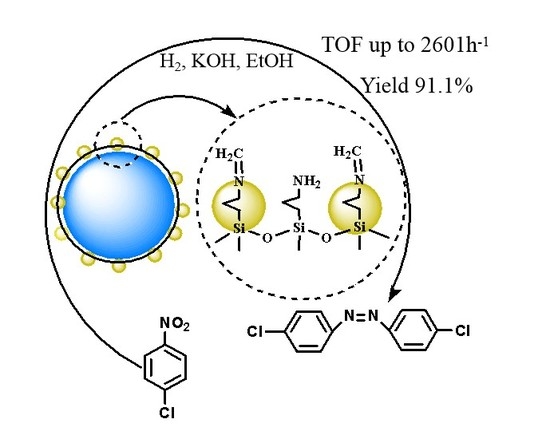
A Schiff-Base Modified Pt Nano-Catalyst for Highly Efficient Synthesis of Aromatic Azo Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalysts Characterization
2.2. Catalytic Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Synthesis
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Catalyst Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, J.; Xiao, J.; Tang, B.; Ju, B.; Zhang, S. Facile synthesis of novel disperse azo dyes with aromatic hydroxyl group. Dyes Pigm. 2019, 160, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, E. Synthesis of azobenzenes: The coloured pieces of molecular materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, E.; Ribagorda, M. Control over molecular motion using thecis–transphotoisomerization of the azo group. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 1071–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neistadt, M.E. Educational Interpretation of “Cooperative Learning as an Approach to Pedagogy”. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1999, 53, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, C.H.; Ledwith, A.; Yagci, Y. Synthesis and reactions of polymers with photoactive terminal groups: 2. New azo-initiator for the synthesis of polymers with N-acyldibenz[b,f] azepine terminal units. Polymer 1978, 19, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizli, A.; Pişkin, E. Dye-ligand affinity systems. J. Biochem. Bioph. Methods 2001, 49, 391–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.Y.; Sharaf, I.A.; Osman, H.M.Y.; El-Khouly, Z.A.; Ahmed, E.I. Synthetic organic food colouring agents and their degraded products: effects on human and rat cholinesterases. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2004, 61, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, C.; Kano, K.; Sasaki, Y.F.; Sato, I.; Tsudua, S. Differential colon DNA damage induced by azo food additives between rats and mice. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 35, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisnetti, F.; Ballardini, R.; Credi, A.; Gandolfi, M.T.; Masiero, S.; Negri, F.; Pieraccini, S.; Spada, G.P. Photochemical and Electronic Properties of Conjugated Bis(azo) Compounds: An Experimental and Computational Study. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Zee, F.P.; Cervantes, F.J. Impact and application of electron shuttles on the redox (bio)transformation of contaminants: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 256–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.G.; Gu, J.D. Physiology and biochemistry of reduction of azo compounds by Shewanella strains relevant to electron transport chain. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, Z.; Zali-Boeini, H. Novel sugar-based azo dyes as multistimuli responsive supramolecular gelators and chemosensors. Dyes Pigm. 2018, 159, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Hanauer, S.B. The pharmacokinetic profiles of oral mesalazine formulations and mesalazine pro-drugs used in the management of ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Therap. 2003, 17, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Suzuki, M.; Peisach, J.; Suzuki, T. Induction of hepatic microsomal drug metabolism by azo compounds: A structure-activity relationship. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1984, 52, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J. Rational selection of oral 5-aminosalicylate formulations and prodrugs for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2939–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedinger, A.; Guardia, P.; Curcio, A.; Garcia, M.A.; Cingolani, R.; Manna, L.; Pellegrino, T. Subnanometer Local Temperature Probing and Remotely Controlled Drug Release Based on Azo-Functionalized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, E.-R.; Aly, E.; Imam Abdel-Hay, F.; Abdeen, R.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G. Synthesis and microbial degradation of azopolymers for possible applications for colon specific drug delivery I. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghbeen, K.; Tan, E.W. Facile Synthesis of Catechol Azo Dyes. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 4503–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raicopol, M.; Andronescu, C.; Atasiei, R.; Hanganu, A.; Manea, A.M.; Rau, I.; Kajzar, F.; Pilan, L. Synthesis of conducting azopolymers by electrochemical grafting of a diazonium salt at polypyrrole electrodes. Synth. Met. 2015, 206, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, R.O.; Lamson, D.W.; Rua, L.; Milewski, C.; Maryanoff, B. Reduction of aromatic nitro compounds with sodium borohydride in dimethyl sulfoxide or sulfolane. Synthesis of azo or azoxy derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 1971, 36, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entwistle, I.D.; Gilkerson, T.; Johnstone, R.A.W.; Telford, R.P. Rapid catalytic transfer reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to hydroxylamines. Tetrahedron 1978, 34, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouoit-Montésinos, S.; Bassus, J.; Perrin, M.; Lamartine, R. Synthesis of new phenylazocalix[n]arenes (n = 4, 5). Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 2563–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, S.; Gowda, D.C. Application of Lead and Ammonium Formate as a New System for the Synthesis of Azo Compounds. Synthesis-Stuttgart 2002, 4, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moglie, Y.; Vitale, C.; Radivoy, G. Synthesis of azo compounds by nanosized iron-promoted reductive coupling of aromatic nitro compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 41, 1828–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Dash, J.; Sudheer, C.; Gupta, R.K. Chemoselective reduction of aromatic nitro and azo compounds in ionic liquids using zinc and ammonium salts. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 7783–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grirrane, A.; Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Gold-Catalyzed Synthesis of Aromatic Azo Compounds from Anilines and Nitroaromatics. Science 2008, 322, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Cao, X.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; Gu, H. Catalysis by Pd nanoclusters generated in situ of high-efficiency synthesis of aromatic azo compounds from nitroaromatics under H2 atmosphere. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 4899–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Cao, X.; Shi, L.; Qi, F.; Guo, Z.; Lu, J.; Gu, H. A Highly Active Nano-Palladium Catalyst for the Preparation of Aromatic Azos under Mild Conditions. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5640–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Zheng, J.; Lu, J.; Sun, X.; Gu, H. Highly efficient synthesis of aromatic azos catalyzed by unsupported ultra-thin Pt nanowires. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3445–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, H.Q.; Ye, S.; Liu, Y.M.; He, H.Y.; Cao, Y. Gold-Catalyzed Direct Hydrogenative Coupling of Nitroarenes To Synthesize Aromatic Azo Compounds. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 7754–7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Serna, P.; García, H. Gold Catalysts Open a New General Chemoselective Route to Synthesize Oximes by Hydrogenation of α,β-Unsaturated Nitrocompounds with H2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 6358–6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boronat, M.; Concepción, P.; Corma, A.; González, S.; Illas, F.; Serna, P. A Molecular Mechanism for the Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Substituted Nitroaromatics with Nanoparticles of Gold on TiO2 Catalysts: A Cooperative Effect between Gold and the Support. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 16230–16237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Su, D.S. Enhanced Chemoselective Hydrogenation through Tuning the Interaction between Pt Nanoparticles and Carbon Supports: Insights from Identical Location Transmission Electron Microscopy and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7844–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; O’Hayre, R.; Shao, Z. The use of nitrogen-doped graphene supporting Pt nanoparticles as a catalyst for methanol electrocatalytic oxidation. Carbon 2013, 52, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.L.; Jiang, S.; Yu, K.; Gu, Z.; Ji, R.; Dong, Y.; Liu, S. Mesoporous silicas functionalized with aminopropyl via co-condensation: Effective supports for chiral Mn(III) salen complex. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2011, 142, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yang, K.; Xie, Y.; Fan, Q.; Yu, J.C.; Shu, Q.; Wang, C. Novel hollow Pt-ZnO nanocomposite microspheres with hierarchical structure and enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, N.; Han, B.; Xiao, X.; Chen, G.; Djerdj, I.; Wang, Y. Nanoparticle cluster gas sensor: Pt activated SnO2 nanoparticles for NH3 detection with ultrahigh sensitivity. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14872–14880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Huang, Z.F.; Pan, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, J.J. Review on selective hydrogenation of nitroarene by catalytic, photocatalytic and electrocatalytic reactions. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 227, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combita, D.; Concepción, P.; Corma, A. Gold catalysts for the synthesis of aromatic azocompounds from nitroaromatics in one step. J. Catal. 2014, 311, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ke, X.; Yang, X.; Sarina, S.; Liu, H. Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds on Supported Gold Nanoparticles by Visible and Ultraviolet Light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9657–9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hao, C.; Jin, G.; Zhu, H.Y.; Guo, X.Y. Copper Nanoparticles on Graphene Support: An Efficient Photocatalyst for Coupling of Nitroaromatics in Visible Light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Sarina, S.; Zhu, H. Tuning the reduction power of visible-light photocatalysts of gold nanoparticles for selective reduction of nitroaromatics to azoxy-compounds—Tailoring the catalyst support. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 209, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Miao, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T. Direct catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to formate over a Schiff-base-mediated gold nanocatalyst. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Entry | Catalyst | Conv. (%) | Sel. (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCAB | DCAOB | p-CNA | |||
| 1 | Pt0.5/SiO2 | 92.4 | 12.1 | 85.5 | 2.4 |
| 2 a | Pt0.5/SiO2 | 10.6 | - | 94.1 | 5.9 |
| 3 | Pt0.5/SiO2-Schiff | 99.0 | 92.1 | 4.7 | 3.2 |
| 4 a | Pt0.5/SiO2-Schiff | 98.6 | 89.1 | 5.8 | 5.1 |
| 5 b | Pt0.5/SiO2-Schiff | 98.2 | 87.1 | 7.0 | 5.9 |
| 6 | Pt0.3/SiO2-Schiff | 97.2 | 57.0 | 40.1 | 2.9 |
| 7 | Pt0.8/SiO2-Schiff | 100 | 93.0 | 2.1 | 4.9 |
| Entry | Solvent | Base | Conv. (%) | Sel. (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCAB | DCAOB | p-CNA | ||||
| 1 | ethanol | - | 96.5 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 97.3 |
| 2 | ethanol | K2CO3 (1 eqv.) | 100 | 8.9 | 52.9 | 38.2 |
| 3 | ethanol | Na2CO3 (1 eqv.) | 98.2 | 6.2 | 27.1 | 66.7 |
| 4 | ethanol | KOH (0.5 eqv.) | 96.5 | 66.2 | 24.4 | 9.4 |
| 5 | ethanol | KOH (1 eqv.) | 97.8 | 78.8 | 10.4 | 10.8 |
| 6 | ethanol | KOH (2 eqv.) | 99.0 | 92.1 | 4.7 | 3.2 |
| 7 | ethanol | KOH (3 eqv.) | 98.9 | 88.1 | 6.8 | 5.1 |
| 8 | methanol | KOH (2 eqv.) | 86.2 | 37.4 | 51.6 | 11.0 |
| 9 | i-propanol | KOH (2 eqv.) | 99.7 | 90.9 | 3.4 | 5.7 |
| 10 | toluene | KOH (2 eqv.) | 8.1 | 5.7 | 88.3 | 6.0 |
| 11 | p-xylene | KOH (2 eqv.) | 6.2 | 49.5 | 43.2 | 7.3 |
| 12 | n-heptane | KOH (2 eqv.) | 14.2 | 12.1 | 43.1 | 44.8 |
| Entry | R | T/°C | Conv. (%) | Sel. (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCAB | DCAOB | p-CNA | ||||
| 1 | H | 50 | 80.4 | 21.4 | 73 | 5.6 |
| 2 | H | 90 | 99.0 | 85.6 | 3.3 | 11.1 |
| 3 | p-CH3 | 50 | 95.9 | 48.1 | - | 51.9 |
| 4 a | p-CH3 | 90 | 99.0 | 87.0 | - | 13.0 |
| 5 | m-Cl | 50 | 97.6 | 89.7 | 2.0 | 8.3 |
| 6 | p-Br | 50 | 98.8 | 75.6 | 9.1 | 15.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Shao, Y.; Li, H.; Liang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, H. A Schiff-Base Modified Pt Nano-Catalyst for Highly Efficient Synthesis of Aromatic Azo Compounds. Catalysts 2019, 9, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9040339
Teng Y, Wang X, Wang M, Liu Q, Shao Y, Li H, Liang C, Chen X, Wang H. A Schiff-Base Modified Pt Nano-Catalyst for Highly Efficient Synthesis of Aromatic Azo Compounds. Catalysts. 2019; 9(4):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9040339
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Yanyan, Xinkui Wang, Min Wang, Qinggang Liu, Yuqing Shao, Haomeng Li, Changhai Liang, Xiao Chen, and Huilong Wang. 2019. "A Schiff-Base Modified Pt Nano-Catalyst for Highly Efficient Synthesis of Aromatic Azo Compounds" Catalysts 9, no. 4: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9040339
APA StyleTeng, Y., Wang, X., Wang, M., Liu, Q., Shao, Y., Li, H., Liang, C., Chen, X., & Wang, H. (2019). A Schiff-Base Modified Pt Nano-Catalyst for Highly Efficient Synthesis of Aromatic Azo Compounds. Catalysts, 9(4), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9040339