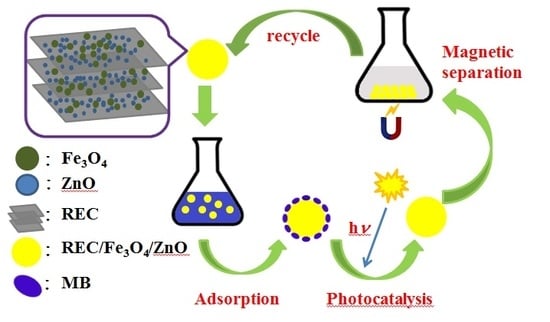
Synthesis of Rectorite/Fe3O4/ZnO Composites and Their Application for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphology and BET Surface Area of the REC/Fe3O4/ZnO Composites
2.2. Structural Characterization of the REC/Fe3O4/ZnO Composites
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) Analysis REC and REC/Fe3O4/ZnO
2.4. Adsorption Equilibrium and Isotherm of MB Dye on REC/Fe3O4/ZnO
2.5. Effect of Component Mass Ratio on the Degradation of MB Dye
2.6. Effect of REC/Fe3O4/ZnO Dosage on the Degradation of MB Dye
2.7. Effect of Solution pH on the Degradation of MB Dye
2.8. Kinetics for the Degradation of MB Dye on REC/Fe3O4/ZnO
2.9. Recovery and Stability of REC/Fe3O4/ZnO
2.10. Mechanism for the Degradation of MB Dye on REC/Fe3O4/ZnO
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of REC/Fe3O4/ZnO
3.2.1. Synthesis of Magnetic REC
3.2.2. Synthesis of REC/Fe3O4/ZnO
3.3. Characterization of the Synthesized Magnetic Materials
3.4. Adsorption of MB Dye on REC/Fe3O4/ZnO
3.5. Photocatalytic Degradation of MB Dye under Simulated Solar Radiation
3.6. Sample and Data Analyses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forgacs, E.; Cserhati, T.; Oros, G. Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, A.K.; Guo, J.; Lee, E.J.; Jeong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Leiknes, T. PDMS/PVDF hybrid electrospun membrane with superhydrophobic property and drop impact dynamics for dyeing wastewater treatment using membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinatloo-Ajabshir, S.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Zinatloo-Ajabshir, Z. Facile size-controlled preparation of highly photocatalytically active praseodymium zirconate nanostructures for degradation and removal of organic pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 177, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Avranas, A.; Lazaridis, N.K. Multi-parametric adsorption effects of the reactive dye removal with commercial activated carbons. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 213, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, A.A.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bashkova, S. Adsorption of methylene blue on cashew nut shell based carbons activated with zinc chloride: The role of surface and structural parameters. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Wang, K.S.; Chao, S.J.; Peng, T.H.; Huang, L.C. Degradation of azo and anthraquinone dyes by a low-cost Fe0/air process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, R.; Boardman, G.D.; Michelsen, D. Fate of azo dyes in sludges. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razo-Flores, E.; Luijten, M.; Donlon, B.; Lettinga, G.; Field, J. Biodegradation of selected azo dyes under methanogenic conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, M.; Peres, J. Decolorization of the azo dye reactive black 5 by Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation. Dyes Pigment. 2006, 71, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Sang, Y.; Liu, H. Heterostructures construction on TiO2 nanobelts: A powerful tool for building high-performance photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 202, 620–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Cao, X.; Wu, X.J.; He, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.; Han, S.; Nam, G.H.; et al. Recent advances in ultrathin two-dimensional nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6225–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirhashemi, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A. Ultrasonic-assisted preparation of plasmonic ZnO/Ag/Ag2WO4 nanocomposites with high visible-light photocatalytic performance for degradation of organic pollutants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 491, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunakaran, C.; Dhanalakshmi, R. Photocatalytic performance of particulate semiconductors under natural sunshine—Oxidation of carboxylic acids. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, J.; Muthuraaman, B.; Murugesan, S.; Anandan, S.; Maruthamuthu, P. Peroxomonosulphate, an efficient oxidant for the photocatalysed degradation of a textile dye, acid red 88. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 1875–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Karthikeyan, S.; Lee, A. G-C3N4-based nanomaterials for visible light-driven photocatalysis. Catalysts 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelle, A.A.; Hmadeh, M.; O’Brien, P.G.; Perovic, D.D.; Ozin, G.A. Photocatalytic properties of all four polymorphs of nanostructured iron oxyhydroxides. ChemNanoMat 2016, 2, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Lan, Z.A.; Wang, X. Conjugated polymers: Catalysts for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15712–15727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Tang, Y.; Yu, Y. Preparation of fenton reagent with H2O2 generated by solar light-illuminated nano-Cu2O/MWNTs composites. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 299, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Kim, J.O. Continuous-flow photocatalytic degradation of organics using modified TiO2 nanocomposites. Catalysts 2018, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Tay, Q.; Qi, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Z. Photocatalytic and adsorption performances of faceted cuprous oxide (Cu2O) particles for the removal of methyl orange (MO) from aqueous media. Molecules 2017, 22, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Hir, Z.; Abdullah, A.; Zainal, Z.; Lim, H. Photoactive hybrid film photocatalyst of polyethersulfone-ZnO for the degradation of methyl orange dye: Kinetic study and operational parameters. Catalysts 2017, 7, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.Y.; Chang, M.C.; Tseng, T.H. Solar and visible light illumination on immobilized nano zinc oxide for the degradation and mineralization of orange G in wastewater. Catalysts 2017, 7, 164. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Sharma, S.; Kaith, B.S.; Rajput, J.; Kaur, M. Synthesis of zno nanoparticles using surfactant free in-air and microwave method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 9661–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Arcibar-Orozco, J.A.; Bandosz, T.J. Key role of terminal hydroxyl groups and visible light in the reactive adsorption/catalytic conversion of mustard gas surrogate on zinc (hydr)oxides. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 174–175, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Dutta, J. Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes with manganese-doped zno nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chava, R.K.; Im, Y.; Kang, M. Nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots as a green luminescent sensitizer to functionalize zno nanoparticles for enhanced photovoltaic conversion devices. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 94, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Jia, H.; Cai, J.; Han, X.; Zheng, Z.; Wamer, W.G.; Yin, J.-J. Production of reactive oxygen species and electrons from photoexcited zno and zns nanoparticles: A comparative study for unraveling their distinct photocatalytic activities. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 3187–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi Prasanna, V.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Insight into the mechanism of antibacterial activity of zno: Surface defects mediated reactive oxygen species even in the dark. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2015, 31, 9155–9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Shao, R.; Chen, Z.; Tang, L.; Dai, Y.; Ding, J. Alkali-dependent synthesis of flower-like zno structures with enhanced photocatalytic activity via a facile hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 5455–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, V.; Bastami, T.R.; Ahmadpour, A. Solar energy harvesting by magnetic-semiconductor nanoheterostructure in water treatment technology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riahi-Madvaar, R.; Taher, M.A.; Fazelirad, H. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic halloysite-iron oxide nanocomposite and its application for naphthol green B removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 137, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middea, A.; Spinelli, L.S.; Souza, F.G., Jr.; Neumann, R.; Fernandes, T.L.A.P.; Gomes, O.D.F.M. Preparation and characterization of an organo-palygorskite-Fe3O4 nanomaterial for removal of anionic dyes from wastewater. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 139, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, A. Preparation, characterization and application on dye adsorption of a well-defined two-dimensional superparamagnetic clay/polyaniline/Fe3O4 nanocomposite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132–133, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Ma, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qiao, N.; Hu, M.; Ma, H. Adsorption of methylene blue onto Fe3O4/activated montmorillonite nanocomposite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Tang, X.; Wu, Z.; Lin, L.; Xu, J.; Xu, N.; Dai, B. Magnetic lignin-derived carbonaceous catalyst for the dehydration of fructose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in dimethylsulfoxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur’aeni; Chae, A.; Jo, S.; Choi, Y.; Park, B.; Park, S.Y.; In, I. Synthesis of β-FeOOH/Fe3O4 hybrid photocatalyst using catechol-quaternized poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) as a double-sided molecular tape. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Yang, X.; Yao, S. Photocatalytic activity of cerium-doped mesoporous TiO2 coated Fe3O4 magnetic composite under uv and visible light. J. Rare Earths 2012, 30, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekofteh-Gohari, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A. Novel magnetically separable Fe3O4@ZnO/AgCl nanocomposites with highly enhanced photocatalytic activities under visible-light irradiation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidnia, Z.; Idris, A. Combination of maghemite and titanium oxide nanoparticles in polyvinyl alcohol-alginate encapsulated beads for cadmium ions removal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.K.; Clament Sagaya Selvam, N. Enhanced visible light-driven photocatalytic performance of ZnO-g-C3N4 coupled with graphene oxide as a novel ternary nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, N.; Gao, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Dong, W. ZnO–montmorillonite as photocatalyst and flocculant for inhibition of cyanobacterial bloom. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc oxide-from synthesis to application: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Guo, H.; Patel, K.; Zhou, H.; Lou, X. High performance, recoverable Fe3O4/ZnO nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of phenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ökte, A.N.; Karamanis, D. A novel photoresponsive ZnO-flyash nanocomposite for environmental and energy applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 142–143, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmed, E.; Hong, Z.L.; Xu, J.F.; Khalid, N.R.; Elhissi, A.; Ahmed, W. A facile one-step approach to synthesizing ZnO/graphene composites for enhanced degradation of methylene blue under visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 274, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Brindley, G.W.; Kodama, H.; Martin, R.T. Report of the clay-minerals-society nomenclature committee for 1980–1981—Nomenclature for regular interstratifications. Clays Clay Miner. 1982, 30, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, G.; Gan, H. Synthesis, characterization and visible light photocatalytic properties of Bi2WO6/rectorite composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 369, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Chang, P.R.; Zheng, P.; Ma, X. Rectorite–TiO2–Fe3O4 composites: Assembly, characterization, adsorption and photodegradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Zhou, P.J.; Zhang, W.S.; Chen, S.; Peng, H. Effective photocatalytic decolorization of methylene blue utilizing ZnO/rectorite nanocomposite under simulated solar irradiation. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 616, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Fang, J.; Xu, W.; Cen, C. Bismuth-modified rectorite with high visible light photocatalytic activity. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 373, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, G.; Gao, Y. Stable TiO2/rectorite: Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 51, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.Z.; Zhang, G.K.; Gao, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.Q. Preparation and photocatalytic properties of visible light responsive n-doped TiO2/rectorite composites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 136, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Z.; He, S.; Wang, J. Sodium alginate/Na+-rectorite composite films: Preparation, characterization, and properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Pal, U.; Serrano, J.G.; Ucer, K.B.; Williams, R.T. Photoluminesence and ftir study of ZnO nanoparticles: The impurity and defect perspective. Phys. Status Solid 2006, 3, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Ren, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Sun, R. Preparation and characterization of new quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan/rectorite nanocomposite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, W.T.; Hong, H. An ftir investigation of hexadecyltrimethylammonium intercalation into rectorite. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2008, 71, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, D.H.; Nguyen, P.T. Magnetic properties of Cr doped Fe3O4 porous nanoparticles prepared through a co-precipitation method using surfactant. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.C.A.; Gonçalves, M.; Guerreiro, M.C.; Ramalho, T.C.; Fabris, J.D.; Pereira, M.C.; Sapag, K. A new catalyst material based on niobia/iron oxide composite on the oxidation of organic contaminants in water via heterogeneous fenton mechanisms. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 316, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirafuji, T.; Nomura, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Goto, M. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometric analysis of degradation products after treatment of methylene blue aqueous solution with three-dimensionally integrated microsolution plasma. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Xing, B. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by carbon nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]













| BET Surface Area (m2·g−1) | ZnO | REC | REC/Fe3O4 | REC/ZnO | ZnO/REC/Fe3O4 |
| 5.3 | 11.7 | 15.6 | 16.8 | 16.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhou, P.; Guo, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, H.; Yuan, Y. Synthesis of Rectorite/Fe3O4/ZnO Composites and Their Application for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye. Catalysts 2018, 8, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8030107
Wang H, Zhou P, Guo R, Wang Y, Zhan H, Yuan Y. Synthesis of Rectorite/Fe3O4/ZnO Composites and Their Application for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye. Catalysts. 2018; 8(3):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8030107
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huanhuan, Peijiang Zhou, Rui Guo, Yifei Wang, Hongju Zhan, and Yunfei Yuan. 2018. "Synthesis of Rectorite/Fe3O4/ZnO Composites and Their Application for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye" Catalysts 8, no. 3: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8030107
APA StyleWang, H., Zhou, P., Guo, R., Wang, Y., Zhan, H., & Yuan, Y. (2018). Synthesis of Rectorite/Fe3O4/ZnO Composites and Their Application for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye. Catalysts, 8(3), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8030107