Influence of the Type and the Amount of Surfactant in Phillipsite on Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium
Abstract
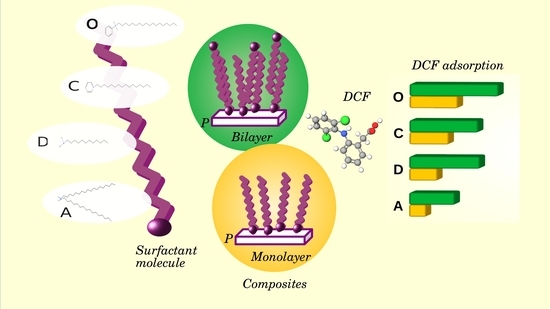
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of O and D Composites
2.2. Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium
2.3. Characterization after Adsorption: FTIR–ATR and Zeta Potential
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Zorpas, A.A. Handbook of Natural Zeolites; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.V. Definition of a Zeolite. Zeolites 1984, 4, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delkash, M.; Ebrazi Bakhshayesh, B.; Kazemian, H. Using Zeolitic Adsorbents to Cleanup Special Wastewater Streams: A Review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 214, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemić, J.; Tomašević-Čanović, M.; Adamović, M.; Kovačević, D.; Milićević, S. Competitive Adsorption of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons on Organo-Zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 105, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaelides, P. Application of Natural Zeolites in Environmental Remediation: A Short Review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 144, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, E.; Karapinar, N.; Donat, R. The Removal of Heavy Metal Cations by Natural Zeolites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural Zeolites as Effective Adsorbents in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albino, V.; Cioffi, R.; Pansini, M.; Colella, C. Disposal of Lead-Containing Zeolite Sludges in Cement Matrix. Environ. Technol. 1995, 16, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, R.; Pansini, M.; Caputo, D.; Colella, C. Evaluation of Mechanical and Leaching Properties of Cement-Based Solidified Materials Encapsulating Cd-Exchanged Natural Zeolites. Environ. Technol. 1996, 17, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, C.; de’ Gennaro, M.; Langella, A.; Pansini, M. Evaluation of Natural Phillipsite and Chabazite as Cation Exchangers for Copper and Zinc. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansini, M.; Colella, C. Dynamic Data on Lead Uptake from Water by Chabazite. Desalination 1990, 78, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggerty, G.M.; Bowman, R.S. Sorption of Chromate and Other Inorganic Anions by Organo-Zeolite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradović, M.; Daković, A.; Smiljanić, D.; Ožegović, M.; Marković, M.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Krstić, J. Ibuprofen and Diclofenac Sodium Adsorption onto Functionalized Minerals: Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 335, 111795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennaro, B.; Mercurio, M.; Cappelletti, P.; Catalanotti, L.; Daković, A.; De Bonis, A.; Grifa, C.; Izzo, F.; Kraković, M.; Monetti, V.; et al. Use of Surface Modified Natural Zeolite (SMNZ) in Pharmaceutical Preparations. Part 2. A New Approach for a Fast Functionalization of Zeolite-Rich Carriers. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 235, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, P.; Colella, A.; Langella, A.; Mercurio, M.; Catalanotti, L.; Monetti, V.; de Gennaro, B. Use of Surface Modified Natural Zeolite (SMNZ) in Pharmaceutical Preparations Part 1. Mineralogical and Technological Characterization of Some Industrial Zeolite-Rich Rocks. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 250, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, P.J.; Fallowfield, H.J. The Toxicity of Cationic Surfactant HDTMA-Br, Desorbed from Surfactant Modified Zeolite, towards Faecal Indicator and Environmental Microorganisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Bowman, R.S. Sorption of Perchloroethylene by Surfactant-Modified Zeolite as Controlled by Surfactant Loading. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2278–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, N.; Hadi, M.; Gholami, M.; Fard, R.F.; Aminabad, M.S. Sorption of Acid Dye by Surfactant Modificated Natural Zeolites. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 59, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Makuch, D.; Pillai, S.D.; Guan, H.; Bowman, R.; Couroux, E.; Hielscher, F.; Totten, J.; Espinosa, I.Y.; Kretzschmar, T. Surfactant-Modified Zeolite Can Protect Drinking Water Wells from Viruses and Bacteria. EOS 2002, 83, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Lin, J.; Qiu, Y.; Gao, N.; Zhu, Z. Adsorption of Humic Acid from Aqueous Solution on Bilayer Hexadecyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide-Modified Zeolite. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2011, 5, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.S. Applications of Surfactant-Modified Zeolites to Environmental Remediation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennaro, B. Surface modification of zeolites for environmental applications. In Modified Clay and Zeolite Nanocomposite Materials: Environmental and Pharmaceutical Applications; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 57–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennaro, B.; Catalanotti, L.; Bowman, R.S.; Mercurio, M. Anion Exchange Selectivity of Surfactant Modified Clinoptilolite-Rich Tuff for Environmental Remediation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gennaro, B.; Aprea, P.; Liguori, B.; Galzerano, B.; Peluso, A.; Caputo, D. Zeolite-Rich Composite Materials for Environmental Remediation: Arsenic Removal from Water. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimas Rivera, G.L.; Martínez Hernández, A.; Pérez Cabello, A.F.; Rivas Barragán, E.L.; Liñán Montes, A.; Flores Escamilla, G.A.; Sandoval Rangel, L.; Suarez Vazquez, S.I.; De Haro Del Río, D.A. Removal of Chromate Anions and Immobilization Using Surfactant-Modified Zeolites. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 39, 101717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apreutesei, R.E.; Catrinescu, C.; Teodosiu, C. Surfactant-Modified Natural Zeolites for Environmental Applications in Water Purification. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2008, 7, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrenovic, J.; Rozic, M.; Sekovanic, L.; Anic-Vucinic, A. Interaction of Surfactant-Modified Zeolites and Phosphate Accumulating Bacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, D.; de Gennaro, B.; Daković, A.; Galzerano, B.; Germinario, C.; Izzo, F.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Langella, A. Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs from Water by Zeolite-Rich Composites: The Interference of Inorganic Anions on the Ibuprofen and Naproxen Adsorption. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 286, 112168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, D.; de Gennaro, B.; Izzo, F.; Langella, A.; Daković, A.; Germinario, C.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Spasojević, M. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water by Zeolite-Rich Composites: A First Approach Aiming at Diclofenac and Ketoprofen. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 289, 110057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, M.; Geisslinger, G. COX-Dependent Mechanisms Involved in the Antinociceptive Action of NSAIDs at Central and Peripheral Sites. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 107, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Boateng, L.K.; Flora, J.R.V.; Oh, J.; Braswell, M.C.; Son, A.; Yoon, Y. Competitive Adsorption of Selected Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Activated Biochars: Experimental and Molecular Modeling Study. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Petrović, M.; Ginebreda, A.; Barceló, D. Removal of Pharmaceuticals during Wastewater Treatment and Environmental Risk Assessment Using Hazard Indexes. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonappan, L.; Brar, S.K.; Das, R.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Diclofenac and Its Transformation Products: Environmental Occurrence and Toxicity—A Review. Environ. Int. 2016, 96, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loos, R.; Carvalho, R.; António, D.C.; Comero, S.; Locoro, G.; Tavazzi, S.; Paracchini, B.; Ghiani, M.; Lettieri, T.; Blaha, L.; et al. EU-Wide Monitoring Survey on Emerging Polar Organic Contaminants in Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6475–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.C.G.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Barbosa, M.O.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T. A Review on Environmental Monitoring of Water Organic Pollutants Identified by EU Guidelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, E.E.; Tsang, Y.F. Occurrences and Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Drinking Water and Water/Sewage Treatment Plants: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596–597, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaks, J.L.; Meteyer, C.U.; Rideout, B.A.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Gilbert, M.; Virani, M.; Watson, R.T.; Khan, A.A. Diagnostic Investigation of Vulture Mortality: The Anti-Inflammatory Drug Diclofenac Is Associated with Visceral Gout. In Proceedings of the Raptor Worldwide, 6th World Conference on Birds of Prey and Owls, Budapest, Hungary, 18–23 May 2003; pp. 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Balmford, A. Pollution, Politics, and Vultures. Science 2013, 339, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefille, B.; Gomez, E.; Courant, F.; Escande, A.; Fenet, H. Diclofenac in the Marine Environment: A Review of Its Occurrence and Effects. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, T.; Guégan, R.; Thiebault, T.; Le Milbeau, C.; Muller, F.; Teixeira, V.; Giovanela, M.; Boussafir, M. Adsorption of Diclofenac onto Organoclays: Effects of Surfactant and Environmental (PH and Temperature) Conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, D.B.; Trigueiro, P.; Silva Filho, E.C.; Fonseca, M.G.; Jaber, M. Monitoring Diclofenac Adsorption by Organophilic Alkylpyridinium Bentonites. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, G.S.; de Andrade, J.R.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium onto Commercial Organoclay: Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Study. Powder Technol. 2019, 345, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Sorption and Retention of Diclofenac on Zeolite in the Presence of Cationic Surfactant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, F.; Mercurio, M.; de Gennaro, B.; Aprea, P.; Cappelletti, P.; Daković, A.; Germinario, C.; Grifa, C.; Smiljanic, D.; Langella, A. Surface Modified Natural Zeolites (SMNZs) as Nanocomposite Versatile Materials for Health and Environment. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2019, 182, 110380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, M.; Izzo, F.; Langella, A.; Grifa, C.; Germinario, C.; Daković, A.; Aprea, P.; Pasquino, R.; Cappelletti, P.; Graziano, F.S.; et al. Surface-Modified Phillipsite-Rich Tuff from the Campania Region (Southern Italy) as a Promising Drug Carrier: An Ibuprofen Sodium Salt Trial. Am. Mineral. 2018, 103, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, P.; Gunasekaran, S. Quantum Mechanical Calculations and Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman and UV) Investigations, Molecular Orbital, NLO, NBO, NLMO and MESP Analysis of 4-[5-(4-Methylphenyl)-3-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl] Benzene-1-Sulfonamide. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1081, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, M.; Daković, A.; Krajišnik, D.; Kragović, M.; Milić, J.; Langella, A.; de Gennaro, B.; Cappelletti, P.; Mercurio, M. Evaluation of the Surfactant/Phillipsite Composites as Carriers for Diclofenac Sodium. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 222, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajišnik, D.; Daković, A.; Milojević, M.; Malenović, A.; Kragović, M.; Bogdanović, D.B.; Dondur, V.; Milić, J. Properties of Diclofenac Sodium Sorption onto Natural Zeolite Modified with Cetylpyridinium Chloride. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajišnik, D.; Daković, A.; Malenović, A.; Kragović, M.; Milić, J. Ibuprofen Sorption and Release by Modified Natural Zeolites as Prospective Drug Carriers. Clay Miner. 2015, 50, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Orta, M.M.; Flores, F.M.; Morantes, C.F.; Curutchet, G.; Torres Sánchez, R.M. Interrelations of Structure, Electric Surface Charge, and Hydrophobicity of Organo-Mica and -Montmorillonite, Tailored with Quaternary or Primary Amine Cations. Preliminary Study of Pyrimethanil Adsorption. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 223, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the Modeling of Adsorption Isotherm Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhana Krishna Kumar, A.; Ramachandran, R.; Kalidhasan, S.; Rajesh, V.; Rajesh, N. Potential Application of Dodecylamine Modified Sodium Montmorillonite as an Effective Adsorbent for Hexavalent Chromium. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiess, A.-N.; Neumeyer, N. An Evaluation of R2 as an Inadequate Measure for Nonlinear Models in Pharmacological and Biochemical Research: A Monte Carlo Approach. BMC Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glatting, G.; Kletting, P.; Reske, S.N.; Hohl, K.; Ring, C. Choosing the Optimal Fit Function: Comparison of the Akaike Information Criterion and the F-Test. Med. Phys. 2007, 34, 4285–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvar, J.L.; Martín, J.; del Orta, M.M.; Medina-Carrasco, S.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Simultaneous and Individual Adsorption of Ibuprofen Metabolites by a Modified Montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 189, 105529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghemit, R.; Makhloufi, A.; Djebri, N.; Flilissa, A.; Zerroual, L.; Boutahala, M. Adsorptive Removal of Diclofenac and Ibuprofen from Aqueous Solution by Organobentonites: Study in Single and Binary Systems. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, D.; Daković, A.; Obradović, M.; Ožegović, M.; Izzo, F.; Germinario, C.; de Gennaro, B. Application of Surfactant Modified Natural Zeolites for the Removal of Salicylic Acid—A Contaminant of Emerging Concern. Materials 2021, 14, 7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Rasmussen, J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J. Organokaolin for the Uptake of Pharmaceuticals Diclofenac and Chloramphenicol from Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennaro, B.; Aprea, P.; Pepe, F.; Colella, C. Cation Selectivity of a Ca2+ Pre-Exchanged Clinoptilolite Tuff. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2007, 170, 2128–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gennaro, B.; Aprea, P.; Colella, C.; Buondonno, A. Comparative Ion-Exchange Characterization of Zeolitic and Clayey Materials for Pedotechnical Applications-Part 2: Interaction with Nutrient Cations. J. Porous Mater. 2007, 16, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennaro, B.; Colella, A.; Cappelletti, P.; Pansini, M.; de’ Gennaro, M.; Colella, C. Effectiveness of Clinoptilolite in Removing Toxic Cations from Water: A Comparative Study. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2005, 158B, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, M.; Daković, A.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Kragović, M.; Petković, A.; Krajišnik, D.; Milić, J.; Mercurio, M.; de Gennaro, B. Adsorption of the Mycotoxin Zearalenone by Clinoptilolite and Phillipsite Zeolites Treated with Cetylpyridinium Surfactant. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 151, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Khan, M.A.; Kameda, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Xia, M.; Yoshioka, T. New Insights into the Capture Performance and Mechanism of Hazardous Metals Cr3+ and Cd2+ onto an Effective Layered Double Hydroxide Based Material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Xia, M.; Chu, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Lei, W.; Wang, F.; Muhmood, T.; Wang, A. Adsorption and Desorption of Pb(II) on L-Lysine Modified Montmorillonite and the Simulation of Interlayer Structure. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 169, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Mass Loss (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25–200 °C | 200–700 °C | 700–1000 °C | ∑25–1000 °C | |
| P | 7.44 | 3.77 | 0.08 | 11.29 |
| PO100 | 6.46 | 8.02 | 0.07 | 14.55 |
| PO200 | 6.35 | 11.35 | 0.03 | 17.73 |
| PD100 | 6.47 | 5.94 | 0.04 | 12.45 |
| PD200 | 7.49 | 6.98 | 0.05 | 14.52 |
| Drug | Sample | Model | Parameters | Goodness-of-Fit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K (L/mg) | n | Qmax (mg/g) | R2 | AICw | |||
| DCF | PO100 | Langmuir | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 21.1 ± 0.9 | 0.974 | 0.974 | |
| Freundlich | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 2.9 ± 0.4 | 0.937 | 0.026 | |||
| PO200 | Langmuir | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 38.4 ± 0.9 | 0.984 | 0.998 | ||
| Freundlich | 9.9 ± 0.9 | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 0.925 | 0.002 | |||
| PD100 | Langmuir | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 12.3 ± 0.8 | 0.947 | 0.852 | ||
| Freundlich | 2.4 ± 0.5 | 2.9 ± 0.4 | 0.919 | 0.148 | |||
| PD200 | Langmuir | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 30.2± 0.7 | 0.974 | 0.918 | ||
| Freundlich | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 0.952 | 0.082 | |||
| Surfactant Amount | Surfactant Type | * Adsorbed DCF mg/g | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% of ECEC | C | 17.2 | [29] |
| A | 7.4 | [29] | |
| O | 21.1 | This study | |
| D | 12.3 | This study | |
| 200% of ECEC | C | 30.0 | [29] |
| A | 19.9 | [29] | |
| O | 38.8 | This study | |
| D | 30.8 | This study |
| Drug | Sample | Model | Parameters | Goodness-of-Fit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (min−1) | K2 (g mg−1 min−1) | Qmax (mg/g) | R2 | AICw | |||
| DCF | PO100 | PFO | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 12.2 ± 0.4 | 0.676 | 0.005 | |
| PSO | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 13.0 ± 0.3 | 0.929 | 0.995 | |||
| PO200 | PFO | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 22.3 ± 0.8 | 0.950 | 0.006 | ||
| PSO | 0.040 ± 0.008 | 23.6 ± 0.6 | 0.986 | 0.994 | |||
| PD100 | PFO | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 6.7 ± 0.7 | 0.952 | 0.225 | ||
| PSO | 0.006 ± 0.002 | 8.5 ± 0.9 | 0.965 | 0.775 | |||
| PD200 | PFO | 0.27 ± 0.06 | 17.5 ± 0.8 | 0.937 | 0.005 | ||
| PSO | 0.021 ± 0.004 | 19.1 ± 0.6 | 0.983 | 0.995 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smiljanić, D.; Daković, A.; Obradović, M.; Ožegović, M.; Marković, M.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; de Gennaro, B. Influence of the Type and the Amount of Surfactant in Phillipsite on Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium. Catalysts 2023, 13, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010071
Smiljanić D, Daković A, Obradović M, Ožegović M, Marković M, Rottinghaus GE, de Gennaro B. Influence of the Type and the Amount of Surfactant in Phillipsite on Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium. Catalysts. 2023; 13(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmiljanić, Danijela, Aleksandra Daković, Milena Obradović, Milica Ožegović, Marija Marković, George E. Rottinghaus, and Bruno de Gennaro. 2023. "Influence of the Type and the Amount of Surfactant in Phillipsite on Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium" Catalysts 13, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010071
APA StyleSmiljanić, D., Daković, A., Obradović, M., Ožegović, M., Marković, M., Rottinghaus, G. E., & de Gennaro, B. (2023). Influence of the Type and the Amount of Surfactant in Phillipsite on Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium. Catalysts, 13(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13010071