Enzymatic Production of Biodiesel Using Immobilized Lipase on Core-Shell Structured Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) Composites
Abstract
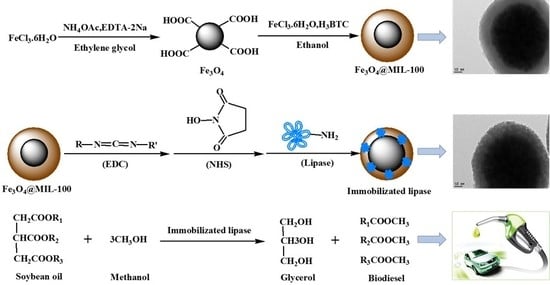
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Enzymatic Activities of the Immobilized Lipase
2.2. Characteristics of the Immobilized Lipase
2.3. Factors Affecting the Immobilization Efficiency and Enzymatic Activity Recovery
2.4. Immobilized Lipase-Catalyzed Transesterification Reaction of Soybean Oil
2.5. Reusability of the Immobilized Lipase
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Core-Shell Structured Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) Composites
3.3. Lipase Immobilization
3.4. Lipase Activity Assay
3.5. Characterizations
3.6. Enzymatic Transesterification Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, Y.C.; Singh, B.; Upadhyay, S.N. Advancements in development and characterization of biodiesel: A review. Fuel 2008, 87, 2355–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aransiola, E.F.; Ojumu, T.V.; Oyekola, O.O.; Madzimbamuto, T.F.; Ikhuomoregbe, D.I.O. A review of current technology for biodiesel production: State of the art. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 61, 276–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wan, F. Immobilization of polyoxometalate-based sulfonated ionic liquids on UiO-66-2COOH metal-organic frameworks for biodiesel production via one-pot transesterification-esterification of acidic vegetable oils. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 365, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Li, H.; Pan, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Yu, Z.; Yang, S. Efficient and green production of biodiesel catalyzed by recyclable biomass-derived magnetic acids. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 181, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzu, M.; Fujimori, A.; Fukakusa, R.T.; Satomi, N.; Yahagi, S. Continuous production of biodiesel by the CaO-catalyzed transesterification operated with continuously stirred tank reactor. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 181, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, H. Immobilized polymeric sulfonated ionic liquid on core-shell structured Fe3O4/SiO2 composites: A magnetically recyclable catalyst for simultaneous transesterification and esterifications of low-cost oils to biodiesel. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, L.P.; Kumar, H.; Zambare, V.P. Enzymatic biodiesel: Challenges and opportunities. Appl. Energy 2014, 119, 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarthy, M.; Saravanan, P.; Gowthaman, M.K.; Rose, C.; Kamini, N.R. Enzymatic transesterification for production of biodiesel using yeast lipases: An overview. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, Z.; Ilham, Z.; Ong, H.C.; Mazaheri, H.; Chen, W.H. State of the art and prospective of lipase-catalyzed transesterification reaction for biodiesel production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 141, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, J. Enzymatic production of biodiesel from soybean oil by using immobilized lipase on Fe3O4/poly(styrene-methacrylic acid) magnetic microsphere as a biocatalyst. Energy Fuel 2014, 28, 2624–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Galan, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Rodrigues, R.C. Potential of different enzyme immobilization strategies to improve enzyme performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2885–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet-Ragel, K.; López-Pou, L.; Tutusaus, G.; Benaiges, M.D.; Valero, F. Rice husk ash as a potential carrier for the immobilization of lipases applied in the enzymatic production of biodiesel. Biocatal. Biotransfor. 2018, 36, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, A.; Thulasidharan, D.; Jegadeesan, G.B. Process optimization of biodiesel production from Hevea brasiliensis oil using lipase immobilized on spherical silica aerogel. Renew. Energy 2008, 116, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolatti, E.P.; Valério, A.; Henriques, R.O.; Moritz, D.E.; Ninow, J.L.; Manoel, E.A.; Freire, D.M.G.; Lafuente, R.F.; Oliveire, D. Nanomaterials for biocatalyst immobilization-state of the art and future trends. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 104675–104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zang, X. Lipase immobilized on ionic liquid-functionalized magnetic silica composites as a magnetic biocatalyst for production of trans-free plastic fats. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netto, C.G.C.M.; Toma, H.E.; Andrade, L.H. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles as versatile carriers and supporting materials for enzymes. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 85–86, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.G.; Besteti, M.D.; Manoel, E.A.; da Silva, A.T.T.; Almeida, R.V.; Simas, A.B.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Pinto, J.C.; Freire, D.M.G. Preparation of core-shell polymer supports to immobilize lipase B from Candida antarctica: Effect of the support nature on catalytic properties. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 100, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharfar, R.; Mohajer, S. Synthesis and characterization of immobilized lipase on Fe3O4 nanoparticles as nano biocatalyst for the synthesis of benzothiazepine and spirobenzothiazine chroman derivatives. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, W.; Li, H.; Lv, P.; Yuan, Z. Lipase immobilization on amino-silane modified superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as biocatalyst for biodiesel production. Fuel 2018, 224, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Han, Y.; Wang, H. Magnetic Fe3O4/MCM-41 composite-supported sodium silicate as heterogeneous catalysts for biodiesel production. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, A.H.; Ahmad, N.; Younus, H.A.; Laypkov, A.; Verpoort, F. Metal-organic frameworks: Versatile heterogeneous catalysts for efficient catalytic organic transformations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6804–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.L.; Yang, N.S.; Chen, Y.T.; Lirio, S.; Wu, C.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, H.Y. Lipase-supported metal-organic framework bioreactor catalyzes warfarin synthesis. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 21, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Wan, F. Basic ionic liquid functionalized magnetically responsive Fe3O4@HKUST-1 composites used for biodiesel production. Fuel 2018, 220, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.W.; Que, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Guan, G.F.; Liu, X. Encapsulation of heteropolyanion-based ionic liquid within the metal-organic framework MIL-100(Fe) for biodiesel production. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.M.; Jin, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhong, Y.J.; Zhu, W.D.; El-Shall, M.S. Polyoxometalates confined in the mesoporous cages of metal-organic framework MIL-100(Fe): Efficient heterogeneous catalysts for esterification and acetalization reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 269, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abednatanzi, S.; Abbasi, A.; Masteri-Farahani, M. Immobilization of catalytically active polyoxotungstate into ionic liquid-modified MIL-100(Fe): A recyclable catalyst for selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Catal. Commun. 2017, 96, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.T.; Ren, X.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Wei, Y.; Qing, L.S.; Liao, X. Covalent immobilization of porcine pancreatic lipase on carboxyl-activated magnetic nanoparticles: Characterization and application for enzymatic inhibition assays. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 38, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.J.; Gu, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.W.; Que, Y.G.; Wang, Q.; Wan, H.; Guan, G.F. Efficient confinement of ionic liquids in the MIL-100(Fe) frameworks by the “impregnation-reaction-encapsulation” strategy for biodiesel production. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 37110–37117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zang, X. Immobilized lipase on core–shell structured Fe3O4–MCM-41 nanocomposites as a magnetically recyclable biocatalyst for interesterification of soybean oil and lard. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Qian, L.; Lv, H.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhao, G.H. Introduction of a Fe3O4 core enhances the photocatalytic activity of MIL-100(Fe) with tunable shell thickness in the presence of H2O2. ChemCatChem 2016, 7, 4148–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, Y. Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase onto graphene oxide Fe3O4 nanocomposite: Characterization and application for biodiesel production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 159, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.M.; Xu, W.H.; Jin, L.; Zha, J.J.; Tao, T.X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Synthesis of amine-functionalized Fe3O4@C nanoparticles for lipase immobilization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18339–18344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guan, Y.; Shen, R.; Liu, H. Immobilization of lipase onto micron-size magnetic beads. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 822, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, J.; Guo, H.; Cai, X. Preparation of immobilized lipase on magnetic nanoparticles dialdehyde starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarno, M.; Luliano, M. Highly active and stable Fe3O4/Au nanoparticles supporting lipase catalyst for biodiesel production from waste tomato. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 474, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.V.; Narasimhan, S.L.; Muthukumar, K. An overview of enzymatic production of biodiesel. Bioresource Technol. 2008, 99, 3975–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z.; Zhao, G.H.; Li, Y.F.; Peng, X.M.; Wang, X.Y. Preparation of amine-functionalized mesoporous magnetic colloidal nanocrystal clusters for glucoamylase immobilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Bao, C.; Ma, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, F. Magnetic responsive metal–organic frameworks nanosphere with core-shell structure for highly efficient removal of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruoka, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Nawafune, H.; Akamatsu, K. Controlled self-assembly of metal-organic frameworks on metal nanoparticles for efficient synthesis of hybrid nanostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2011, 3, 3788–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramić, M.; Leščić, I.; Korica, T.; Vitale, L.; Saenger, W.; Pigac, J. Purification and properties of extracellular lipase from Streptomyces rimosus. Enzym. Microb. Tech. 1999, 25, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standards, B. Fat and Oil Derivatives-Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAME)-Determination of Ester and Linolenic Acid Methyl Ester Contents; Standards Policy and Strategy Committee, British Standards Institute: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]












© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, W.; Huang, M. Enzymatic Production of Biodiesel Using Immobilized Lipase on Core-Shell Structured Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) Composites. Catalysts 2019, 9, 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100850
Xie W, Huang M. Enzymatic Production of Biodiesel Using Immobilized Lipase on Core-Shell Structured Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) Composites. Catalysts. 2019; 9(10):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100850
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Wenlei, and Mengyun Huang. 2019. "Enzymatic Production of Biodiesel Using Immobilized Lipase on Core-Shell Structured Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) Composites" Catalysts 9, no. 10: 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100850
APA StyleXie, W., & Huang, M. (2019). Enzymatic Production of Biodiesel Using Immobilized Lipase on Core-Shell Structured Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) Composites. Catalysts, 9(10), 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100850