The Role of Impregnated Sodium Ions in Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Structural Characterization
2.1.1. BET and XRD Results
2.1.2. NH3-TPD Results
2.1.3. Ex Situ DRIFTs Results
2.1.4. CO2-DRIFTs Results
2.2. Copper Species Variation on Cu/SSZ-13
2.2.1. EPR Results
2.2.2. H2-TPR Results
2.2.3. UV-Vis DRS Results
2.3. NH3-SCR Reactions over Cu/SSZ-13
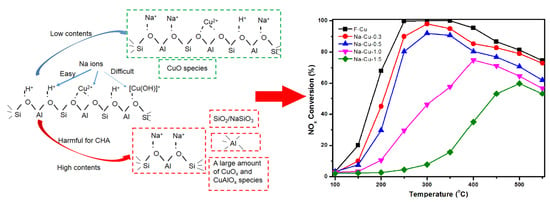
2.3.1. NH3-SCR Activity
2.3.2. Activation Energy (Ea) Measurements
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of Na Ions on CHA Structure over Cu/SSZ-13
3.2. Effect of Na Ions on Acid Sites over Cu/SSZ-13
3.3. Effect of Na on the NH3-SCR Reaction
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
5. Conclusions
- The impregnated Na exchanged with Brönsted acid sites and Cu2+ ions as Si-O(Na+)-Al. The Na intakes declined with the number of acid sites, including Brönsted acid sites and Cu2+ ions. The reduction degree of the number of Brönsted acid sites were greater than that of Cu2+ ions contents.
- Except for sample with highest Na loading (1.5 mmol/g), all Na-impregnated catalysts remained as two types of Cu2+ ions and the overall amounts of Cu2+ ions declined with Na and increase in contents. Na-Cu-1.5 only contained Cu2+ ions in 8 MR and it had the lowest amounts of Cu2+.
- The Na introduced damage to the framework of catalysts and formed SiO2/NaSiO3 and amorphous species when the contents of Na ≥ 1.0 mmol/g, as confirmed using XRD, BET, and NMR results.
- The reduced Cu2+ ions changed into other copper species, CuxO, CuO, and CuAlOx species. Furthermore, CuAlOx species were only generated on Na-Cu-1.5 catalyst.
- For Na-impregnated catalysts, the loss of Cu2+ contents contributed to the inferior SCR activity at low temperatures, while at high temperatures, the reduction in the number of acid sites and Cu2+ ions as well as CuOx species formation lead to low SCR performance.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, F.; Walter, E.D.; Kollar, M.; Wang, Y.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Understanding ammonia selective catalytic reduction kinetics over Cu/SSZ-13 from motion of the Cu ions. J. Catal. 2014, 319, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, C.; Ye, Q.; Cheng, S.; Kang, T.; Dai, H. Effect of Si/Al ratio on catalytic performance of hydrothermally aged Cu-SSZ-13 for the NH3-SCR of NO in simulated diesel exhaust. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Walter, E.D.; Washton, N.M.; Mei, D.; Kovarik, L.; Engelhard, M.H.; Prodinger, S.; Wang, Y.; Peden, C.H.F.; et al. Toward Rational Design of Cu/SSZ-13 Selective Catalytic Reduction Catalysts: Implications from Atomic-Level Understanding of Hydrothermal Stability. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8214–8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistner, K.; Kumar, A.; Kamasamudram, K.; Olsson, L. Mechanistic study of hydrothermally aged Cu/SSZ-13 catalysts for ammonia-SCR. Catal. Today 2018, 307, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Gao, F.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.; Peden, C.H.F.; Yezerets, A. New insights into Cu/SSZ-13 SCR catalyst acidity. Part I: Nature of acidic sites probed by NH3 titration. J. Catal. 2017, 348, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Chen, Z.; Pang, L.; Ming, S.; Zhang, X.; Albert, K.B.; Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Li, T. The influence of Si/Al ratio on the catalytic property and hydrothermal stability of Cu-SSZ-13 catalysts for NH3-SCR. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 550, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, N.; Caputo, D.; Totarella, G.; Lisi, L.; Cimino, S. Me-ZSM-5 monolith foams for the NH3-SCR of NO. Catal. Today 2018, 304, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, S.; Lin, C.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, Y. Barium-promoted hydrothermal stability of monolithic Cu/BEA catalyst for NH3-SCR. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 15038–15048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Si, Z.; Weng, D.; Wu, X.; Ma, Y. Potassium poisoning on Cu-SAPO-34 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Schmieg, S.J.; Weng, D. Role of Brønsted acidity in NH3 selective catalytic reduction reaction on Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts. J. Catal. 2015, 324, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, M.; Li, W. Effects of Na(+) on Cu/SAPO-34 for ammonia selective catalytic reduction. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 70, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Washton, N.M.; Kollár, M.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Effects of Alkali and Alkaline Earth Cocations on the Activity and Hydrothermal Stability of Cu/SSZ-13 NH3–SCR Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6780–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yu, R.; Zhao, R.; Shi, C.; Gies, H.; Xiao, F.-S.; De Vos, D.; Yokoi, T.; Bao, X.; Kolb, U.; et al. Cu-exchanged Al-rich SSZ-13 zeolite from organotemplate-free synthesis as NH3-SCR catalyst: Effects of Na + ions on the activity and hydrothermal stability. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 217, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Liu, F.; Shi, X.; Xiao, F.-S.; He, H. Effects of post-treatment method and Na co-cation on the hydrothermal stability of Cu–SSZ-13 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 179, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Chen, Z.; Pang, L.; Ming, S.; Dong, C.; Brou Albert, K.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Zhu, D.; Chen, H.; et al. Steam and alkali resistant Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx in diesel exhaust. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Fu, Z.; Ma, L.; Niu, H.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. MnOx-CeO2 supported on Cu-SSZ-13: A novel SCR catalyst in a wide temperature range. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 547, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, Z.; Qiao, H.; Yu, H.; Hu, Y.; Chang, L.; Bao, W. Cerium-Stabilized Cu-SSZ-13 Catalyst for the Catalytic Removal of NOx by NH3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xu, M.; Yu, T.; Ma, H.; Shen, M.; Wang, J. Catalytic deactivation mechanism research over Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts for NH3-SCR (II): The impact of copper loading. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 168, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Jangjou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sharma, M.K.; Luo, J.; Li, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Epling, W.S. A comparison of hydrothermal aging effects on NH3-SCR of NOx over Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, D.; Kumar, A.; Li, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.; Yezerets, A. Identification of two types of Cu sites in Cu/SSZ-13 and their unique responses to hydrothermal aging and sulfur poisoning. Catal. Today 2016, 267, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Varga, T.; Peden, C.H.F.; Gao, F.; Hanson, J.C.; Szanyi, J. Following the movement of Cu ions in a SSZ-13 zeolite during dehydration, reduction and adsorption: A combined in situ TP-XRD, XANES/DRIFTS study. J. Catal. 2014, 314, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiksen, A.; Stappen, F.N.; Vennestrøm, P.N.R.; Giordanino, F.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Lundegaard, L.F.; Mossin, S. Coordination Environment of Copper Sites in Cu-CHA Zeolite Investigated by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 23126–23138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Fan, C.; Pang, L.; Ming, S.; Liu, P.; Li, T. The influence of phosphorus on the catalytic properties, durability, sulfur resistance and kinetics of Cu-SSZ-13 for NOx reduction by NH3-SCR. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 237, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.K.; Min, K.M.; Hong, S.B.; Nam, I.-S.; Cho, B.K. Hydrothermal stability of CuSSZ13 for reducing NOx by NH3. J. Catal. 2014, 311, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Walter, E.D.; Washton, N.M.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Synthesis and evaluation of Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts for NH3-SCR 2: Solid-state ion exchange and one-pot synthesis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 162, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Qiu, F.; Chang, H.; Li, X.; Li, J. Identification of active sites and reaction mechanism on low-temperature SCR activity over Cu-SSZ-13 catalysts prepared by different methods. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 6294–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Washton, N.M.; Wang, Y.; Kollár, M.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Effects of Si/Al ratio on Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR catalysts: Implications for the active Cu species and the roles of Brønsted acidity. J. Catal. 2015, 331, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Qiu, F.; Li, J. Design and synthesis of core-shell structured meso-Cu-SSZ-13@mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst for SCR of NOx with NH3: Enhancement of activity, hydrothermal stability and propene poisoning resistance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 195, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, Z.; Qiao, H.; Han, L.; Bao, W.; Chang, L.; Feng, G.; Liu, W. Influence of aging on in situ hydrothermally synthesized Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for NH3-SCR reaction. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 42403–42411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wilken, N.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.W.; Olsson, L.; Yezerets, A. Characterization of Active Species in Cu-Beta Zeolite by Temperature-Programmed Reduction Mass Spectrometry (TPR-MS). Top. Catal. 2013, 56, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistner, K.; Xie, K.; Kumar, A.; Kamasamudram, K.; Olsson, L. Ammonia Desorption Peaks Can Be Assigned to Different Copper Sites in Cu/SSZ-13. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Fan, D.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Hao, T.; Hu, X.; Shen, M.; Li, W. Improvement of low-temperature hydrothermal stability of Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts by Cu2+ species. J. Catal. 2015, 322, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Leistner, K.; Wijayanti, K.; Kumar, A.; Kamasamudram, K.; Olsson, L. Influence of phosphorus on Cu-SSZ-13 for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia. Catal. Today 2017, 297, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistner, K.; Mihai, O.; Wijayanti, K.; Kumar, A.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.W.; Yezerets, A.; Olsson, L. Comparison of Cu/BEA, Cu/SSZ-13 and Cu/SAPO-34 for ammonia-SCR reactions. Catal. Today 2015, 258, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, C.; Khurana, I.; Parekh, A.A.; Li, S.; Shih, A.J.; Li, H.; di Iorio, J.R.; Albarracin-Caballero, J.D.; Yezerets, A.; Miller, J.T.; et al. Dynamic multinuclear sites formed by mobilized copper ions in NOx selective catalytic reduction. Science 2017, 357, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, T.; Shen, M.; Wang, W.; Li, W. The effect of sulfate species on the activity of NH3-SCR over Cu/SAPO-34. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 204, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Samples’ Name | Na Contents (%) 1 | BET Surface Area | ΔS (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| F-Cu | 0 | 792 | — |
| Na-Cu-0.3 | 0.7 | 747 | 5.6 |
| Na-Cu-0.5 | 1.2 | 737 | 6.9 |
| Na-Cu-1.0 | 2.3 | 591 | 25.3 |
| Na-Cu-1.5 | 3.5 | 277 | 65.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Shen, M.; Yan, W.; Kang, X. The Role of Impregnated Sodium Ions in Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR Catalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120593
Wang C, Wang J, Wang J, Wang Z, Chen Z, Li X, Shen M, Yan W, Kang X. The Role of Impregnated Sodium Ions in Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR Catalysts. Catalysts. 2018; 8(12):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120593
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, Jun Wang, Jianqiang Wang, Zhixin Wang, Zexiang Chen, Xiaolan Li, Meiqing Shen, Wenjun Yan, and Xue Kang. 2018. "The Role of Impregnated Sodium Ions in Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR Catalysts" Catalysts 8, no. 12: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120593
APA StyleWang, C., Wang, J., Wang, J., Wang, Z., Chen, Z., Li, X., Shen, M., Yan, W., & Kang, X. (2018). The Role of Impregnated Sodium Ions in Cu/SSZ-13 NH3-SCR Catalysts. Catalysts, 8(12), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120593