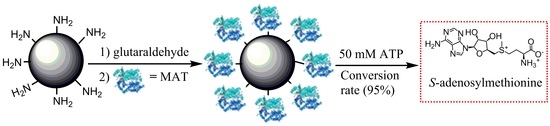
Enzymatic Synthesis of S-Adenosylmethionine Using Immobilized Methionine Adenosyltransferase Variants on the 50-mM Scale
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Purification and Characterization of Wild-Type and I303V MAT
2.2. Product Inhibition of Wild-Type and I303V MAT
2.3. Production of Recombinant I303V MAT in a Bioreactor
2.4. Comparison of Covalent Immobilization Methods
2.5. Thermal Inactivation of Soluble and Immobilized Enzyme
2.6. Effect of pH on Enzyme Stability
2.7. Kinetic Analysis
2.8. Recycling of Immobilized Enzyme for SAM Synthesis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Expression and Purification of Wild-Type and I303V MAT
3.3. Immobilization of I303V MAT
3.4. Determination and Analysis
3.4.1. Spectrophotometric Assay for MAT Activity
3.4.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
3.4.3. Protein Assay
3.4.4. Thermal Stability of the Soluble and Immobilized Enzymes
3.4.5. Effect of pH on the Stability of the Soluble and Immobilized Enzymes
3.5. Reusability of Immobilized Enzyme on Scaled-Up Production of SAM
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fontecave, M.; Atta, M.; Mulliez, E. S-adenosylmethionine: Nothing goes to waste. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, M.A.; Colombatto, S. S-adenosylmethionine and its products. Amino Acids 2008, 34, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosea Blewett, H.J. Exploring the mechanisms behind S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.C.; Mato, J.M. S-adenosylmethionine in liver health, injury, and cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1515–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureddin, M.; Mato, J.M.; Lu, S.C. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Update on pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment and the role of S-adenosylmethionine. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shippy, R.A.; Mendez, D.; Jones, K.; Cergnul, I.; Karpiak, S.E. S-adenosylmethionine (SAM-e) for the treatment of depression in people living with HIV/AIDS. BMC Psychiatry 2004, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Cai, H.; Zhou, C. Progress in the microbial production of S-adenosyl-l-methionine. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Qian, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Progress in the research of S-adenosyl-l-methionine production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dou, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C. Elevated intracellular acetyl-CoA availability by ACS2 overexpression and MLS1 deletion combined with metK1 introduction enhanced SAM accumulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 107, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Deng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, J. A synergistic effect on the production of S-adenosyl-l-methionine in Pichia pastoris by knocking in of S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthase and knocking out of cystathionine-beta synthase. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 126, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Chu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, Z. A novel feeding strategy during the production phase for enhancing the enzymatic synthesis of S-adenosyl-l-methionine by methylotrophic Pichia pastoris. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Qian, J.; Chu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, S. Optimization of l-methionine feeding strategy for improving S-adenosyl-l-methionine production by methionine adenosyltransferase overexpressed Pichia pastoris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, M.; Mizunuma, M.; Fujii, T.; Iefuji, H. A genetic method to enhance the accumulation of S-adenosylmethionine in yeast. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wei, G.; Shao, N. Enhanced co-production of S-adenosylmethionine and glutathione by an ATP-oriented amino acid addition strategy. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Su, E.; Fang, G.; Ren, Y.; Wei, D. A new fermentation strategy for S-adenosylmethionine production in recombinant Pichia pastoris. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 41, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Hang, B.; Zhu, X.; Wang, R.; Shen, M.; Huang, L.; Xu, Z. Improving the productivity of S-adenosyl-l-methionine by metabolic engineering in an industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 236, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, G.; Zhao, F. Expression of secreted His-tagged S-adenosylmethionine synthetase in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris and its characterization, one-step purification, and immobilization. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 24, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hormigo, D.; de la Mata, I.; Acebal, C.; Arroyo, M. Immobilized aculeacin A acylase from Actinoplanes utahensis: Characterization of a novel biocatalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4261–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, S.F.; Shelly, L.L.; Ruppert, S.; Schutz, G.; Chou, J.Y. Cloning and expression of murine S-adenosylmethionine synthetase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 13978–13986. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Chu, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhuang, Y.P.; Yuan, Z.Y. Purification and properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae S-adenosylmethionine synthetase expressed in recombinant Pichia pastoris. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, G.D.; Hafner, E.W.; Tabor, C.W.; Tabor, H. S-adenosylmethionine synthetase from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 9082–9092. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Tai, J.; Roessner, C.A.; Scott, A.I. Enzymatic synthesis of S-adenosyl-l-methionine on the preparative scale. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Tai, J.; Roessner, C.A.; Scott, A.I. Overcoming product inhibition of S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAM) synthetase: preparation of SAM on the 30 mM scale. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1995, 5, 2203–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippe, M.; Brandt, W.; Rost, H.; Schmidt, J.; Wessjohann, L.A. Rationally engineered variants of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) synthase: Reduced product inhibition and synthesis of artificial cofactor homologues. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3637–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komoto, J.; Yamada, T.; Takata, Y.; Markham, G.D.; Takusaqawa, F. Crystal structure of the S-adenosylmethionine synthetase ternary complex: A novel catalytic mechanism of S-adenosylmethionine synthesis from ATP and Met. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamarthapu, V.; Rao, K.V.; Srinivas, P.N.; Reddy, G.B.; Reddy, V.D. Structural and kinetic properties of Bacillus subtilis S-adenosylmethionine synthetase expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knezevic, Z.; Milosavic, N.; Bezbradica, D.; Jakovljevic, Z.; Prodanovic, R. Immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa on Eupergit® C supports by covalent attachment. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 30, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, S.H.; Wu, W.T. Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase on chitosan with activation of the hydroxyl groups. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Support | Enzyme Added (mg/g Support) | Enzyme Loading (mg/g Support) | Enzyme Coupling Yield (%) | Enzyme Activity (U/g Support) | Activity Coupling Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LX-1000 HA (Method I) | 10 | 8.9 ± 0.5 | 89 | 41.7 ± 3.6 | 83.6 |
| 20 | 18.3 ± 1.1 | 91.5 | 76.4 ± 6.4 | 74.5 | |
| 30 | 27.7 ± 0.8 | 92.3 | 109.6 ± 7.6 | 70.7 | |
| 40 | 33.2 ± 1.2 | 83 | 104.9 ± 8.9 | 56.4 | |
| 50 | 35.4 ± 1.6 | 70.8 | 108 ± 7.7 | 54.5 | |
| LX-1000 EP (Method II) | 10 | 9.1 ± 0.4 | 91 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 20 | 17.5 ± 1.2 | 87.5 | 3.3 ± 0.36 | 3.3 | |
| 30 | 25.4 ± 0.5 | 84.7 | 3.9 ± 0.29 | 2.7 | |
| 40 | 30.8 ± 0.8 | 77 | 2.7 ± 0.21 | 1.5 | |
| 50 | 32.7 ± 1.2 | 65.4 | 3 ± 0.23 | 1.6 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, W.; Cao, S.; Yang, M.; Xu, L. Enzymatic Synthesis of S-Adenosylmethionine Using Immobilized Methionine Adenosyltransferase Variants on the 50-mM Scale. Catalysts 2017, 7, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7080238
Niu W, Cao S, Yang M, Xu L. Enzymatic Synthesis of S-Adenosylmethionine Using Immobilized Methionine Adenosyltransferase Variants on the 50-mM Scale. Catalysts. 2017; 7(8):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7080238
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Weining, Shanshan Cao, Menglin Yang, and Le Xu. 2017. "Enzymatic Synthesis of S-Adenosylmethionine Using Immobilized Methionine Adenosyltransferase Variants on the 50-mM Scale" Catalysts 7, no. 8: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7080238
APA StyleNiu, W., Cao, S., Yang, M., & Xu, L. (2017). Enzymatic Synthesis of S-Adenosylmethionine Using Immobilized Methionine Adenosyltransferase Variants on the 50-mM Scale. Catalysts, 7(8), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7080238