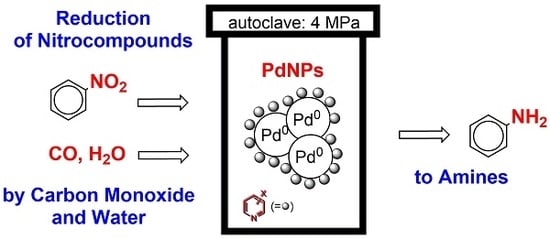
Reduction of Nitrobenzene to Aniline by CO/H2O in the Presence of Palladium Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Palladium Nanoparticles
3.3. Analysis of PdNPs
3.4. The Procedure of the Reduction of Nitrobenzene
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ono, N. The Nitro Group in Organic Synthesis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tafesh, A.M.; Weiguny, J. A Review of the Selective Catalytic Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds into Aromatic Amines, Isocyanates, Carbamates, and Ureas Using CO. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2035–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragaini, F. Away from phosgene: Reductive carbonylation of nitroarenes and oxidative carbonylation of amines, understanding the mechanism to improve performance. Dalton Transactions 2009, 32, 6251–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, R.S.; Kunkeler, P.J.; vanBekkum, H. Catalytic syntheses of aromatic amines. Catal. Today 1997, 37, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, P.F.; Gerulis, J.J. Amines, Aromatic. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Gerhartz, W., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/14356007.a02_037 (accessed on 18 March 2019).
- Zhao, S.L.; Liang, H.D.; Zhou, Y.F. Selective hydrogenation of m-dinitrobenzene to m-nitroaniline. catalyzed by PVP-Ru/Al2O3. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Q.; Qiao, B.T.; Chen, Z.J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, Y.Q. Novel chemoselective hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds over ferric hydroxide supported nanocluster gold in the presence of CO and H2O. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosi, A.; Denmark, S.E. Harnessing the Power of the Water-Gas Shift Reaction for Organic Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12164–12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, K.; Cole, T.; Slegeir, W.; Pettit, R. Catalytic Reductions Using Carbon-Monoxide and Water in Place of Hydrogen. 2. Reduction of Aromatic Nitro-Compounds to Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 3969–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K. Efficient Selective Reduction of Aromatic Nitro-Compounds by Ruthenium Catalysis under Co/H2O Conditions. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 1995, 95, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogul, A.; Litwinienko, G. Application of Pd(II) Complexes with Pyridines as Catalysts for the Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds by CO/H2O. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar]
- Krogul, A.; Skupinska, J.; Litwinienko, G. Catalytic activity of PdCl2 complexes with pyridines in nitrobenzene carbonylation. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2011, 337, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoccaro, P. Reactivity of Mono-Methoxycarbonyl and Di-Methoxycarbonyl Complexes of Pd(II) Towards Amines and Copper Amine Complexes - Role of Copper in the Catalyzed Palladium Copper Oxidative Carbonylation of Amines. J. Organomet. Chem. 1994, 470, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skupinska, J.; Karpinska, M. Nitrobenzene transformations in the carbonylation reaction in the presence of the PdCl2/Fe/I2/Py catalyst system. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2004, 267, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skupinska, J.; Karpinska, M.; Olowek, M.; Kasprzycka-Guttman, T. The effect of the components of the PdCl2/Fe/I2/Py catalytic system on nitrobenzene carbonylation to ethyl N-phenylcarbamate. Cen. Eur. J. Chem. 2005, 3, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaini, F.; Cenini, S. Mechanistic studies of palladium-catalysed carbonylation reactions of nitro compounds to isocyanates, carbamates and ureas. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 1996, 109, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widegren, J.A.; Finke, R.G. A review of the problem of distinguishing true homogeneous catalysis from soluble or other metal-particle heterogeneous catalysis under reducing conditions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 198, 317–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogul-Sobczak, A.; Kasperska, P.; Litwinienko, G. N-heterocyclic monodentate ligands as stabilizing agents for catalytically active Pd-nanoparticles. Catal. Commun. 2018, 104, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, Y.; Noujima, A.; Mitsudome, T.; Mizugaki, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Kaneda, K. Highly Chemoselective Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds Using a Hydrotalcite-supported Silver-nanoparticle Catalyst under a CO Atmosphere. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, L.-C.; Sun, H.; Ni, J.; Cao, Y.; He, H.-Y.; Fan, K.-N. Efficient and Selective Room-Temperature Gold-Catalyzed Reduction of Nitro Compounds with CO and H2O as the Hydrogen Source. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9538–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhaus, F.A.; Sorribes, I.; Wienhofer, G.; Junge, K.; Beller, M. Reduction of Nitroarenes Using CO and H2O in the Presence of a Nanostructured Cobalt Oxide/Nitrogen-Doped Graphene (NGr) Catalyst. Synlett 2015, 26, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Handa, S.; Gallou, F.; Lipshutz, B.H. Safe and Selective Nitro Group Reductions Catalyzed by Sustainable and Recyclable Fe/ppm Pd Nanoparticles in Water at Room Temperature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8979–8983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astruc, D.; Lu, F.; Aranzaes, J.R. Nanoparticles as recyclable catalysts: The frontier between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7852–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astruc, D. Palladium nanoparticles as efficient green homogeneous and heterogeneous carbon-carbon coupling precatalysts: A unifying view. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.T.S.; Van Der Sluys, M.; Jones, C.W. On the nature of the active species in palladium catalyzed Mizoroki-Heck and Suzuki-Miyaura couplings—Homogeneous or heterogeneous catalysis, a critical review. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 348, 609–679. [Google Scholar]
- Pun, D.; Diao, T.N.; Stahl, S.S. Aerobic Dehydrogenation of Cyclohexanone to Phenol Catalyzed by Pd(TFA)(2)/2-Dimethylaminopyridine: Evidence for the Role of Pd Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8213–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Weinstein, A.B.; White, P.B.; Stahl, S.S. Ligand-Promoted Palladium-Catalyzed Aerobic Oxidation Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 2636–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, R.H. Resolving Heterogeneity Problems and Impurity Artifacts in Operationally Homogeneous Transition Metal Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1536–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, L.N. Chemical catalysis by colloids and clusters. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 2693–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, J.D.; Finke, R.G. A review of modern transition-metal nanoclusters: Their synthesis, characterization, and applications in catalysis. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 1999, 145, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiens, C.; Ciuculescu-Pradines, D.; Philippot, K. Controlled metal nanostructures: Fertile ground for coordination chemists. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 308, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, K.A.; Sullivan, J.A.; Mueller-Bunz, H. Preparation and characterization of 4-dimethylaminopyridine-stabilized palladium nanoparticles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12508–12520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megiel, E. Surface modification using TEMPO and its derivatives. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 250, 158–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J. Alkane activation by oxide-bound organorhodium complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1985, 18, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Hackett, M.; Brainard, R.L.; Lavalleye, J.P.P.M.; Sowinski, A.F.; Izumi, A.N.; Moore, S.S.; Brown, D.W.; Staudt, E.M. Suppression of Unwanted Heterogeneous Platinum(0)-Catalyzed Reactions by Poisoning with Mercury(0) in Systems Involving Competing Homogeneous Reactions of Soluble Organoplatinum Compounds - Thermal-Decomposition of Bis(Triethylphosphine)-3,3,4,4-Tetramethylplatinacyclopentanet. Organometallics 1985, 4, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree, R.H.; Mellea, M.F.; Mihelcic, J.M.; Quirk, J.M. Alkane Dehydrogenation by Iridium Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.N. On the Mechanism of Metal Colloid Catalyzed Hydrosilylation - Proposed Explanations for Electronic Effects and Oxygen Cocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 5998–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornstein, B.J.; Aiken, J.D.; Finke, R.G. Nanoclusters in catalysis: A comparison of CS2 catalyst poisoning of polyoxoanion- and tetrabutylammonium-stabilized 40 +/- 6 angstrom Rh(0) nanoclusters to 5% Rh/Al2O3, including an analysis of the literature related to the CS2 to metal stoichiometry issue. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Widegren, J.A.; Bennett, M.A.; Finke, R.G. Is it homogeneous or heterogeneous catalysis? Identification of bulk ruthenium metal as the true catalyst in benzene hydrogenations starting with the monometallic precursor, Ru(II)(eta(6)-C6Me6)(OAC)(2), plus kinetic characterization of the heterogeneous nucleation, then autocatalytic surface-growth mechanism of metal film formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10301–10310. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-H.; Liu, R.-H.; Sun, Q.-J.; Chang, J.-B.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.-T.; Kang, Z.-H.; Wang, S.-D. Controlled synthesis and synergistic effects of graphene-supported PdAu bimetallic nanoparticles with tunable catalytic properties. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6356–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Entry | Pd-species/Ligand | Additive (XPy) | YAN [%] | TOF c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PdNPs d/4MePy | - | 73 | 521 |
| 2 | PdNPs/4MePy | 2ClPy | 80 | 571 |
| 3 | PdNPs/4MePy | 4MePy | 35 | 250 |
| 4 | PdAgglom e/4MePy | - | 27 | 193 |
| 5 | PdAgglom/4MePy | 2ClPy | 38 | 271 |
| 6 | PdAgglom/4MePy | 4MePy | 10 | 71 |
| 7 | PdNPs/DMAP | - | 40 | 286 |
| 8 | PdNPs/DMAP | 2ClPy | 48 | 343 |
| 9 | PdAgglom/DMAP | - | 20 | 143 |
| 10 | PdAgglom/DMAP | 2ClPy | 29 | 207 |
| 11 | PdNPs/4EtPy | - | 54 | 386 |
| 12 | PdNPs/4EtPy | 2ClPy | 62 | 443 |
| 13 | PdAgglom/4EtPy | - | 24 | 171 |
| 14 | PdAgglom/4EtPy | 2ClPy | 37 | 264 |
| 15 | Pdblack/4MePy f | - | 12 | 86 |
| 16 | Pdblack/4MePy f | 2ClPy | 25 | 179 |
| 17 | Pdblack/4MePy f | 4MePy | 10 | 71 |
| 18 g | - | 2ClPy | - | 0 |
| 19 | PdCl2(4MePy)2 | - | 45 | 321 |
| 20 | PdCl2(4MePy)2 | 2ClPy | 50 | 357 |
| 21 | PdCl2(4MePy)2 | 4MePy | 34 | 243 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krogul-Sobczak, A.; Cedrowski, J.; Kasperska, P.; Litwinienko, G. Reduction of Nitrobenzene to Aniline by CO/H2O in the Presence of Palladium Nanoparticles. Catalysts 2019, 9, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050404
Krogul-Sobczak A, Cedrowski J, Kasperska P, Litwinienko G. Reduction of Nitrobenzene to Aniline by CO/H2O in the Presence of Palladium Nanoparticles. Catalysts. 2019; 9(5):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050404
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrogul-Sobczak, Agnieszka, Jakub Cedrowski, Patrycja Kasperska, and Grzegorz Litwinienko. 2019. "Reduction of Nitrobenzene to Aniline by CO/H2O in the Presence of Palladium Nanoparticles" Catalysts 9, no. 5: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050404
APA StyleKrogul-Sobczak, A., Cedrowski, J., Kasperska, P., & Litwinienko, G. (2019). Reduction of Nitrobenzene to Aniline by CO/H2O in the Presence of Palladium Nanoparticles. Catalysts, 9(5), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050404