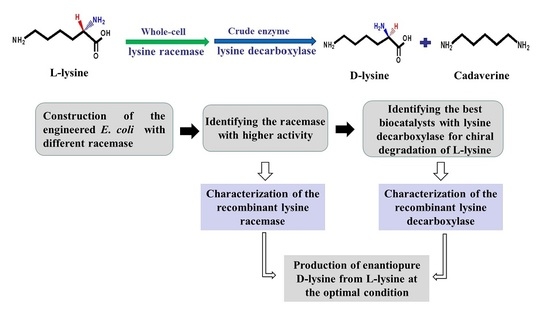
Efficient Production of Enantiopure d-Lysine from l-Lysine by a Two-Enzyme Cascade System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Construction of a Highly Efficient E. coli Whole-Cell Biocatalyst for dl-Lysine Production
2.2. A Two-Step Process for Enantiopure d-Lysine Preparation
2.3. Optimization of Reaction Conditions for the Two-Step d-Lysine Production Process
2.3.1. Characterization of the Whole-Cell BL21-LYR
2.3.2. Characterization of the Recombinant Lysine Decarboxylase
2.4. Determining the Optimal Condition of the Two-Step d-Lysine Production Process
2.5. d-Lysine Production at Different Substrate Concentrations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Enzymes
4.2. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.3. Construction of Plasmids
4.4. Expression of Recombinant Proteins in E. coli BL21(DE3)
4.5. Racemase and Decarboxylase Activity Characterization
4.6. The Microbial Production of Enantiopure d-Lysine and Cadaverine
4.7. Analysis Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leuchtenberger, W.; Huthmacher, K.; Drauz, K. Biotechnological production of amino acids and derivatives: Current status and prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 69, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, H.M.; Feix, J.B. Effects of d-lysine substitutions on the activity and selectivity of antimicrobial peptide CM15. Polymers 2011, 3, 2088–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, E.; Furui, M.; Seko, H.; Shibatani, T. d-Lysine production from l-lysine by successive chemical racemization and microbial asymmetric degradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 47, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jiao, Q.; Yin, X. Preparation of d-lysine by chemical reaction and microbial asymmetric transformation. Front. Chem. Eng. China 2008, 2, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhu, H. Distribution, industrial applications, and enzymatic synthesis of d-amino acids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3341–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastassiadis, S. l-Lysine fermentation. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2007, 1, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, S.B.; Cava, F. Environmental roles of microbial amino acid racemases. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, Y.C.; Kao, C.H.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, C.C.; Hu, H.Y.; Hsu, W.H. Biochemical characterization of a novel lysine racemase from Proteus mirabilis BCRC10725. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 1914–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Hemmi, H.; Yoshimura, T. Lysine racemase from a lactic acid bacterium, Oenococcus oeni: Structural basis of substrate specificity. J. Biochem. 2012, 152, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, Y.; Iwai, S.; Nishiya, Y.; Kumagai, S.; Yamada, T.; Azuma, M. Identification and characterization of d-succinylase, and a proposed enzymatic method for d-amino acid synthesis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 2041–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, K.; Tamauchi, H.; Fuhshuku, K.-I.; Nagasawa, S.; Asano, Y. A simple enzymatic method for production of a wide variety of d-amino acids using l-amino acid oxidase from Rhodococcus sp. AIU Z-35-1. Enzym. Res. 2010, 2010, 567210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Haruta, H.; Ikeda, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Murakami, M.; Moriguchi, M.; Wakayama, M. Engineering the substrate specificity of alcaligenes d-aminoacylase useful for the production of d-amino acids by optical resolution. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 3247–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukin, A.V.; Boeriu, C.G.; Scott, E.L.; Sanders, J.P.M.; Franssen, M.C.R. An efficient enzymatic synthesis of 5-aminovaleric acid. J. Mol. Catal. B 2010, 65, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, A.; Xiang, D.F.; Xu, C.; Song, L.; Yew, W.S.; Raushel, F.M.; Gerlt, J.A. Evolution of enzymatic activities in the enolase superfamily: N-succinylamino acid racemase and a new pathway for the irreversible conversion of d- to l-amino acids. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 4455–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.M.; Kuan, Y.C.; Chu, C.H.; Hsu, W.H.; Wang, W.C. Crystal structures of lysine-preferred racemases, the non-antibiotic selectable markers for transgenic plants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Cao, W.; Zhang, B.; Chen, K.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, P. Engineering a pyridoxal 5′-phosphate supply for cadaverine production by using Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen-munsberg, F.; Vickers, C.; Kohls, H.; Land, H.; Mallin, H.; Nobili, A.; Skalden, L.; van den Bergh, T.; Joosten, H.; Berglund, P.; et al. Bioinformatic analysis of a PLP-dependent enzyme superfamily suitable for biocatalytic applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 566–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Shin, J.H.; Bhatia, S.K.; Sathiyanarayanan, G.; Seo, H.M.; Choi, K.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Park, K. Optimization of direct lysine decarboxylase biotransformation for cadaverine production with whole-cell biocatalysts at high lysine concentration. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranova, V.; Zahradnickova, H.; Janous, D.; Skene, K.R.; Matharu, A.S.; Rejsek, K.; Formanek, P. The significance of d-amino acids in soil, fate and utilization by microbes and plants: Review and identification of knowledge gaps. Plant Soil 2012, 354, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radkov, A.D.; Moe, L.A. Bacterial synthesis of d-amino acids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5363–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, N. d-Amino acids in living higher organisms. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2002, 32, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, B.D.; VanDemark, A.P.; Heroux, A.; Hill, C.P.; Kay, M.S. Potent d-peptide inhibitors of HIV-1 entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16828–16833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.M.; Duan, X.; Huang, A.S.; Liu, C.Y.; Ming, G.; Song, H.; Snyder, S.H. Aspartate racemase, generating neuronal d-aspartate, regulates adult neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3175–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couñago, R.M.; Davlieva, M.; Strych, U.; Hill, R.E.; Krause, K.L. Biochemical and structural characterization of alanine racemase from Bacillus anthracis (Ames). BMC Struct. Biol. 2009, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, T.; Esak, N. Amino acid racemases: Functions and mechanisms. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 96, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagni, N.; Creus, J.; Pistocchi, R. Distribution of cadaverine and lysine decarboxylase activity in Nicotiana glauca plants. J. Plant Physiol. 1986, 125, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogle, E.J.; Toney, M.D. Analysis of catalytic determinants of diaminopimelate and ornithine decarboxylases using alternate substrates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Proteins Proteomics. 2011, 1814, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreini, C.; Bertini, I.; Cavallaro, G.; Holliday, G.L.; Thornton, J.M. Metal ions in biological catalysis: From enzyme databases to general principles. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 13, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condon Adaptation Tool Division Home Page. Available online: http://www.jcat.de/ (accessed on 20 November 2015).






| l-Lysine (mM) | d-Lysine (mM) | Cadaverine (mM) | d-Lysine Yield | Enantiomeric Excess |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 680 | 287.2 | 323.5 | 46.9% | 99.5% |
| 1030 | 446.0 | 479 | 48.1% | 99.5% |
| 1370 | 601.0 | 628.5 | 48.8% | 99.4% |
| 1710 | 750.7 | 783.4 | 48.8% | 99.3% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Cao, W.; Ying, H.; Chen, K.; Ouyang, P. Efficient Production of Enantiopure d-Lysine from l-Lysine by a Two-Enzyme Cascade System. Catalysts 2016, 6, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6110168
Wang X, Yang L, Cao W, Ying H, Chen K, Ouyang P. Efficient Production of Enantiopure d-Lysine from l-Lysine by a Two-Enzyme Cascade System. Catalysts. 2016; 6(11):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6110168
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin, Li Yang, Weijia Cao, Hanxiao Ying, Kequan Chen, and Pingkai Ouyang. 2016. "Efficient Production of Enantiopure d-Lysine from l-Lysine by a Two-Enzyme Cascade System" Catalysts 6, no. 11: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6110168
APA StyleWang, X., Yang, L., Cao, W., Ying, H., Chen, K., & Ouyang, P. (2016). Efficient Production of Enantiopure d-Lysine from l-Lysine by a Two-Enzyme Cascade System. Catalysts, 6(11), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6110168