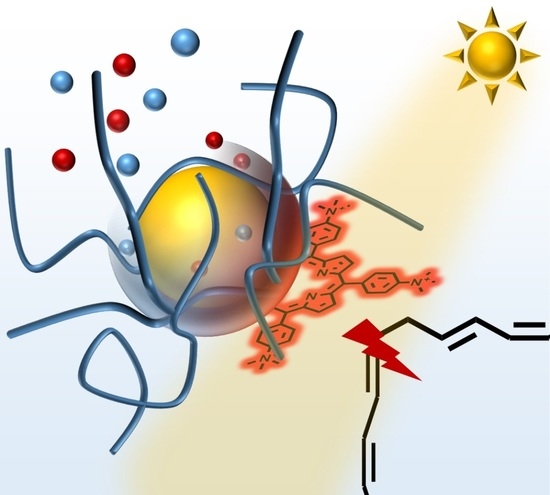
The Shell Matters: Self-Organized CdS-ZnS/MnS-Core-Shell—Porphyrin-Polymer Nano-Assemblies for Photocatalysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.; Fisher, B.; Eisler, H.-J.; Bawendi, M. Type-II quantum dots: CdTe/CdSe(core/shell) and CdSe/ZnTe(core/shell) heterostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11466–11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Sundar, V.C.; Heine, J.R.; Bawendi, M.G.; Jensen, K.F. Full Color Emission from II-VI Semiconductor Quantum Dot-Polymer Composites. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robel, I.; Subramanian, V.; Kuno, M.; Kamat, P.V. Quantum dot solar cells. harvesting light energy with CdSe nanocrystals molecularly linked to mesoscopic TiO2 films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-L.; Lo, Y.-S. Highly Efficient Quantum-Dot-Sensitized Solar Cell Based on Co-Sensitization of CdS/CdSe. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyadyusha, L.; Yin, H.; Jaiswal, S.; Brown, T.; Baumberg, J.J.; Booy, F.P.; Melvin, T. Quenching of CdSe quantum dot emission, a new approach for biosensing. Chem. Commun. 2005, 25, 3201–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medintz, I.L.; Clapp, A.R.; Mattoussi, H.; Goldman, E.R.; Fisher, B.; Mauro, J.M. Self-assembled nanoscale biosensors based on quantum dot FRET donors. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, A.; Zika, A.; Gröhn, F. Functional Nano-Objects by Electrostatic Self-Assembly: Structure, Switching, and Photocatalysis. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 779360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, S.; Düring, J.; Haschke, S.; Barr, M.K.S.; Stiegler, L.; Schühle, P.; Bachmann, J.; Hirsch, A.; Gröhn, F. Tunable Photocatalytic Activity of PEO-Stabilized ZnO–Polyoxometalate Nanostructures in Aqueous Solution. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2002130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Waleska, N.; Gröhn, F. Hybrid Organic–Platinum Nanoparticles for Hydrogenation Reactions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 4329–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Herron, N. Nanometer-sized semiconductor clusters: Materials synthesis, quantum size effects, and photophysical properties. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor Clusters, Nanocrystals, and Quantum Dots. Science 1996, 271, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyuzhny, G.; Murray, R.W. Ligand effects on optical properties of CdSe nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 7012–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comparelli, R.; Zezza, F.; Striccoli, M.; Curri, M.L.; Tommasi, R.; Agostiano, A. Improved optical properties of CdS quantum dots by ligand exchange. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2003, 23, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Wang, Y.A.; Peng, X. Formation and Stability of Size-, Shape-, and Structure-Controlled CdTe Nanocrystals: Ligand Effects on Monomers and Nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4300–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandia, A.; Parewa, V.; Rathore, K.S. Synthesis and characterization of CdS and Mn doped CdS nanoparticles and their catalytic application for chemoselective synthesis of benzimidazoles and benzothiazoles in aqueous medium. Catal. Commun. 2012, 28, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-M.; Liu, F.-Q.; Guo, H.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, Z.-G. Surface states induced photoluminescence from Mn2+ doped CdS nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 2000, 115, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambidurai, M.; Muthukumarasamy, N.; Agilan, S.; Sabari Arul, N.; Murugan, N.; Balasundaraprabhu, R. Structural and optical characterization of Ni-doped CdS quantum dots. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 3200–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henglein, A. Photo-Degradation and Fluorescence of Colloidal-Cadmium Sulfide in Aqueous Solution. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Sun, Z.; Cao, S.; Shen, R.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Long, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; et al. Facile synthesis of Ag-doped ZnCdS nanocrystals and transformation into Ag-doped ZnCdSSe nanocrystals with Se treatment. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Yi, L.; Han, W.; Teng, F.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Gao, M. Synthesis, optical properties, and superlattice structure of Cu(I)-doped CdS nanocrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 33112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiano, V.; Matarangolo, M.; Murcia, J.J.; Rojas, H.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C. Enhanced photocatalytic removal of phenol from aqueous solutions using ZnO modified with Ag. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 225, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiano, V.; Iervolino, G.; Rizzo, L. Cu-doped ZnO as efficient photocatalyst for the oxidation of arsenite to arsenate under visible light. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 238, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamoschos, N.; Bairamis, F.; Andrikopoulos, K.S.; Konstantinou, I.; Tasis, D. Metal-doped CdS/MoS2 heterojunctions for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Processing 2022, 144, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Dutta, J. Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes with manganese-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamal, D.B.; Klabunde, K.J. Synthesis, characterization, and visible light activity of new nanoparticle photocatalysts based on silver, carbon, and sulfur-doped TiO2. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 311, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapin, D.V.; Mekis, I.; Götzinger, S.; Kornowski, A.; Benson, O.; Weller, H. CdSe/CdS/ZnS and CdSe/ZnSe/ZnS Core−Shell−Shell Nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 18826–18831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckel, J.S.; Zimmer, J.P.; Coe-Sullivan, S.; Stott, N.E.; Bulović, V.; Bawendi, M.G. Blue Luminescence from (CdS)ZnS Core–Shell Nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, I.; Kato, H.; Kudo, A. Visible-Light-Induced H2 Evolution from an Aqueous Solution Containing Sulfide and Sulfite over a ZnS-CuInS2-AgInS2 Solid-Solution Photocatalyst. Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 3631–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Strassert, C.A.; Gröhn, F. Hierarchical electrostatic nanotemplating and assembly of electron-transferring hybrid nanostructures: CdS-polymer-porphyrin particles. Nanoscale 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Maheshwari, V. Controlled Element Specific Nanoscale Domains by Self-Assembly for High Performance Bifunctional Alkaline Water Splitting Catalyst. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, C.D.; Ennaoui, A.; Patil, P.S.; Giersig, M.; Muller, M.; Diesner, K.; Tributsch, H. Process and characterisation of chemical bath deposited manganese sulphide (MnS) thin films. Thin Solid Film. 1998, 330, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.G.; Wamser, C.C.; Ruwitch, J.; Zhao, Y.; Braden, D.; Stevens, M.; Denman, A.; Pi, R.; Rudine, A.; Pessiki, P.J. Syntheses and optoelectronic properties of amino/carboxyphenylporphyrins for potential use in dye-sensitized TiO2 solar cells. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2007, 11, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthard, C.; Schmidt, M.; Gröhn, F. Porphyrin-polymer networks, worms, and nanorods: pH-triggerable hierarchical self-assembly. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeißer, S.; Gröhn, F. Catalytic activity of macroion-porphyrin nanoassemblies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14267–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonietti, M.; Gröhn, F.; Hartmann, J.; Bronstein, L. Nonclassical Shapes of Noble-Metal Colloids by Synthesis in Microgel Nanoreactors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1997, 36, 2080–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröhn, F.; Bauer, B.J.; Akpalu, Y.A.; Jackson, C.L.; Amis, E.J. Dendrimer Templates for the Formation of Gold Nanoclusters. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 6042–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Kumacheva, E. Polymer microgels: Reactors for semiconductor, metal, and magnetic nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7908–7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Fang, B.; Drechsler, M.; Müllner, M.; Bolisetty, S.; Ballauff, M.; Müller, A.H.E. Hybrids of Magnetic Nanoparticles with Double-Hydrophilic Core/Shell Cylindrical Polymer Brushes and Their Alignment in a Magnetic Field. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düring, J.; Hölzer, A.; Kolb, U.; Branscheid, R.; Gröhn, F. Supramolecular Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Assemblies with Tunable Particle Size: Interplay of Three Noncovalent Interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8742–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhel, L.; Haase, M.; Weller, H.; Henglein, A. Photochemistry of colloidal semiconductors. Surface modification and stability of strong luminescing CdS particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, L.E. A simple model for the ionization potential, electron affinity, and aqueous redox potentials of small semiconductor crystallites. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Gao, X. The big red shift of photoluminescence of Mn dopants in strained CdS: A case study of Mn-doped MnS-CdS heteronanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6618–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.H.; Hofman, E.; Chen, K.; Li, Z.-J.; Khammang, A.; Zamani, H.; Franck, J.M.; Maye, M.M.; Meulenberg, R.W.; Zheng, W. Exciton Energy Shifts and Tunable Dopant Emission in Manganese-Doped Two-Dimensional CdS/ZnS Core/Shell Nanoplatelets. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 2516–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, O.; Angerhofer, A.; Cao, Y.C. Radial-Position-Controlled Doping of CdS/ZnS Core/Shell Nanocrystals: Surface Effects and Position-Dependent Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 3186–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuanqian, L.; Jingmei, H.; Jingguo, Y.; Bo, Z.; Yuanqing, H. Multi-component analysis by flow injection-diode array detection-spectrophotometry using partial least squares calibration model for simultaneous determination of zinc, cadmium and lead. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 461, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inada, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Inamo, M.; Nomura, M.; Funahashi, S. Structural characterization and formation mechanism of sitting-atop (SAT) complexes of 5, 10, 15, 20-tetraphenylporphyrin with divalent metal ions. Structure of the Cu(II)-SAT complex as determined by fluorescent extended X-ray absorption fine structure. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 39, 4793–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semitsoglou-Tsiapou, S.; Meador, T.B.; Peng, B.; Aluwihare, L. Photochemical (UV-vis/H2O2) degradation of carotenoids: Kinetics and molecular end products. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Cui, L.; Pu, T.; Song, J.; Zhang, X. Core-shell CdS@MnS nanorods as highly efficient photocatalysts for visible light driven hydrogen evolution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.; Chattopadhyay, A. Redox-Tuned Three-Color Emission in Double (Mn and Cu) Doped Zinc Sulfide Quantum Dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, P.; Li, W.; Tong, X.; Wang, X.; Cai, Q. Development of a high performance hollow CuInSe 2 nanospheres-based photoelectrochemical cell for hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18974–18987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagner, M.; Gröhn, F. The Shell Matters: Self-Organized CdS-ZnS/MnS-Core-Shell—Porphyrin-Polymer Nano-Assemblies for Photocatalysis. Catalysts 2022, 12, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080907
Wagner M, Gröhn F. The Shell Matters: Self-Organized CdS-ZnS/MnS-Core-Shell—Porphyrin-Polymer Nano-Assemblies for Photocatalysis. Catalysts. 2022; 12(8):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080907
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagner, Maximilian, and Franziska Gröhn. 2022. "The Shell Matters: Self-Organized CdS-ZnS/MnS-Core-Shell—Porphyrin-Polymer Nano-Assemblies for Photocatalysis" Catalysts 12, no. 8: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080907
APA StyleWagner, M., & Gröhn, F. (2022). The Shell Matters: Self-Organized CdS-ZnS/MnS-Core-Shell—Porphyrin-Polymer Nano-Assemblies for Photocatalysis. Catalysts, 12(8), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080907