Efficient Degradation of Aqueous Carbamazepine by Bismuth Oxybromide-Activated Peroxide Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. CBZ Degradation
2.1.1. Degradation of CBZ under Pure Water Background
2.1.2. Degradation of CBZ under Actual Water Background
2.2. Stability of BiOBr as a PMS Activator
2.3. Reactive Species
2.4. Bromate Formation
2.5. Detoxification Performance
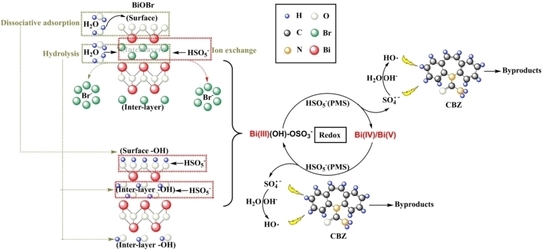
2.6. Degradation Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of BiOX Microstructures
3.3. Experimental Procedures
3.4. Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, X.; Metcalfe, C.D. Determination of carbamazepine and its metabolites in aqueous samples using liquid chromatography−electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3731–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternes, T.A. Occurrence of drugs in german sewage treatment plants and rivers. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3245–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberer, T. Tracking persistent pharmaceutical residues from municipal sewage to drinking water. J. Hydrol. 2002, 266, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginebreda, A.; Muñoz, I.; de Alda, M.L.; Brix, R.; López-Doval, J.; Barceló, D. Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in rivers: Relationships between hazard indexes and aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity indexes in the Llobregat River (NE Spain). Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benotti, M.J.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.J.; Holady, J.C.; Stanford, B.D.; Snyder, S.A. Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in us drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Geißen, S.U.; Gal, C. Carbamazepine and diclofenac: Removal in wastewater treatment plants and occurrence in water bodies. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clara, M.; Strenn, B.; Kreuzinger, N. Carbamazepine as a possible anthropogenic marker in the aquatic environment: Investigations on the behaviour of carbamazepine in wastewater treatment and during groundwater infiltration. Water Res. 2004, 38, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joss, A.; Keller, E.; Alder, A.C.; Göbel, A.; McArdell, C.S.; Ternes, T.; Siegrist, H. Removal of pharmaceuticals and fragrances in biological wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3139–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjenovic, J.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Analysis of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and removal using a membrane bioreactor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballa, M.; Omil, F.; Lema, J.M.; Llompart, M.; Garcia-Jares, C.; Rodrı́guez, I.; Gómez, M.; Ternes, T. Behavior of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and hormones in a sewage treatment plant. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2918–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, S.; Carballa, M.; Omil, F.; Lema, J.M. How are pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) removed from urban wastewaters? Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Li, F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, S.; Li, B. Construction of amorphous TiO2/BiOBr heterojunctions via facets coupling for enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 292, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Huang, B.; Dai, Y. Engineering BiOX (X = Cl, Br, I) nanostructures for highly efficient photocatalytic applications. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2009–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, S.; Qian, C.; He, L.; Chen, K.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; Ye, M. The role of adsorption in photocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen under visible light irradiation by BiOBr microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 297, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Ma, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Lin, L.; Zhang, C. Efficient degradation of atrazine by magnetic porous copper ferrite catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation via the formation of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5431–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, H.; Croué, J.P. Production of sulfate radical from peroxymonosulfate induced by a magnetically separable CuFe2O4 spinel in water: Efficiency, stability, and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hong, C. Effect of hydrogen peroxide, periodate and persulfate on photocatalysis of 2-chlorobiphenyl in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Effect of inorganic, synthetic and naturally occurring chelating agents on Fe(II) mediated advanced oxidation of chlorophenols. Water Res. 2009, 43, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Shan, L.; Zhang, W.; Shao, X.; Niu, R. Degradation efficiencies of azo dye acid orange 7 by the interaction of heat, uv and anions with common oxidants: Persulfate, peroxymonosulfate and hydrogen peroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Sonntag, C. Advanced oxidation processes: Mechanistic aspects. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.; Lopata, V.J. Some phase relationships between basic bismuth chlorides in aqueous solutions at 25 °C. Can. J. Chem. 1987, 65, 2824–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pignatello, J.J.; Ma, J.; Mitch, W.A. Comparison of halide impacts on the efficiency of contaminant degradation by sulfate and hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, D.A. Kinetics and mechanism of oxidations by peroxydisulfate. Chem. Rev. 1962, 62, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Choi, H.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Iron–cobalt mixed oxide nanocatalysts: Heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate activation, cobalt leaching, and ferromagnetic properties for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 88, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Stathatos, E.; Dionysiou, D.D. Heterogeneous activation of oxone using Co3O4. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13052–13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, O.S.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Mechanism of base activation of persulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6423–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Jiang, D.; Gao, E.; Sun, S. Photoreduction of CO2 on BiOCl nanoplates with the assistance of photoinduced oxygen vacancies. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Parsons, R.; Jordan, J. Standard Potentials in Aqueous Solution; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 180–187. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, J.; Torrent-Sucarrat, M.; Anglada, J.M. The reactions of SO3 with HO2 radical and H2O…HO2 radical complex. Theoretical study on the atmospheric formation of HSO5 and H2SO4. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, L.; Jin, X.; Liu, C.; Ding, C.; Xie, H.; Chu, K.; Wong, P. Thickness-ultrathin and bismuth-rich strategies for BiOBr to enhance photoreduction of CO2 into solar fuels. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 187, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogna, D.; Marotta, R.; Andreozzi, R.; Napolitano, A.; d’Ischia, M. Kinetic and chemical assessment of the UV/H2O2 treatment of antiepileptic drug carbamazepine. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutze, H.V.; Bakkour, R.; Kerlin, N.; von Sonntag, C.; Schmidt, T.C. Formation of bromate in sulfate radical based oxidation: Mechanistic aspects and suppression by dissolved organic matter. Water Res. 2014, 53, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Shang, C. Bromate formation from bromide oxidation by the UV/persulfate process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8976–8983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Fang, J.; Chen, L. Influence of pH on the formation of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in the UV/peroxymonosulfate system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9308–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsalvo, V.M.; Lopez, J.; Munoz, M.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodriguez, J.J. Application of Fenton-like oxidation as pre-treatment for carbamazepine biodegradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.F.; Qu, L.; Yang, H.; Chu, W. Degradation of carbamazepine by Fe(II)-activated persulfate process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghrir, R.; Drogui, P.; Dimboukou-Mpira, A.; El Khakani, M. Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of carbamazepine using Ti/TiO2 nanostructured electrodes deposited by means of a pulsed laser deposition process. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2756–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.; Drogui, P.; Zaviska, F.; Brar, S.K. Sonochemical degradation of the persistent pharmaceutical carbamazepine. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Chemical Structure | O−O Bond Energy (E, kJ∙mol−1) | pKa | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2 |  | 213.3 | pKa = 11 | [19,20] |
| PS |  | 140 | no change in dissociation form pH > 3 | [19] |
| PMS |  | 140 < EPMS < 213.3 | pKa = 9.4 | [16,19] |
| DOM (mg/L) | Bicarbonate (mg/L) | (mg/L) | pH | NO3−-N (mg/L) | UV254 (cm−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | 3.73 | 107.06 | 3.43 | 7.84 | 0.24 | 3.38 |
| QZL | 6.61 | 97.95 | 2.80 | 7.83 | 0.25 | 4.99 |
| ESF | 3.17 | 100.11 | 2.36 | 7.82 | 0.01 | 3.10 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Chu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Shao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ye, M. Efficient Degradation of Aqueous Carbamazepine by Bismuth Oxybromide-Activated Peroxide Oxidation. Catalysts 2017, 7, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7110315
Zhang T, Chu S, Li J, Wang L, Chen R, Shao Y, Liu X, Ye M. Efficient Degradation of Aqueous Carbamazepine by Bismuth Oxybromide-Activated Peroxide Oxidation. Catalysts. 2017; 7(11):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7110315
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tuqiao, Shipeng Chu, Jian Li, Lili Wang, Rong Chen, Yu Shao, Xiaowei Liu, and Miaomiao Ye. 2017. "Efficient Degradation of Aqueous Carbamazepine by Bismuth Oxybromide-Activated Peroxide Oxidation" Catalysts 7, no. 11: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7110315
APA StyleZhang, T., Chu, S., Li, J., Wang, L., Chen, R., Shao, Y., Liu, X., & Ye, M. (2017). Efficient Degradation of Aqueous Carbamazepine by Bismuth Oxybromide-Activated Peroxide Oxidation. Catalysts, 7(11), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7110315