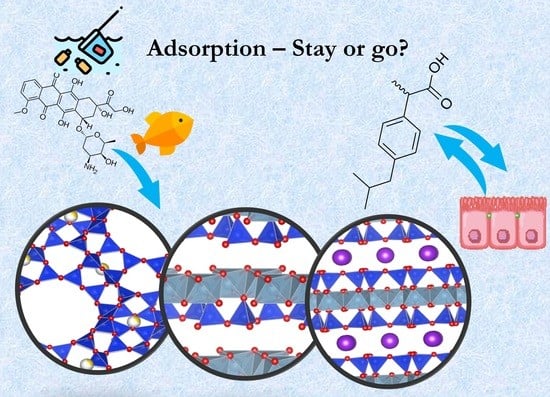
Environmental and Pharmacokinetic Aspects of Zeolite/Pharmaceuticals Systems—Two Facets of Adsorption Ability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Low Silica Zeolites: Si/Al ≤ 2
- Intermediate Silica Zeolites: 2 < Si/Al ≤ 5
- High Silica Zeolites: Si/Al > 5 [9].
- Small-pore zeolites (8-member rings) with pore diameter of 0.3–0.45 nm
- Medium-pore zeolites (10-member rings) with pore diameter of 0.45–0.6 nm
- Large-pore zeolites (12-member rings) with pore diameter of 0.6–0.8 nm
2. Zeolites in the Removal of Pharmaceuticals from the Environment
2.1. Where to Start?
2.2. Examples of Effective Removal of Pharmaceuticals with Zeolites
2.3. Use of Theoretical Calculation for Predicting Interactions
3. Zeolite-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Application
3.1. Zeolites for Dental Applications
3.2. Zeolites as Drug Carriers in Pharmacotherapy
3.2.1. Zeolites as Carriers of Anti-inflammatory Drugs
3.2.2. Zeolites as Carriers of Anticancer Drugs
4. Conclusions
- -
- main interactions in the pollutant-zeolite system assisted by spectroscopic methods, especially in post-adsorption studies;
- -
- targeted interactions lead to a comprehensive understanding of the adsorption mechanism. Once we know the mechanism in detail, we can elucidate a number of target pollutants. If a designed zeolite adsorbent shows substantial adsorption capacity for one species, can it be applied for the other or their occurring mixtures?
- -
- sometimes zeolites are designated as costly materials, and novel routes for synthesis, from waste materials, are beneficial;
- -
- what to do with the spent adsorbent, does this impose a significant shortcoming of mainly physical removal techniques? Some innovative solutions are offered, mostly in the pyrolysis of the spent adsorbents and subsequent employment as electrode materials;
- -
- environmentally relevant concentrations and/or flow techniques may be employed in the second step of the adsorption test aimed at pharmaceuticals removal. This requires HPLC/UPLC techniques, preferably with sensitive detection such as mass spectrometry. For volatile pharmaceuticals, GC/MS methods are also available.
- -
- a focus needs to be shifted to real effluents, with a range of concurrent adsorbing ions, mostly metals, and organic matter;
- -
- test whether the adsorption, as a removal technique, leaves the environment more toxic than the pollutant itself;
- -
- apply a range of quantum mechanical calculations to guide future adsorbent design as this state-of-the-art calculation can point out exactly what to expect from your adsorption system and enable future predictions.
- -
- first, there is a need to study and ensure the lowest possible level of toxicity;
- -
- expand the therapeutic range of DDS, improving more benefits and less side effects of pharmacological active compounds;
- -
- raise the specificity of targeted sensitive sites of DDS action;
- -
- work to achieve appropriate kinetics of release of pharmacologically active components. Parallel development of reliable, sensitive and specific analytical methods for following such a low concentration level of drugs in situ are more than desired.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramesh, K.; Reddy, D.D. Zeolites and Their Potential Uses in Agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2011, 113, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, E.; Salvi, L.; Paoli, F.; Fucile, M.; Masciandaro, G.; Manzi, D.; Massini, C.M.; Mattii, G.B. Application of Zeolites in Agriculture and Other Potential Uses: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.A.; Flanigen, E.M.; Jansen, J.C.; van Bekkum, H. Introduction to Zeolite Science and Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Coombs, D.S.; Alberti, A.; Armbruster, T.; Artioli, G.; Colella, C.; Galli, E.; Grice, J.D.; Liebau, F.; Mandarino, J.A.; Minato, H.; et al. Recommended Nomenclature for Zeolite Minerals: Report of the Subcommittee on Zeolites of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names. Can. Mineral. 1997, 35, 1571–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Derbe, T.; Temesgen, S.; Bitew, M.A. Short Review on Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Zeolites. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6637898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M. Natural vs. Synthetic Zeolites. Crystals 2020, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.K.; Zarrintaj, P.; Hosseiniamoli, H.; Mashhadzadeh, A.H.; Saeb, M.R.; Ramsey, J.D.; Ganjali, R.M.; Mozafari, M. Zeolites for theranostic applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5992–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrer, R.M. Porous crystals: A perspective. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986, 58, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianfar, E. Zeolites: Properties, Applications, Modification and Selectivity. In Zeolites: Advances in Research and Application; Mahler, A., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bacakova, L.; Vandrovcova, M.; Kopova, I.; Jirka, I. Applications of zeolites in biotechnology and medicine—A review. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Bein, T. Mesoporosity—A new dimension for zeolites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Database of Zeolite Structures. Available online: http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/ (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Coombs, D.S.; Alberti, A.; Armbruster, T.; Artioli, G.; Colella, C.; Galli, E.; Grice, J.D.; Liebau, F.; Mandarino, J.A.; Minato, H.; et al. Recommended nomenclature for zeolite minerals: Report of the subcommittee on zeolites of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names. Mineral. Mag. 1998, 62, 533–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.J. Properties and applications of zeolites. Sci. Prog. 2010, 93, 223–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, J. Emerging applications of zeolites in catalysis, separation and host–guest assembly. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1156–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, J.; Corma, A. Applications of Zeolites to C1 Chemistry: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Opportunities. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serati-Nouri, H.; Jafari, A.; Roshangar, L.; Dadashpour, M.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Zarghami, N. Biomedical applications of zeolite-based materials: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, J. Applications of Zeolites in Sustainable Chemistry. Chem 2017, 3, 928–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasiljević, B.N.; Obradović, M.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D.; Milojević-Rakić, M.; Jovanović, Z.; Gavrilov, N.; Holclajtner-Antunović, I. In Situ synthesis of potassium tungstophosphate supported on BEA zeolite and perspective application for pesticide removal. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janićijević, D.; Uskoković-Marković, S.; Ranković, D.; Milenković, M.; Jevremović, A.; Nedić Vasiljević, B.; Milojević-Rakić, M.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D. Double active BEA zeolite/silver tungstophosphates—Antimicrobial effects and pesticide removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevremović, A.; Vasiljević, B.N.; Popa, A.; Uskoković-Marković, A.; Ignjatović, L.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D.; Milojević-Rakić, M. The environmental impact of potassium tungstophosphate/ZSM-5 zeolite: Insight into catalysis and adsorption processes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 315, 110925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevremović, A.; Božinović, N.; Đorđević, D.; Marmakov, S.; Vasiljević, B.N.; Uskoković-Marković, S.; Bajuk-Bogdanovic, D.; Milojević-Rakić, M. Modulation of cytotoxicity by consecutive adsorption of tannic acid and pesticide on surfactant functionalized zeolites. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojević-Rakić, M.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D.; Vasiljević, B.N.; Rakić, A.; Škrivanj, S.; Ignjatović, L.; Dondur, V.; Mentus, S.; Ćirić-Marjanović, G. Polyaniline/FeZSM-5 composites—Synthesis, characterization and their high catalytic activity for the oxidative degradation of herbicide glyphosate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 267, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, F.R. How many life-years have new drugs saved? A three-way fixed-effects analysis of 66 diseases in 27 countries, 2000–2013. Int. Health 2019, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Giustina, S.V.D.; Llorca, M.; Barceló, D.; Schubert, S.; Berendonk, T.; Michael-Kordatou, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Martinez, J.L.; et al. Antibiotic residues in final effluents of European wastewater treatment plants and their impact on the aquatic environment. Environ. Int. 2020, 140, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalla, A.K.; Vannarath, A.S. Occurrence and environmental risks of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in urban wastewater in the southwest monsoon region of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, and the European Economic and Social Committee: European Union Strategic Approach to Pharmaceuticals in the Environment. Communication 2019, 128, 1–12. Available online: https://www.eumonitor.eu/9353000/1/j9vvik7m1c3gyxp/vkwpg8sb9wx8 (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Merlin, C. Reducing the Consumption of Antibiotics: Would That Be Enough to Slow Down the Dissemination of Resistances in the Downstream Environment? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kidd, K.A.; Paterson, M.J.; Rennie, M.D.; Podemski, C.L.; Findlay, D.L.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Liber, K. Direct and indirect responses of a freshwater food web to a potent synthetic oestrogen. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2014, 369, 20130578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heberer, T. Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment: A review of recent research data. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 131, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetan, S.K.; Collins, T.J. Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: A challenge to green chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2319–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Nielsen, S.N.; Lanzky, P.; Ingerslev, F.; Lützhøft, H.H.; Jørgensen, S. Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—A review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 357–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelic, A.; Gros, M.; Ginebreda, A.; Cespedes-Sánchez, R.; Ventura, F.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Occurrence, partition and removal of pharmaceuticals in sewage water and sludge during wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe Disposal of Medicines. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/ensuring-safe-use-medicine/safe-disposal-medicines (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Nikolaou, A.; Meric, S.; Fatta, D. Occurrence patterns of pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater environments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- der Beek, T.A.; Weber, F.-A.; Bergmann, A.; Hickmann, S.; Ebert, I.; Hein, A.; Küster, A. Pharmaceuticals in the environment-Global occurrences and perspectives. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberer, T. Tracking persistent pharmaceutical residues from municipal sewage to drinking water. J. Hydrol. 2002, 266, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanc, M.; Kosjek, T.; Petkovšek, M.; Dular, M.; Kompare, B.; Širok, B.; Blažeka, Ž.; Heath, E. Removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater by biological processes, hydrodynamic cavitation and UV treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.C. Occurrence, sources, and fate of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment and soil. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaseem, M.; Kumar, P.; John, R.M. An overview of waste management in pharmaceutical industry. Pharma Innov. 2017, 6 Pt C, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, M.R.; Leung, C.; Bonk, F.; Zhu, Y.; Edwards, L.; Arnold, R.G.; Sáez, A.E.; Klečka, G. Assessment of the effectiveness of secondary wastewater treatment technologies to remove trace chemicals of emerging concern. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baresel, C.; Cousins, A.P.; Hörsing, M.; Ek, M.; Ejhed, H.; Allard, A.-S.; Magnér, J.; Westling, K.; Wahlberg, C.; Fortkamp, U. Pharmaceutical Residues and Other Emerging Substances in the Effluent of Sewage Treatment Plants. IVL Svenska Miljöinstitutet. 2015. (B-Rapport). Available online: http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:ivl:diva-2969 (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Fukahori, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Ito, R.; Funamizu, N. pH-Dependent adsorption of sulfa drugs on high silica zeolite: Modeling and kinetic study. Desalination 2011, 275, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasioli, S.; Martucci, A.; Paul, G.; Gigli, L.; Cossi, M.; Johnston, C.T.; Marchese, L.; Braschi, I. Removal of sulfamethoxazole sulfonamide antibiotic from water by high silica zeolites: A study of the involved host–guest interactions by a combined structural, spectroscopic, and computational approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 419, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, A.; Pasti, L.; Marchetti, N.; Cavazzini, A.; Dond, F.; Alberti, A. Adsorption of pharmaceuticals from aqueous solutions on synthetic zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 148, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, N.; Dogan, E.C. Adsorption kinetics of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin on bentonite, activated carbon, zeolite, and pumice. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 53, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, D.N.R.; Insa, S.; Mozeto, A.A.; Petrovic, M.; Chaves, T.F.; Fadini, P.S. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of the adsorption of antibiotics from aqueous solutions onto powdered zeolites. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Jubouri, S.M.; Al-Jendeel, H.A.; Rashid, S.A.; Al-Batty, S. Antibiotics adsorption from contaminated water by composites of ZSM-5 zeolite nanocrystals coated carbon. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.Y. Removal of Antibiotics from Contaminated Waters Using Natural Zeolite. Master’s Thesis, CUNY City College, New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Belviso, C.; Guerra, G.; Abdolrahimi, M.; Peddis, D.; Maraschi, F.; Cavalcante, F.; Ferretti, M.; Martucci, A.; Sturini, M. Efficiency in Ofloxacin Antibiotic Water Remediation by Magnetic Zeolites Formed Combining Pure Sources and Wastes. Processes 2021, 9, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumrani, S.H.; Soomro, R.A.; Zhang, X.; Bhutto, D.A.; Buxa, N.; Ji, X. Coal fly ash driven zeolites for the adsorptive removal of the ceftazidime drug. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 26110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, A.; Kuc, J.; Bajda, T. A Review on the Application of Zeolites and Mesoporous Silica Materials in the Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Antibiotics from Water. Materials 2021, 14, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajo, P.; Preis, S.; Vornamo, T.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen, M.; Louhi-Kultanen, M. Hospital wastewater treatment with pilot-scale pulsed corona discharge for removal of pharmaceutical residues. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shearer, L.; Pap, S.; Gibb, S.W. Removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater: A review of adsorptive approaches, modelling and mechanisms for metformin and macrolides. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, X.; Liang, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Xie, X. Effective removal of two fluoroquinolone antibiotics by PEG-4000 stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron supported onto zeolite (PZ-NZVI). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 710, 136289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, H.; Roques-Carmes, T.; Potier, O.; Koubaissy, B.; Pontvianne, S.; Lenouvel, A.; Hamieh, T. Iron-impregnated zeolite catalyst for efficient removal of micropollutants at very low concentration from Meurthe river. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34950–34967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-rimawi, F.; Daana, M.; Khamis, M.; Karaman, R.; Khoury, H.; Qurie, M. Removal of Selected Pharmaceuticals from Aqueous Solutions Using Natural Jordanian Zeolite. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, D.; de Gennaro, B.; Daković, A.; Galzerano, B.; Germinario, C.; Izzo, F.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Langella, A. Removal of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from water by zeolite-rich composites: The interference of inorganic anions on the ibuprofen and naproxen adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasti, L.; Sarti, E.; Cavazzini, A.; Marchetti, N.; Dondi, F.; Martucci, A. Factors affecting drug adsorption on beta zeolites. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, T.; Ruiz-Salvador, A.R.; Rivera, A. Interaction studies between drugs and a purified natural clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.; Rivera, A. Theoretical study of the interaction of surfactants and drugs with natural zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 91, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Xiong, Z.-H.; Lia, C.; Zhang, J. Zeolitic imidazolate metal organic framework ZIF-8 with ultra-high adsorption capacity bound tetracycline in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82127–82137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyonyi, F.S.; Pembere, A.; Mutua, G.K.; Orata, F.; Louis, H. Computational screening of zeolites for the adsorption of selected pharmaceutical pollutants. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, P.; Ghosh, N. A review on the use of DFT for the prediction of the properties of nanomaterials. RSC Adv. 2021, 45, 27897–27924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braschi, I.; Gatti, G.; Paul, G.; Gessa, C.; Cossi, M.; Marchese, L. Sulfonamide Antibiotics Embedded in High Silica Zeolite Y: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study of Host−Guest and Guest−Guest Interactions. Langmuir 2010, 26, 9524–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessou, E.P.; Ponce-Vargas, M.; Mensah, J.-B.; Tielens, F.; Santos, J.C.; Badawi, M. Dibenzyl Disulfide Adsorption on Cationic Exchanged Faujasites: A DFT Study. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatouros, D.; Douroumis, D.; Nikolakis, V.; Ntais, S.; Moschovi, A.; Trivedi, V.; Khima, B.; Roldo, M.; Nazar, H.; Cox, P. In Vitro and In Silico investigations of drug delivery via zeolite BEA. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7789–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanakis, M.; Bouropoulos, N.; Theodoropoulos, D.; Sygellou, I.; Ewart, S.; Moschovi, A.; Siokou, A.; Niopas, I.; Kachrimanis, K.; Nikolakis, V.; et al. Controlled release of 5-fluorouracil from microporous zeolites. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M. Simulation-based evaluation of zeolite adsorbents for the removal of emerging contaminants. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purnomo; Setyarini, P.H.; Sulistyaningsih, D. Zeolite-based biomaterials for biomedical application: A review. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1977, 030013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastinu, A.; Kumar, A.; Maccarinelli, G.; Bonini, S.A.; Premoli, M.; Aria, F.; Gianoncelli, A.; Memo, M. Zeolite Clinoptilolite: Therapeutic Virtues of an Ancient Mineral. Molecules 2019, 24, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavelić, S.K.; Medica, J.S.; Gumbarević, D.; Filošević, A.; Pržulj, N.; Pavelić, K. Critical Review on Zeolite Clinoptilolite Safety and Medical Applications In Vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rininingsih, E.M.U. Correlation between Antioxidant Activity of Synthetic Zeolites Pillared Titanium Dioxide and Iron (III) Oxide with Adsorption DPPH. Master’s Thesis, IPB University, Bogor, Indonesia, 2014. Available online: http://repository.ipb.ac.id/handle/123456789/68404 (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Janićijević, D.; Jevremović, A.; Ležaić, A.J.; Vasiljević, B.N.; Uskoković-Marković, S.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D.; Milojević-Rakić, M. Comparative assessment of pesticide adsorption capacity and antioxidant activity of Silver Dodecatungstophosphate/HΒEA Zeolite composites. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojević-Rakić, M.; Popadić, D.; Ležaić, A.J.; Jevremović, A.; Vasiljević, B.N.; Uskoković-Marković, S.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D. MFI, BEA and FAU zeolite scavenging role in neonicotinoids and radical species elimination. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomašević-Čanović, M.; Daković, A.; Rottinghaus, G.; Đuričić, M. Surfactant modified zeolites—New efficient adsorbents for mycotoxins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipek, H.; Avci, M.; Aydilek, N.; Yerturk, M. The effect of zeolite on oxidant/antioxidant status in healthy dairy cows. Acta Vet. Brno. 2012, 81, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, J.; Lang, S.; Mante, F.; Pavelić, K.; Ozer, F. Antimicrobial and Mechanical Effects of Zeolite Use in Dental Materials: A Systematic Review. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2021, 55, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, D.C.; Davies, J.E.; Santerre, J.P.; Friedman, S. The hemolytic and cytotoxic properties of a zeolite-containing root filling material In Vitro. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2003, 95, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchwald, Z. Calcium-Rich 13X Zeolite as a Filler with Remineralizing Potential for Dental Composites. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3843–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, K.N.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, Y.K. Antibacterial Effect of Silver-Zeolites in Glass-Ionomer Cements. Key Eng. Mater. 2007, 330–332, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, M.; Selim, M.; Beherei, H.H.; El-Gohary, M.I. Incorporation effect of silver and zinc-zeolites into commercial glass ionomer cement. Int. Ceram. Rev. 2013, 62, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun-Jin, K.; Sik, S.J.; Kyo-Han, K.; Tae-Yub, K. Antimicrobial Activity of Glass Ionomer Cement Incorporated with Chlorhexidine-Loaded Zeolite Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 1450–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Santerre, J.P.; Friedman, S. Suppression of Bacterial Adherence by Experimental Root Canal Sealers. J. Endod. 2000, 26, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatole, K.; Gowdra, R.; Azher, S.S.; Sabharwal, S. Enhancing the antibacterial activity of the gold standard intracanal medicament with incorporation of silver zeolite: An In Vitro study. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2016, 6, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odabaş, M.E.; Çinar, Ç.; Akça, G.; Araz, I.; Ulusu, T.; Yücel, H. Short-term antimicrobial properties of mineral trioxide aggregate with incorporated silver-zeolite. Dent. Traumatol. 2011, 27, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokogawa, Y.; Sakanishi, M.; Morikawa, N.; Nakamura, A.; Kishida, I.; Varma, H.K. VCS Adsorptive Properties in Ion Exchanged Zeolite Materials in Gaseous and Aqueous Medium. Procedia Eng. 2012, 36, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saravanan, M.; Kumar, V.; Padmanabhan, T.; Banu, F. Viscoelastic properties and antimicrobial effects of soft liners with silver zeolite in complete dental prosthesis wearers: An in vivo study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naji, G.A.; Omar, R.; Yahya, R. Influence of sodalite zeolite infiltration on the coefficient of thermal expansion and bond strength of all-ceramic dental prostheses. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 67, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljafery, A.M.; Al-Jubouri, O.M.; Wally, Z.J.; Almusawi, R.M.; Abdulrudha, N.H.; Haider, J. The Effects of Incorporating Ag-Zn Zeolite on the Surface Roughness and Hardness of Heat and Cold Cure Acrylic Resins. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, J. Antibacterial and anti-adhesive zeolite coatings on titanium alloy surface. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 146, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.C.; Ribeiro, C.; Sencadas, V.; Botelho, G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Effect of filler content on morphology and physical–chemical characteristics of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/NaY zeolite-filled membranes. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 3361–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Calcium orthophosphates in dentistry. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1335–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandomierski, M.; Buchwald, Z.; Koczorowski, W.; Voelkel, A. Calcium forms of zeolites A and X as fillers in dental restorative materials with remineralizing potential. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 294, 109899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Bhardwaj, B.; Nag, M. Resin based restorative dental materials: Characteristics and future perspectives. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2019, 55, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matinlinna, J.P.; Lung, C.Y.K.; Tsoi, J.K.H. Silane adhesion mechanism in dental applications and surface treatments: A review. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydınoğlu, A.; Yoruç, A.B.H. Effects of silane-modified fillers on properties of dental composite resin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 79, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandomierski, M.; Okulus, Z.; Voelkel, A. Active diazonium-modified zeolite fillers for methacrylate-based composites. Compos. Interfaces 2019, 26, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gennaro, B.; Catalanotti, L.; Cappelletti, P.; Langella, A.; Mercurio, M.; Serri, C.; Biondi, M.; Mayol, L. Surface modified natural zeolite as a carrier for sustained diclofenac release: A preliminary feasibility study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 130, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazarçeviren, E.; Erdemli, Ö.; Keskin, D.; Tezcaner, A. Clinoptilolite/PCL–PEG–PCL composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. J. Biomater. Appl. 2017, 31, 1148–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thawabeia, R.A.; Hodali, H.A. Use of Zeolite ZSM-5 for Loading and Release of 5-Fluorouracil. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 403597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd-Elsatar, A.G.; Farag, M.M.; Youssef, H.F.; Salih, S.A.; Mounier, M.M.; El-Meliegy, E. Different zeolite systems for colon cancer therapy: Monitoring of ion release, cytotoxicity and drug release behavior. Prog. Biomater. 2019, 8, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amorim, R.; Vilaça, N.; Martinho, O.; Reis, R.M.; Sardo, M.; Rocha, J.; Fonseca, A.M.; Baltazar, F.; Neves, I.C. Zeolite Structures Loading with an Anticancer Compound as Drug Delivery Systems. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 25642–25650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paradee, N.; Sirivat, A. Encapsulation of Folic Acid in Zeolite Y for Controlled Release via Electric Field. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 13, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, S.; Garmarudi, A.B.; Rahmani, N.; Khanmohammadi, M. The β-cyclodextrin-modified nanosized ZSM-5 zeolite as a carrier for curcumin. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32348–32356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, X.; Yang, F.; Ke, Q.-F.; Xie, X.-T.; Guo, Y.-P. Hollow mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolite/chitosan ellipsoids loaded with doxorubicin as pH-responsive drug delivery systems against osteosarcoma. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7866–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, W.; Samuels, C.S.; Snyman, J.R. Potentiated clinoptilolite: Artificially enhanced aluminosilicate reduces symptoms associated with endoscopically negative gastroesophageal reflux disease and nonsteroidal anti–inflammatory drug induced gastritis. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Serri, C.; de Gennaro, B.; Quagliariello, V.; Iaffaioli, R.V.; de Rosa, G.; Catalanotti, L.; Biondi, M.; Mayol, L. Surface modified zeolite-based granulates for the sustained release of diclofenac sodium. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquino, R.; Di Domenico, M.; Izzo, F.; Gaudino, D.; Vanzanella, V.; Grizzuti, N.; de Gennaro, B. Rheology-sensitive response of zeolite-supported anti-inflammatory drug systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 146, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajisnik, D.; Dakovic, A.; Milojevic, M.; Malenovic, A.; Kragovic, M.; Bogdanovic, D.B.; Dondur, V.; Milic, J. Properties of diclofenac sodium sorption onto natural zeolite modified with cetylpyridinium chloride. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajisnik, D.; Dakovic, A.; Malenovic, A.; Milojevic-Rakic, M.; Dondur, V.; Radulovic, Z.; Milic, J. Investigation of adsorption and release of diclofenac sodium by modified zeolites composites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 83–84, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serri, C.; de Gennaro, B.; Catalanotti, L.; Cappelletti, P.; Langella, A.; Mercurio, M.; Mayol, L.; Biondi, M. Surfactant-modified phillipsite and chabazite as novel excipients for pharmaceutical applications? Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 224, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.M.; Cipagauta-Ardila, C.C.; Molina-Velasco, D.R.; Ríos-Reyes, C.A. Surfactant-modified natural zeolites as carriers for diclofenac sodium release: A preliminary feasibility study for pharmaceutical applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 256, 123644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağir, T.; Huysal, M.; Durmus, Z.; Kurt, B.Z.; Senel, M.; Isık, S. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of 5-fluorouracil loaded magnetite–zeolite nanocomposite (5-FU-MZNC) for cancer drug delivery applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 77, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-Y.; Qin, C.; Wang, X.-L.; Yang, G.-S.; Shao, K.-Z.; Lan, Y.-Q.; Su, Z.-M.; Huang, P.; Wang, C.-G.; Wang, E.-B. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 as efficient pH-sensitive drug delivery vehicle. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; Singh, A.; Garg, N.; Randhawa, J.K. Curcumin encapsulated zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as stimuli responsive drug delivery system and their interaction with biomimetic environment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Habibizadeh, M.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Khatamian, M.; Divband, B. Preparation and characterization of nanocomposites based on different zeolite frameworks as carriers for anticancer drug: Zeolite Y versus ZSM-5. Polym. Bull. 2018, 76, 2233–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, Z.-M.; Wang, F.-L.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Liu, X.; Zhai, D.-D.; Chen, W.-D. Curcumin and its promise as an anticancer drug: An analysis of its anticancer and antifungal effects in cancer and associated complications from invasive fungal infections. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 772, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadeh, Z.A.; Saviano, G.; Ballirano, P.; Santonicola, M.G. Curcumin-loaded zeolite as anticancer drug carrier: Effect of curcumin adsorption on zeolite structure. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 92, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilaça, N.; Bertão, A.R.; Prasetyanto, E.A.; Granja, S.; Costa, M.; Fernandes, R.; Figueiredo, F.; Fonseca, A.M.; De Cola, L.; Baltazar, F.; et al. Surface functionalization of zeolite-based drug delivery systems enhances their antitumoral activity In Vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 120, 111721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divband, B.; Rashidi, M.R.; Khatamian, M.; Eslamian, G.R.K.; Gharehaghaji, N.; Tabriz, F.D. Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: Cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency. Open Chem. 2018, 16, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Wen, X.; Ke, Q.-F.; Xie, X.-T.; Guo, Y.-P. pH-responsive mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolites/chitosan core-shell nanodisks loaded with doxorubicin against osteosarcoma. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 85, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasian, P.; Radmansouri, M.; Habibi, M.; Ghasemi, M.V.; Mohammadi, A.; Irani, M.; Jazi, F.S. Incorporation of magnetic NaX zeolite/DOX into the PLA/chitosan nanofibers for sustained release of doxorubicin against carcinoma cells death in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 121, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeri, N.; Rezaie, H.R.; Javadpour, J.; Kharaziha, M. Effect of pH on cisplatin encapsulated zeolite nanoparticles: Release mechanism and cytotoxicity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 273, 124964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, N.; Rezaie, H.R.; Javadpour, J.; Kharaziha, M. Cisplatin loaded polycaprolactone—Zeolite nanocomposite scaffolds for bone cancer treatment. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2021, 7, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lázaro, I.A.; Lázaro, S.A.; Forgan, R.S. Enhancing anticancer cytotoxicity through bimodal drug delivery from ultrasmall Zr MOF nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2792–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H. Mineralization of pH-Sensitive Doxorubicin Prodrug in ZIF-8 to Enable Targeted Delivery to Solid Tumors. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11453–11461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Phua, S.Z.F.; Lim, W.O.; Zhao, Y.L. ZnO-DOX@ZIF-8 core-shell nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hou, S.; Chen, J.; He, C.E.; Gao, Y.E.; Lu, Y.; Jia, D.; Ma, X.; Xue, P.; Kang, Y.; et al. Engineering silk sericin decorated zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanoplatform to enhance chemotherapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Milašin, I.S.; Eken, Z.B.; Mravak-Stipetic, M.; Pavelic, K.; Ozer, F. Effects of Zeolite as a Drug Delivery System on Cancer Therapy: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proenza, Y.G.; Longo, R.L. Simulation of the Adsorption and Release of Large Drugs by ZIF-8. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevremović, A.; Stanojković, A.; Arsenijević, D.; Arsenijević, A.; Arzumanyan, G.; Mamatkulov, K.; Petrović, J.; Vasiljević, B.N.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D.; Milojević-Rakić, M. Mitigating toxicity of acetamiprid removal techniques—Fe modified zeolites in focus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popadić, D.; Gavrilov, N.; Ignjatović, L.; Krajišnik, D.; Mentus, S.; Milojević-Rakić, M.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D. How to Obtain Maximum Environmental Applicability from Natural Silicates. Catalysts 2022, 12, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildernew, E.; Tareq, S.; Yang, S. Three-Dimensional Graphene with Preserved Channeling as a Binder Additive for Zeolite 13X for Enhanced Thermal Conductivity, Vapor Transport, and Vapor Adsorption Loading Kinetics. Catalysts 2022, 12, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Synthetic | Natural | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Zeolite Type | Structure | Zeolite Type |
| LTL | Zeolite L | HEU | Clinoptilolite |
| LTA | Zeolite A | MOR | Mordenite |
| MFI | ZSM-5 Zeolite | CHA | Chabazite |
| FAU | Zeolite X | ||
| Zeolite Y | |||
| BEA | Beta Zeolite | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mijailović, N.R.; Nedić Vasiljević, B.; Ranković, M.; Milanović, V.; Uskoković-Marković, S. Environmental and Pharmacokinetic Aspects of Zeolite/Pharmaceuticals Systems—Two Facets of Adsorption Ability. Catalysts 2022, 12, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080837
Mijailović NR, Nedić Vasiljević B, Ranković M, Milanović V, Uskoković-Marković S. Environmental and Pharmacokinetic Aspects of Zeolite/Pharmaceuticals Systems—Two Facets of Adsorption Ability. Catalysts. 2022; 12(8):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080837
Chicago/Turabian StyleMijailović, Nataša R., Bojana Nedić Vasiljević, Maja Ranković, Vladimir Milanović, and Snežana Uskoković-Marković. 2022. "Environmental and Pharmacokinetic Aspects of Zeolite/Pharmaceuticals Systems—Two Facets of Adsorption Ability" Catalysts 12, no. 8: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080837
APA StyleMijailović, N. R., Nedić Vasiljević, B., Ranković, M., Milanović, V., & Uskoković-Marković, S. (2022). Environmental and Pharmacokinetic Aspects of Zeolite/Pharmaceuticals Systems—Two Facets of Adsorption Ability. Catalysts, 12(8), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080837