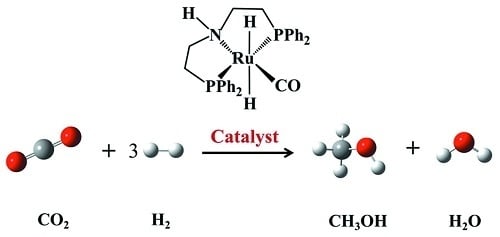
Theoretical Study of the Mechanism for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol Catalyzed by trans-RuH2(CO)(dpa)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide
2.2. Hydrogenation of Formic Acid
2.3. Hydrogenation of Formaldehyde
2.4. The Regeneration of the Catalyst
3. Computational Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jadhav, S.G.; Vaidya, P.D.; Bhanage, B.M.; Joshi, J.B. Catalytic Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation to Methanol: A Review of Recent Studies. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 2557–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.; Alberico, E.; Baumann, W.; Drexler, H.J.; Junge, H.; Gladiali, S.; Beller, M. Low-temperature aqueous-phase methanol dehydrogenation to hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Nature 2013, 495, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberico, E.; Nielsen, M. Towards a Methanol Economy Based on Homogeneous Catalysis: Methanol to H2 and CO2 to Methanol. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6714–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goeppert, A.; Czaun, M.; Jones, J.P.; Prakash, G.K.S.; Olah, G.A. Recycling of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol and Derived Products-Closing the Loop. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7995–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii. Available online: http://co2now.org/ (accessed on 11 December 2017).
- Monastersky, R. Global Carbon Dioxide Levels near Worrisome Milestone. Nature 2013, 497, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.Q.; Xu, Z.H.; Fan, M.H.; Gupta, R.; Slimane, R.B.; Bland, A.E.; Wright, I. Progress in Carbon Dioxide Separation and Capture: A Review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Eden, M.R.; Gani, R. Toward the Development and Deployment of Large-Scale Carbon Dioxide Capture and Conversion Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 3383–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aresta, M.; Dibenedetto, A.; Angelini, A. Catalysis for the Valorization of Exhaust Carbon: From CO2 to Chemicals, Materials, and Fuels. Technological Use of CO2. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1709–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aresta, M.; Dibenedetto, A. Utilisation of CO2 as A Chemical Feedstock: Opportunities and Challenges. Dalton Trans. 2007, 28, 2975–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centi, G.; Perathoner, S. Opportunities and Prospects in the Chemical Recycling of Carbon Dioxide to Fuels. Catal. Today 2009, 148, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; Gong, J. Recent Advances in Catalytic Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3703–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porosoff, M.D.; Yan, B.; Chen, J.G. Catalytic Reduction of CO2 by H2 for Synthesis of CO, Methanol and Hydrocarbons: Challenges and Opportunities. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, G.A.; Goeppert, A.; Prakash, G.K.S. Chemical Recycling of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol and Dimethyl Ether: From Greenhouse Gas to Renewable, Environmentally Carbon Neutral Fuels and Synthetic Hydrocarbons. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moret, S.; Dyson, P.J.; Laurenczy, G. Direct Synthesis of Formic Acid from Carbon Dioxide by Hydrogenation in Acidic Media. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, M.; Studt, F.; Kasatkin, I.; Kuhl, S.; Havecker, M.; Pedersen, F.A.; Zander, S.; Girgsdies, F.; Kurr, P.; Kniep, B.L.; et al. The Active Site of Methanol Synthesis over Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 Industrial Catalysts. Science 2012, 336, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-N.; Ma, R.; He, L.-N.; Diao, Z.-F. Homogeneous Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, I.M.; Granados, M.L.; Fierro, J.L.G. Reverse Topotactic Transformation of a Cu-Zn-Al Catalyst during Wet Pd Impregnation: Relevance for the Performance in Methanol Synthesis from CO2/H2 Mixtures. J. Catal. 2002, 210, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, I.M.; Granados, M.L.; Fierro, J.L.G. Pd-Modified Cu-Zn Catalysts for Methanol Synthesis from CO2/H2 Mixtures: Catalytic Structures and Performance. J. Catal. 2002, 210, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Mao, D.; Wang, S.; Wu, G.; Lu, G. Combustion Synthesis of CuO-ZnO-ZrO2 Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabow, L.C.; Mavrikakis, M. Mechanism of Methanol Synthesis on Cu through CO2 and CO Hydrogenation. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahruji, H.; Bowker, M.; Hutchings, G.; Dimitratos, N.; Wells, P.; Gibson, E.; Jones, W.; Brookes, C.; Morgan, D.; Lalev, G. Pd/ZnO Catalysts for Direct CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol. J. Catal. 2016, 343, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Tsubaki, N. A New Method of Low-Temperature Methanol Synthesis on Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 Catalysts from CO/CO2/H2. Fuel 2008, 87, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, C.A.; Sanford, M.S. Cascade Catalysis for the Homogeneous Hydrogenation of CO2 to Methanol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18122–18125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselbaum, S.; Stein, T.V.; Klankermayer, J.; Leitner, W. Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol by Using a Homogeneous Ruthenium-Phosphine Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7499–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haunschild, R. Theoretical study on the reaction mechanism of carbon dioxide reduction to methanol using a homogeneous ruthenium(II) phosphine catalyst. Polyhedron 2015, 85, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, W.; Matsumoto, T.; Ino, Y.; Ogata, O. Novel Ruthenium Carbonyl Complex Having a Tridentate Ligand and Manufacturing Method and Usage Therefor. PCT International Patent Application WO/2011/048727 A1, 28 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama, W.; Matsumoto, T.; Ogata, O.; Ino, Y.; Aoki, K.; Tanaka, S.; Ishida, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Sayo, N.; Saito, T. Catalytic Hydrogenation of Esters. Development of an Efficient Catalyst and Processes for Synthesising (R)-1,2-Propanediol and 2-(l-Menthoxy)ethanol. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2012, 16, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Rong, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Ding, K. Catalytic Hydrogenation of Cyclic Carbonates: A Practical Approach from CO2 and Epoxides to Methanol and Diols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 13041–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, T.; Ishii, A.; Dub, P.A.; Ikariya, T. Practical Selective Hydrogenation of α-Fluorinated Esters with Bifunctional Pincer-Type Ruthenium(II) Catalysts Leading to Fluorinated Alcohols or Fluoral Hemiacetals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9600–9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09 (Revision A.02); Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Csonka, G.I.; Ruzsinszky, A.; Tao, J.; Perdew, J.P. Energies of Organic Molecules and Atoms in Density Functional Theory. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2005, 101, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, D.; Sader, C.A.; Fischer, U.; Wagner, K.; Jones, P.J.; Xing, M.; Fandrick, K.R.; Gonnella, N.C. Systematic Investigation of DFT-GIAO 15N NMR Chemical Shift Prediction Using B3LYP/cc-pVDZ: Application to Studies of Regioisomers, Tautomers, Protonation States and N-oxides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woon, D.E.; Dunning, T.H. Gaussian Basis Sets for Use in Correlated Molecular Calculations. III. The Atoms Aluminum through Argon. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 1358–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossi, M.; Scalmani, G.; Rega, N.; Barone, V. New Developments in the Polarizable Continuum Model for Quantum Mechanical and Classical Calculations on Molecules in Solution. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Heterogeneous Catalysts | Homogeneous Catalysts | |
|---|---|---|
| Catalysts | Metal/Metallic oxide | Metal complex |
| Temperature | 200–300 °C | Most are below 200 °C |
| Catalytic activity | Relatively low | Much higher than Heterogeneous |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Huang, L.; Yan, W.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Lu, X. Theoretical Study of the Mechanism for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol Catalyzed by trans-RuH2(CO)(dpa). Catalysts 2018, 8, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060244
Zhou J, Huang L, Yan W, Li J, Liu C, Lu X. Theoretical Study of the Mechanism for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol Catalyzed by trans-RuH2(CO)(dpa). Catalysts. 2018; 8(6):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060244
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jinxia, Liangliang Huang, Wei Yan, Jun Li, Chang Liu, and Xiaohua Lu. 2018. "Theoretical Study of the Mechanism for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol Catalyzed by trans-RuH2(CO)(dpa)" Catalysts 8, no. 6: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060244
APA StyleZhou, J., Huang, L., Yan, W., Li, J., Liu, C., & Lu, X. (2018). Theoretical Study of the Mechanism for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol Catalyzed by trans-RuH2(CO)(dpa). Catalysts, 8(6), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060244