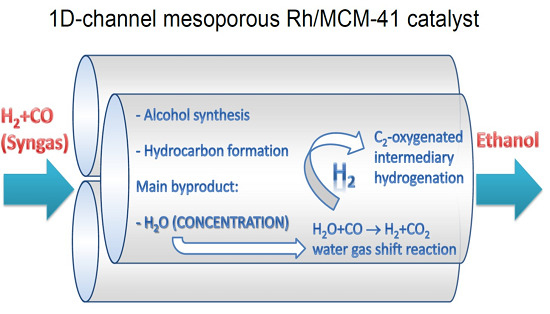
Synthesis of Ethanol from Syngas over Rh/MCM-41 Catalyst: Effect of Water on Product Selectivity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalytic Performances of Rh/SiO2 and Rh/MCM-41

| Catalyst | Syngas Ratio H2/CO | GHSV (mL/g·h) | Conversion (%) | TOF (s−1) | Total Selectivity to C2-oxygenated (%) | Selectivity between C2-oxygenated. (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol (%) | Acetaldehyde (%) | Acetic Acid (%) | ||||||
| Rh/SiO2 | 2/1 | 12000 | 2.8 | 0.039 | 34 | 21 | 54 | 24 |
| 2/1 * | 6000 | 1.6 | 0.011 | 18 | 8 | 83 | 9 | |
| 1/1 | 6000 | 2.1 | 0.022 | 32 | 16 | 51 | 34 | |
| Rh/MCM-41 | 2/1 | 3000 | 2.8 | 0.010 | 32 | 77 | 15 | 8 |
| 2/1 * | 3000 | 1.0 | 0.005 | 1 | 65 | 35 | 0 | |
| 1/1 | 3000 | 0.4 | 0.002 | 35 | 69 | 10 | 21 | |
2.1.1. Addition of Water Vapor and Lower Syngas Ratio (H2/CO = 1/1)




2.2. Catalyst Characterization
2.2.1. N2-Physisorption
2.2.2. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
| Catalyst | Condition | Surface Area (m2/g) | Change in Surface Area | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Rh0 | Rh3+ | Rh/Si | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | Binding energy (eV) | % | Binding energy (eV) | ||||||
| Rh/SiO2 | Pure support | 238 | - | 0.87 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Before catalytic testing | 236 | 0.5% * | 0.90 | 86.5 | 307.3 | 13.4 | 309.7 | 0.0057 | |
| After catalytic testing (280 °C, 20 bar, 12,000 mL/g·h): only syngas | 228 | 3.7% ** | 0.90 | 82.4 | 307.3 | 17.6 | 309.7 | 0.0064 | |
| After catalytic testing (280 °C, 20 bar, 6000 mL/g h): syngas and water | 212 | 10.3% ** | 0.88 | 100 | 307.2 | - | - | 0.0079 | |
| Rh/ MCM-41 | Pure support | 970 | - | 1.08 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Before catalytic testing | 961 | 0.9% * | 1.15 | 80.6 | 307.1 | 19.4 | 308.6 | 0.0079 | |
| After catalytic testing (280 °C, 20 bar, 3000 mL/g·h): only syngas | 875 | 9.0% ** | 1.04 | 90.8 | 307.4 | 9.2 | 309.3 | 0.0087 | |
| After catalytic testing (280 °C, 20 bar, 3000 mL/g·h): syngas and water | 776 | 19.3% ** | 0.94 | 100 | 307.1 | - | - | 0.0100 | |
2.2.3. Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD)

2.2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)

2.2.5. Temperature Programmed Reduction (TPR)

2.3. Interpretation of the Catalytic Performance of Rh/MCM-41 Compared to Rh/SiO2
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Catalyst Preparation and Characterization Techniques
3.2. Catalytic Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Energy Agency. Renewable Energy: Medium-Term Market (Market Trends and Projections to 2018); International Energy Agency—IEA: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Carriquiry, M.A. Flex-fuel vehicle adoption and dynamics of ethanol prices: Lessons from Brazil. Energy Policy 2013, 59, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, F.O. Ethanol Industry Outlook 2008–2013 Reports. Available online: http://www.afdc.energy.gov/data/ (accessed on 9 September 2014).
- Chabrelie, M.F.; Gruson, J.F.; Sagnes, C. Overview of Second-Generation Biofuel Projects; IFP Energies Nouvelles: Paris, Fance, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.C. Thermochemical Processing of Biomass Conversion into Fuels, Chemicals and Power; Wiley: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez Paris, R.; Lopez, L.; Barrientos, J.; Pardo, F.; Boutonnet, M.; Jaras, S. Chapter 3 catalytic conversion of biomass-derived synthesis gas to fuels. In Catalysis: Volume 27; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2015; Volume 27, pp. 62–143. [Google Scholar]
- Spivey, J.J.; Egbebi, A. Heterogeneous catalytic synthesis of ethanol from biomass-derived syngas. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1514–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, V.; Gangwal, S.K. A review of recent literature to search for an efficient catalytic process for the conversion of syngas to ethanol. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 814–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.T.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Bao, X.H. Temperature-programmed surface reaction study on C2-oxygenate synthesis over sio2 and nanoporous zeolitic material supported Rh-Mn catalysts. Surf. Interface Anal. 2001, 32, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Guo, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, G. Direct conversion of syngas to ethanol over Rh/Mn-supported on modified SBA-15 molecular sieves: Effect of supports. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Guo, C.-Y.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, G. Synthesis of ethanol from syngas over iron-promoted Rh immobilized on modified SBA-15 molecular sieve: Effect of iron loading. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechete, I.; Wang, Y.; Védrine, J.C. The past, present and future of heterogeneous catalysis. Catal. Today 2012, 189, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Prieto, G. The application of zeolites and periodic mesoporous silicas in the catalytic conversion of synthesis gas. Top. Catal. 2009, 52, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biz, S.; Occelli, M.L. Synthesis and characterization of mesostructured materials. Catal. Rev. 1998, 40, 329–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, H.; Takeuchi, K.; Matsuzaki, T.; Sugi, Y. Effect of metal dispersion on the activity and selectivity of Rh/SiO2 catalyst for high pressure co hydrogenation. Chem. Lett. 1984, 13, 1607–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, R.P.; Bell, A.T. Influence of particle size on carbon monoxide hydrogenation over silica- and lanthana-supported rhodium. Appl. Catal. 1987, 34, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tago, T.; Hanaoka, T.; Dhupatemiya, P.; Hayashi, H.; Kishida, M.; Wakabayashi, K. Effects of Rh content on catalytic behavior in CO hydrogenation with Rh-silica catalysts prepared using microemulsion. Catal. Lett. 2000, 64, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.T.; Zhao, H.; Ma, D.; Miao, S.J.; Cheng, M.J.; Bao, X.H. The effect of Rh particle size on the catalytic performance of porous silica supported rhodium catalysts for co hydrogenation. Z. Phys. Chem. 2005, 219, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, L.; Velasco, J.; Cabrera, S.; Boutonnet, M.; Järås, S. Effect of syngas conversion and catalyst reduction temperature in the synthesis of ethanol: Concentration of water vapor in mesoporous Rh/MCM-41 catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2015, 69, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakov, A.Y.; Zholobenko, V.L.; Bechara, R.; Durand, D. Impact of aqueous impregnation on the long-range ordering and mesoporous structure of cobalt containing MCM-41 and SBA-15 materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 79, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, M.V.; Varkey, S.P.; Herskowitz, M.; Regev, O.; Pevzner, S.; Sen, T.; Luz, Z. Wetting stability of Si-MCM-41 mesoporous material in neutral, acidic and basic aqueous solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 33, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodziński, A.; Bonarowska, M. Relation between crystallite size and dispersion on supported metal catalysts. Langmuir 1997, 13, 5613–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehwald, H.; Ewald, H.; Gutschick, D.; Hermann, M.; Miessner, H.; Ohlmann, G.; Schierhorn, E. A bicomponent catalyst for the selective formation of ethanol from synthesis gas. Appl. Catal. 1991, 76, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.; McCabe, R.W. Effects of oxidation/reduction treatments on the morphology of silica-supported rhodium catalysts. J. Catal. 1987, 107, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.D.; McNicol, B.D.; de Baas, J.H.; Kloet, S.C.; Jenkins, J.W. Determination of reducibility and identification of alloying in copper-nickel-on-silica catalysts by temperature-programmed reduction. J. Catal. 1975, 37, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpranot, J.; Goodwin, J.G., Jr.; Sayari, A. Synthesis and characteristics of MCM-41 supported coru catalysts. Catal. Today 2002, 77, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, D.; Rousseau, R.; Kathmann, S.M.; Glezakou, V.-A.; Engelhard, M.H.; Jiang, W.; Wang, C.; Gerber, M.A.; White, J.F.; Stevens, D.J. Ethanol synthesis from syngas over Rh-based/SiO2 catalysts: A combined experimental and theoretical modeling study. J. Catal. 2010, 271, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.C.; Stevens, R., Jr.; Khatri, R. Mechanism of C2+ oxygenate synthesis on Rh catalysts. Top. Catal. 2005, 32, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.B.; Højlund Nielsen, P.E. Methanol synthesis. In Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis; Ertl, G., Knözinger, H., Weitkamp, J., Eds.; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bowker, M. On the mechanism of ethanol synthesis on rhodium. Catal. Today 1992, 15, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medford, A.J.; Lausche, A.C.; Abild-Pedersen, F.; Temel, B.; Schjodt, N.C.; Norskov, J.K.; Studt, F. Activity and selectivity trends in synthesis gas conversion to higher alcohols. Top. Catal. 2014, 57, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.M.; Liu, P. Mechanism of ethanol synthesis from syngas on Rh(111). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13054–13061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, S.; El Haskouri, J.; Guillem, C.; Latorre, J.; Beltrán-Porter, A.; Beltrán-Porter, D.; Marcos, M.D.; Amorós, P. Generalised syntheses of ordered mesoporous oxides: The atrane route. Solid State Sci. 2000, 2, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haskouri, J.; Cabrera, S.; Guillem, C.; Latorre, J.; Beltrán, A.; Beltrán, D.; Marcos, M.D.; Amorós, P. Atrane precursors in the one-pot surfactant-assisted synthesis of high zirconium content porous silicas. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 5015–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomew, C.H.; Farrauto, R.J. Fundamentals of Industrial Catalytic Processes, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, P. Introduction to Chemical Adsorption Analytical Techniques and Their Applications to Catalysis; Micromeritics Instrument Corp.: Norcross, GA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, R.; Boutonnet, M.; Järås, S. On-line gas chromatographic analysis of higher alcohol synthesis products from syngas. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1247, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsevier. Chapter 15 quantitative analysis by gas chromatography measurement of peak area and derivation of sample composition. In Journal of Chromatography Library; Georges, G., Claude, L.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA; Tokyo, Japan, 1988; Volume 42, pp. 629–659. [Google Scholar]
- Madon, R.J.; Boudart, M. Experimental criterion for the absence of artifacts in the measurement of rates of heterogeneous catalytic reactions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund. 1982, 21, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez, L.; Velasco, J.; Montes, V.; Marinas, A.; Cabrera, S.; Boutonnet, M.; Järås, S. Synthesis of Ethanol from Syngas over Rh/MCM-41 Catalyst: Effect of Water on Product Selectivity. Catalysts 2015, 5, 1737-1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5041737
Lopez L, Velasco J, Montes V, Marinas A, Cabrera S, Boutonnet M, Järås S. Synthesis of Ethanol from Syngas over Rh/MCM-41 Catalyst: Effect of Water on Product Selectivity. Catalysts. 2015; 5(4):1737-1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5041737
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez, Luis, Jorge Velasco, Vicente Montes, Alberto Marinas, Saul Cabrera, Magali Boutonnet, and Sven Järås. 2015. "Synthesis of Ethanol from Syngas over Rh/MCM-41 Catalyst: Effect of Water on Product Selectivity" Catalysts 5, no. 4: 1737-1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5041737
APA StyleLopez, L., Velasco, J., Montes, V., Marinas, A., Cabrera, S., Boutonnet, M., & Järås, S. (2015). Synthesis of Ethanol from Syngas over Rh/MCM-41 Catalyst: Effect of Water on Product Selectivity. Catalysts, 5(4), 1737-1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5041737