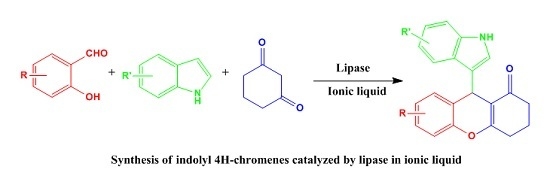
Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Indolyl 4H-Chromenes via a Multicomponent Reaction in Ionic Liquid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. General Procedure of the Synthesis of Indolyl 4H-Chromenes Catalyzed by Lipase
3.3. Reusability of [EMIM][BF4]s
3.4. Immobilization of MML
3.5. Systhesis of Indolyl 4H-Chromenes Catalyzed by the Immobilized MML
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Limsuwan, S.; Trip, E.N.; Kouwen, T.R.H.M.; Piersma, S.; Hiranrat, A.; Mahabusarakam, W.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P.; Dijl, J.M.; Kayser, O. Rhodomyrtone: A new candidate as natural antibacterial drug from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardcastle, I.R.; Cockcroft, X.L.; Curtin, N.J.; El-Murr, M.D.; Leahy, J.J.; Stockley, M.; Golding, B.T.; Rigoreau, L.; Richardson, C.; Smith, G.C.M.; et al. Discovery of Potent Chromen-4-one Inhibitors of the DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase (DNA-PK) Using a Small-Molecule Library Approach. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7829–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melander, R.J.; Minvielle, M.J.; Melander, C. Controlling bacterial behavior with indole-containing natural products and derivatives. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 6363–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrus, J.I.; Kelso, M.J.; Bremner, J.B.; Ball, A.R.; Casadei, G.; Lewis, K. Structure-activity relationships of 2-aryl-1H-indole inhibitors of the NorA efflux pump in Staphylococcus aureus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4294–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidwai, M.; Saxena, S.; Khan, M.K.R.; Thukral, S.S. Aqua mediated synthesis of substituted 2-amino-4H-chromenes and in vitro study as antibacterial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 4295–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Shao, S. Novel indole based colorimetric and “turn on” fluorescent sensors for biologically important fluoride anion sensing. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2011, 103, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kniess, T.; Laube, M.; Bergmann, R.; Sehn, F.; Graf, F.; Steinbach, J.; Wuest, F.; Pietzsch, J. Radiosynthesis of a 18 F-labeled 2,3-diarylsubstituted indole via McMurry coupling for functional characterization of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in vitro and in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 3410–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Reddy, V.B.; Sharad, S.; Dube, U.; Kapur, S. A facile one-pot green synthesis and antibacterial activity of 2-amino-4H-pyrans and 2-amino-5-oxo-5, 6, 7, 8-tetrahydro-4H-chromenes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3805–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casapullo, A.; Bifulco, G.; Bruno, I.; Riccio, R. New Bisindole Alkaloids of the Topsentin and Hamacanthin Classes from the Mediterranean Marine Sponge Rhaphisia lacazei. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathrotiya, H.G.; Patel, M.P. Microwave-assisted synthesis of 3’-indolyl substituted 4H-chromenes catalyzed by DMAP and their antimicrobial activity. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 3406–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasralikar, H.M.; Jadhavar, S.C.; Bhusare, S.R. Synthesis and molecular docking studies of oxochromenyl xanthenone and indolyl xanthenone derivatives as anti-HIV-1 RT inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3882–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.P.; Das, A.R. Nanocrystalline and reusable ZnO catalyst for the assembly of densely functionalized 4H-chromenes in aqueous medium via one-pot three component reactions: A greener “NOSE” approach. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 6170–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, V.S.; Yong, S.J.; Yeon, T.J. A metal-free tandem C–C/C–O bond formation approach to densely functionalized indolyl 4H-chromenes catalyzed by polystyrene-supported p-toluenesulfonic acid under solvent-free conditions. Mol. Divers. 2015, 19, 367–383. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan, A.; Kothandapani, J.; Nanubolu, J.B.; Ganesan, S.S. Oleic acid: A benign Brønsted acidic catalyst for densely substituted indole derivative synthesis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 28597–28600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratibha, R.; Madhulika, S.; Snehlata, Y.; Jaya, S.; Jagdamba, S. β-Cyclodextrin: A Biomimetic Catalyst used for the Synthesis of 4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile and Tetrahydro-1H-xanthen-1-one Derivatives. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh, U.C.; Kholiya, R.; Thakur, A.; Rawat, D.S. [TBA][Gly] ionic liquid promoted multi-component synthesis of 3-substituted indoles and indolyl-4H-chromenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 1790–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindulkar, S.D.; Jeong, D.; Cho, E.; Kim, D.; Jung, S. Microbial cyclosophoraose as a catalyst for the synthesis of diversified indolyl 4H-chromenes via one-pot three component reactions in water. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3620–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.; Gupta, M.N. Lipase promiscuity and its biochemical applications. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Fu, J.P.; He, Y.H. Biocatalytic promiscuity: Lipase-catalyzed asymmetric aldol reaction of heterocyclic ketones with aldehydes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 4959–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Ramírez, J.D.; Escalante, J.; López-Munguía, A.; Marty, A.; Castillo, E. Thermodynamically controlled chemoselectivity in lipase-catalyzed aza-Michael additions. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2015, 112, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Z.G.; Guo, L.T.; Jiang, G.F.; Yang, X.B.; Liu, H.Q. Henry reaction catalyzed by Lipase A from Aspergillus niger. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2013, 6, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Xiang, Y.; Yang, D.C.; Guan, Z.; He, Y.H. Biocatalytic asymmetric Mannich reaction of ketimines using wheat germ lipase. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3963–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, H.R.; Zhang, H.; Su, Y.L.; Ji, T.F.; Wang, L. Lipase-catalyzed Knoevenagel condensation between α, β-unsaturated aldehydes and active methylene compounds. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, M.T.; Mondière, R.; Carballeira, J.D. Enzyme promiscuity: First protein-catalyzed Morita-Baylis-Hillman reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 1679–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, D.F.; Barbosa, O.; Burguete, M.I.; Lozano, P.; Luis, S.V.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; García-Verdugo, E. Tuning lipase B from Candida antarctica C-C bond promiscuous activity by immobilization on poly-styrene-divinylbenzene beads. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6219–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, W.A.; Yang, F.J.; Guo, C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Ji, D.; Zhou, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wang, L. Synthesis of dihydropyrano[4,3-b]pyranes via a multicomponent reaction catalyzed by lipase. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2017, 10, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, P.P.; Bihani, M.; Bez, G. Multicomponent synthesis of dihydropyrano [2, 3-c] pyrazoles catalyzed by lipase from Aspergillus niger. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 92, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłossowski, S.; Wiraszka, B.; Berłożecki, S.; Ostaszewski, R. Model studies on the first enzyme-catalyzed Ugi reaction. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.R.; Zhang, H.; Yue, H.; Wang, L. Enzyme catalytic promiscuity: Lipase catalyzed synthesis of substituted 2H-chromenes by a three-component reaction. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 25633–25636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, K.; Harami, H.; Matsubara, Y.; Nokami, T.; Katada, N.; Itoh, T. Lipase-mediated dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) of secondary alcohols in the presence of zeolite using an ionic liquid solvent system. Catal. Today 2015, 255, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Zheng, L.; Xu, H.; Li, M. Enantioselective esterification of (R,S)-flurbiprofen catalyzed by lipase in ionic liquid. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2017, 10, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, C.; Liu, C.Z. Efficient kinetic resolution of (R,S)-2-octanol catalyzed by magnetite-immobilized Yarrowia lipolytica lipase in mixed ionic liquids. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.K.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, R.; Sinha, A.K. Biocatalytic promiscuity of lipase in chemoselective oxidation of aryl alcohols/acetates: A unique synergism of CAL-B and [hmim] Br for the metal-free H2O2 activation. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4846–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Xie, Z.B.; Zhou, L.H.; Yu, X.Q. Ionic liquid as a recyclable and efficient medium for lipase-catalyzed asymmetric cross aldol reaction. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 110, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kazlauskas, R.J. Biocatalysis in ionic liquids-advantages beyond green technology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Laua, R.M.; Sorgedragera, M.J.; Rantwijka, F.V.; Seddon, K.R. Biocatalysis in ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanmamed, Y.A.; González-Salgado, D.; Troncoso, J.; Cerdeiriña, C.A.; Romaní, L. Viscosity-induced errors in the density determination of room temperature ionic liquids using vibrating tube densitometry. Fluid Phase Equilibr. 2007, 252, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.D.; Row, K.H. Recent applications of ionic liquids in separation technology. Molecules 2010, 15, 2405–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Torres, R.; Fernández-Lafuente, R. Modifying enzyme activity and selectivity by immobilization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6290–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoel, E.A.; Santos, J.C.S.; Freire, D.M.G.; Rueda, N.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Immobilization of lipases on hydrophobic supports involves the open form of the enzyme. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2015, 71, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueda, N.; Santos, J.C.S.; Ortiz, C.; Torres, R.; Barbosa, O.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Chemical Modification in the Design of Immobilized Enzyme Biocatalysts: Drawbacks and Opportunities. Chem. Rec. 2016, 16, 1436–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.F.; Cheng, Y.M.; Cao, S.G. Resolution of 2-octanol by SBA-15 immobilized Pseudomonas sp. lipase. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2007, 48, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xun, E.N.; Wang, J.X.; Chen, G.; Cheng, T.X.; Wang, Z.; Ji, T.F.; Wang, L. Immobilization of laccase for oxidative coupling of trans-resveratrol and its derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, E.N.; Lv, X.L.; Kang, W.; Wang, J.X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Immobilization of Pseudomonas fluorescens lipase onto magnetic nanoparticles for resolution of 2-octanol. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolatti, E.P.; Valério, A.; Henriques, R.O.; Moritz, D.E.; Ninow, J.L.; Freire, D.M.G.; Manoel, E.A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Oliveira, D. Nanomaterials for biocatalyst immobilization-state of the art and future trends. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 104675–104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.M.; Qiu, J.H.; Wu, X.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Sakai, E.; Wei, Y. Preparation of magnetic chitosan nanoparticles as support for cellulase immobilization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3448–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





| Entry | Enzyme | Isolated Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MML (Mucor miehei lipase) | 93 |
| 2 | PPL (Porcine pancreatic lipase) | 81 |
| 3 | PSL (Lipase from Pseudomonas sp.) | 62 |
| 4 | CRL (C. rugosa lipase) | 48 |
| 5 | CalB (C. antarctica lipase B) | 68 |
| 6 | denatured MML c | N.D. d |
| 7 | Albumin from bovine serum (BSA) | N.D. d |
| 8 | Control | N.D. d |
| Entry | Ionic Liquid | Isolated Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [BMIM][Otf] | 79 |
| 2 | [BMIM]N(Tf)2 | 57 |
| 3 | [BMIM][PF6] | 68 |
| 4 | [BMIM][Ac] | 11 |
| 5 | [BMIM][NO3] | 15 |
| 6 | [BMIM][BF4] | 85 |
| 7 | [EMIM][BF4] | 93 |
| 8 | [HMIM][BF4] | 72 |
| 9 | Ethanol | 80 |
| 10 | Water | 67 |
 |
 |
| Catalyst | Bound Protein (mg/g) | Isolated Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Free MML | - | 93 |
| Immobilized MML | 180 | 86 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, R.; Wang, L. Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Indolyl 4H-Chromenes via a Multicomponent Reaction in Ionic Liquid. Catalysts 2017, 7, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7060185
Zhang W, Zhao Z, Wang Z, Guo C, Wang C, Zhao R, Wang L. Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Indolyl 4H-Chromenes via a Multicomponent Reaction in Ionic Liquid. Catalysts. 2017; 7(6):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7060185
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Weian, Ziyuan Zhao, Zhi Wang, Chao Guo, Chunyu Wang, Rui Zhao, and Lei Wang. 2017. "Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Indolyl 4H-Chromenes via a Multicomponent Reaction in Ionic Liquid" Catalysts 7, no. 6: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7060185
APA StyleZhang, W., Zhao, Z., Wang, Z., Guo, C., Wang, C., Zhao, R., & Wang, L. (2017). Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Indolyl 4H-Chromenes via a Multicomponent Reaction in Ionic Liquid. Catalysts, 7(6), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7060185