Enzymatic Synthesis of Ascorbic Acid-Ketone Body Hybrids
Abstract
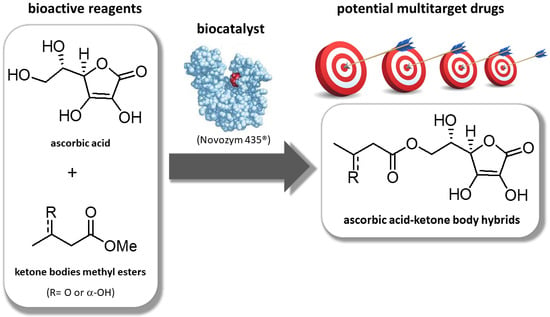
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis of 6-O-acetoacetyl Acorbic Acid 3
3.3. Synthesis of 6-O-(R)-3-hydroxybutyril Ascorbic Acid 5: Direct Transesterification of the Methyl (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate 4 with Ascorbic Acid 2
3.4. Preparative HPLC Purification of Product 5
3.5. Synthesis of Methyl (R)-3-O-trimethylsilyl-3-hydroxybutyrate 7b
3.6. Synthesis of 6-O-(R)-3-hydroxybutyril Ascorbic Acid 5: Transesterification of Methyl (R)-3-O-methoxymethyl-3-hydroxybutyrate 7c and Subsequent Deprotection of the Intermediate 8c
3.7. Antioxidant Activity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patil, B.S.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Chidambara Murthy, K.N.; Vikram, A. Bioactive compounds: Historical perspectives, opportunities, and Challenges. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8142–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, B.; Dhingra, A.K. Natural products: A lead for drug discovery and development. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4660–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, Y.; Silakari, O. Multifunctional compounds: Smart molecules for multifactorial diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 76, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, C.T.; Borisy, A.A.; Stockwell, B.R. Multicomponent therapeutics for networked systems. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Franco, J.L.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Welmaker, G.S.; Houghten, R.A. Shifting from the single to the multitarget paradigm in drug discovery. Drug Discov. 2013, 18, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esposito, C.; Johansson, C.; Di Micco, S. Novel strategies in drug development against multifactorial diseases. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérubé, G. An overview of molecular hybrids in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, M. Hybrid molecules incorporating natural products: Applications in cancer therapy, neurodegenerative disorders and beyond. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, L.F.; Bell, H.P.; Chandrasekhar, S. Natural product hybrids as new leads for drug discovery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3996–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macan, A.M.; Gazivoda Kraljević, T.; Raić-Malić, S. Therapeutic perspective of vitamin C and its derivatives. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Cullen, J.J.; Buettner, G.R. Ascorbic acid: Chemistry, biology and the treatment of cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, E.; del Carmen Ortega-Liébana, M.; Salido, S.; Salido, G.M.; Altarejos, J.; Rosado, J.A.; Redondo, P.C. Evaluation of the antiaggregant activity of ascorbyl phenolic esters with antioxidant properties. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, N.; Singh, M.; Dwivedi, P.; Ahluwalia, V.; Sangwan, R.S.; Mishra, B.B. Synthesis of food-grade 6-O-ascorbyl fatty esters and their semi-synthesis from low-value oils as resources. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Tarannuma, S.; Yariswamy, M.; Vivek, H.K.; Siddesha, J.M.; Angaswamy, N.; Vishwanath, B.S. Ascorbic acid 6-palmitate: A potent inhibitor of human and soybean lipoxygenase-dependent lipid peroxidation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 66, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spickenreither, M.; Braun, S.; Bernhardt, G.; Dove, S.; Buschauer, A. Novel 6-O-acylated vitamin C derivatives as hyaluronidase inhibitors with selectivity for bacterial lyases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 5313–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesato, S.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kaijima, T.; Tokuda, H.; Okuda, M.; Mou, X.Y.; Mukainaka, T.; Nishino, H. Inhibitory effects of 6-O-acylated L-ascorbic acids possessing a straight- or branched-acyl chain on Epstein-Barr virus activation. Cancer Lett. 2001, 166, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, M.; Carević, M.; Mihailović, M.; Veličković, D.; Dimitrijević, A.; Milosavić, N.; Bezbradica, D. Influence of fatty acid on lipase-catalyzed synthesis of ascorbyl esters and their free radical scavenging capacity. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2014, 62, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrat, N.; Aissa, I.; Sghaier, M.; Bouaziz, M.; Sellami, M.; Laouini, D.; Gargouri, Y. Lipophilization of ascorbic acid: A monolayer study and biological and antileishmanial activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9118–9127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, R.; Dharmappa, K.K.; Tarannum, S.; Jameel, N.M.; Kannum, S.A.; Ashrafulla, H.S.; Rai, L.; JMD’ Souza, C.; Shekhar, M.A.; Vishwanath, B.S. Chemical modification of ascorbic acid and evaluation of its lipophilic derivatives as inhibitors of secretory phospholipase A2 with anti-inflammatory activity. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 345, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-H.; Lv, Y.-Q.; Zhi, G.-Y.; Yuwen, L.-X. Kinetic biosynthesis of L-ascorbyl acetate by immobilized Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase (Lipozyme TLIM). Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 34, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilliraj, L.N.; Schiuma, G.; Lara, D.; Strazzabosco, G.; Clement, J.; Giovannini, P.P.; Trapella, C.; Narducci, M.; Rizzo, R. The evolution of ketosis: Potential impact on clinical conditions. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altayyar, M.; Nasser, J.A.; Thomopoulos, D.; Bruneau Jr., M. The implication of physiological ketosis on the cognitive brain: A narrative review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, T.R.; Stubbs, B.J.; Juul, S.E. Exogenous ketone bodies as promising neuroprotective agents for developmental brain injury. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 40, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Karwi, Q.G.; Ho, K.L.; Pherwani, S.; Ketema, E.B. Ketone metabolism in the failing heart. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goerlitzer, K.; Baltrusch, H.J. Strategies for the synthesis of nifedipine analogous esters from L-ascorbic acid. Pharmazie 2001, 56, 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, C.; Ferreira, M.L.; Barbosa, O.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Briand, L.E.; Fernan-dez-Lafuente, R. Novozym 435: The “perfect” lipase immobilized biocatalyst? Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 2380–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löfgren, J.; Görbe, T.; Oschmann, M.; Svedendahl Humble, M.; Bäckvall, J.E. Transesterification of a tertiary alcohol by engineered Candida antarctica Lipase A. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 1438–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Kunioka, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Soga, K. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies on poly(β-3-hydroxybutyrate) and a copolyester of β-hydroxybutyrate and β-hydroxyvalerate isolated from Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Macromolecules 1986, 19, 2860–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Ogawa, A.; Yoshida, S.; Kobayashi, J. Taurospongin A, a novel acetylenic fatty acid derivative inhibiting DNA polymerase β and HIV reverse transcriptase from sponge Hippospongia sp. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 3831–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Komatsu, T.; Maruyama, K. Allylic organometallic way to control acyclic stereochemistry and its application to the synthesis of carbohydrates. J. Organomet. Chem. 1985, 285, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, T.W.; Wuts, P.G.M. Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Prior, R.L.; Wu, X.; Schaich, K. Standardized methods for the determination of antioxidant capacity and phenolics in foods and dietary supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4290–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.J.; Ou, B.X.; Prior, R.L. The chemistry behind antioxidant capacity assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montone, C.M.; Zenezini Chiozzi, R.; Marchetti, N.; Cerrato, A.; Antonelli, M.; Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; Piovesana, S.; Laganà, A. Peptidomic approach for the identification of peptides with potential antioxidant and anti-hyperthensive effects derived from asparagus by-products. Molecules 2019, 24, 3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maietti, A.; Tedeschi, P.; Catani, M.; Stevanin, C.; Pasti, L.; Cavazzini, A.; Marchetti, N. Nutrient composition and antioxidant performances of bread-making products enriched with stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) leaves. Foods 2021, 10, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Acyl Donors | Catalyst | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Phenolic acids | H2SO4 | [12] |
| LCFA a (C12-C18) | H2SO4 | [13] |
| SCFA b, MCFA c and LCFA (C2-C18) | Lipase d | [18] |
| SCFA, MCFA, LCFA (C2-C18) chlorides or methyl esters e | C5H5N f; lipase g | [15] |
| vinyl acetate | Lipase h | [20] |
| SCFA, MCFA and LCFA (C4-C17) i methyl esters | H2SO4 | [16] |
| MCFA and LCFA (C6-C18) | H2SO4 | [19] |
| 4-Cl-butanoyl and 5-Cl-pentanoyl chlorides | C5H11N | [19] |
| Compound | PCL (nmolTE/mgds) 1 | DPPH (nmolTE/mgds) 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | (4.4 ± 0.1) 10−4 | (10 ± 1) 10−3 |
| 2 | 7.5 ± 0.3 | 15.5 ± 0.6 |
| 3 | 0.75 ± 0.02 | 1.92 ± 0.02 |
| 4 | (9.8 ± 0.1) 10−5 | (3.7 ± 1.2) 10−3 |
| 5 | 1.86 ± 0.05 | 4.88 ± 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venturi, V.; Lerin, L.A.; Presini, F.; Giovannini, P.P.; Catani, M.; Buratti, A.; Marchetti, N.; Dilliraj, L.N.; Aprile, S. Enzymatic Synthesis of Ascorbic Acid-Ketone Body Hybrids. Catalysts 2023, 13, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040691
Venturi V, Lerin LA, Presini F, Giovannini PP, Catani M, Buratti A, Marchetti N, Dilliraj LN, Aprile S. Enzymatic Synthesis of Ascorbic Acid-Ketone Body Hybrids. Catalysts. 2023; 13(4):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040691
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenturi, Valentina, Lindomar Alberto Lerin, Francesco Presini, Pier Paolo Giovannini, Martina Catani, Alessandro Buratti, Nicola Marchetti, Latha Nagamani Dilliraj, and Simona Aprile. 2023. "Enzymatic Synthesis of Ascorbic Acid-Ketone Body Hybrids" Catalysts 13, no. 4: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040691
APA StyleVenturi, V., Lerin, L. A., Presini, F., Giovannini, P. P., Catani, M., Buratti, A., Marchetti, N., Dilliraj, L. N., & Aprile, S. (2023). Enzymatic Synthesis of Ascorbic Acid-Ketone Body Hybrids. Catalysts, 13(4), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040691