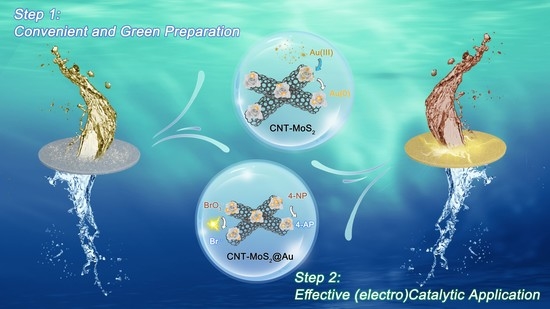
Facile Synthesis and Environmental Applications of Noble Metal-Based Catalytic Membrane Reactors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Facile Synthesis of CNT-MoS2@Au Catalytic Membrane
2.2. Characterization of the CNT-MoS2@Au Catalytic Membrane
2.3. Hydrogenation Reaction of 4-NP
2.4. Electrocatalytic Reduction of BrO3−
2.5. Generality of the Electrocatalytic Membranes
2.6. Working Mechanism of the Au-Immobilized CMR
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Fabrication of Catalytic Membrane Reactors
3.3. Catalytic Filtration Experiments
3.4. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Winter, L.R.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, W.; Hedtke, T.; Kim, J.-H.; Elimelech, M. Electrified membranes for water treatment applications. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 725–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Li, F.; Shen, C.; Huang, M.; Li, J.; Nasaruddin, R.R.; Xie, J. Rational design of high-performance continuous-flow microreactors based on gold nanoclusters and graphene for catalysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15425–15433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xu, J.; Xu, H.; Bao, H. Electrostatic interaction-controlled formation of pickering emulsion for continuous flow catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wen, M.; Yu, B.; Ye, G.; Huo, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J. Polydopamine induced in-situ formation of metallic nanoparticles in confined microchannels of porous membrane as flexible catalytic reactor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14735–14743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolatkhah, A.; Jani, P.; Wilson, L.D. Redox-responsive polymer template as an advanced multifunctional catalyst support for silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10560–10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Min, D. Nano silver decorating three-dimensional porous wood used as a catalyst for enhancing azo dyes hydrogenation in wastewater. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 175, 114268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Ben Amar, M.; Yang, D.; Brinza, O.; Kanaev, A.; Duten, X.; Vega-González, A. Plasma catalysis application of gold nanoparticles for acetaldehyde decomposition. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lan, J.Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Luo, Z.; Wang, W.; Sun, L. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles on rice husk silica for catalysis applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 5656–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, D.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, W.; Jia, H.; Chen, J. A novel redox precipitation to synthesize Au-doped α-MnO2 with high dispersion toward low-temperature oxidation of formaldehyde. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4728–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, H.; Reske, R.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Greeley, J.; Strasser, P.; Cuenya, B.R. Exceptional size-dependent activity enhancement in the electroreduction of CO2 over Au nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16473–16476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, E.; Peljo, P.; Scanlon, M.D.; Girault, H.H. Interfacial redox catalysis on gold nanofilms at soft interfaces. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6565–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H. Nanoporous gold: Preparation and applications to catalysis and sensors. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2018, 18, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priecel, P.; Adekunle Salami, H.; Padilla, R.H.; Zhong, Z.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A. Anisotropic gold nanoparticles: Preparation and applications in catalysis. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1619–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.; Zhu, H.; Su, R.; Qi, W.; He, Z. Catalytic membrane reactor immobilized with alloy nanoparticle-loaded protein fibrils for continuous reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11263–11273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Matsumura, Y.; Suda, H.; Haraya, K. Experimental study of steam reforming of methane in a thin (6 μM) Pd-based membrane reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Sandoval, J.; Gomez-Herrero, E.; Munoz, M.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A. Palladium-based catalytic membrane reactor for the continuous flow hydrodechlorination of chlorinated micropollutants. Appl. Catal. B 2021, 293, 120235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Park, H.H.; Han, S.S. Synthesis and characterization of biomatrixed-gold nanoparticles by the mushroom flammulina velutipes and its heterogeneous catalytic potential. Chemosphere 2015, 141, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhou, J.; Fu, R.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Jiao, B.; He, Y. Multicolor colorimetric detection of ochratoxin a via structure-switching aptamer and enzyme-induced metallization of gold nanorods. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, K.-T.; Sahoo, Y.; Swihart, M.T.; Prasad, P.N. Synthesis and plasmonic properties of silver and gold nanoshells on polystyrene cores of different size and of gold–silver core–shell nanostructures. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 290, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fausey, C.L.; Zucker, I.; Lee, D.E.; Shaulsky, E.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Elimelech, M. Tunable molybdenum disulfide-enabled fiber mats for high-efficiency removal of mercury from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18446–18456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mi, B. Environmental applications of 2D molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8229–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; He, P.; Wu, J.; Chen, N.; Xu, T.; Shi, E.; Pan, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y. Conversion of 2H MoS2 to 1 T MoS2 via lithium ion doping: Effective removal of elemental mercury. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, G.; Gao, X.; Pang, C.H.; Kingman, S.W.; Wu, T. Hg0 capture over CoMoS/γ-Al2O3 with MoS2 nanosheets at low temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voiry, D.; Goswami, A.; Kappera, R.; Silva, C.d.C.C.e.; Kaplan, D.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M.; Asefa, T.; Chhowalla, M. Covalent functionalization of monolayered transition metal dichalcogenides by phase engineering. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sim, A.; Urban, J.J.; Mi, B. Removal and recovery of heavy metal ions by two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets: Performance and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9741–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tu, Q.; Sim, A.; Yu, J.; Duan, Y.; Poon, S.; Liu, B.; Han, Q.; Urban, J.J.; Sedlak, D.; et al. Superselective removal of lead from water by two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets and layer-stacked membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12602–12611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghagoli, M.J.; Shemirani, F. Hybrid nanosheets composed of molybdenum disulfide and reduced graphene oxide for enhanced solid phase extraction of Pb(II) and Ni(II). Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zeng, X.; Warner, J.H.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, J.; Jin, W.; Wang, S.; Lu, J.; et al. Photoresponse-bias modulation of a high-performance MoS2 photodetector with a unique vertically stacked 2H-MoS2/1T@2H-MoS2 structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33325–33335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Han, Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, S.; Shu, Y.; Pedersen, J.A.; Wang, Z. Synergistic effect of metal cations and visible light on 2D MoS2 nanosheet aggregation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16379–16389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Song, S. Two-dimensional molybdenum fisulfide as a duperb sdsorbent for removing Hg2+ from water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7410–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano, F.J.; Marinas, J.M. Hydrogenolysis of organohalogen compounds over palladium supported catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2001, 173, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, F.; Beletskaya, I.P.; Yus, M. Metal-mediated reductive hydrodehalogenation of organic halides. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4009–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wei, W.; Qin, G.; Xiao, T.; Tang, W.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, S. Electrochemical reduction of nitrate in a catalytic carbon membrane nano-reactor. Water Res. 2022, 208, 117862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, F.; Shen, C.; Wu, Z. Extremely efficient electro-Fenton-like Sb(III) detoxification using nanoscale Ti-Ce binary oxide: An effective design to boost catalytic activity via non-radical pathway. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2519–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Wei, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, D.B.; Song, L.; Ni, B.J. Photochemical decomposition of perfluorochemicals in contaminated water. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Shen, C.; Li, F.; Huang, M.; Wang, Z.; Sand, W.; et al. Supported atomically-precise gold nanoclusters for enhanced flow-through electro-Fenton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5913–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Zhang, P.Y.; Shao, T.; Wang, J.L.; Jin, L.; Li, X.Y. Different nanostructured In2O3 for photocatalytic decomposition of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; You, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Redox-active nanohybrid filter for selective recovery of gold from water. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, T.; Lin, H.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liu, F. Meso-/macro-porous microspheres confining Au nanoparticles based on PDLA/PLLA stereo-complex membrane for continuous flowing catalysis and separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Du, B.; Nasaruddin, R.R.; Chen, T.; Xie, J. Golden carbon nanotube membrane for continuous flow catalysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Gu, J. Specific recovery and in situ reduction of precious metals from waste to create MOF composites with immobilized nanoclusters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 13975–13982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Ji, H.; Li, F.; Shen, C.; Fang, X.; Li, X.; Duan, X. A novel electrocatalytic filtration system with carbon nanotube supported nanoscale zerovalent copper toward ultrafast oxidation of organic pollutants. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Luo, B.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Min, D. In situ growth gold nanoparticles in three-dimensional sugarcane membrane for flow catalytical and antibacterial application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Su, R.; Huang, R.; Qi, W.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; He, Z. Facile in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles on procyanidin-grafted eggshell membrane and their catalytic properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 4638–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Shen, C.; Li, F.; Yang, B.; Huang, M.; Ma, C.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.; Sand, W. One-step phosphite removal by an electroactive CNT filter functionalized with TiO2/CeOx nanocomposites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, R.; Zhao, X.; Qu, J. Electrochemical reduction of bromate by a Pd modified carbon fiber rlectrode: Kinetics and mechanism. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 132, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Martin, C.R. Voltage charging rnhances ionic conductivity in gold nanotube membranes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 8266–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, O.S.G.P.; Ramalho, P.S.F.; Fernandes, A.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Catalytic bromate reduction in water: Influence of carbon support. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, N.; Zhou, J.; Du, L.; Wang, P. Microfabricated electrochemical cell-based biosensors for analysis of living cells in vitro. Biosensors 2012, 2, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Hou, B.; Hu, Y. Performance improvement of air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cell using a mesoporous carbon modified anode. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 7458–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Coronado, A.M.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Calvo, L.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Gilarranz, M.A.; Pereira, M.F.R. Catalytic reduction of bromate over catalysts based on Pd nanoparticles synthesized via water-in-oil microemulsion. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 237, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Yang, Q.; Yan, M.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Zhong, Y.; Yin, H.; Chen, S.; Fu, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Synergistic adsorption and electrocatalytic reduction of bromate by Pd/N-doped loofah sponge-derived biochar electrode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhushree, R.; UC, J.R.J.; Pinheiro, D.; KR, S.D. The catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using MoS2/ZnO nanocomposite. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2022, 10, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-M.; Cheng, R.; Nan, J.; Chen, X.-Q.; Huang, C.; Cao, D.; Bai, C.-H.; Han, J.-L.; Liang, B.; Li, Z.-L.; et al. Effective electrocatalytic hydrodechlorination of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by a novel Pd/MnO2/Ni foam cathode. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 3823–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, N.; Matsuda, N. Bromate ion removal by electrochemical reduction using an activated carbon felt electrode. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H.; Namba, N.; Takahashi, T.; Nogi, M.; Nishina, Y. Renewable wood pulp paper reactor with hierarchical micro/nanopores for continuous-flow nanocatalysis. Chem. Sus. Chem 2017, 10, 2560–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopiraman, M.; Saravanamoorthy, S.; Baskar, R.; Ilangovan, A.; Ill-Min, C. Green synthesis of Ag@Au bimetallic regenerated cellulose nanofibers for catalytic applications. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 17090–17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-F.; Mao, L.-B.; Ge, J.; Yu, Z.-L.; Liu, J.-W.; Yu, S.-H. Three-dimensional melamine sponge loaded with Au/ceria nanowires for continuous reduction of p-nitrophenol in a consecutive flow system. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Fiore, B.; La Parola, V.; Lazzara, G.; Guernelli, S.; Zaccheroni, N.; Riela, S. Gold nanoparticles stabilized by modified halloysite nanotubes for catalytic applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, N.; Chen, F. Monolithic carbon foam-supported Au nanoparticles with excellent catalytic performance in a fixed-bed system. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 15027–15032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Facile Synthesis and Environmental Applications of Noble Metal-Based Catalytic Membrane Reactors. Catalysts 2022, 12, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080861
Yan H, Liu F, Zhang J, Liu Y. Facile Synthesis and Environmental Applications of Noble Metal-Based Catalytic Membrane Reactors. Catalysts. 2022; 12(8):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080861
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Haochen, Fuqiang Liu, Jinna Zhang, and Yanbiao Liu. 2022. "Facile Synthesis and Environmental Applications of Noble Metal-Based Catalytic Membrane Reactors" Catalysts 12, no. 8: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080861
APA StyleYan, H., Liu, F., Zhang, J., & Liu, Y. (2022). Facile Synthesis and Environmental Applications of Noble Metal-Based Catalytic Membrane Reactors. Catalysts, 12(8), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080861