Mechanistic Analysis of Water Oxidation Catalyst cis-[Ru(bpy)2(H2O)2]2+: Effect of Dimerization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
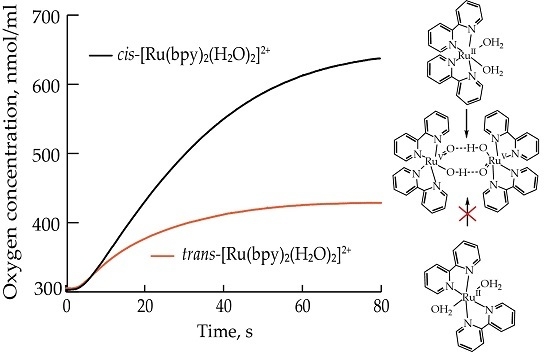
2.1. Oxygen Evolution Measurements
2.2. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Measurements
2.3. Density Functional Theory Calculations
3. Discussion
3.1. Oxygen Evolution by cis-[Ru(bpy)2(H2O)2]2+ with DFT and EPR Characterization
3.2. Comparison to Other Single-Site Ru WOC’s
4. Materials and Methods
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hull, J.F.; Balcells, D.; Blakemore, J.D.; Incarvito, C.D.; Eisenstein, O.; Brudvig, G.W.; Crabtree, R.H. Highly active and robust Cp* iridium complexes for catalytic water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8730–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakemore, J.D.; Schley, N.D.; Balcells, D.; Hull, J.F.; Olack, G.W.; Incarvito, C.D.; Eisenstein, O.; Brudvig, G.W.; Crabtree, R.H. Half-sandwich iridium complexes for homogeneous water-oxidation catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16017–16029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasylenko, D.J.; Palmer, R.D.; Berlinguette, C.P. Homogeneous water oxidation catalysts containing a single metal site. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, R.; Thummel, R.P. A new family of Ru complexes for water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12802–12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concepcion, J.J.; Jurss, J.W.; Templeton, J.L.; Meyer, T.J. One site is enough. Catalytic water oxidation by [Ru(tpy)(bpm)(OH2)]2+ and [Ru(tpy)(bpz)(OH2)]2+. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16462–16463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaveevivitchai, N.; Zong, R.; Tseng, H.W.; Chitta, R.; Thummel, R.P. Further observations on water oxidation catalyzed by mononuclear Ru(II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 2930–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, M.; Tajima, S.; Komia, M.; Yamazakia, H. Highly active and tunable catalysts for O2 evolution from water based on mononuclear ruthenium(II) monoaquo complexe. Dalt. Trans. 2011, 40, 3802–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gersten, S.W.; Samuels, G.J.; Meyer, T.J. Catalytic oxidation of water by an oxo-bridged ruthenium dimer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 4029–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Tsuge, K.; Tanaka, K. Electrochemical oxidation of water to dioxygen catalyzed by the oxidized form of the bis(ruthenium-hydroxo) complex in H2O. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 1479–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.C.; Maji, S.; Francàs, L.; Böhnisch, T.; Dechert, S.; Llobet, A.; Meyer, F. Highly efficient binuclear ruthenium catalyst for water oxidation. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Tseng, H.W.; Zong, R.; Wang, D.; Thummel, R. Preparation and study of a family of dinuclear Ru(II) complexes that catalyze the decomposition of water. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 1835–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limburg, B.; Bouwman, E.; Bonnet, S. Molecular water oxidation catalysts based on transition metals and their decomposition pathways. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, I.; Ertem, M.Z.; Maji, S.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Keidel, A.; Kuhlmann, U.; Hildebrandt, P.; Cramer, C.J.; Batista, V.S.; Llobet, A. A self-improved water-oxidation catalyst: Is one site really enough? Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2014, 126, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, I.; Maji, S.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Llobet, A. Oxo-bridge scenario behind single-site water-oxidation catalysts. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubonouchi, Y.; Lin, S.; Parent, A.R.; Brudvig, G.W.; Sakai, K. Light-induced water oxidation catalyzed by an oxido-bridged triruthenium complex with a Ru–O–Ru–O–Ru motif. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8018–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, B.; Wilson, S.R.; Hodgson, D.J.; Meyer, T.J. Cis-trans photoisomerization in Ru(bpy)2(OH2)22+. Crystal structure of trans-[Ru(bpy)2(OH2)(OH)](ClO4)2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J.C.; Meyer, T.J. Redox properties and ligand loss chemistry in aqua/hydroxo/oxo complexes derived from cis-and trans-[(bpy)2RuII(OH2)2]2+. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 3283–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, X.; Ertem, M.Z.; Vigara, L.; Todorova, T.K.; Chen, W.; Rocha, R.C.; Aquilante, F.; Cramer, C.J.; Gagliardi, L.; Llobet, A. The cis-[RuII(bpy)2(H2O)2]2+ water-oxidation catalyst revisited. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 7745–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, N.; Vigara, L.; Cady, C.; Miró, P.; Huang, P.; Hammarström, L.; Styring, S.; Leidel, N.; Dau, H.; Haumann, M.; et al. Electronic structure of oxidized complexes derived from cis-[RuII(bpy)2(H2O)2]2+ and its photoisomerization mechanism. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 11134–11142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengel, A.C.; Griffith, W.P. Studies on transition-metal oxo and nitrido complexes. 12. Synthesis, spectroscopic properties, and reactions of stable ruthenium(V) and osmium(V) oxo complexes containing α-hydroxy carboxylate and α-amino carboxylate ligands. Inorg. Chem. 1991, 30, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Hurst, J.K. Dynamical investigations of the catalytic mechanisms of water oxidation by the [(bpy)2Ru(OH2)]2O4+ ion. Inorganica Chim. Acta 1994, 226, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonshiram, D.; Alperovich, I.; Concepcion, J.J.; Meyer, T.J.; Pushkar, Y. Experimental demonstration of radicaloid character in a RuV=O intermediate in catalytic water oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 3765–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moonshiram, D.; Jurss, J.W.; Concepcion, J.J.; Zakharova, T.; Alperovich, I.; Meyer, T.J.; Pushkar, Y. Structure and electronic configurations of the intermediates of water oxidation in blue ruthenium dimer catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4625–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Bozoglian, F.; Mandal, S.; Stewart, B.; Privalov, T.; Llobet, A.; Sun, L. A molecular ruthenium catalyst with water-oxidation activity comparable to that of photosystem II. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushkar, Y.; Moonshiram, D.; Purohit, V.; Yan, L.; Alperovich, I. Spectroscopic analysis of catalytic water oxidation by [RuII(bpy)(tpy)H2O]2+ suggests that RuV=O is not a rate-limiting intermediate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11938–11945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moonshiram, D.; Purohit, V.; Concepcion, J.J.; Meyer, T.J.; Pushkar, Y. Mechanism of catalytic water oxidation by the ruthenium blue dimer catalyst: Comparative study in D2O versus H2O. Materials 2013, 6, 392–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zong, R.; Pushkar, Y. Unexpected ligand lability in condition of water oxidation catalysis. J. Catal. 2015, 330, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.J.; Thompson, M.S.; Pipes, D.W.; Meyer, T.J. Redox and spectral properties of monooxo polypyridyl complexes of ruthenium and osmium in aqueous media. Inorg. Chem. 1984, 23, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasylenko, D.J.; Ganesamoorthy, C.; Kolvisto, B.D.; Henderson, M.A.; Berllnguette, C.P. Insight into water oxidation by mononuclear polypyridyl Ru catalysts. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 2202–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.G.; Sanguantrakun, N.; Schulze, B.; Schubert, U.S.; Berlinguette, C.P.; Wasylenko, D.J.; Ganesamoorthy, C.C.; Kolvisto, B.D.; Henderson, M.A.; Berllnguette, C.P.; et al. Unraveling the roles of the acid medium, experimental probes, and terminal oxidant, (NH4)2[Ce(NO3)6], in the study of a homogeneous water oxidation catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 49, 2202–2209. [Google Scholar]
- Concepcion, J.J.; Jurss, J.W.; Norris, M.R.; Chen, Z.; Templeton, J.L.; Meyer, T.J. Catalytic water oxidation by single-site ruthenium catalysts. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Molecule 1 | Free Energy 2 (kcal/mol) | E0/V Calculated | E0/V Experimental |
| RuII-2H2O; 2H2O | −3.601133 × 106 | - | - |
| RuIII-2H2O; 2H2O | −3.601006 × 106 | - | - |
| RuIII-2H2O; 2H2O + 1e− = RuII-2H2O; 2H2O | - | 1.04 [25] | 0.88 [17] |
| RuIV-OH,OH; 2H2O | −3.600339 × 106 | - | - |
| RuIV-OH,OH; 2H2O + 1e− + 2H+ = RuIII-2H2O; 2H2O | - | 1.18 [25] | 1.19 [17] |
| RuV=O,OH; 2H2O | −3.599935 × 106 | - | - |
| RuV=O,OH; 2H2O + 1e− + H+ = RuIV-OH,OH; 2H2O | - | 1.47 [25] | 1.34 [17] |
| Molecule 2 | Free Energy (kcal/mol) | Change in Free Energy (kcal/mol) | |
| H2ORuIIIORuIIIOH2 | −6.961716 × 106 | - | |
| O2 | −9.433726 × 104 | - | |
| H2O | −4.794981 × 104 | - | |
| 2RuV=O,OH + H2O = H2ORuIIIORuIIIOH2 + O2 | - | −36.04 | |
| [RuV=O,OH]2 | −7.008076 × 106 | - | |
| 2RuV=O,OH = [RuV=O,-OH]2 | - | −6.28 | |
| HORuIVOORuIVOH | −7.008084 × 106 | - | |
| [RuV=O,-OH]2 = HORuIVOORuIVOH | - | −7.67 | |
| HORuIVOORuIVOH + H2O = H2ORuIIIORuIIIOH2 + O2 | - | −22.09 | |
| Molecule | Free Energy (kcal/mol) | E0/V Calculated | E0/V Experimental |
|---|---|---|---|
| RuII-H2O; 2H2O | −3.708209 × 106 | - | - |
| RuIII-H2O; 2H2O | −3.708082 × 106 | - | - |
| RuIII-H2O; 2H2O + 1e− = RuII-H2O; 2H2O | - | 1.06 [25] | 1.04 [28] |
| RuIV=O; 2H2O | −3.707414 × 106 | - | - |
| RuIV=O; 2H2O + 1e− + 2H+ = RuIII-H2O ; 2H2O | - | 1.23 [25] | 1.39 [28] |
| RuV=O; 2H2O | −3.707418 × 106 | - | - |
| RuV=O; 2H2O + 1e− = RuII-H2O ; 2H2O | - | 2.13 [25] | 1.60 [5], 1.73 [29], 1.80 [30] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erdman, D.; Pineda-Galvan, Y.; Pushkar, Y. Mechanistic Analysis of Water Oxidation Catalyst cis-[Ru(bpy)2(H2O)2]2+: Effect of Dimerization. Catalysts 2017, 7, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020039
Erdman D, Pineda-Galvan Y, Pushkar Y. Mechanistic Analysis of Water Oxidation Catalyst cis-[Ru(bpy)2(H2O)2]2+: Effect of Dimerization. Catalysts. 2017; 7(2):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020039
Chicago/Turabian StyleErdman, Darren, Yuliana Pineda-Galvan, and Yulia Pushkar. 2017. "Mechanistic Analysis of Water Oxidation Catalyst cis-[Ru(bpy)2(H2O)2]2+: Effect of Dimerization" Catalysts 7, no. 2: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020039
APA StyleErdman, D., Pineda-Galvan, Y., & Pushkar, Y. (2017). Mechanistic Analysis of Water Oxidation Catalyst cis-[Ru(bpy)2(H2O)2]2+: Effect of Dimerization. Catalysts, 7(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020039