism of solution metallic nanocatalysis with solid and hollow nanoparticles: Homogeneous or heterogeneous. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 21886–21893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonels, N.C.; Meijboom, R. Preparation of Well-Defined Dendrimer Encapsulated Ruthenium Nanoparticles and Their Evaluation in the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol According to the Langmuir–Hinshelwood Approach. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13433–13442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohantorabi, M.; Gholami, M.R. AgPt nanoparticles supported on magnetic graphene oxide nanosheets for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol: Studies of kinetics and mechanism. App. Org. Chem. 2017, 31, e3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wunder, S.; Lu, Y.; Ballauff, M.; Fenger, R.; Rademann, K.; Jaquet, B.; Zaccone, A. Kinetic analysis of the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by metallic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 18618–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiBretto, N.J.; Xu, Y.C.; Quigley, A. Olefin oligomerization by main group Ga3+ and Zn2+ single site catalysts on SiO2. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Smolenski, P.; Kuznetsov, M.L.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Oxorhenium Complexes Bearing the Water-Soluble Tris(pyrazol-1-yl)methanesulfonate, 1,3,5-Triaza-7-phosphaadamantane, or Related Ligands, as Catalysts for Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation of Ketones. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alegria, E.C.B.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Kirillova, M.V.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Baeyer-Villiger oxidation of ketones catalyzed by rhenium complexes bearing N- or O-ligands. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 443–444, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faísca Phillips, A.M.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Kopylovich, M.N. Recent advances in cascade reactions initiated by alcohol oxidation. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shul’pin, G.B. C–H functionalization: Thoroughly tuning ligands at a metal ion, a chemist can greatly enhance catalyst’s activity and selectivity. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 12794–12818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Tris(pyrazol-1yl) methane metal complexes for catalytic mild oxidative functionalizations of alkanes, alkenes and ketones. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 265, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.M.D.R.S. C-scorpionate complexes: Ever young catalytic tools. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 396, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegria, E.C.B.; Kirillova, M.V.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Pyrazole and Tris(pyrazolyl)methane Rhenium Complexes as Catalysts for Ethane and Cyclohexane Oxidations. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 357, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, M.L.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Radical Formation in the [MeReO3]-Catalyzed Aqueous Peroxidative Oxidation of Alkanes: A Theoretical Mechanistic Study. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirillov, A.M.; Haukka, M.; Silva, M.F.C.G.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Preparation and Crystal Structures of Benzoylhydrazido- and-diazenidorhenium Complexes with N,O-Ligands and Their Catalytic Activity Towards Peroxidative Oxidation of Cycloalkanes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 11, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.M.; Haukka, M.; Kirillova, M.V.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Single-Pot Ethane Carboxylation Catalyzed by New Oxorhenium(V) Complexes with N,O-Ligands. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2005, 347, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsi, E.P.; Bryalov, K.P. Chemo- and stereoselective CH oxidations and epoxidations/cis-dihydroxylations with H2O2, catalyzed by non-heme iron and manganese complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 1418–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Thanasekaran, P.; Lin, K.-C.; Liu, S.-B. Well-dispersed rhenium nanoparticles on three-dimensional carbon nanostructures: Efficient catalysts for the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2017, 506, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Huh, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, B.J.; Kim, B.S.; Park, J.H. Structure and size distribution of Os, Re, and Ru nanoparticles produced by thermal decomposition of Os3(CO)12, [Re2(CO)10], and Ru3(CO)12. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2003, 42, 835–837. [Google Scholar]
- Iben Ayad, A.; Luart, D.; Ould Dris, A.; Guénin, E. Kinetic Analysis of 4-Nitrophenol Reduction by “Water-Soluble” Palladium Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, M.M.A.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Ferraria, A.M.; Botelho do Rego, A.M.; Correia, L.; Saraiva, M.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Ultrasound and radiation-induced catalytic oxidation of 1-phenylethanol to acetophenone with iron-containing particulate catalysts. Molecules 2020, 25, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pakrieva, E.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Kolobova, E.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; German, D.; Pichugina, D.; Jiang, C.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Bogdanchikova, N.; et al. Supported Gold Nanoparticles as Catalysts in Peroxidative and Aerobic Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol under Mild Conditions. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Buijnsters, J.G.; Avalos-Borja, M.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S. Solvent-free oxidation of 1-phenylethanol catalysed by gold nanoparticles supported on carbon powder materials. Catal. Today 2020, 357, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.C.A.; Bernardo, J.R.; Florindo, P.R.; Fernandes, A.C. Efficient and selective oxidation of alcohols catalyzed by oxo-rhenium complexes. Catal. Commun. 2013, 40, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitri, R.; Teresa, G.; Corrado, C.; Erica, F. Iron-Catalyzed Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol and Glycerol With Hydrogen Peroxide in Water Medium: Effect of the Nitrogen Ligand on Catalytic Activity and Selectivity. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon Based Materials Surface Data. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Figueiredo, J.L. Production Process of Ketones from Secondary Alcohols. WO 2017/116253, PCT/PT2016/000019, PT109062, 29 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Highly efficient and reusable CNT supported iron(II) catalyst for microwave assisted alcohol oxidation. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 6816–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Buijnsters, J.G.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Heterogenised C-scorpionate iron(II) complex on nanostructured carbon materials as catalysts for microwave-assisted oxidation reactions. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payra, S.; Challagulla, S.; Chakraborty, C.; Roy, S. A hydrogen evolution reaction induced unprecedentedly rapid electrocatalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol over ZIF-67 compare to ZIF-8. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 853, 113545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWAP (UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme). The United Nations World Water Development Report 2019: 34 Leaving No One Behind; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, S.; Xu, S.; Yuan, Y.; Xiong, L. Kinetics and mechanisms of p-nitrophenol biodegradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa HS-D38. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Health Effects Assessment for Nitrophenols; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1987.
- Wunder, F.; Lu, Y.; Albrecht, M. Catalytic activity of facetted gold nanoparticles studied by a model reaction: Evidence for substrate-induced surface restructuring. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, F.; Hikmah, U.; Stavilab, E.; Aimona, A.H. Microwave-assisted reduction method under nitrogen at-mosphere for synthesis and electrical conductivity improvement of reduced graphene oxide (rGO). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 52391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Entry | Catalyst | Cat. Amount b | T | kapp × 103 | [4NP] × 103 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (µmol of Re) | (°C) | (s−1) | (M) | ||
| 1 | Re/C | 0.2 | 35 | 1.34 | 3.36 |
| 2 | 0.02 | 1.47 | 3.10 | ||
| 3 | 0.2 | 50 | 1.37 | 3.30 | |
| 4 | 0.02 | 1.58 | 2.91 | ||
| 5 | Re/G | 0.2 | 35 | 1.36 | 3.32 |
| 6 | 0.02 | 1.53 | 2.99 | ||
| 7 | 0.2 | 50 | 1.45 | 3.14 | |
| 8 | 0.02 | 1.62 | 2.84 |
| Entry | Cat. Amount | Temp. | Time | Yield b | TON c | TOF d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μmol of Re) | (°C) | (min) | (%) | (h−1) | ||
| 1 | 0 | 50 | 60 | 0.9 | - | - |
| 2 | 2 | 50 | 60 | 44.8 | 1.12 × 103 | 1.12 × 103 |
| 3 | 10 | 50 | 5 | 9.8 | 49 | 588 |
| 4 | 10 | 50 | 10 | 11.3 | 57 | 339 |
| 5 | 10 | 50 | 15 | 12. 9 | 65 | 258 |
| 6 | 10 | 50 | 30 | 72.5 | 363 | 725 |
| 7 | 20 | 35 | 30 | 10.7 | 27 | 54 |
| 8 | 20 | 50 | 30 | 65.0 | 163 | 325 |
| 9 | 20 | 50 | 60 | 98.8 | 247 | 247 |
| 10 | 20 | 80 | 30 | 15.2 | 38 | 76 |
| 11 | 20 | 80 | 60 | 57.2 | 143 | 143 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Cat. Amount | Yield b | TON c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μmol of Re) | (%) | or TOF (h−1) d | ||
| 1 | Re/G | 0.02 | 54.3 | 1.36 × 105 |
| 2 | 2 | 30.6 | 765 | |
| 3 | 20 | 20.8 | 52 | |
| 4 | Re/C | 0.02 | 43.7 | 1.09 × 105 |
| 5 | 2 | 22.4 | 560 | |
| 6 | 20 | 18.1 | 45 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Yield b (%) | TON c or TOF (h−1) d |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Re/G | 30.6 | 765 |
| 2 | 6.3 | 158 | |
| 3 | 0.5 | 13 | |
| 4 | Re/C | 22.4 | 560 |
| 5 | 2.6 | 65 | |
| 6 | 0.6 | 15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Santos, B.M.; Faustino, R.F.C.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S. C-Heterogenized Re Nanoparticles as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol. Catalysts 2022, 12, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12030285
Ribeiro APC, Santos BM, Faustino RFC, Pombeiro AJL, Martins LMDRS. C-Heterogenized Re Nanoparticles as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol. Catalysts. 2022; 12(3):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12030285
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Ana P. C., Beatriz M. Santos, Rute F. C. Faustino, Armando J. L. Pombeiro, and Luísa M. D. R. S. Martins. 2022. "C-Heterogenized Re Nanoparticles as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol" Catalysts 12, no. 3: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12030285
APA StyleRibeiro, A. P. C., Santos, B. M., Faustino, R. F. C., Pombeiro, A. J. L., & Martins, L. M. D. R. S. (2022). C-Heterogenized Re Nanoparticles as Effective Catalysts for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol. Catalysts, 12(3), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12030285