Effect of CO Concentration on the α-Value of Plasma-Synthesized Co/C Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Mn = mole fraction of a hydrocarbon with chain length n
- n = number of total carbon atoms
- α = probability of chain growth (α < 1)
- (1 − α) = probability of chain termination
2. Results
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
2.1.1. BET Surface Area Analysis
2.1.2. Elemental Analysis
2.1.3. Microscopy: Elemental and Particle Size Analysis
2.1.4. XRD and RQA Analysis
2.1.5. XANES Analysis
2.2. Catalyst Activity Testing
2.3. Catalyst Selectivity
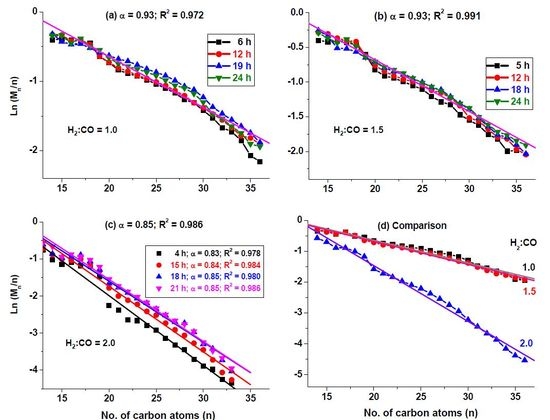
2.4. Determination of α-Values
3. Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Research Objectives
- (i)
- Use a specially designed liquid sampling column to provide empirical evidence for the gradual development of the longer-chain hydrocarbons from real-time liquid-phase analysis, illustrating hydrocarbon-chain propagation with TOS;
- (ii)
- Determine the true α-value of the plasma-synthesized Co/C catalyst as being above 0.85, which could only be ascertained after over 15 h on stream, since any α-values determined below this time period may be misleading;
- (iii)
- Establish that the application of CO-rich syngas, which may in future be derived from biomass, is a viable alternative that can replace the current use of H2-rich syngas in generating high molecular FTS products.
3.2. Application of Biomass and Bio-Syngas as Game Changer in Fuel Industry
3.3. Catalyst Selectivity and α-Values
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Catalyst Synthesis: Reagents
4.2. Catalyst Characterization
4.3. Reactor Designs
4.3.1. Plasma Synthesis Reactor
4.3.2. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Reactor (3-φ-CSTSR)
4.4. Liquid Sampling
4.5. Catalyst Testing
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASF | Anderson-Schulz-Flory distribution |
| ASAP | Accelerated surface area porosimeter (Micromeritics ASAP-2020) instrument |
| BET | Brunauer-Emmett-Teller method for specific surface area analysis |
| EDX | Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| FCC | Face centred cubic structure |
| FTS | Fischer-Tropsch synthesis |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| GHSV | Gas hourly space velocity |
| HCP | Hexagonal closed packing structure |
| ICP-MS | Inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry |
| LT-FTS | Low-temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthesis |
| RQA | Rietveld quantitative analysis |
| RTP | Room temperature and pressure |
| SASOL | South African Synthetic Oil Ltd. |
| SCCM | Standard cubic centimetre per minute |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SPS | Suspension plasma-spray technology |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| TOS | Time-on-stream |
| XANES | X-ray absorption near-edge structure analysis by Synchrotron light |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction analysis |
| 3-φ-CSTSR | Three-phase continuously-stirred-tank slurry reactor |
References
- Thomas, J.M.; Thomas, W.J. Principles and Practice of Heterogeneous Catalysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997; p. 526. [Google Scholar]
- Vosloo, A.C. Fischer–Tropsch: A futuristic view. Fuel Process. Technol. 2001, 71, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Yang, Y.; Wu, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, H.; Li, Y. Study of phase transformation and catalytic performance on precipitated iron-based catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 303, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, G.; Kim, D.-E.; Kim, Y.T.; Park, H.-G.; Kang, S.C.; Ha, K.-S.; Juna, K.-W.; Lee, Y.-J. Enhanced catalytic activity of cobalt catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis via carburization and hydrogenation and its application to regeneration. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 4594–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Jiang, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, Z. Effect of carbon support on Fischer–Tropsch synthesis activity and product distribution over Co-based catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 110, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, L.; Barnes, S.; Regalbuto, J.R. The simple, effective synthesis of highly dispersed Pd/C and CoPd/C heterogeneous catalysts via charge-enhanced dry impregnation. Catalysts 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluha, J.; Braidy, N.; Dalai, A.; Abatzoglou, N. Low-temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthesis using plasma-synthesised nanometric Co/C and Fe/C catalysts. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 94, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-J.; Zou, J.; Yu, K.; Cheng, D.; Han, Y.; Zhan, J.; Ratanatawanate, C.; Jang, B.W.-L. Plasma application for more environmentally friendly catalyst preparation. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluha, J.; Boahene, P.; Dalai, A.; Hu, Y.; Bere, K.; Braidy, N.; Abatzoglou, N. Synthesis and characterisation of nanometric Co/C and Fe/C catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: A comparative study using a fixed-bed reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 10661–10674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristantini, D.; Lögdberg, S.; Gevert, B.; Borg, Ø.; Holmen, A. The effect of synthesis gas composition on the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over Co/γ-Al2O3 and Co–Re/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.T.; Bej, S.K.; Bakhshi, N.N.; Dalai, A.K. Steam gasification of biomass-derived char for the production of carbon monoxide-rich synthesis gas. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yu, F.; Lu, Y. Application of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis in biomass to liquid conversion. Catalysts 2012, 2, 303–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluha, J.; Braidy, N.; Dalai, A.; Abatzoglou, N. Low-temperature fischer-tropsch synthesis with carbon-supported nanometric iron-cobalt catalysts. In Proceedings of the 23rd European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, Vienna, Austria, 1–4 June 2015.
- van der Laan, G.P.; Beenackers, A.A.C.M. Hydrocarbon selectivity model for the gas-solid Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on precipitated iron catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomew, C.H.; Farrauto, R.J. Fundamentals of Industrial Catalytic Processes; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; p. 403. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, T.; Li, Z. Review of recent development in Co-based catalysts supported on carbon materials for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 135, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Das, T.K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Racoillet, G.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Support, loading, and promoter effects on the reducibility of cobalt catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 2002, 233, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Ma, W.; Gao, P.; Todic, B.; Bhatelia, T.; Bukur, D.B.; Davis, B.H. The application of synchrotron methods in characterizing iron and cobalt Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts. Catal. Today 2013, 214, 100–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Yang, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, L. Study on reduction and carburization behaviors of iron-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst. Energy Procedia 2014, 61, 2267–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakov, A.Y.; Chu, W.; Fongarland, P. Advances in the development of novel cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts for synthesis of long-chain hydrocarbons and clean fuels. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1692–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Berge, P.J.; van de Loosdrecht, J.; Barradas, S.; van der Kraan, A.M. Oxidation of cobalt based Fischer-Tropsch catalysts as a deactivation mechanism. Catal. Today 2000, 58, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Loosdrecht, J.; Balzhinimaev, B.; Dalmon, J.A.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W.; Tsybulya, S.V.; Saib, A.M.; van-Berge, P.J.; Visagie, J.L. Cobalt Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Deactivation by oxidation? Catal. Today 2007, 123, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabaho, D.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W.H.; Claeys, M.; van Steen, E. Hydrogen spillover in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: An analysis of gold as a promoter for cobalt-alumina catalysts. Catal. Today 2016, 275, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Otter, J.H.; Nijveld, S.R.; de Jong, K.P. Synergistic promotion of Co/SiO2 Fischer-Tropsch catalysts by niobia and platinum. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, T.; Hanaoka, T.; Shimura, K.; Hirata, S. Ruthenium modification on Mn and Zr-modified Co/SiO2 catalysts for slurry-phase Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Catalysts 2015, 5, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajín, J.L.C.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S.; Gomes, J.R.B. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on multicomponent catalysts: What can we learn from computer simulations? Catalysts 2015, 5, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Ma, W.; Davis, B.H. Influence of reduction promoters on stability of cobalt/γ-alumina Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts. Catalysts 2014, 4, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Davies, T.E.; Morgan, D.J.; Karim, K.; Hayward, J.S.; Bartley, J.K.; Taylor, S.H.; Hutchings, G.J. Fischer Tropsch synthesis using cobalt based carbon catalysts. Catal. Today 2016, 275, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytter, E.; Holmen, A. Deactivation and regeneration of commercial type Fischer-Tropsch Co-catalysts—A mini-review. Catalysts 2015, 5, 478–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluha, J.; Bere, K.; Abatzoglou, N.; Gitzhofer, F. Synthesis of nano-catalysts by induction suspension plasma technology (SPS) for Fischer-Tropsch reaction. Plasma Chem. Plasma P 2016, 36, 1325–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, Ø.; Eri, S.; Blekkan, E.A.; Storsæter, S.; Wigum, H.; Rytter, E.; Holmen, A. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over γ-alumina-supported cobalt catalysts: Effect of support variables. J. Catal. 2007, 248, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaslou, R.M.M.; Tavassoli, A.; Soltan, J.; Dalai, A.K. Iron catalysts supported on carbon nanotubes for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Effect of catalytic site position. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 367, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trépanier, M.; Tavasoli, A.; Dalai, A.K.; Abatzoglou, N. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over carbon nanotubes supported cobalt catalysts in a fixed bed reactor: Influence of acid treatment. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Huang, C.; Lv, J.; Li, Z. Fuel production through Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on carbon nanotubes supported co catalyst prepared by plasma. Fuel 2014, 121, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezemer, G.L.; Bitter, J.H.; Kuipers, H.P.C.E.; Oosterbeek, H.; Holewijn, J.E.; Xu, X.; Kapteijn, F.; van Dillen, A.J.; de Jong, K.P. Cobalt particle size effects in the Fischer-Tropsch reaction studied with carbon nanofiber supported catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3956–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Osa, A.R.; Romero, A.; Dorado, F.; Valverde, J.L.; Sánchez, P. Influence of cobalt precursor on efficient production of commercial fuels over FTS Co/SiC catalyst. Catalysts 2016, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami, N.; Mahmoudi, H.; Rahbar, K.; Panahifar, P.; Tsolakis, A.; Wyszynski, M.L. Catalytic performance of cobalt-silica catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Effects of reaction rates on efficiency of liquid synthesis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 134, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami, N.; Wyszynski, M.L.; Mahmoudi, H.; Tsolakis, A.; Zou, Z.; Panahifar, P.; Rahbar, K. Modelling of a fixed bed reactor for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis of simulated N2-rich syngas over Co/SiO2: Hydrocarbon production. Fuel 2015, 154, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Chu, W.; Chernavskii, P.A.; Khodakov, A.Y. Cobalt species and cobalt-support interaction in glow discharge plasma-assisted Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. J. Catal. 2010, 273, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschemann, T.O.; Bitter, J.H.; de Jong, K.P. Effects of loading and synthesis method of titania-supported cobalt catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Catal. Today 2014, 228, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandas, J.C.; Gnanamani, M.K.; Jacobs, G.; Ma, W.; Ji, Y.; Khalid, S.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Characterization and reaction testing of cobalt carbide. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, J.; Abatzoglou, N. Nano-iron carbide synthesized by plasma as catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis in slurry reactors: The role of iron loading and K, Cu promoters. Catal. Today 2014, 237, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.H. The Two-Alpha Value for Iron Fischer-Tropsch Catalysts: Fact or Fiction? ACS Fuel: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006; Argonne National Laboratory: San Francisco, CA, USA; pp. 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-X.; Su, H.-Y.; Sun, D.-P.; Zhang, B.-Y.; Li, W.-X. Crystallographic dependence of Co activation on cobalt catalysts: HCP versus FCC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16284–16287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducreux, O.; Rebours, B.; Lynch, J.; Roy-Auberger, M.; Bazin, D. Microstructure of supported cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Rev. IFP 2009, 64, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.E.M.; Sales, F.G.; Fernandes, F.A.N. Effect of operating conditions and potassium content on Fischer-Tropsch liquid products produced by potassium-promoted iron catalysts. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2008, 17, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, H. Short history and present trends of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Appl. Catal. A 1999, 186, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyser, J.; van Vuuren, M.J.; Kupi, G. Advances in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, catalysts, and catalysis. In The Value of a Two Alpha Model in the Elucidation of a Full Product Spetrum for Fe-LTFT; Davis, B.H., Occelli, M.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakoli, A.; Sohrabi, M.; Kargari, A. Application of Anderson-Schulz-Flory (ASF) equation in the product distribution of slurry phase FT synthesis with nanosized iron catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 136, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dictor, R.A.; Bell, A.T. An explanation for deviations of Fischer-Tropsch products from a Schulz-Flory distribution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Proc. Des. Dev. 1983, 22, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesia, E.; Reyes, S.C.; Madon, R.J.; Soled, S.L. Selectivity control and catalyst design in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Sites, pellets, and reactors. Adv. Catal. 1993, 39, 221–302. [Google Scholar]
- Aluha, J.; Abatzoglou, N. Synthetic fuels from 3-φ Fischer-Tropsch synthesis using syngas feed and novel nanometric catalysts synthesised by plasma. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 95, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dry, M.E. Catalytic aspects of industrial Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Mol. Catal. 1982, 17, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Catalyst | Catalyst | FTS Reaction | Reference | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthesis Method * | Support # | Metal Particle Size (nm) θ | Reactor | GHSV (cm3∙g−1∙h−1) | H2:CO | Pressure (MPa) | Temp (°C) | % CO Conversion $ | ||
| Co/Al2O3 | IWI | Al2O3 | 11–28 | Fixed-bed | 6100–9500 | 2.1 | 2 | 210 | 50 | [31] |
| Co/C | IWI | CNTs | 9–24 | Fixed-bed | 2000 | 2 | 2 | 270 | 90 | [32] |
| Co/C | IWI | CNTs | 4–20 | Fixed-bed | 3600 | 2 | 2 | 220 | 50 | [33] |
| Co/C | DBD-plasma | CNTs | 5–26 | Fixed-bed | 1800 | 2 | 2 | 230 | 95 | [34] |
| Co/C | IWI, DP, IA | CNFBs | 2.6–27 | Plug-flow | - | 2 | 3.5 | 210–250 | 60–80 | [35] |
| Co/C | Induction SPS | Carbon | 9–11 | CSTR | 3600 | 2 | 2 | 220 | 42 | [7] |
| Co/SiC | IM | SiC | 15–35 | Fixed-bed | 6000 | 2 | 2 | 220 | 25 | [36] |
| 250 | 92 | |||||||||
| Co/SiO2 | - | SiO2 | - | Fixed-bed | 6000 | 1.9 | 1.5–2.5 | 230 | 42 | [37,38] |
| Co/SiO2 | IWI, GD-plasma | SiO2 | 5.8–10.2 | Fixed-bed | 1800 | 2 | 0.1 | 220 | 22 | [39] |
| Co/TiO2 | DP, IWI | TiO2 | 2–13 | Fixed-bed | 3450–5850 | 2 | 2 | 220 | 35 | [40] |
| Property | Auxiliary Plasma Reactor * | Main Plasma Reactor * |
|---|---|---|
| BET surface area (m2∙g−1) | 55.5 | 54.4 |
| Average pore diameter (nm) $ | 27.4 | 28.3 |
| Total pore volume (cm3∙g−1) # | 0.38 | 0.39 |
| Feed Gas (H2:CO Ratio) | Product Fraction (%) | α-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CH4 | C2 | C5–C12 | C13–C20 | C21+ | H2O (cm3) | ||
| 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 0.1 | 16.4 | 46.4 | 31.1 | 21 | 0.93 |
| 1.5 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 0.3 | 21.6 | 45.6 | 28.5 | 33 | 0.93 |
| 2.0 | 0.2 | 3.6 | 0.3 | 29.8 | 45.1 | 20.6 | 52 | 0.85 |
| Measurement | Method | Catalyst Property | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal loading in carbon support | Carbon ignition, SEM | Co atomic-mass (g/g) | 0.25 |
| Catalyst composition | XRD, XANES | Phases present | Co0, Co3C |
| Dominant structure | FCC | ||
| Porosity | N2 physisorption by BET | BET surface area (m2∙g−1) | 56 |
| Mean pore diameter (nm) | 28 | ||
| Total pore volume (cm3∙g−1) | 0.39 | ||
| Metal nanoparticles | Microscopy, TEM | Mean particle size (nm) | 11 |
| Alpha-values | ASF product distribution | H2:CO ratio 1.0 | 0.93 |
| H2:CO ratio 1.5 | 0.93 | ||
| H2:CO ratio 2.0 | 0.85 | ||
| Catalyst activity | GC analysis | CO conversion (220 °C, 2 MPa) H2:CO ratio 1.0 | 10% |
| H2:CO ratio 1.5 | 20% | ||
| H2:CO ratio 2.0 | 40% | ||
| Selectivity | Liquid-GC analysis FTS at 220 °C, 2 MPa, H2:CO = 2.0 | Sample product distribution: CO2 | 0.2 |
| CH4 | 3.6 | ||
| C2–C4 | 0.3 | ||
| C5–C12 (Gasoline) | 29.8 | ||
| C13–C20 (Diesel) | 45.1 | ||
| C21+ (Wax) | 20.6 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aluha, J.; Hu, Y.; Abatzoglou, N. Effect of CO Concentration on the α-Value of Plasma-Synthesized Co/C Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. Catalysts 2017, 7, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020069
Aluha J, Hu Y, Abatzoglou N. Effect of CO Concentration on the α-Value of Plasma-Synthesized Co/C Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. Catalysts. 2017; 7(2):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020069
Chicago/Turabian StyleAluha, James, Yongfeng Hu, and Nicolas Abatzoglou. 2017. "Effect of CO Concentration on the α-Value of Plasma-Synthesized Co/C Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis" Catalysts 7, no. 2: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020069
APA StyleAluha, J., Hu, Y., & Abatzoglou, N. (2017). Effect of CO Concentration on the α-Value of Plasma-Synthesized Co/C Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. Catalysts, 7(2), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7020069