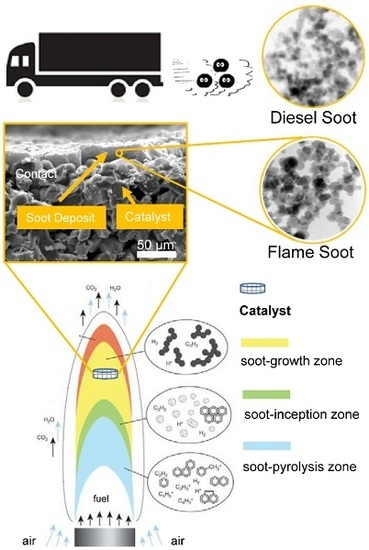
Simulating Real World Soot-Catalyst Contact Conditions for Lab-Scale Catalytic Soot Oxidation Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Nature of Soots
2.2. Temperature-Programmed-Oxidation (TPO)
2.3. Kinetics Analysis Based on Nonisothermal Experiments
2.4. Kinetic Analysis from Isothermal Studies (nth Order Model)
2.5. BET Surface Area
2.6. Flame Deposit Contact vs. Realistic Contact
3. Discussion
3.1. Microstructure and Reactivity
3.2. Soot Oxidation Kinetics
3.3. Implications of This Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Soot Collection
4.2. Soot Characterization
4.3. Temperature Programmed Oxidation & Soot Oxidation & Kinetics
4.3.1. Kinetics from Nonisothermal Experiments
4.3.2. Kinetics from Isothermal Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russo, N.; Fino, D.; Saracco, G.; Specchia, V. Studies on the redox properties of chromite perovskite catalysts for soot combustion. J. Catal. 2005, 229, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, K. Kinetics of diesel nanoparticle oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J. Effect of Fuel Formulation on Soot Properties and Regeneration of Diesel Particulate Filters, in Energy and Geo-Environmental Engineering. Ph.D. Thesis, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, State College, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Stanmore, B.R.; Brilhac, J.F.; Gilot, P. The oxidation of soot: A review of experiments, mechanisms and models. Carbon 2001, 39, 2247–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Su, C.; McGinn, P.J. Application of potash glass as a catalyst for diesel soot oxidation. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeft, J.P.A.; Nijhus, T.X.; Smakman, E.; Makkee, M.; Moulijn, J.A. Kinetics of the oxidation of diesel soot. Fuel 1997, 76, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Wal, R.L.; Tomasek, A.J. Soot nanostructure: Dependence upon synthesis condition. Combust. Flame 2004, 136, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Wal, R.L.; Yezeret, A.; Currier, N.W.; Kim, D.H.; Wang, C.M. HRTEM Study of diesel soot collected from diesel particulate filters. Carbon 2007, 45, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Wal, R.L.; Tomasek, A.J. Soot oxidation: Dependence upon initial nanostructure. Combust. Flame 2003, 134, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehman, A.L.; Song, J.; Alam, M. Impact of biodiesel blending on diesel soot and the regeration of particulate filters. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelec, A.; Toops, T.J.; Daw, C.S. Oxygen reactivity of devolatilized diesel engine particulates from conventional and biodiesel fuels. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 3944–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfe, M.; Apicella, B.; Barbella, R.; Rouzaud, J.-N.; Tregrossi, A.; Ciajolo, A. Structure–property relationship in nanostructures of young and mature soot in premixed flames. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, R.H.; Crawford, G.P.; Shim, H.S. Equilibrium nanostructure of primary soot particles. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2000, 28, 2539–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Wal, R.L. Onset of carbonization: Spatial location via simultaneous LIF-LII and characterization via TEM. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1996, 118, 343–360. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Su, C.; Clerc, J.; Harinath, A.; Rogoski, L. Experimental and Modeling Study of Ash Impact on DPF Backpressure and Regeneration Behaviors. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yezerets, A.; Currier, N.; Eadler, H.; Popuri, S.; Suresh, A. Quantitative Flow-Reactor Study of Diesel Soot Oxidation Process; SAE Technical Paper, 2002-01-1684; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yezerets, A.; Currier, N.; Eadler, H.A. Experimental Determination of the Kinetics of Diesel Soot Oxidation by O2—Modeling Consequences; SAE Technical Paper, 2003-01-0833; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S. Understanding the difference in oxidative properties between flame and diesel soot nanoparticles: The role of metals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeft, J.P.A.; Makee, M.; Moulijn, J.A. Catalysts for the oxidation of soot from diesel exhaust gases. I. An exploratory study. Appl. Catal. Environ. 1996, 8, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xi, Y.; Su, C.; Liu, Z.G. Lab Study of Urea Deposit Formation and Chemical Transformation Process of Diesel Aftertreatment System; SAE Technical Paper, 2017-01-0915; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Atribak, I.; Bueno-López, A.; García-García, A. Uncatalysed and catalysed soot combustion under NOx + O2: Real diesel versus model soots. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 2086–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Setten, B.A.A.L.; Schouten, J.M.; Makkee, M.; Moulijn, J.A. Realistic contact for soot with an oxidation catalyst for laboratory studies. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 28, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Sahajwalla, V.; Kong, C.; Harris, D. Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis and its application to various coals. Carbon 2001, 39, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yezerets, A.; Currier, N.W.; Kim, D.H.; Eadler, H.A.; Epling, W.S.; Peden, C.H. Differential kinetic analysis of diesel particulate matter (soot) oxidation by oxygen using a step–response technique. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2005, 61, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; McGinn, P.J. The effect of Ca2+ and Al3+ additions on the stability of potassium disilicate glass as a soot oxidation catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 138, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; McGinn, P.J. Application of glass soot catalysts on metal supports to achieve low soot oxidation temperature. Catal. Commun. 2014, 43, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H. Introduction to Carbon Science, 1st ed.; Butterworths: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C. Stabilization of Potassium in Soot Oxidation Catalysts and Their Application on Diesel Particulate Filters. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- NLaine, N.R.; Vastola, F.J.; Walker, P.L., Jr. The importance of active surface area in the coarbon-oxygen reaction. J. Phys. Chem. 1963, 67, 2030–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Tighe, C.J.; Twigg, M.V.; Hayhurst, A.N.; Dennis, J.S. The kinetics of oxidation of Diesel soots and a carbon black (Printex U) by O2 with reference to changes in both size and internal structure of the spherules during burnout. Carbon 2016, 107, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fino, D.; Bensaid, S.; Piumetti, M.; Russo, N. A review on the catalytic combustion of soot in diesel particulate filters for automotive applications: from powder catalysts to structured reactors. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 509, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno-López, A. Diesel soot combustion ceria catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 146, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zokoe, J.; McGinn, P.J. Catalytic diesel soot oxidation by hydrothermally stable glass catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kumar, A.; Klippstein, D.; Stafford, R.; Su, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zokoe, J.; McGinn, P. Development and Demonstration of a Soot Generator Integrated Bench Reactor; SAE Technical Paper, No. 2014-01-1589; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McGinn, P.J.; Su, C. Glass Catalysts for Soot Combustion and Methods of Manufacturing the Same. U.S. Patent 9,592,490, 14 March 2017. [Google Scholar]













| Soot Sample | C | H | N | S | O | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Black | 95.3 | 0.5 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 2.7 | <0.1 |
| Engine soot | 80.1 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 0.20 | 14.6 | 1.5 |
| Flame soot-FS100 | 96.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 2.8 | <0.1 |
| Soot Symbol | Soot Origin | d002 (nm) | Lc | La | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB | Printex Carbon black | 0.360 | 1.268 | 6.89 | ~4 |
| DS | Diesel engine soot | 0.359/0.336 | 1.446/22.42 | 7.26 | ~4/~67 |
| FS25 | Flame soot, h = 25 mm | 0.357 | 1.422 | 7.24 | ~4 |
| FS50 | Flame soot, h = 50 mm | 0.358 | 1.413 | 7.27 | ~4 |
| FS100 | Flame soot, h = 100 mm | 0.358 | 1.426 | 7.22 | ~4 |
| FS150 | Flame soot, h = 150 mm | 0.359 | 1.418 | 7.18 | ~4 |
| Soot Sample | Reaction Order of C | Reaction Order of O2 | Ea-nth Order Model (kJ/mol) | Ea-Model Free (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Printex-U carbon black | 0.86 | 0.72 | 160 | 145 |
| Printex-U carbon black * | 1 | 0.71 | 132 | -- |
| FS100 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 167 | 147 |
| Engine soot | -- | -- | -- | 139 |
| Engine soot * | 1 | 0.61 | 137 | -- |
| Sample | Content of HC | Initial SA (m2/g) | Final SA (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Printex-U | <3% | 112 | 110 |
| FS-20 | <3% | 108 | 109 |
| FS-50 | <3% | 103 | 103 |
| FS-100 | <3% | 97 | 98 |
| FS-150 | <3% | 71 | 73 |
| Diesel soot | 22–25% | 121 | 171 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, C.; Wang, Y.; Kumar, A.; McGinn, P.J. Simulating Real World Soot-Catalyst Contact Conditions for Lab-Scale Catalytic Soot Oxidation Studies. Catalysts 2018, 8, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060247
Su C, Wang Y, Kumar A, McGinn PJ. Simulating Real World Soot-Catalyst Contact Conditions for Lab-Scale Catalytic Soot Oxidation Studies. Catalysts. 2018; 8(6):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060247
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Changsheng, Yujun Wang, Ashok Kumar, and Paul J. McGinn. 2018. "Simulating Real World Soot-Catalyst Contact Conditions for Lab-Scale Catalytic Soot Oxidation Studies" Catalysts 8, no. 6: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060247
APA StyleSu, C., Wang, Y., Kumar, A., & McGinn, P. J. (2018). Simulating Real World Soot-Catalyst Contact Conditions for Lab-Scale Catalytic Soot Oxidation Studies. Catalysts, 8(6), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060247